Template:Networking rut manual routing: Difference between revisions
make template |
Gytispieze (talk | contribs) m Text replacement - "\{\{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_fw_disclosure (.*) (.*) (.*) (.*) \}\}" to "{{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | series = {{{series}}} | name = {{{name}}} | fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = {{{series}}} | name = {{{name}}} }} }}" |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
| fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
This chapter | This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the <b>Routing</b> page for {{{name}}} devices. | ||
==Static Routes== | ==Static Routes== | ||
Static | <b>Static Routes</b> specify over which interface and gateway a certain host or network can be reached. In this page you can configure your own custom routes. | ||
[[Image:Network routing static routes.PNG]] | [[Image:Network routing static routes.PNG]] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 19: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Routing table</td> | <td>Routing table</td> | ||
<td>Main | WAN | WAN2 | WAN3; | <td>Main | WAN | WAN2 | WAN3; default: '''Main'''</td> | ||
<td>Defines which table will be used for the route in question</td> | <td>Defines which table will be used for the route in question.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Interface</td> | <td>Interface</td> | ||
<td>LAN | WAN(Wired) | WAN2(Mobile) | WAN3(WiFi) | VPN instances; | <td>LAN | WAN(Wired) | WAN2(Mobile) | WAN3(WiFi) | VPN instances; default: '''LAN'''</td> | ||
<td>The zone where the target network resides</td> | <td>The zone where the target network resides.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Destination address | <td>Destination address<b style="color:#1E90FF;">*</b></td> | ||
<td>ip; | <td>ip; default: '''none'''</td> | ||
<td>The address of the destination network</td> | <td>The address of the destination network.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Netmask | <td>Netmask<b style="color:#1E90FF;">*</b></td> | ||
<td>ip; | <td>ip; default: '''none'''</td> | ||
<td>A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies</td> | <td>A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Gateway</td> | <td>Gateway</td> | ||
<td>ip; | <td>ip; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule</td> | <td>Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Metric</td> | <td>Metric</td> | ||
<td>integer; | <td>integer; default: '''none'''</td> | ||
<td>The '''Metric''' value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the higher metric is applied</td> | <td>The '''Metric''' value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the higher metric is applied.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
'''*Additional notes on Destination & Netmask:''' | '''<b style="color:#1E90FF;">*</b>Additional notes on Destination & Netmask:''' | ||
You can define a rule that applies to a single IP like this: Destination - some IP; Netmask - 255.255.255.255. Furthermore, you can define a rule that applies to a segment of IPs like this: Destination – some IP that STARTS some segment; Netmask – Netmask that defines how large the segment is. e.g.: | You can define a rule that applies to a single IP like this: Destination - some IP; Netmask - 255.255.255.255. Furthermore, you can define a rule that applies to a segment of IPs like this: Destination – some IP that STARTS some segment; Netmask – Netmask that defines how large the segment is. e.g.: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 83: | Line 90: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}| | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT2XX| | |||
===Static IPv6 Routes=== | ===Static IPv6 Routes=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Settings for Static IPv6 routes are similar to IPv4. | Settings for Static IPv6 routes are similar to IPv4. | ||
[[Image:Networking rut2xx manual static ipv6 routes.png|border]] | [[Image:Networking rut2xx manual static ipv6 routes.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Interface</td> | <td>Interface</td> | ||
<td>Wired WAN IPv6 | <td>Wired WAN IPv6 {{!}} Mobile WAN IPv6 {{!}} Wi-Fi IPv6; default: '''Wired WAN IPv6'''</td> | ||
<td>Defines which interface will be used</td> | <td>Defines which interface will be used.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Target</td> | <td>Target</td> | ||
<td> | <td>default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>The address of the destination network</td> | <td>The address of the destination network.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>IPv6-Gateway</td> | <td>IPv6-Gateway</td> | ||
<td>ipv6; | <td>ipv6; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule</td> | <td>Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Metric</td> | <td>Metric</td> | ||
<td>integer; | <td>integer; default: '''none'''</td> | ||
<td>The '''Metric''' value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the higher metric is applied</td> | <td>The '''Metric''' value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the higher metric is applied.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
}} | |}} | ||
===Static ARP entries=== | ===Static ARP entries=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Static ARP entries are used to bind a MAC address to a specific IP address. For example, if you want a device to get the same IP every time it connects to the router, you can create a Static ARP entry by binding that device’s MAC address to the desired IP address. The router will then create an entry in the ARP table, which in turn will make sure that that device will get the specified IP address every time. | Static ARP entries are used to bind a MAC address to a specific IP address. For | ||
example, if you want a device to get the same IP every time it connects to the | |||
router, you can create a Static ARP entry by binding that device’s MAC address | |||
to the desired IP address. The router will then create an entry in the ARP table, | |||
which in turn will make sure that that device will get the specified IP address every time. | |||
[[Image:Network routing static routes static arp entries.PNG]] | [[Image:Network routing static routes static arp entries.PNG]] | ||
| Line 128: | Line 141: | ||
===BGP Protocol=== | ===BGP Protocol=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
'''Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)''' is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet. The protocol is often classified as a path vector protocol but is sometimes also classed as a distance-vector routing protocol. The Border Gateway Protocol makes routing decisions based on paths, network policies, or rule-sets configured by a network administrator and is involved in making core routing decisions. | '''Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)''' is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed | ||
to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet. | |||
The protocol is often classified as a path vector protocol but is sometimes also classed | |||
as a distance-vector routing protocol. The Border Gateway Protocol makes routing decisions | |||
based on paths, network policies, or rule-sets configured by a network administrator and is | |||
involved in making core routing decisions. | |||
====General Settings==== | ====General Settings==== | ||
| Line 137: | Line 155: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles the BGP protocol | <td>Toggles the BGP protocol on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable vty</td> | <td>Enable vty</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles vty access from LAN ON or OFF</td> | <td>Toggles vty access from LAN ON or OFF.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Import config</td> | <td>Import config</td> | ||
<td>-</td> | <td>-</td> | ||
<td>Uploads an external BGP configuration</td> | <td>Uploads an external BGP configuration.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 161: | Line 179: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Networking_{{lc:{{{series}}}}}_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_instance_v1.PNG|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles the BGP instance | <td>Toggles the BGP instance on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT2XX| | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Use IPv6</td> | |||
<td>yes {{!}} no; default: '''no'''</td> | |||
<td>Use IPv6 address family in the configuration.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
|}} | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>AS</td> | <td>AS</td> | ||
<td>integer: | <td>integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>AS number is an identification of an autonomous system. BGP protocol uses the AS number for detecting whether the BGP connection is an internal one or external one. '''[Required]'''</td> | <td>AS number is an identification of an autonomous system. BGP protocol uses the AS number for detecting whether the BGP connection is an internal one or external one. '''[Required]'''.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>BGP router ID</td> | <td>BGP router ID</td> | ||
<td>string; | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>The router id is used by BGP to identify the routing device from which a packet originated. Default router ID | <td>The router id is used by BGP to identify the routing device from which a packet originated. Default router ID Value is selected as the largest IP Address of the interface.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Network</td> | <td>Network</td> | ||
<td>string; | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Add an announcement network(s)</td> | <td>Add an announcement network(s).</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Redistribution options</td> | ||
<td> | <td>Connected routes {{!}} Kernel added routes {{!}} OSPF routes {{!}} Static routes; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Select routes which you want to redistribute into BGP.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT9XX| | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Deterministic MED</td> | |||
<td>yes {{!}} no; default: '''no'''</td> | |||
<td>Enable to compare MED between same autonomous system ignoring their age.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
|}} | |||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 203: | Line 235: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles the BGP peer | <td>Toggles the BGP peer on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Remote AS</td> | <td>Remote AS</td> | ||
<td>integer: | <td>integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Neighbour's remote AS</td> | <td>Neighbour's remote AS.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Remote address</td> | <td>Remote address</td> | ||
<td>ip; | <td>ip; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Neighbour's remote IPv4 address</td> | <td>Neighbour's remote IPv4 address.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 231: | Line 263: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles the Access filter | <td>Toggles the Access filter on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Peer</td> | <td>Peer</td> | ||
<td>bgp peer; | <td>bgp peer; default: '''first peer on list'''</td> | ||
<td>Applies the rule for the specified peer</td> | <td>Applies the rule for the specified peer.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Action</td> | <td>Action</td> | ||
<td>Permit | Deny; | <td>Permit | Deny; default: '''Permit'''</td> | ||
<td>Denies or permits matched entry</td> | <td>Denies or permits matched entry.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Network</td> | <td>Network</td> | ||
<td>Any | ip; | <td>Any | ip; default: '''Any'''</td> | ||
<td>Applies filter rule for this source network</td> | <td>Applies filter rule for this source network.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Direction</td> | <td>Direction</td> | ||
<td>Inbound | Outbound; | <td>Inbound | Outbound; default: '''Inbound'''</td> | ||
<td>If direction is '''Inbound''', the access list is applied to input routes. If direction is '''Outbound''' the access list is applied to advertised routes</td> | <td>If direction is '''Inbound''', the access list is applied to input routes. If direction is '''Outbound''', the access list is applied to advertised routes.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
===RIP Protocol=== | ===RIP Protocol=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
The '''Routing Information Protocol (RIP)''' is one of the oldest distance-vector routing protocols which employ the hop count as a routing metric. RIP prevents routing loops by implementing a limit on the number of hops allowed in a path from source to destination. The maximum number of hops allowed for RIP is 15, which limits the size of networks that RIP can support. A hop count of 16 is considered an infinite distance and the route is considered unreachable. RIP implements the split horizon, route poisoning and holddown mechanisms to prevent incorrect routing information from being propagated. | The '''Routing Information Protocol (RIP)''' is one of the oldest distance-vector routing | ||
protocols which employ the hop count as a routing metric. RIP prevents routing loops by | |||
implementing a limit on the number of hops allowed in a path from source to destination. | |||
The maximum number of hops allowed for RIP is 15, which limits the size of networks that | |||
RIP can support. A hop count of 16 is considered an infinite distance and the route is | |||
considered unreachable. RIP implements the split horizon, route poisoning and holddown | |||
mechanisms to prevent incorrect routing information from being propagated. | |||
====General==== | ====General==== | ||
| Line 273: | Line 312: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles RIP Protocol | <td>Toggles RIP Protocol on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable vty</td> | <td>Enable vty</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles vty access from LAN | <td>Toggles vty access from LAN on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Import config</td> | <td>Import config</td> | ||
<td>-</td> | <td>-</td> | ||
<td>Uses imported RIP configurations</td> | <td>Uses imported RIP configurations.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Version</td> | <td>Version</td> | ||
<td>2 | 1; | <td>2 | 1; default: '''2'''</td> | ||
<td>Specifies the version of RIP</td> | <td>Specifies the version of RIP.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Neighbor</td> | <td>Neighbor</td> | ||
<td>ip; | <td>ip; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Neighbour IP addres</td> | <td>Neighbour IP addres.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 311: | Line 350: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles RIP Interface | <td>Toggles RIP Interface on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Interface</td> | <td>Interface</td> | ||
<td>network interface; | <td>network interface; default: '''lo'''</td> | ||
<td>Network interface to be used with the RIP interface</td> | <td>Network interface to be used with the RIP interface.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Passive interface</td> | <td>Passive interface</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Sets the specified interface to passive mode. On passive mode interface, all receiving packets are processed as normal and ripd does not send either multicast or unicast RIP packets</td> | <td>Sets the specified interface to passive mode. On passive mode interface, all receiving packets are processed as normal and ripd does not send either multicast or unicast RIP packets.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 339: | Line 378: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles the Access filter | <td>Toggles the Access filter on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>RIP interface</td> | ||
<td> | <td>RIP interface; default: '''first interface on list'''</td> | ||
<td>Applies the rule for the specified | <td>Applies the rule for the specified interface.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Action</td> | <td>Action</td> | ||
<td>Permit | Deny; | <td>Permit | Deny; default: '''Permit'''</td> | ||
<td>Denies or permits matched entry</td> | <td>Denies or permits matched entry.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Network</td> | <td>Network</td> | ||
<td>Any | ip; | <td>Any | ip; default: '''Any'''</td> | ||
<td>Applies filter rule for this source network</td> | <td>Applies filter rule for this source network.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Direction</td> | <td>Direction</td> | ||
<td>Inbound | Outbound; | <td>Inbound | Outbound; default: '''Inbound'''</td> | ||
<td>If direction is '''Inbound''', the access list is applied to input routes. If direction is '''Outbound''' the access list is applied to advertised routes</td> | <td>If direction is '''Inbound''', the access list is applied to input routes. If direction is '''Outbound''' the access list is applied to advertised routes.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
===OSPF Protocol=== | ===OSPF Protocol=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
'''Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)''' is a routing protocol for Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It uses a link state routing (LSR) algorithm and falls into the group of interior gateway protocols (IGPs), operating within a single autonomous system (AS). It is defined as OSPF Version 2 in RFC 2328 for IPv4. | '''Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)''' is a routing protocol for Internet Protocol (IP) networks. | ||
It uses a link state routing (LSR) algorithm and falls into the group of interior gateway | |||
protocols (IGPs), operating within a single autonomous system (AS). It is defined as OSPF | |||
Version 2 in RFC 2328 for IPv4. | |||
====General Settings==== | ====General Settings==== | ||
| Line 380: | Line 423: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles OSPF Protocol | <td>Toggles OSPF Protocol on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable vty</td> | <td>Enable vty</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles vty access from LAN | <td>Toggles vty access from LAN on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Import config</td> | <td>Import config</td> | ||
<td>-</td> | <td>-</td> | ||
<td>Uses imported OSPF configurations</td> | <td>Uses imported OSPF configurations.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Router ID</td> | <td>Router ID</td> | ||
<td>ip; | <td>ip; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Sets the router | <td>Sets the router ID of the OSPF process. The router ID may be an IP address of the router, but not necessary, it also can be any arbitrary 32bit number.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 412: | Line 455: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles OSPF interface | <td>Toggles OSPF interface on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Cost</td> | <td>Cost</td> | ||
<td>integer [1..65535]; | <td>integer [1..65535]; default: '''10'''</td> | ||
<td>The cost | <td>The cost Value is set to router-LSA’s metric field and used for SPF calculation.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Hello interval</td> | <td>Hello interval</td> | ||
<td>integer [1..65535]; | <td>integer [1..65535]; default: '''10'''</td> | ||
<td>Hello packets will be sent at the frequency specified in this field (in seconds)</td> | <td>Hello packets will be sent at the frequency specified in this field (in seconds).</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Router dead interval</td> | <td>Router dead interval</td> | ||
<td>integer [1..65535]; | <td>integer [1..65535]; default: '''40'''</td> | ||
<td>This | <td>This Value must be the same for all routers attached to a common network.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Retransmit</td> | <td>Retransmit</td> | ||
<td>integer [1..65535]; | <td>integer [1..65535]; default: '''5'''</td> | ||
<td>This | <td>This Value is used when re-transmitting Database Description and Link State Request packets.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Priority</td> | <td>Priority</td> | ||
<td>integer [0..255]; | <td>integer [0..255]; default: '''1'''</td> | ||
<td>The router with the highest priority will be more eligible to become the Designated Router. Setting the | <td>The router with the highest priority will be more eligible to become the Designated Router. Setting the Value to 0, makes the router ineligible to become the Designated Router.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Type</td> | <td>Type</td> | ||
<td>Broadcast | Nonbroadcast | Point-to-point | Point-to-multipoint; | <td>Broadcast | Nonbroadcast | Point-to-point | Point-to-multipoint; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Set explicit network type for the specified interface</td> | <td>Set explicit network type for the specified interface.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Authentication</td> | <td>Authentication</td> | ||
<td>None | Password | MD5 HMAC; | <td>None | Password | MD5 HMAC; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Specifies the authentication mode that should be used for the interface</td> | <td>Specifies the authentication mode that should be used for the interface.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 465: | Line 508: | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: '''no'''</td> | ||
<td>Toggles OSPF network | <td>Toggles OSPF network on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Network</td> | <td>Network</td> | ||
<td>[a.b.c.d/m]; | <td>[a.b.c.d/m]; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>This command specifies the OSPF enabled interface. If the interface has an address from the range '''a.b.c.d/m''' then enables OSPF on this interface so the router can provide network information to the other OSPF routers via this interface</td> | <td>This command specifies the OSPF enabled interface. If the interface has an address from the range '''a.b.c.d/m''' then enables OSPF on this interface so the router can provide network information to the other OSPF routers via this interface.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Area</td> | <td>Area</td> | ||
<td>ospf area; | <td>ospf area; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Specifies OSPF area</td> | <td>Specifies OSPF area.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
[[Category:{{{name}}} | {{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT9XX| | ||
===NHRP=== | |||
---- | |||
Next Hop Resolution Protocol ('''NHRP''') is a protocol or method that can be used so that a computer sending data to another computer can learn the most direct route (the fewest number of hops) to the receiving computer. | |||
====General Settings==== | |||
---- | |||
Below is an example of NHRP '''General''' settings section. | |||
[[File:Networking_Rut9xx_manual_dynamic_routes_nhrp_general_v1.png|alt=|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable service</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: '''off'''</td> | |||
<td>Toggles NHRP between on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable logging</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: '''off'''</td> | |||
<td>Toggles NHRP logging between on or off.</td> | |||
</tr></table> | |||
====Interfaces==== | |||
---- | |||
Below is an example of NHRP '''Interface''' settings section. | |||
[[File:Networking Rut9xx manual dynamic routes nhrp interfaces v1.png|alt=|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable</td> | |||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: '''off'''</td> | |||
<td>Toggles interface on or off.</td> | |||
</tr></table> | |||
By pressing '''Edit''' button you can find more settings related to '''NHRP Interface.''' | |||
====Interface parameters==== | |||
---- | |||
[[File:Networking_Rut9xx_manual_dynamic_routes_nhrp_parameters_v1.png|alt=|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable</td> | |||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: '''off'''</td> | |||
<td>Enables DMVPN client.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Interface</td> | |||
<td>interfaces; default: '''br-lan'''</td> | |||
<td>Interface which will be using NHRP.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Network ID</td> | |||
<td>number; default: '''none'''</td> | |||
<td>Network ID of NHRP.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>NHS</td> | |||
<td>None <nowiki>|</nowiki> Dynamic <nowiki>|</nowiki> Custom; default: '''none'''</td> | |||
<td>IP address of Next-Hop Server.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>NBMA</td> | |||
<td>ip; default: '''none'''</td> | |||
<td>Non-Broadcast Multi-Access(NBMA) network IP address.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Hold-time</td> | |||
<td>number; default: '''7200'''</td> | |||
<td>Specifies the holding time for NHRP Registration Requests and Resolution Replies sent from this interface or shortcut-target. The holdtime is specified in seconds and defaults to two hours.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>IPsec support</td> | |||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: '''off'''</td> | |||
<td>Use NHRP over IPsec.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
====Interface mapping==== | |||
---- | |||
[[File:Networking_Rut9xx_manual_dynamic_routes_nhrp_mappings_v1.png|alt=|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>IP address</td> | |||
<td>ip; default: '''none'''</td> | |||
<td>Network ID of NHRP.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>NBMA</td> | |||
<td>ip; default: '''none'''</td> | |||
<td>IP address of Next-Hop Server.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
}} | |||
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:08, 24 October 2023
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the Routing page for {{{name}}} devices.
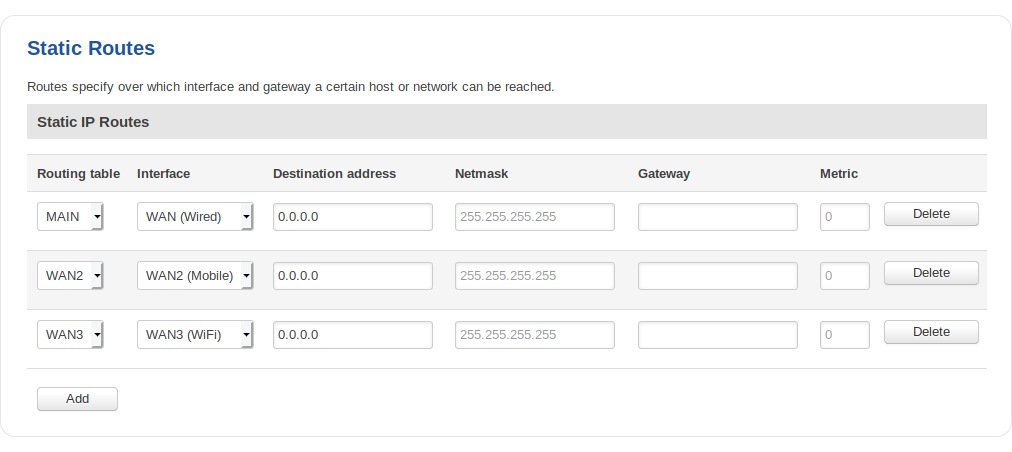
Static Routes
Static Routes specify over which interface and gateway a certain host or network can be reached. In this page you can configure your own custom routes.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Routing table | Main | WAN | WAN2 | WAN3; default: Main | Defines which table will be used for the route in question. |
| Interface | LAN | WAN(Wired) | WAN2(Mobile) | WAN3(WiFi) | VPN instances; default: LAN | The zone where the target network resides. |
| Destination address* | ip; default: none | The address of the destination network. |
| Netmask* | ip; default: none | A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies. |
| Gateway | ip; default: none | Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule. |
| Metric | integer; default: none | The Metric value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the higher metric is applied. |
*Additional notes on Destination & Netmask:
You can define a rule that applies to a single IP like this: Destination - some IP; Netmask - 255.255.255.255. Furthermore, you can define a rule that applies to a segment of IPs like this: Destination – some IP that STARTS some segment; Netmask – Netmask that defines how large the segment is. e.g.:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.55.161 | 255.255.255.255 | Only applies to 192.168.55.161 |
| 192.168.55.0 | 255.255.255.240 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.55.0 - 192.168.55.15 |
| 192.168.55.240 | 255.255.255.240 | 192.168.55.240 - 192.168.55.255 |
| 192.168.55.161 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.55.0 - 192.168.55.255 |
| 192.168.0.0 | 255.255.0.0 | 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 |
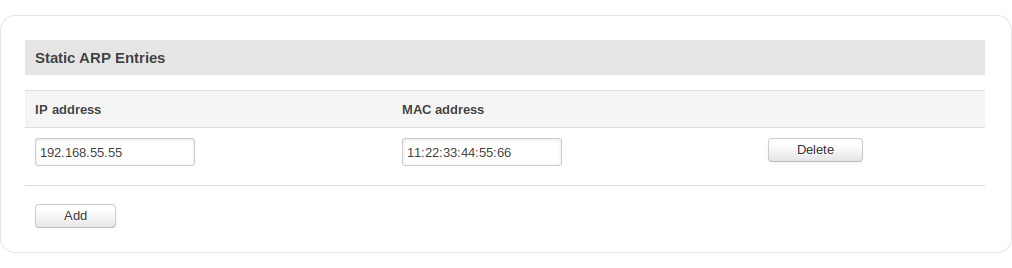
Static ARP entries
Static ARP entries are used to bind a MAC address to a specific IP address. For example, if you want a device to get the same IP every time it connects to the router, you can create a Static ARP entry by binding that device’s MAC address to the desired IP address. The router will then create an entry in the ARP table, which in turn will make sure that that device will get the specified IP address every time.
Dynamic Routes
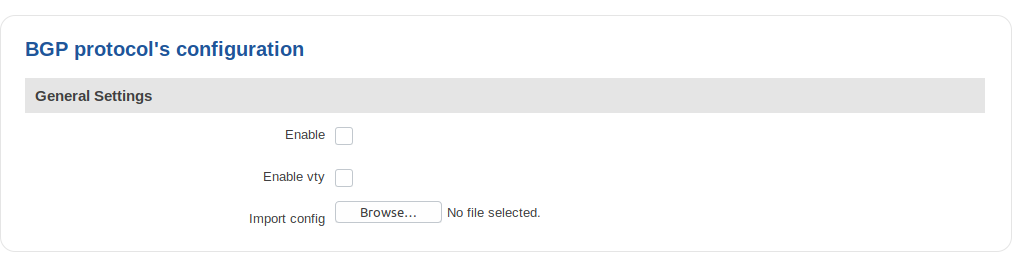
BGP Protocol
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet. The protocol is often classified as a path vector protocol but is sometimes also classed as a distance-vector routing protocol. The Border Gateway Protocol makes routing decisions based on paths, network policies, or rule-sets configured by a network administrator and is involved in making core routing decisions.
General Settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles the BGP protocol on or off. |
| Enable vty | yes | no; default: no | Toggles vty access from LAN ON or OFF. |
| Import config | - | Uploads an external BGP configuration. |
BGP Instance
[[Image:Networking_{{{series}}}_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_instance_v1.PNG|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles the BGP instance on or off. |
| AS | integer; default: none | AS number is an identification of an autonomous system. BGP protocol uses the AS number for detecting whether the BGP connection is an internal one or external one. [Required]. |
| BGP router ID | string; default: none | The router id is used by BGP to identify the routing device from which a packet originated. Default router ID Value is selected as the largest IP Address of the interface. |
| Network | string; default: none | Add an announcement network(s). |
| Redistribution options | Connected routes | Kernel added routes | OSPF routes | Static routes; default: none | Select routes which you want to redistribute into BGP. |
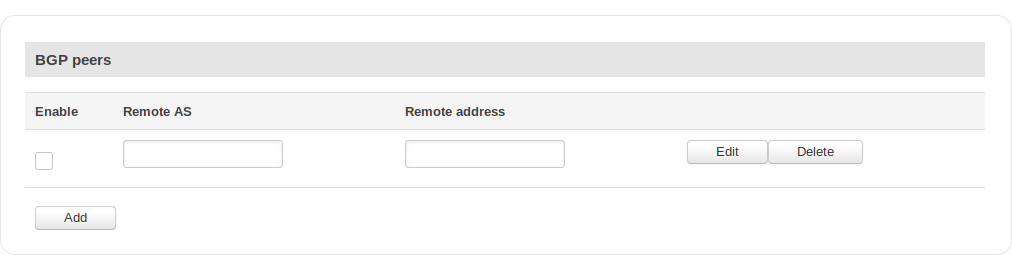
BGP Peers
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles the BGP peer on or off. |
| Remote AS | integer; default: none | Neighbour's remote AS. |
| Remote address | ip; default: none | Neighbour's remote IPv4 address. |
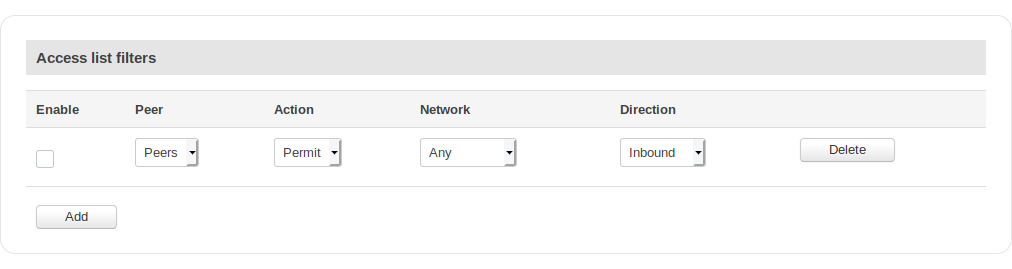
Access List Filters
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles the Access filter on or off. |
| Peer | bgp peer; default: first peer on list | Applies the rule for the specified peer. |
| Action | Permit | Deny; default: Permit | Denies or permits matched entry. |
| Network | Any | ip; default: Any | Applies filter rule for this source network. |
| Direction | Inbound | Outbound; default: Inbound | If direction is Inbound, the access list is applied to input routes. If direction is Outbound, the access list is applied to advertised routes. |
RIP Protocol
The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is one of the oldest distance-vector routing protocols which employ the hop count as a routing metric. RIP prevents routing loops by implementing a limit on the number of hops allowed in a path from source to destination. The maximum number of hops allowed for RIP is 15, which limits the size of networks that RIP can support. A hop count of 16 is considered an infinite distance and the route is considered unreachable. RIP implements the split horizon, route poisoning and holddown mechanisms to prevent incorrect routing information from being propagated.
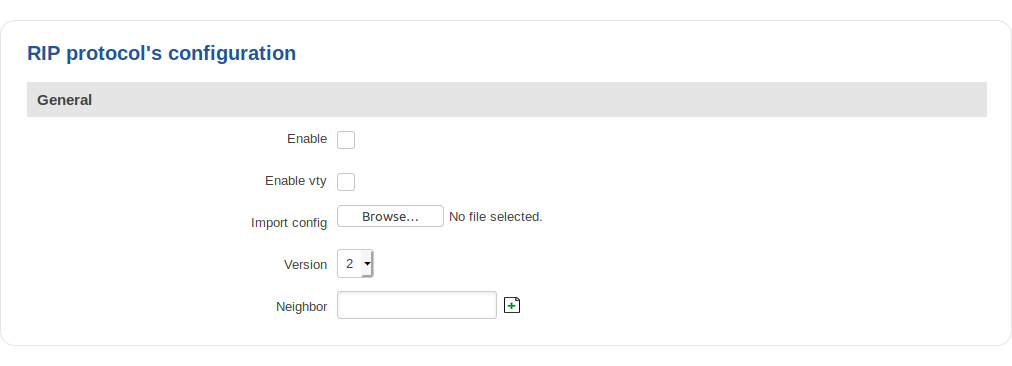
General
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles RIP Protocol on or off. |
| Enable vty | yes | no; default: no | Toggles vty access from LAN on or off. |
| Import config | - | Uses imported RIP configurations. |
| Version | 2 | 1; default: 2 | Specifies the version of RIP. |
| Neighbor | ip; default: none | Neighbour IP addres. |
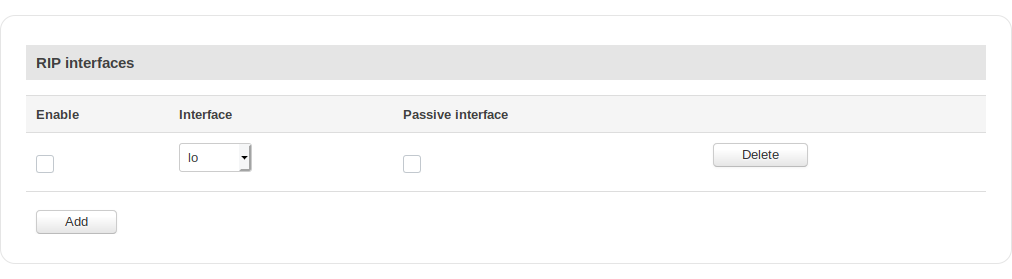
RIP Interfaces
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles RIP Interface on or off. |
| Interface | network interface; default: lo | Network interface to be used with the RIP interface. |
| Passive interface | yes | no; default: no | Sets the specified interface to passive mode. On passive mode interface, all receiving packets are processed as normal and ripd does not send either multicast or unicast RIP packets. |
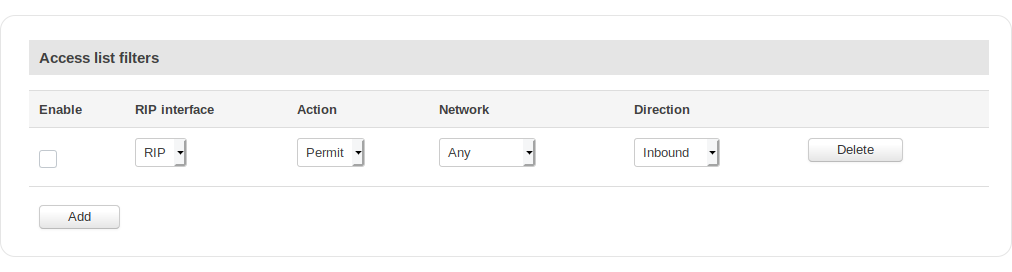
Access list filters
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles the Access filter on or off. |
| RIP interface | RIP interface; default: first interface on list | Applies the rule for the specified interface. |
| Action | Permit | Deny; default: Permit | Denies or permits matched entry. |
| Network | Any | ip; default: Any | Applies filter rule for this source network. |
| Direction | Inbound | Outbound; default: Inbound | If direction is Inbound, the access list is applied to input routes. If direction is Outbound the access list is applied to advertised routes. |
OSPF Protocol
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol for Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It uses a link state routing (LSR) algorithm and falls into the group of interior gateway protocols (IGPs), operating within a single autonomous system (AS). It is defined as OSPF Version 2 in RFC 2328 for IPv4.
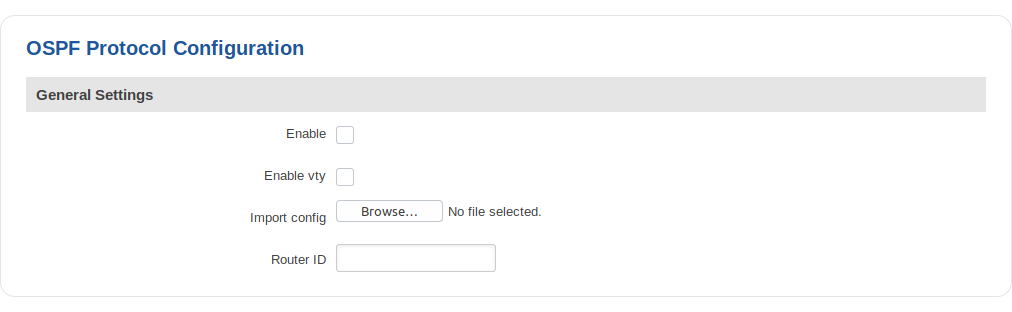
General Settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles OSPF Protocol on or off. |
| Enable vty | yes | no; default: no | Toggles vty access from LAN on or off. |
| Import config | - | Uses imported OSPF configurations. |
| Router ID | ip; default: none | Sets the router ID of the OSPF process. The router ID may be an IP address of the router, but not necessary, it also can be any arbitrary 32bit number. |
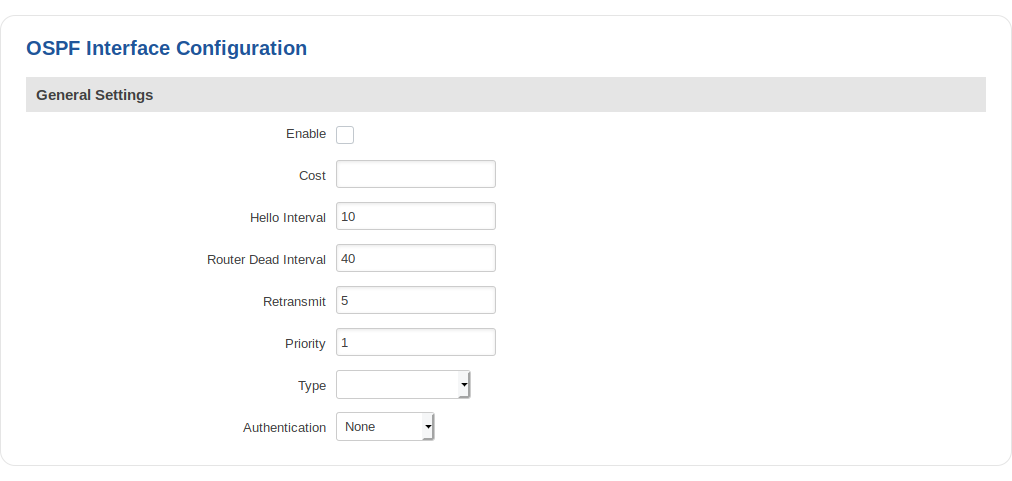
OSPF Interface
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles OSPF interface on or off. |
| Cost | integer [1..65535]; default: 10 | The cost Value is set to router-LSA’s metric field and used for SPF calculation. |
| Hello interval | integer [1..65535]; default: 10 | Hello packets will be sent at the frequency specified in this field (in seconds). |
| Router dead interval | integer [1..65535]; default: 40 | This Value must be the same for all routers attached to a common network. |
| Retransmit | integer [1..65535]; default: 5 | This Value is used when re-transmitting Database Description and Link State Request packets. |
| Priority | integer [0..255]; default: 1 | The router with the highest priority will be more eligible to become the Designated Router. Setting the Value to 0, makes the router ineligible to become the Designated Router. |
| Type | Broadcast | Nonbroadcast | Point-to-point | Point-to-multipoint; default: none | Set explicit network type for the specified interface. |
| Authentication | None | Password | MD5 HMAC; default: none | Specifies the authentication mode that should be used for the interface. |
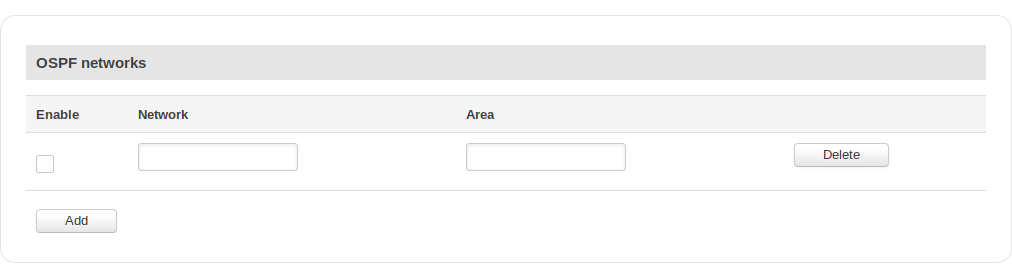
OSPF Networks
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Toggles OSPF network on or off. |
| Network | [a.b.c.d/m]; default: none | This command specifies the OSPF enabled interface. If the interface has an address from the range a.b.c.d/m then enables OSPF on this interface so the router can provide network information to the other OSPF routers via this interface. |
| Area | ospf area; default: none | Specifies OSPF area. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]