Modbus and Bluetooth data sending to Node-RED: Difference between revisions
Justas.Cip (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Justas.Cip (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
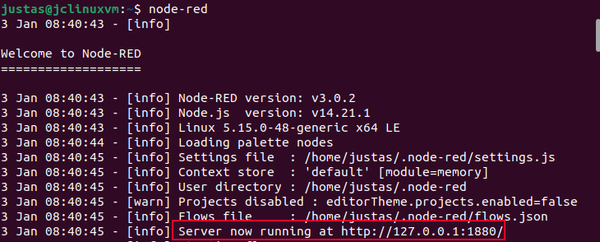
Use the command ''node-red'' to start a local server. Here is how the terminal should look like if the server starts correctly: | Use the command ''node-red'' to start a local server. Here is how the terminal should look like if the server starts correctly: | ||
[[File:Server is running node red terminal.png|border|600px|class=tlt-border]] | |||
---- | |||
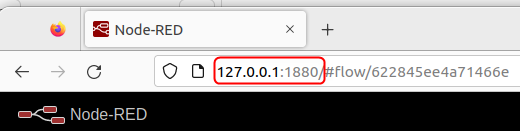
Once you have the local server running, use the local IP and port number in your internet browser. In this case, we are using 127.0.0.1:1880: | |||
[[File:Use server address in web browser.png|border|600px|class=tlt-border]] | |||
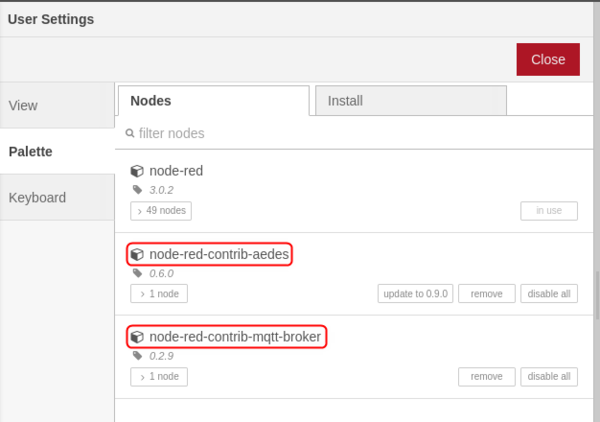
For MQTT usage, we are going to need MQTT-specific nodes. Use the side menu to navigate to Manage Palette section and install these nodes: | |||
*node-red-contrib-aedes | *node-red-contrib-aedes | ||
*node-red-contrib-mqtt-broker | *node-red-contrib-mqtt-broker | ||
[[File:Manage palette and download these mqtt nodes.png|border|600px|class=tlt-border]] | |||
==MQTT Gateway== | |||
Revision as of 15:33, 12 January 2023
Introduction
The information in this page is updated in accordance with the RUTXXX_R_00_07_03 firmware version.
Node-RED is a flow-based programming tool developed by IBM Emerging Technology and written in Node.js. It provides a browser-based editor for wiring together hardware devices, APIs, and online services using a visual programming interface.
This article provides an extensive configuration example with details on how to use Node-RED with Teltonika Routers via MQTT and HTTP protocols.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Before we begin, let's overview the configuration that we are attempting to achieve and the prerequisites that make it possible.
Prerequisites:
- Teltonika RUTXXX router or TRBXXX gateway. We are going to use the RUTX11 in this example.
- At least one end device (PC, Laptop, Tablet, Smartphone) to configure the devices.
- Linux Virtual Machine to host Node-RED server.
There are a couple of different use cases with Node-RED and Teltonika devices and here are the connection topologies for these use cases.
Topology 1 – Modbus data to server using either Node-RED or Teltonika device as MQTT broker.
Topology 2 – Bluetooth data to server using Teltonika device as MQTT broker.
Topology 3 – MQTT gateway using either Node-RED or Teltonika device as MQTT broker.
Topology 4 – HTTP data to Node-RED server. Italic text
Node-RED installation and setup
We are going to set up Node-RED in Linux virtual machine. For Node-RED to work, you would need to install Node.js version 14.00 or higher, if you already have Node.js installed, verify Node.js version using this command:
node -v
If you do not have Node.js installed, run these commands to install it:
sudo apt install curl curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | sudo -E bash – sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
Once we have Node.js installed, we can install Node-RED. Use this command to install:
sudo npm install -g –unsafe-perm node-red
Use the command node-red to start a local server. Here is how the terminal should look like if the server starts correctly:
Once you have the local server running, use the local IP and port number in your internet browser. In this case, we are using 127.0.0.1:1880:
For MQTT usage, we are going to need MQTT-specific nodes. Use the side menu to navigate to Manage Palette section and install these nodes:
- node-red-contrib-aedes
- node-red-contrib-mqtt-broker