Template:Networking rutos manual vrrp: Difference between revisions
Gytispieze (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===VRRP=== | |||
====Summary==== | |||
---- | |||
==Summary== | |||
<b>Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol</b> (<b>VRRP</b>) is a computer networking protocol used for automatic default gateway selection for clients on a LAN network in case the main router (Master) becomes unavailable. Another VRRP router (Backup) then assumes the role of Master; thus backing up the connection. | <b>Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol</b> (<b>VRRP</b>) is a computer networking protocol used for automatic default gateway selection for clients on a LAN network in case the main router (Master) becomes unavailable. Another VRRP router (Backup) then assumes the role of Master; thus backing up the connection. | ||
This page is an overview of the VRRP section of {{{name}}} devices. | This page is an overview of the VRRP section of {{{name}}} devices. | ||
{{# | {{#switch: {{{series}}} | ||
<u><b> | |RUTX|RUTM = | ||
|#default = | |||
Note:</b> VRRP is additional software that can be installed from the <b> | <u><b>Note:</b> VRRP is additional software that can be installed from the <b>System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]]</b> page.</u> | ||
==VRRP Configuration== | }} | ||
====VRRP Configuration==== | |||
---- | |||
The <b>VRRP Configuration</b> section lists VRRP instances currently existing on the device. By default the list is empty thus, you must first create at least one instance in order to begin configuring VRRP. | The <b>VRRP Configuration</b> section lists VRRP instances currently existing on the device. By default the list is empty thus, you must first create at least one instance in order to begin configuring VRRP. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 20: | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_vrrp_add_new_configuration_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<b id="link"></b>After clicking the 'Edit' button you should be redirected to that VRRP instance's configuration page, which should look similar to this: | <b id="link"></b>After clicking the 'Edit' button you should be redirected to that VRRP instance's configuration page, which should look similar to this: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_vrrp_vrrp_configuration_settings_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 64: | Line 56: | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Advertisement interval</td> | |||
<td>integer [1..255]; default: <b>100</b></td> | |||
<td>Time interval (in seconds) between router advertisements on the VRRP network.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 74: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
==Check connection== | ====Check connection==== | ||
---- | |||
The <b>Check connection</b> section is used to set the parameters that | The <b>Check connection</b> section is used to set the parameters that | ||
define how the router will determine whether the connection is still | define how the router will determine whether the connection is still | ||
| Line 133: | Line 130: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:23, 8 January 2024
VRRP
Summary
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is a computer networking protocol used for automatic default gateway selection for clients on a LAN network in case the main router (Master) becomes unavailable. Another VRRP router (Backup) then assumes the role of Master; thus backing up the connection.
This page is an overview of the VRRP section of {{{name}}} devices. Note: VRRP is additional software that can be installed from the System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]] page.
VRRP Configuration
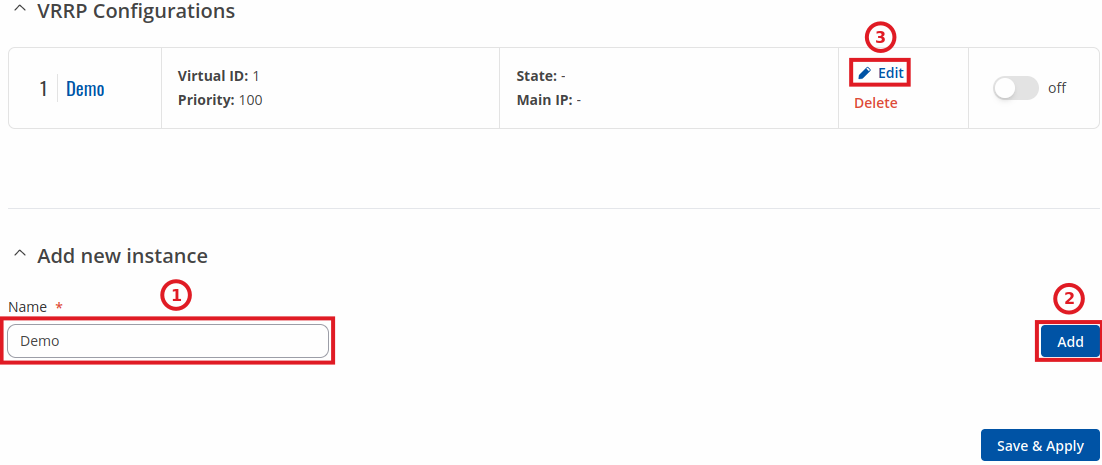
The VRRP Configuration section lists VRRP instances currently existing on the device. By default the list is empty thus, you must first create at least one instance in order to begin configuring VRRP.
- Enter a custom name for the new VRRP configuration in the 'Name' field.
- Click the 'Add' button.
- Click the 'Edit' button next to the newly created instance.
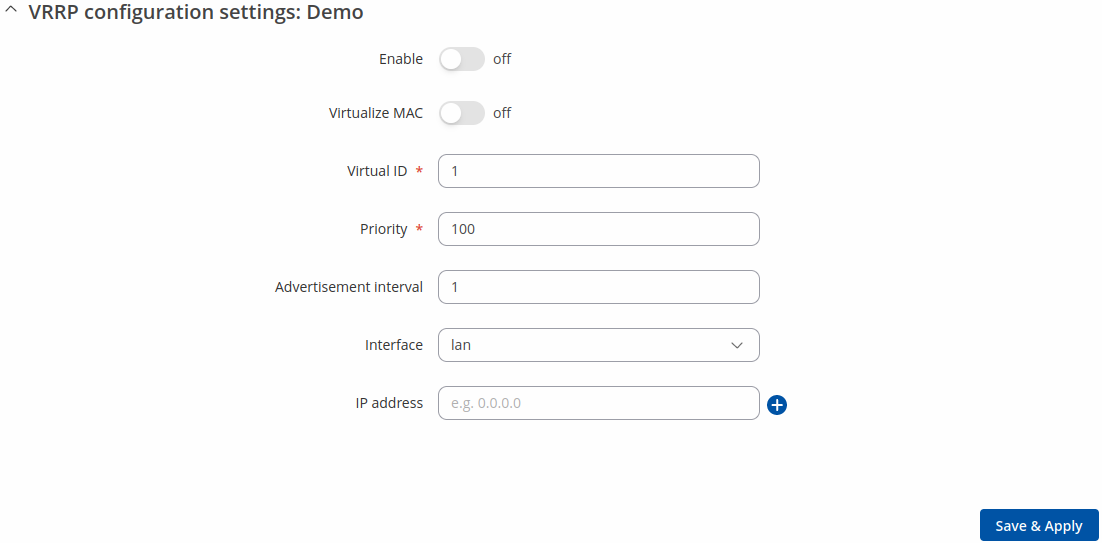
After clicking the 'Edit' button you should be redirected to that VRRP instance's configuration page, which should look similar to this:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns VRRP on or off. |
| Virtualize MAC | off | on; default: off | Turns the possibility to use virtual MAC addresses on or off. |
| Virtual ID | integer [1..255]; default: 1 | The Virtual Router Identifier (VRID) is a field in the VRRP packet IP header used to identify the virtual router in the VRRP cluster. Routers with identical IDs will be grouped in the same VRRP cluster. |
| Priority | integer [1..255]; default: 100 | VRRP priority of the virtual router. Higher values equal higher priority. The router with the highest priority is considered to be the Master router while other routers are Backup routers.
|
| Advertisement interval | integer [1..255]; default: 100 | Time interval (in seconds) between router advertisements on the VRRP network. |
| Interface | network interface; default: LAN | Selects which interface VRRP will operate on. |
| IP address | ip; default: none | Virtual IP address for the router's VRRP cluster. |
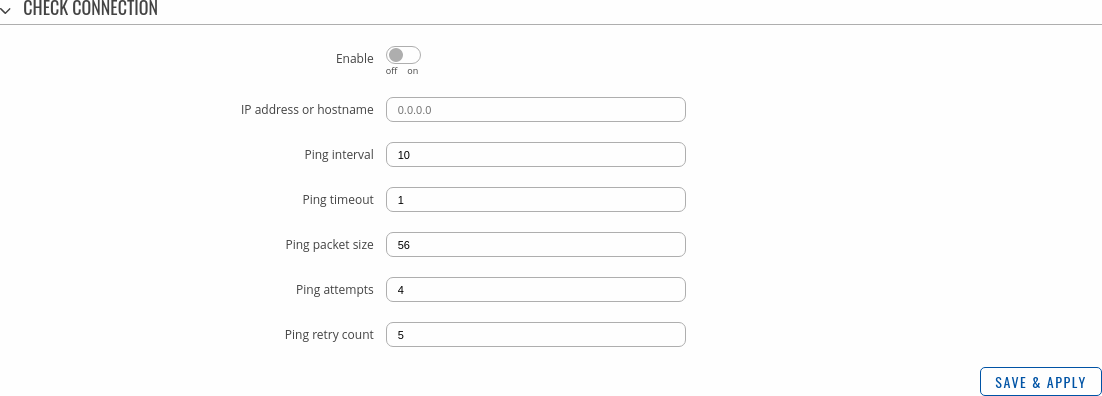
Check connection
The Check connection section is used to set the parameters that define how the router will determine whether the connection is still available or not. This is done by periodically sending ICMP packets from interface, configured in VRRP Configuration section, to a defined host and awaiting responses. If no response is received after a defined period of time, the connection is determined to be down, and thus the role of Master is assumed by another router in the network.
Refer to the figure and table below for information on the fields contained in the Check connection section.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Turns connection checking on or off. |
| IP address or hostname | ip | host; default: none | IP address or hostname to which the router will send ICMP packets. This is used to determine whether the connection is still available or not. ICMP packets will be send from interface, configured in VRRP Configuration section, therefore make sure you enter reachable IP address or hostname. |
| Ping interval | integer; default: 10 | Time interval (in seconds) between two pings. |
| Ping timeout | integer; default: 1 | The maximum amount of time in seconds the router will wait for a response to a ping request. If it does not receive a response within the amount of time defined in this field, the ping request will be considered to have failed. |
| Ping packet size | integer; default: 56 | The size (in bytes) of sent ICMP packets. |
| Ping attempts | integer; default: 4 | Number of ping packets sent. |
| Ping retry count | integer; default: 5 | How many times the router will retry sending ping requests before determining that the connection has failed. |