Template:Networking rut manual administration: Difference between revisions
Gytispieze (talk | contribs) m Text replacement - "\{\{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_fw_disclosure (.*) (.*) (.*) \}\}" to "{{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | series = {{{series}}} | name = {{{name}}} | fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = {{{series}}} | name = {{{name}}} }} }}" Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
|||
| (91 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
| fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
This | This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the Administration page for {{{name}}} devices. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 15: | ||
The <b>General</b> section is used to set up some of the router's managerial parameters, such as password, name, language, etc. For more information on the General section, refer to figure and table below. | The <b>General</b> section is used to set up some of the router's managerial parameters, such as password, name, language, etc. For more information on the General section, refer to figure and table below. | ||
{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT2XX| | |||
[[File:{{{file_general}}}]] | [[File:{{{file_general}}}]] | ||
|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT9XX| | |||
[[File:{{{file_general}}}|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
|}} | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 29: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Router name</td> | <td>Router name</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b> | <td>string; default: <b>{{{name}}}</b></td> | ||
<td>The router's model name.</td> | <td>The router's model name.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Host name</td> | <td>Host name</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b>Teltonika- | <td>string; default: <b>Teltonika-{{{name}}}.com</b></td> | ||
<td>The router's hostname. This can be used | <td>The router's hostname. This can be used for communication with other LAN hosts.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | |||
<td>Current password</td> | <td>Current password</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>The router's current password.</td> | <td>The router's current password.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>New password | Confirm new password</td> | <td>New password | Confirm new password</td> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 72: | ||
<td>Turns the router's LED indications on or off.</td> | <td>Turns the router's LED indications on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT2XX| | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Min time</td> | ||
<td>integer [5..60]; default: <b>5</b></td> | <td>integer [5..60]; default: <b>5</b></td> | ||
<td>Specifies the minimum amount of time (in seconds) that the reset button has to be pressed and held down in order to initiate a factory reset.</td> | <td>Specifies the minimum amount of time (in seconds) that the reset button has to be pressed and held down in order to initiate a factory reset.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Restore to default</td> | <td>Max time</td> | ||
<td>integer [5..100]; default: <b>30</b></td> | |||
<td>Specifies the maximum amount of time (in seconds) that the reset button has to be pressed and held down in order to initiate a factory reset.</td> | |||
</tr>|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT9XX| | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Min time</td> | |||
<td>integer [0..60]; default:<b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Minimum time 0-60 (in seconds) that the button needs to be held to perform an action.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Max time</td> | |||
<td>integer [0..59]; default:<b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Maximum time 1-60 (in seconds) that the button can be held to perform an action, after which no action will be performed.</td> | |||
</tr>|}} | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Action</td> | |||
<td>Reboot|User's defaults configuration|Factory defaults configuration; default:<b>Reboot</b> </td> | |||
<td>The action to be performed when this rule is met.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Restore to User's default</td> | |||
<td>-(interactive button)</td> | <td>-(interactive button)</td> | ||
<td>Restores the router to | <td>Restores the router to custom configuration set by the user.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Restore to Factory default's</td> | |||
<td>-(interactive button)</td> | |||
<td>Restores the router to manufacturer default settings.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
==Troubleshoot== | ==Troubleshoot== | ||
The <b>Troubleshoot</b> section is used to download various files that contain information used for troubleshooting the router. Refer to the figure and table below for information on the Troubleshoot page. | |||
[[File:{{{file_troubleshoot}}}]] | [[File:{{{file_troubleshoot}}}]] | ||
| Line 119: | Line 158: | ||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>yes</b></td> | <td>yes | no; default: <b>yes</b></td> | ||
<td>When checked, includes the router's chat script information in log file.</td> | <td>When checked, includes the router's chat script information in log file.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr>{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT9XX| | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Include network topology information</td> | <td>Include network topology information</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>no</b></td> | <td>yes <nowiki>|</nowiki> no; default: <b>no</b></td> | ||
<td>When checked, includes the router's network topology information in the log file.</td> | <td>When checked, includes the router's network topology information in the log file.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr>|}} | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>System log</td> | <td>System log</td> | ||
| Line 148: | Line 187: | ||
<td>Enable TCP dump<span class="asterisk">*</span></td> | <td>Enable TCP dump<span class="asterisk">*</span></td> | ||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>no</b></td> | <td>yes | no; default: <b>no</b></td> | ||
<td>Turns TCP dump on or off.</td> | <td>Turns TCP dump packets capture on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<font size="-1"><span class="asterisk">*</span> More on TCP dump in the [[#TCP_dump|next section]].</font> | |||
===TCP dump=== | |||
---- | |||
<b>TCP dump</b> is a program used to capture packets moving through network interfaces. By default, the router does not store TCP dump information. You must enable TCP dump and save the changes before you can download the file. | |||
If you enable TCP dump, you will notice additional configuration fields appear. Refer to the figure and table below for realted information. | |||
[[File:{{{file_tcpdump}}}]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable TCP dump</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>no</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns TCP dump packet capture on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Select interface</td> | |||
<td>network interface; default: <b>any</b></td> | |||
<td>Only captures packets that move through the specified network interface.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Select protocol filter</td> | |||
<td>all | icmp | tcp | udp | arp; default: <b>all</b></td> | |||
<td>Only captures packets that match the specified protocol.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Select packets direction</td> | |||
<td>IN/OUT | Incoming | Outgoing; default: <b>IN/OUT</b></td> | |||
<td>Only captures packets coming from the specified direction.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Host</td> | |||
<td>ip | host; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Only captures packets related to the specified host.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Port</td> | |||
<td>integer [0..65335]; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Only captures packets related to the specified communication port.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Select storage</td> | |||
<td>Internal storage; default: <b>Internal storage</b></td> | |||
<td>Specifies where the TCP dump file will be stored.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
==Backup== | ==Backup== | ||
{{ | |||
The <b>Backup</b> page is used to generate the user's defaults configuration and download or upload backup files to the router. | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT9XX| | |||
===User's Defaults Configuration=== | |||
---- | |||
The following section is used to create a custom default configuration that will be applied after resetting the device. | |||
The corresponding preset is automatically generated according to the current router's configuration by pressing the 'Create' button. | |||
With the help of this feature, the device can have two different default configuration presets: | |||
<ul> | |||
<li><b>User defaults</b> - custom configuration set by the user</li> | |||
<li><b>Factory defaults</b> - default configuration set by the manufacturer</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
The device can be reset to selected default configuration by pressing and holding the reset button for a [[{{{name}}}_Administration#General|specified period of time]]. | |||
<b>Note</b>: the backup file does not contain <b>User's Defaults Configuration</b>. | |||
[[File:Networking_rut9xx_administration_backup_users_default_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
|}} | |||
===Backup and Restore Configuration=== | |||
---- | |||
The <b>Backup</b> and <b>Restore Configuration</b> sections are used to download or upload configuration | |||
backup files to the router. Backup files can be uploaded only from identical devices with | |||
identical or older {{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUT9XX|(no older than <i>RUT9XX_R_00.03.726</i>) |}} firmware. | |||
Once a backup file is uploaded to a router, that router will have identical configuration | |||
as the router from which the backup file originated (was downloaded from). | |||
[[File:Networking_rut2xx_administration_backup_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<ul> | |||
<li><b>Backup Configuration</b> - generates and downloads the router's backup file based on the current configuration. | |||
Section also contains MD5, SHA256 checksum fields generated from latest downloaded backup.</li> | |||
<li><b>Restore Configuration</b> - uploads a configuration backup file to the router. | |||
Once uploaded you will be redirected to [[#Backup Security Check|backup security check page]].</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<b>Important</b>: backup files can be uploaded only when taken from a device with identical | |||
<b>Product code</b>, which can be checked in <b>Status → [[{{{name}}} Device|Device]]</b>, and identical or older firmware. | |||
===Backup Security Check=== | |||
---- | |||
After uploading backup you will be redirected to the following page to verify if the checksums | |||
of uploaded backup matches any of your downloaded backups. | |||
[[File:Networking_rut2xx_administration_backup_security_check_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
==Access Control== | ==Access Control== | ||
The <b>Access Control</b> page is used to manage remote and local access to the router. | |||
<b>Important</b>: turning on remote access leaves the router vulnerable to external attackers. Make sure you use a strong password. | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
The | The <b>General</b> section is used to manage SSH, HTTP(S) and CLI access to the router. | ||
<br><br> | |||
<b>SSH</b> | |||
---- | |||
[[File:{{{file_access_ssh}}}]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable SSH access</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>yes</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns SSH access from the local network (LAN) on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Remote SSH access</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>no</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns SSH access from remote networks (WAN) on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Port</td> | |||
<td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b>22</b></td> | |||
<td>Selects which port to use for SSH access.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<br> | |||
<b>WebUI</b> | |||
---- | |||
[[File:Networking_rutxxx_manual_administration_access_control_general_webui_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable HTTP access</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>yes</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns HTTP access from the local network (LAN) to the router's WebUI on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable HTTPS access</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>yes</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns HTTPS access from the local network (LAN) to the router's WebUI on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Redirect to HTTPS</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>no</b></td> | |||
<td>Redirects connection attempts from HTTP to HTTPS.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable remote HTTP access</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>no</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns HTTP access from remote networks (WAN) to the router's WebUI on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Port</td> | |||
<td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b>80</b></td> | |||
<td>Selects which port to use for HTTP access.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable remote HTTPS access</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>no</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns HTTPS access from remote networks (WAN) to the router's WebUI on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Port</td> | |||
<td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b>443</b></td> | |||
<td>Selects which port to use for HTTPS access.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>uhttpd certificate</td> | |||
<td>- (interactive button)</td> | |||
<td> In order to reach the router using HTTPS, you should first download the uhttpd certificate and add it to your trusted CA list. </td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable JSON RPC</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>yes</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns JSON-RPC access via ubus on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>RFC1918 Filter</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>yes</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns Address Allocation for Private Internets on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<br> | |||
<b>CLI</b> | |||
---- | |||
[[File:{{{file_access_cli}}}]] | |||
[[ | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable CLI</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>yes</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns CLI access from the local network (LAN) on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable remote CLI</td> | |||
<td>yes | no; default: <b>no</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns CLI access from remote networks (WAN) on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Port range</td> | |||
<td>range of integers [0..65534]-[1..65535]; default: <b>4200-4220</b></td> | |||
<td>Selects which ports to use for CLI access.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Shell limit</td> | |||
<td>integer [1..10]; default: <b>5</b></td> | |||
<td>Maximum number of active CLI connections.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
===Safety=== | ===Safety=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
The <b>Safety</b> section is used to manage the <i>List Of Blocked Addresses</i>. After a user attempts to login to this devices via SSH/HTTP, he will have a limited amount of retries in case of unsuccessful login attempts. This limit is called <i>Fail count</i> and is set in this page. After the user exhausts the maximum number of attempts, his IP address will be blocked from making more attempts and added to the <i>List Of Blocked Addresses</i>. | |||
[[ | <br><br> | ||
<b>Block Unwanted Access</b> | |||
---- | |||
[[File:{{{file_access_unwanted}}}]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: <b>yes</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns secure SSH/HTTP access on or off. If this is checked, devices logging in have a limited amount of tries specified in the <i>Fail count</i> field to log in to the router via SSH/HTTP.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Clean after reboot</td> | <td>Clean after reboot</td> | ||
<td>yes | no; | <td>yes | no; default: <b>no</b></td> | ||
<td>If this field is checked, | <td>If this field is checked, addresses are removed from the <i>List Of Blocked Addresses</i> after every router reboot.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Fail count</td> | <td>Fail count</td> | ||
<td>integer; | <td>integer; default: <b>5</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Maximum login fail count after which the device's address is blocked and added to the <i>List Of Blocked Addresses</i>.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
<br> | |||
<b>List Of Blocked Addresses</b> | |||
---- | |||
[[File:{{{file_access_list}}}]] | |||
The screenshot above is of a list that contains one blocked address. If you or someone you know gets blocked accidentally, you can unblock users from this section by deleting their IP addresses from the list. | |||
<b>Note</b>: the list gets cleared after a factory reset. | |||
==Diagnostics== | ==Diagnostics== | ||
The | The <b>Diagnostics</b> section is used to execute simple network diagnostic tests, including <i>ping</i>, <i>traceroute</i> and <i>nslookup</i>. | ||
[[File:{{{file_diagnostics}}}]] | |||
Enter an address in the <i>Host</i> field and execute one of the following actions: | |||
<ul> | |||
<li><b>Ping</b> - sends ICMP requests to the specified address.</li> | |||
<li><b>Traceroute</b> - displays the path that packets have to take in order to reach the specified address.</li> | |||
<li><b>Nslookup</b> - obtains domain name address and IP address mapping information.</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
==MAC Clone== | ==MAC Clone== | ||
[[ | The <b>MAC Clone</b> section is used to change the router's WAN MAC address. You can change the MAC address by entering a new custom value in the <i>WAN MAC address</i> field or click the 'Get PC MAC address' button to obtain your PC's MAC address and use it to fill the field. | ||
[[File:{{{file_mac_clone}}}]] | |||
In some cases access to a local network is protected by a MAC filter. For example, your company's main router may bind the MAC addresses of devices to the physical Internet sockets they usually connect to. In these cases only the device that is bound to the socket may gain access to the network. You can use MAC Clone to "clone" your PCs address and apply it to your router's WAN Ethernet port to gain access to such networks. | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The | The <b>Overview</b> section is used to select which widgets should be visible in the Status → [[{{{name}}} Overview|Overview]] page. | ||
[[File:{{{file_overview}}}]] | |||
Simply select the widgets that you would like to view in the Overview page and click the 'Save' button. | |||
==RMS== | ==RMS== | ||
{{ | |||
<b>RMS</b> (<b>Remote Management System</b>) is a cloud system designed by Teltonika and intended for remote monitoring and management of [[Main Page|Teltonika-Networks products]]. | |||
In order to add a device(s) to RMS, get yourself acquainted by watching [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bZeqdrAcdVU this instructional video] and register an account by [https://rms.teltonika.lt/ clicking here]. <b>Each unique device receives a free month-long RMS license</b> when added to RMS for the first time. | |||
---- | |||
The figure below is a screenshot of the RMS section taken from a device which has been connected to RMS: | |||
[[File:{{{file_rms_connected}}}]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Connection type</td> | |||
<td>Enabled | Standby | Disabled; default: <b>Enabled</b></td> | |||
<td>Defines how the device will connect to RMS: | |||
<ul> | |||
<li><b>Enabled</b> - the device attempts to connect to RMS every 2-5 minutes (every 2 minutes the first hour; then every 5 minutes). If it cannot connect for 14 days, it will enter Standby mode.</li> | |||
<li><b>Standby</b> - the device attempts to connect to RMS every 6 hours.</li> | |||
<li><b>Disabled</b> - RMS functionality is disabled.</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Hostname</td> | |||
<td>host | ip; default: <b>rms.teltonika.lt</b></td> | |||
<td>Address of the RMS server. If you're using regular RMS, just leave the default address (<i><nowiki>rms.teltonika.lt</nowiki></i>).</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Port</td> | |||
<td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b>15009</b></td> | |||
<td>Port number for connecting to RMS. If you're using regular RMS, just leave the default port (<i>15009</i>).</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<br> | |||
---- | |||
The RMS server waits for incoming connections. Since the device attempts to connect at a fixed interval, it may not connect instantly after you add it to RMS. While it is disconnected, you can check how much time is left until the next connection attempt in the Status section: | |||
[[File:{{{file_rms_disconnected}}}]] | |||
To speed up the process by initiating an immediate connection attempt, click the 'Connect' button. | |||
For more information on Teltonika's Remote Management System (RMS) refer to the <b>[[RMS Manual]]</b> or <b>[[RMS FAQ]]</b> pages. | |||
==Root CA== | ==Root CA== | ||
[[Category: | The <b>Root CA</b> section is used to add a root CA certificate file to the router. There is a default file already preloaded on the device which will be overwritten by any uploaded file. The certificates must be in .pem format, maximum file size is 300 KB. These certificates are only needed if you want to use HTTPS for your services and the default file should be sufficient in most cases. | ||
[[File:{{{file_root_ca}}}]] | |||
[[Category:{{{name}}} System section]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:24, 24 October 2023
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the Administration page for {{{name}}} devices.
General
The General section is used to set up some of the router's managerial parameters, such as password, name, language, etc. For more information on the General section, refer to figure and table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Router name | string; default: {{{name}}} | The router's model name. |
| Host name | string; default: Teltonika-{{{name}}}.com | The router's hostname. This can be used for communication with other LAN hosts. |
| Current password | string; default: none | The router's current password. |
| New password | Confirm new password | string; default: none | A new password for the router. The password must be comprised of 8-32 characters, including at least one upper case letter, one lower case letter and one digit. |
| Language | English | Deutsch | Français | Turkish; default: English | Selects the router's WebUI language. |
| IPv6 Support | yes | no; default: no | Turns IPv6 support on or off. |
| Show mobile info at login page | yes | no; default: no | Shows mobile data connection information (signal strength, state, service mode) at login page. |
| Show WAN IP at login page | yes | no; default: no | Shows the router's WAN IP address at login page. |
| LEDs Indication | yes | no; default: yes | Turns the router's LED indications on or off. |
| Action | Reboot|User's defaults configuration|Factory defaults configuration; default:Reboot | The action to be performed when this rule is met. |
| Restore to User's default | -(interactive button) | Restores the router to custom configuration set by the user. |
| Restore to Factory default's | -(interactive button) | Restores the router to manufacturer default settings. |
Troubleshoot
The Troubleshoot section is used to download various files that contain information used for troubleshooting the router. Refer to the figure and table below for information on the Troubleshoot page.
[[File:{{{file_troubleshoot}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| System log level | Debug | Info | Notice | Warning | Error | Critical | Alert | Emergency; default: debug | Specifies the information output level of the system log.
|
| Save log in | RAM memory | Flash memory; default: RAM memory | Specifies which type of memory to use for storing system logs. |
| Include GSMD information | yes | no; default: yes | When checked, includes the router's GSMD information in the log file. |
| Include PPPD information | yes | no; default: no | When checked, includes the router's PPPD information in the log file. |
| Include chat script information | yes | no; default: yes | When checked, includes the router's chat script information in log file. |
| System log | - (interactive button) | Displays the contents of the router's system log file. The system log contains records of various system related events, such as starts/stops of various services, errors, reboots, etc. |
| Kernel log | - (interactive button) | Displays the contents of the router's kernel log file. The kernel log contains records of various events related to the processes of the operating system (OS). |
| Troubleshoot file | - (interactive button) | Downloads the router's Troubleshoot file. It contains the router's configuration information, logs and some other files. When requesting support, it is recommended to always provide the router's Troubleshoot file to Teltonika engineers for analysis. |
| TCP dump file | - (interactive button) | Downloads the router's TCP dump file. TCP dump is a program used to capture packets moving through network interfaces. By default, the router does not store TCP dump information. You must enable TCP dump and save the changes before you can download the file. |
| Enable TCP dump* | yes | no; default: no | Turns TCP dump packets capture on or off. |
* More on TCP dump in the next section.
TCP dump
TCP dump is a program used to capture packets moving through network interfaces. By default, the router does not store TCP dump information. You must enable TCP dump and save the changes before you can download the file.
If you enable TCP dump, you will notice additional configuration fields appear. Refer to the figure and table below for realted information.
[[File:{{{file_tcpdump}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable TCP dump | yes | no; default: no | Turns TCP dump packet capture on or off. |
| Select interface | network interface; default: any | Only captures packets that move through the specified network interface. |
| Select protocol filter | all | icmp | tcp | udp | arp; default: all | Only captures packets that match the specified protocol. |
| Select packets direction | IN/OUT | Incoming | Outgoing; default: IN/OUT | Only captures packets coming from the specified direction. |
| Host | ip | host; default: none | Only captures packets related to the specified host. |
| Port | integer [0..65335]; default: none | Only captures packets related to the specified communication port. |
| Select storage | Internal storage; default: Internal storage | Specifies where the TCP dump file will be stored. |
Backup
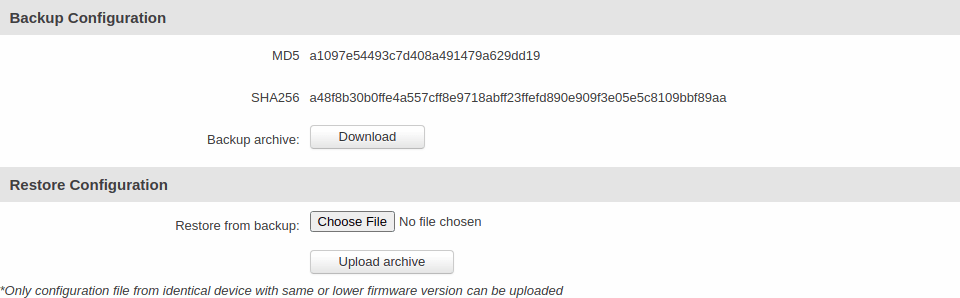
The Backup page is used to generate the user's defaults configuration and download or upload backup files to the router.
Backup and Restore Configuration
The Backup and Restore Configuration sections are used to download or upload configuration backup files to the router. Backup files can be uploaded only from identical devices with identical or older firmware. Once a backup file is uploaded to a router, that router will have identical configuration as the router from which the backup file originated (was downloaded from).
- Backup Configuration - generates and downloads the router's backup file based on the current configuration. Section also contains MD5, SHA256 checksum fields generated from latest downloaded backup.
- Restore Configuration - uploads a configuration backup file to the router. Once uploaded you will be redirected to backup security check page.
Important: backup files can be uploaded only when taken from a device with identical Product code, which can be checked in Status → [[{{{name}}} Device|Device]], and identical or older firmware.
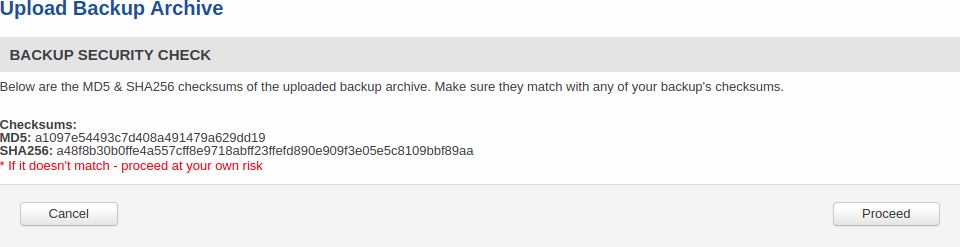
Backup Security Check
After uploading backup you will be redirected to the following page to verify if the checksums of uploaded backup matches any of your downloaded backups.
Access Control
The Access Control page is used to manage remote and local access to the router.
Important: turning on remote access leaves the router vulnerable to external attackers. Make sure you use a strong password.
General
The General section is used to manage SSH, HTTP(S) and CLI access to the router.
SSH
[[File:{{{file_access_ssh}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable SSH access | yes | no; default: yes | Turns SSH access from the local network (LAN) on or off. |
| Remote SSH access | yes | no; default: no | Turns SSH access from remote networks (WAN) on or off. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 22 | Selects which port to use for SSH access. |
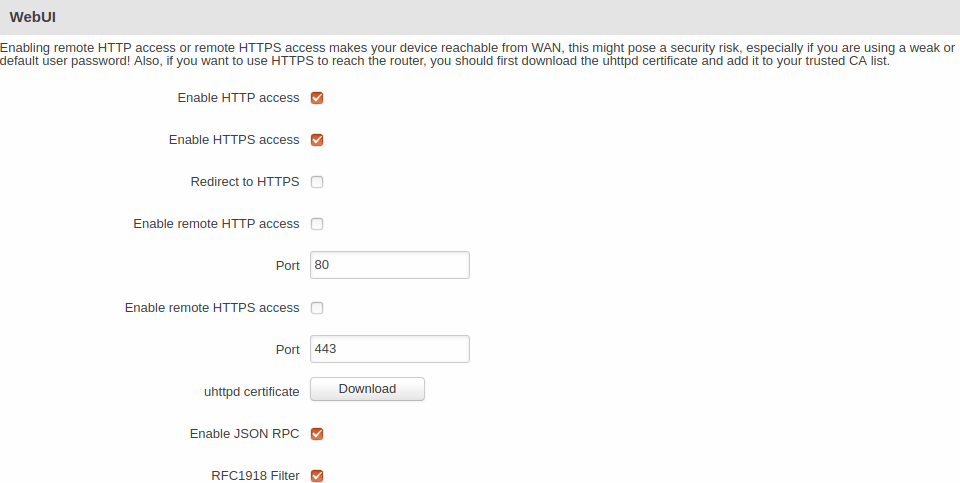
WebUI
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable HTTP access | yes | no; default: yes | Turns HTTP access from the local network (LAN) to the router's WebUI on or off. |
| Enable HTTPS access | yes | no; default: yes | Turns HTTPS access from the local network (LAN) to the router's WebUI on or off. |
| Redirect to HTTPS | yes | no; default: no | Redirects connection attempts from HTTP to HTTPS. |
| Enable remote HTTP access | yes | no; default: no | Turns HTTP access from remote networks (WAN) to the router's WebUI on or off. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 80 | Selects which port to use for HTTP access. |
| Enable remote HTTPS access | yes | no; default: no | Turns HTTPS access from remote networks (WAN) to the router's WebUI on or off. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 443 | Selects which port to use for HTTPS access. |
| uhttpd certificate | - (interactive button) | In order to reach the router using HTTPS, you should first download the uhttpd certificate and add it to your trusted CA list. |
| Enable JSON RPC | yes | no; default: yes | Turns JSON-RPC access via ubus on or off. |
| RFC1918 Filter | yes | no; default: yes | Turns Address Allocation for Private Internets on or off. |
CLI
[[File:{{{file_access_cli}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable CLI | yes | no; default: yes | Turns CLI access from the local network (LAN) on or off. |
| Enable remote CLI | yes | no; default: no | Turns CLI access from remote networks (WAN) on or off. |
| Port range | range of integers [0..65534]-[1..65535]; default: 4200-4220 | Selects which ports to use for CLI access. |
| Shell limit | integer [1..10]; default: 5 | Maximum number of active CLI connections. |
Safety
The Safety section is used to manage the List Of Blocked Addresses. After a user attempts to login to this devices via SSH/HTTP, he will have a limited amount of retries in case of unsuccessful login attempts. This limit is called Fail count and is set in this page. After the user exhausts the maximum number of attempts, his IP address will be blocked from making more attempts and added to the List Of Blocked Addresses.
Block Unwanted Access
[[File:{{{file_access_unwanted}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: yes | Turns secure SSH/HTTP access on or off. If this is checked, devices logging in have a limited amount of tries specified in the Fail count field to log in to the router via SSH/HTTP. |
| Clean after reboot | yes | no; default: no | If this field is checked, addresses are removed from the List Of Blocked Addresses after every router reboot. |
| Fail count | integer; default: 5 | Maximum login fail count after which the device's address is blocked and added to the List Of Blocked Addresses. |
List Of Blocked Addresses
[[File:{{{file_access_list}}}]]
The screenshot above is of a list that contains one blocked address. If you or someone you know gets blocked accidentally, you can unblock users from this section by deleting their IP addresses from the list.
Note: the list gets cleared after a factory reset.
Diagnostics
The Diagnostics section is used to execute simple network diagnostic tests, including ping, traceroute and nslookup.
[[File:{{{file_diagnostics}}}]]
Enter an address in the Host field and execute one of the following actions:
- Ping - sends ICMP requests to the specified address.
- Traceroute - displays the path that packets have to take in order to reach the specified address.
- Nslookup - obtains domain name address and IP address mapping information.
MAC Clone
The MAC Clone section is used to change the router's WAN MAC address. You can change the MAC address by entering a new custom value in the WAN MAC address field or click the 'Get PC MAC address' button to obtain your PC's MAC address and use it to fill the field.
[[File:{{{file_mac_clone}}}]]
In some cases access to a local network is protected by a MAC filter. For example, your company's main router may bind the MAC addresses of devices to the physical Internet sockets they usually connect to. In these cases only the device that is bound to the socket may gain access to the network. You can use MAC Clone to "clone" your PCs address and apply it to your router's WAN Ethernet port to gain access to such networks.
Overview
The Overview section is used to select which widgets should be visible in the Status → [[{{{name}}} Overview|Overview]] page.
[[File:{{{file_overview}}}]]
Simply select the widgets that you would like to view in the Overview page and click the 'Save' button.
RMS
RMS (Remote Management System) is a cloud system designed by Teltonika and intended for remote monitoring and management of Teltonika-Networks products.
In order to add a device(s) to RMS, get yourself acquainted by watching this instructional video and register an account by clicking here. Each unique device receives a free month-long RMS license when added to RMS for the first time.
The figure below is a screenshot of the RMS section taken from a device which has been connected to RMS:
[[File:{{{file_rms_connected}}}]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Connection type | Enabled | Standby | Disabled; default: Enabled | Defines how the device will connect to RMS:
|
| Hostname | host | ip; default: rms.teltonika.lt | Address of the RMS server. If you're using regular RMS, just leave the default address (rms.teltonika.lt). |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 15009 | Port number for connecting to RMS. If you're using regular RMS, just leave the default port (15009). |
The RMS server waits for incoming connections. Since the device attempts to connect at a fixed interval, it may not connect instantly after you add it to RMS. While it is disconnected, you can check how much time is left until the next connection attempt in the Status section:
[[File:{{{file_rms_disconnected}}}]]
To speed up the process by initiating an immediate connection attempt, click the 'Connect' button.
For more information on Teltonika's Remote Management System (RMS) refer to the RMS Manual or RMS FAQ pages.
Root CA
The Root CA section is used to add a root CA certificate file to the router. There is a default file already preloaded on the device which will be overwritten by any uploaded file. The certificates must be in .pem format, maximum file size is 300 KB. These certificates are only needed if you want to use HTTPS for your services and the default file should be sufficient in most cases.
[[File:{{{file_root_ca}}}]]
[[Category:{{{name}}} System section]]