TAP200 Wireless: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_wireless | {{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_wireless | ||
| name = TAP200 | <!------------------------DEVICE-----------------------> | ||
| series | | name = TAP200 | ||
| wifi = 5 }} | | series = TAP200 | ||
<!----------------------SEPARATORS---------------------> | |||
| wifi = 5 <!-- 5 or 2 (GHz) --> | |||
}} | |||
Latest revision as of 10:27, 26 October 2023
Main Page > TAP Access Points > TAP200 > TAP200 Manual > TAP200 WebUI > TAP200 Network section > TAP200 WirelessThe information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version TAP200_R_00.07.10.2.
Summary
The Wireless section of the Network tab can be used to manage and configure WiFi Access Points, WiFi Stations (clients) and WiFi devices. This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the Wireless section for TAP200 devices.
Wireless
TAP200 devices support IEEE 802.11ac (WiFi 5) with data transmission rates up to 867 Mbps (Dual Band, MU-MIMO), 802.11r fast transition.
SSIDS
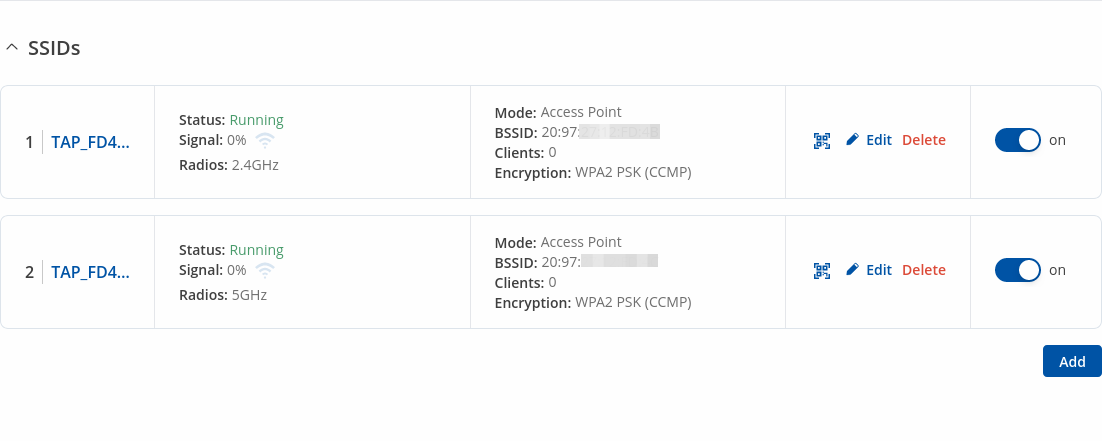
The SSIDs section is used to configure your wireless access points (AP) and wireless clients (STA).
Above is the overview of the SSIDS Overview window. It displays active access points. Here you can turn on or off your WiFi interfaces, remove them or start configuring by clicking on
Edit button on the right side of interface.
Radio
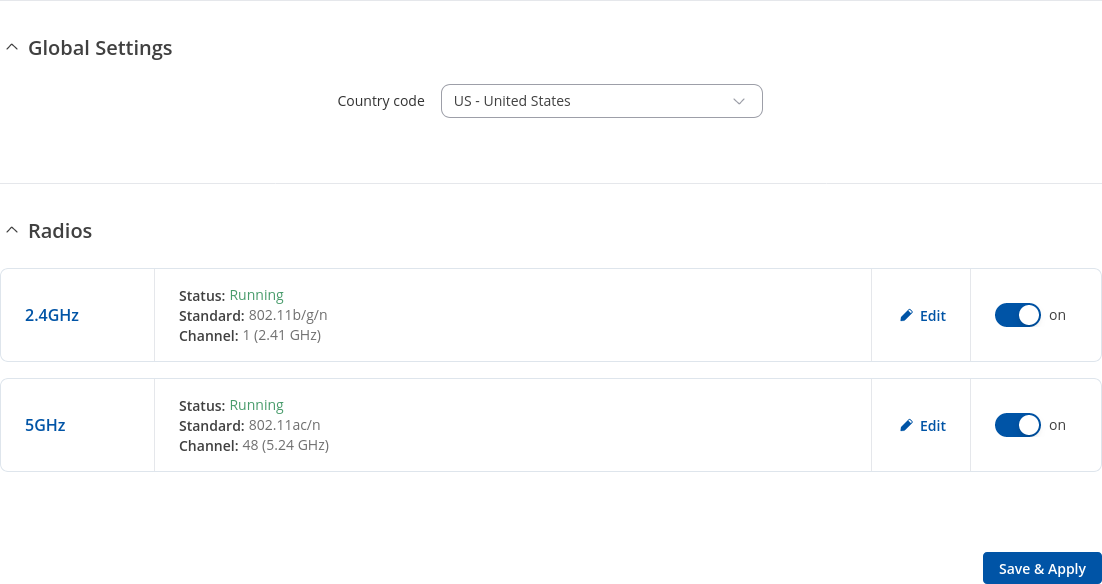
The Global Settings section is used for configuring the country code which is used for regulatory purposes (different areas allow different maximum transmit power and operating frequencies) and WiFi hardware parameters. You can change parameters by clicking the 'Edit' button next to a wireless device (not an interface) in the Network → SSIDS page:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Country code | country code; default: US - United States | SO/IEC 3166 alpha2 country codes as defined in ISO 3166-1 standard. |
General Setup
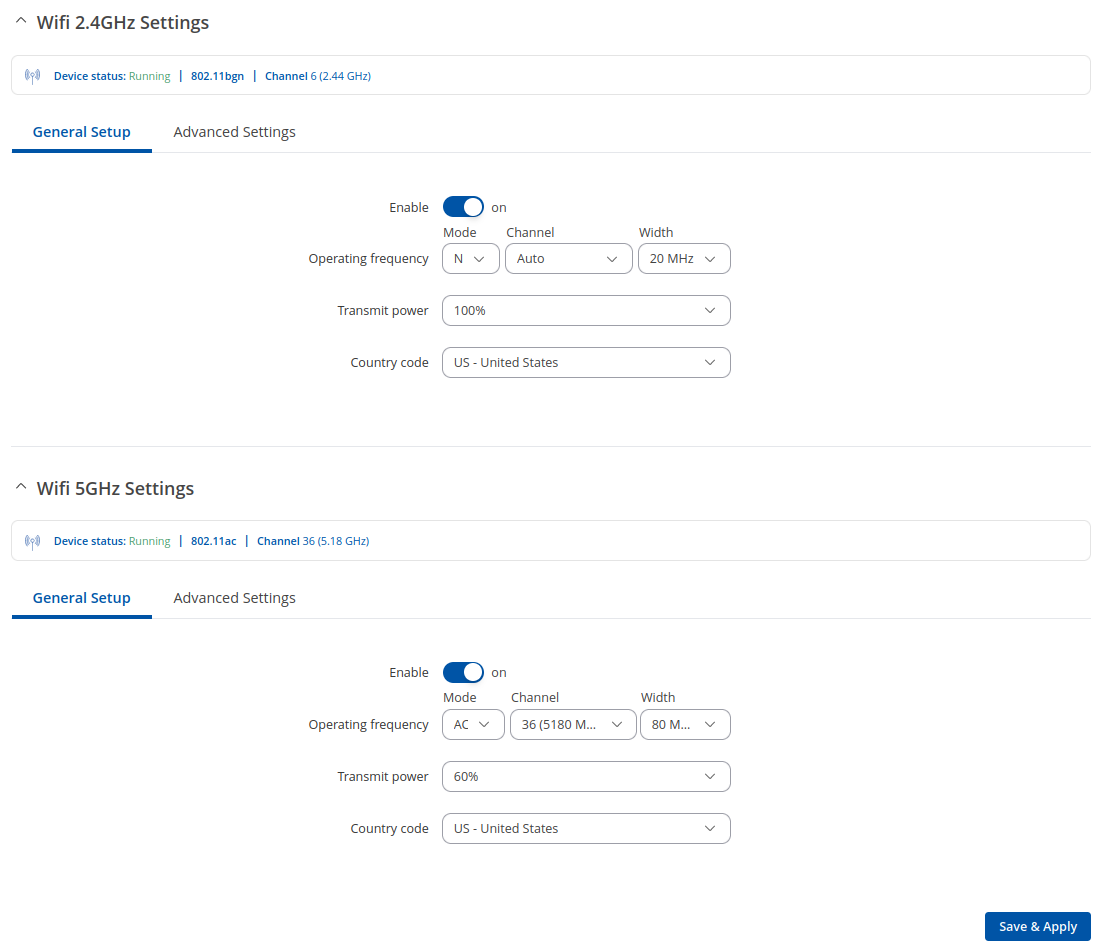
The General Setup section is used to turn a wireless device on or off, select the operating frequency (WiFi mode, channel and channel width) and transmit power.
A wireless 2.4 GHz WiFi channel requires a signaling band roughly 22 MHz wide, radio frequencies of neighboring channels numbers significantly overlap each other. Choose a WiFi channel according to the busyness of other channels. You can download a free WiFi analyzer app on your phone, laptop or other WiFi device and check which channel is the least populated.
Many home networks utilize routers that by default run on channel 6 on the 2.4 GHz band. Neighboring WiFi home networks that run over the same channel generate radio interference that can cause significant network performance slowdowns for users. Reconfiguring a network to run on a different wireless channel helps minimize these slowdowns. Therefore, pick a channel with no other active Access Points and preferably one that has no active Access Point on two adjacent channels on each side as well. If you don't feel like doing this, set the 'Channel' field to Auto and the device will pick the least busy channel in your location automatically.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: on | Turns Wireless device on or off. |
| Operating Frequency (2.4 GHz) | ||
| Mode | N | Legacy; default: N | Wireless N (802.11n) supports a maximum theoretical transfer rate of 300mbps with 2 antennas. It can reach up to 450 Mbps with 3 antennas. Though typical speeds are more accurately around 130 Mbps. The legacy standards include 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g. |
| Channel | Auto | 1 (2412 MHz) | 2 (2417 MHz) | 3 (2422 MHz) | 4 (2427 MHz) | 5 (2432 MHz) | 6 (2437 MHz) | 7 (2442 MHz) | 8 (2447 MHz) | 9 (2452 MHz) | 10 (2457 MHz) | 11 (2462 MHz); default: Auto | A wireless 2.4 GHz WiFi channel requires a signaling band roughly 22 MHz wide, radio frequencies of neighboring channels numbers significantly overlap each other. Therefore, pick a channel with no other active Access Points and preferably one that has no active Access Point on two adjacent channels on each side as well. |
| Width | 20 MHz | 40 MHz; default: 20 MHz | A 40 MHz channel width bonds two 20 MHz channels together, forming a 40 MHz channel width; therefore, it allows for greater speed and faster transfer rates. But not if those channels are crowded with noise and interference. In crowded areas with a lot of frequency noise and interference, a single 20MHz channel will be more stable. 40MHz channel width allows for greater speed and faster transfer rates but it doesn’t perform as well in crowded areas. |
| Operating Frequency (5 GHz) | ||
| Mode | N | AC; default: AX | Choose between 802.11n and 802.11ac standards. |
| Channel | Auto | 36(5180 MHz) | 40(5200 MHz) | 44(5220 MHz) | 48(5240 MHz) | 52(5260 MHz) | 56(5280 MHz) | 60(5300 MHz) | 64(5320 MHz) | 68(5340 MHz) | 72(5360 MHz) | 76(5380 MHz) | 80(5400 MHz) | 84(5420 MHz) | 88(5440 MHz) | 92(5460 MHz) | 96(5480 MHz) | 100(5500 MHz) | 104(5520 MHz) | 108(5540 MHz) | 112(5560 MHz) | 116(5580 MHz) | 120(5600 MHz) | 124(5620 MHz) | 128(5640 MHz) | 132(5660 MHz) | 136(5680 MHz) | 140(5700 MHz) | 144 (5720 MHz) | 149 (5745 MHz) | 153 (5765 MHz) |157 (5785 MHz) | 161 (5805 MHz) | 165 (5825 MHz); default: Auto | A wireless 5 GHz WiFi channel also requires a signaling band roughly 22 MHz wide, but since its channel with is 20 MHZ ir overlaps less with neighboring channels, but it is still recommended to pick a channel with no other active Access Points and preferably one that has no active Access Point on two adjacent channels on each side as well. |
| Width | 20 MHz | 40 MHz | 80 MHz ; default: 80MHz | A 40 MHz channel width bonds two 20 MHz channels together, forming a 40 MHz channel width, 8 MHZ channel bonds four 20 MHz channels; therefore, it allows for greater speed and faster transfer rates. But not if those channels are crowded with noise and interference. In crowded areas with a lot of frequency noise and interference, a single 20MHz channel will be more stable. 80 MHz width channel is faster than 40MHz which is faster than 20 MHz but it doesn’t perform as well in crowded areas. |
| Transmit Power | [13%...100%]; default: 100 % | The transmit power of an access point radio is proportional to its effective range – the higher the transmit power, the more distance that a signal can travel, and/or the more physical materials that it can effectively penetrate and still have data successfully resolved at the receiver. |
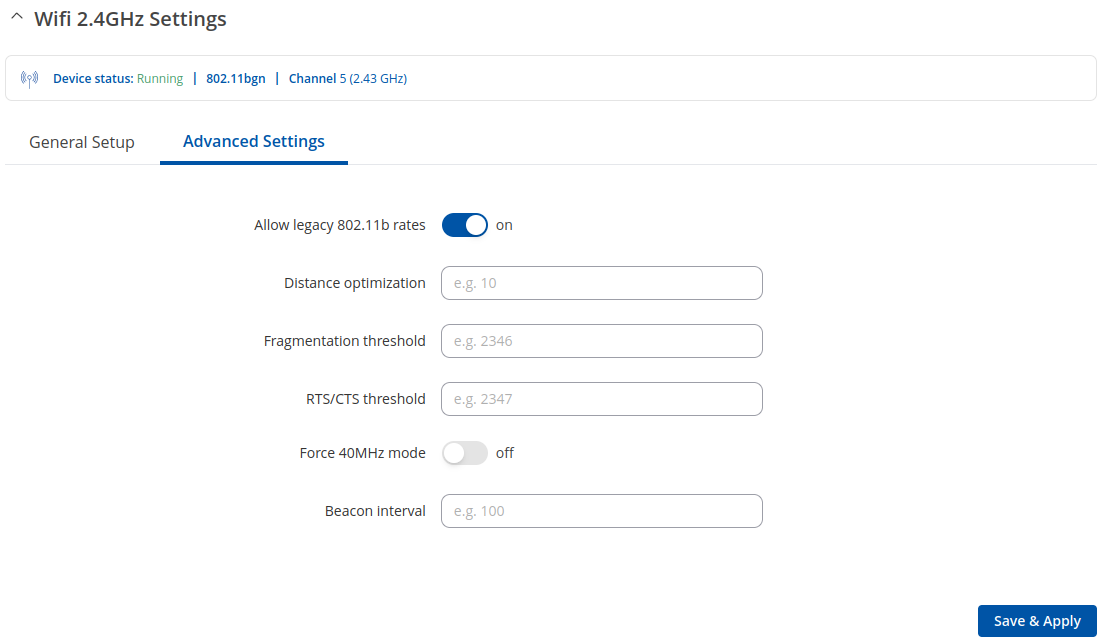
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings section is used to configure how the wireless Access Point will work from a hardware perspective.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Frequency (2.4 GHz) | ||
| Allow legacy 802.11b rates | off | on; default: on | Turn on to enable connections that uses legacy 802.11b standard. |
| Distance Optimization | integer [0..65535]; default: none | HT Distance to farthest network member in meters. |
| Fragmentation threshold | integer [256..2346]; default: none | The smallest packet size that can be fragmented and transmitted by multiple frames. In areas were interference is a problem, setting a lower fragment threshold might help reduce the probability of unsuccessful packet transfers, thus increasing speed |
| RTS/CTS threshold | integer [0..2347]; default: none | RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to Send) are mechanisms, used to reduce frame collisions introduced by the hidden node problem. It can help resolve problems arising when several access points are in the same area, contending |
| Force 40MHz mode | off | on; default: off | Always use 40MHz channels even if the secondary channel overlaps. Using this option does not comply with IEEE 802.11n-2009! |
| Beacon interval | integer [15..65535]; default: none | Beacon signal interval in seconds. |
| Operating Frequency (5 GHz) | ||
| Distance Optimization | integer [0..65535]; default: none | HT Distance to farthest network member in meters. |
| Fragmentation threshold | integer [256..2346]; default: none | The smallest packet size that can be fragmented and transmitted by multiple frames. In areas were interference is a problem, setting a lower fragment threshold might help reduce the probability of unsuccessful packet transfers, thus increasing speed |
| RTS/CTS threshold | integer [0..2347]; default: none | RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to Send) are mechanisms, used to reduce frame collisions introduced by the hidden node problem. It can help resolve problems arising when several access points are in the same area, contending |
| Force 40MHz mode | off | on; default: off | Always use 40MHz channels even if the secondary channel overlaps. Using this option does not comply with IEEE 802.11n-2009! |
| Beacon interval | integer [15..65535]; default: none | Beacon signal interval in seconds. |
| ACS exclude DFS | off | on; default: off | Turn this option on to exclude DFS channels from automatic channel selection. |
SSIDs Configuration
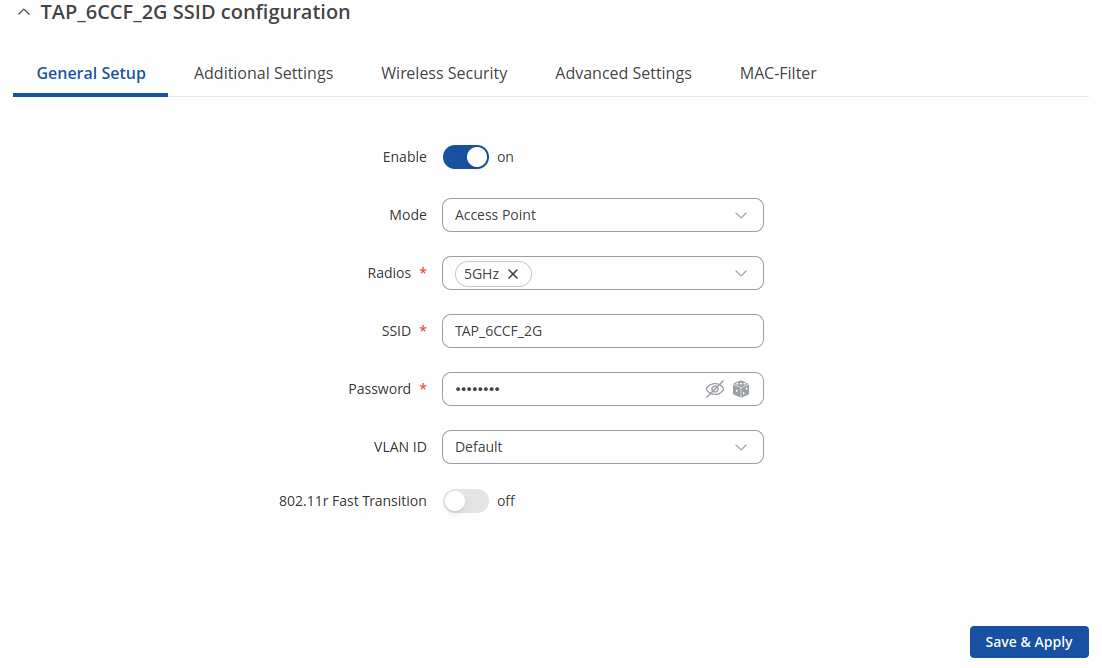
The Interface Configuration section is used to configure the parameters of Wireless Access Points . You can find this section by clicking the 'Edit' button next to a wireless interface (not a device) in the Network → SSIDs page:
General Setup
The General Setup tab contains basic options for SSID and network interface.
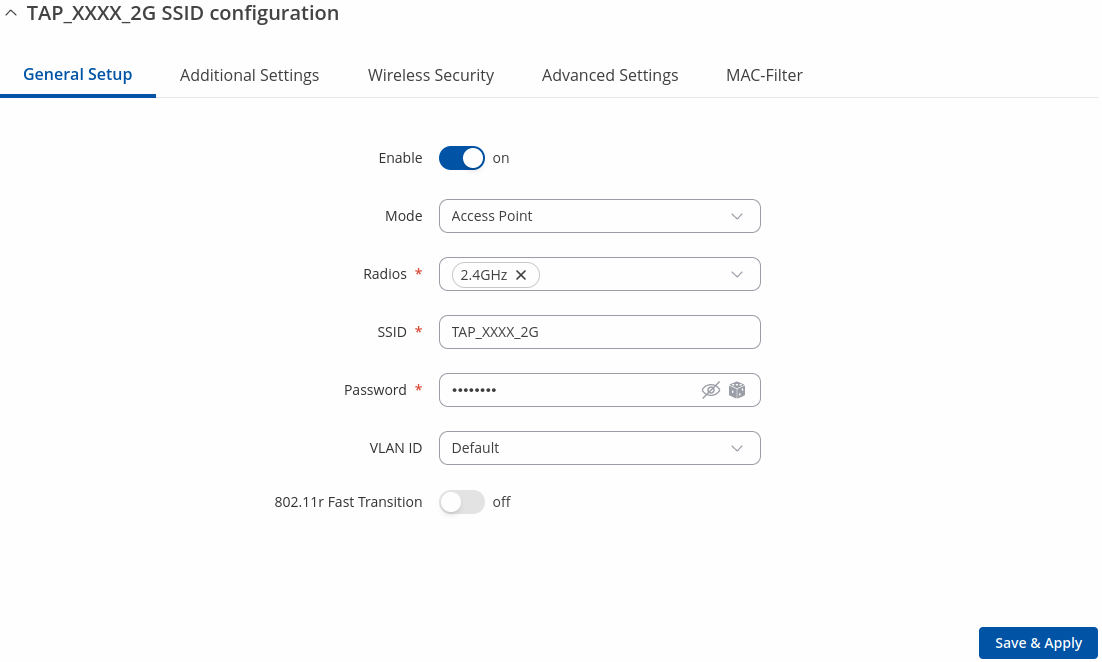
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: on | Enables or disables WiFi interface. |
| Mode | Access Point | Mesh ; default: Access Point | Defines what role this interface will do, Access point to supply WiFi for other devices, Client to use other devices WiFi for WWAN and Mesh to act as mesh network gateway or a node in a mesh network. |
| Access Point mode | ||
| Radios | 2.4 GHz | 5GHz; default: 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz | SSID will use these radios. Use one of them if you want seperate SSIDs for each radio or use all of them if you want combined SSID. |
| SSID | Factory SSID is different for every device; default: | Service Set Identifier is a name used to identify access point which is shown when client tries to connect to it. |
| Password | string; default: none | |
| VLAN ID | default | +add new; default: default | Use tagged VLAN from the network as untagged VLAN on the SSID. |
| 802.11r Fast Transition | off | on; default: off | Enables fast roaming among access points that belong to the same Mobility Domain |
| Mesh mode | ||
| Mesh ID | integer; default: none | Mesh network identifier. |
| Radios | 2.4 GHz | 5GHz; default: 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz | SSID will use these radios. Use one of them if you want seperate SSIDs for each radio or use all of them if you want combined SSID. |
| Password | string; default: none |
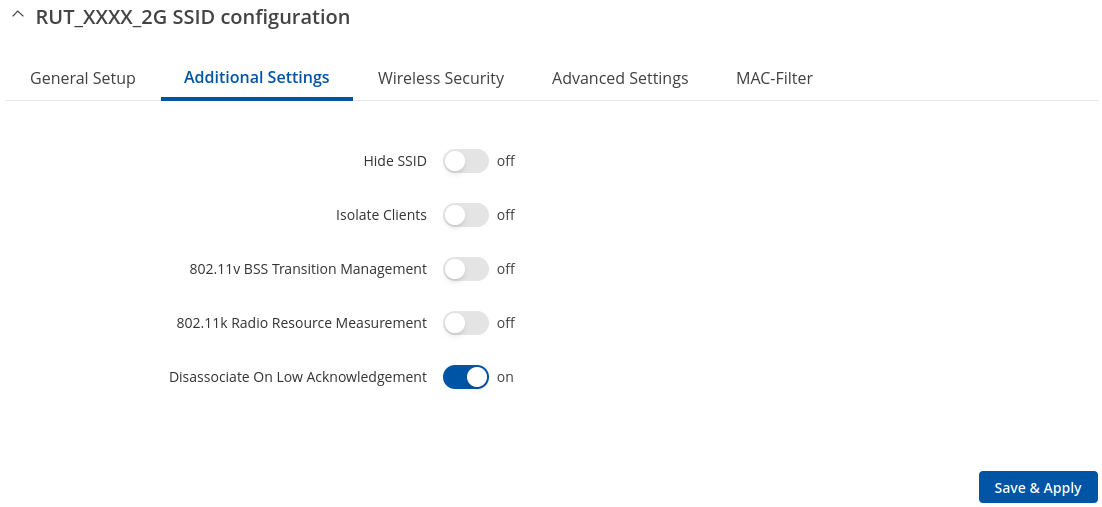
Additional Settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Access point | ||
| Hide SSID | on | off; default: off | Hide Service Set Identifier |
| Isolate Clients | off | on; default: off | Prevents client to client communication on the same subnet. |
| 802.11v BSS Transition Management | on | off; default: off | A suggestion (or advice) given to a client, which the client can choose to follow or ignore |
| 802.11k Radio Resource Measurement | on | off; default: off | Helps devices search quickly for nearby APs that are available as roaming targets by creating an optimized list of channels. |
| Disassociate On Low Acknowledgement | off | on; default: on | Allow AP mode to disconnect stations/clients based on low Acknowledgement condition. |
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
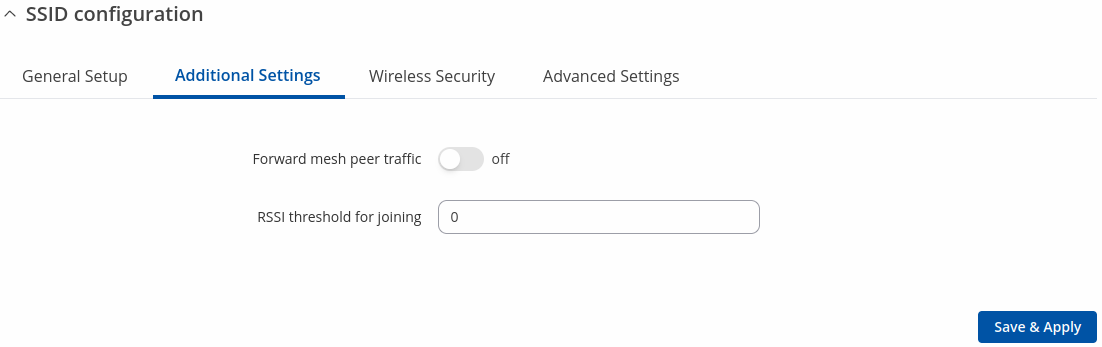
| Mesh | ||
| Forward mesh peer traffic | off | on; default: off | Enables mesh peer traffic forwarding. |
| RSSI threshold for joining | integer [0..1]; default: 0 | 0 = not using RSSI threshold, 1 = do not change driver default. |
Wireless Security
The Wireless Security tab is used to determine what kind of encryption your WLAN will use.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | No encryption | WPA-PSK | WPA2-PSK | WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Mixed Mode | WPA3-SAE | WPA2-PSK/WPA3-SAE Mixed Mode | OWE | WPA-EAP | WPA2-EAP | WPA2-EAP/WPA3-EAP Mixed Mode | WPA3-EAP Mixed Mode | WPA3-EAP; default: WPA2-PSK | The type of encryption used on this Wireless Interface.
Opportunistic Wireless Encryption (OWE) - no password is required and all wireless traffic is encrypted (safer than No Encryption). |
| WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Mixed Mode, WPA3-EAP | ||
| Cipher | Auto | Force CCMP (AES) | Force TKIP | Force TKIP and CCMP (AES); default: Auto | An algorithm for performing encryption or decryption. |
| WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Mixed Mode, WPA3-SAE, WPA2-PSK/WPA3-SAE Mixed Mode | ||
| Password | string; default: none | |
| WPA-EAP, WPA2-EAP, WPA2-EAP/WPA3-EAP Mixed Mode, WPA3-EAP | ||
| Radius-Authentication-Server | string; default: none | Ip address of the authentification server. |
| Radius-Authentication-Port | string; default: none | Default port for the server is 1812. |
| Radius-Authentication-Secret | string; default: none | Server's shared secret. |
| Radius-Accounting-Server | string; default: none | Ip address of the accounting server. |
| Radius-Accounting-Port | string; default: none | Default port for the server is 1813. |
| Radius-Accounting-Secret | string; default: none | Server's shared secret. |
| NAS id | string; default: none | Network access server identifier. |
| Mesh mode: WPA3-SAE, No encryption | ||
| Password | string; default: none |
MAC Filter
The MAC Filter tab is used for setting up rules that allow or exclude devices with specified MAC addresses from connecting to your WiFi network.
This tab is only visible when Wireless interface Mode is set to Access Point.
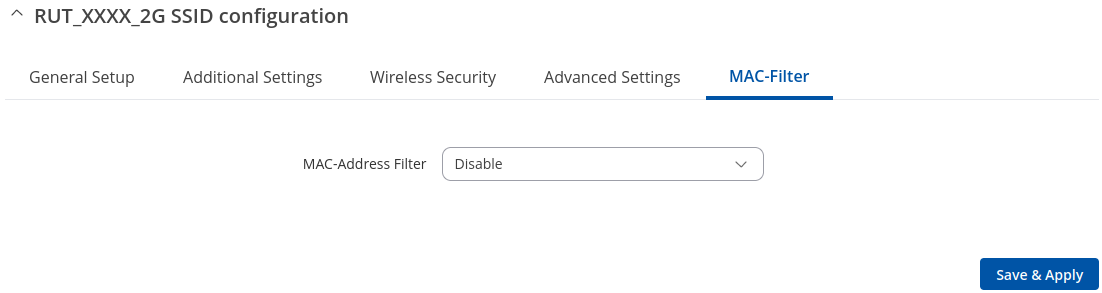
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MAC-address filter | Disable | Allow listed only | Allow all except listed; default: Disable | Defines how the MAC Filter should function.
|
| MAC-List | MAC; default: none | List of MAC addresses to be included or excluded from connecting to your Wireless Access Point. |
| Remove from whitelist | off | on; default: off | Enables MAC removal from whitelist when device reaches IP block counter. |
Advanced Settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Access point | ||
| Short Preamble | off | on; default: on | Uses Short Preamble, it uses shorter data strings that adds less data to transmit the error redundancy check which means that it is much faster. |
| DTIM interval | seconds; default: none | Delivery Traffic Indication Message Interval. |
| Time interval for rekeying GTK | seconds; default: none | Period of time in between automatic changes of the group key, which all devices on the network share. |
| Disable Inactivity Polling | off | on; default: off | Inactivity polling can be disabled to disconnect stations based on inactivity timeout so that idle stations are more likely to be disconnected even if they are still in range of the AP. |
| Station inactivity limit | seconds; default: none | Station inactivity limit in seconds. If a station/client does not send anything in st time frame, an empty data frame is sent to it in order to verify whether it is still in range. If this frame is not acknowledged, the station will be disassociated and then deauthenticated. |
| Maximum allowed Listen Interval | positive integer; default: none | Association will be refused if a client/station attempts to associate with a listen interval greater than this value. |
| WDS | off | on; default: off | A Wireless Distribution System (WDS) is a system that enables the wireless interconnection of access points (APs) in a network. |
| WMM Mode | off | on; default: on | Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM), previously known as Wireless Multimedia Extensions (WME), is a subset of the 802.11e wireless LAN (WLAN) specification that enhances quality of service (QoS) on a network by prioritizing data packets according to four categories. |
| 802.11w Management frame protection | Disabled | Optional | Required; default: Disabled | Enables Management frame protection (MFP or PMF). By default it is set to 'Required' when using WPA3 encryption. |
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh | ||
| Short Preamble | off | on; default: on | Uses Short Preamble, it uses shorter data strings that adds less data to transmit the error redundancy check which means that it is much faster. |
| DTIM interval | seconds; default: none | Delivery Traffic Indication Message Interval. |
| Time interval for rekeying GTK | seconds; default: none | Period of time in between automatic changes of the group key, which all devices on the network share. |
| Disable Inactivity Polling | off | on; default: off | Inactivity polling can be disabled to disconnect stations based on inactivity timeout so that idle stations are more likely to be disconnected even if they are still in range of the AP. |
| Station inactivity limit | seconds; default: none | Station inactivity limit in seconds. If a station/client does not send anything in st time frame, an empty data frame is sent to it in order to verify whether it is still in range. If this frame is not acknowledged, the station will be disassociated and then deauthenticated. |
| Maximum allowed Listen Interval | positive integer; default: none | Association will be refused if a client/station attempts to associate with a listen interval greater than this value. |
Fast Transition
The Fast Transition tab is only available when in General setup section 802.11r Fast Transition option is enabled.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NAS id | string; default: empty | Used for fast transition and Radius server. |
| Mobility Domain | HEX string; default: empty | 4-character hexadecimal ID |
| Reassociation Deadline | integer [1000..65535]; default: empty | Time units (TUs / 1.024 ms) |
| FT protocol | FT over DS | FT over Air; default: FT over DS | Defines how nagotiation will happen using Fast Transition protocol. |
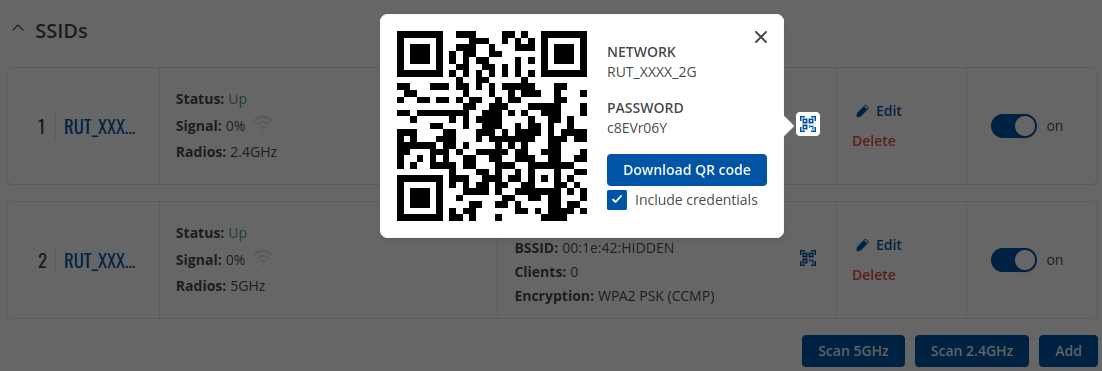
WiFi QR codes
Each WiFi interface has a specially designed QR code that contains information about the SSID and password of the WiFi network. After pressing the button ![]() , a QR code appears with the network's SSID and password, which you can download locally by pressing the 'Download' button. If you only want a QR code without additional information, uncheck the 'Include credentials' box.
, a QR code appears with the network's SSID and password, which you can download locally by pressing the 'Download' button. If you only want a QR code without additional information, uncheck the 'Include credentials' box.