Template:Networking tswos manual spanning tree: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_fw_disclosure | fw_version ={{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_latest_fw | series = {{{series}}} | name = {{{name}}} }} }} __TOC__ =...") |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: | {{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | ||
| fw_version ={{Template: | | series = {{{series}}} | ||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
| fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | | series = {{{series}}} | ||
| name = {{{name}}} | | name = {{{name}}} | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that builds a loop-free logical topology for Ethernet networks. | The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that builds a loop-free logical topology for Ethernet networks. STP's primary function is to prevent loops in Ethernet networks. Ethernet loops can occur when there are redundant paths between network switches, and if not managed properly, they can lead to broadcast storms and network congestion. Spanning tree also allows a network design to include backup links providing fault tolerance if an active link fails. | ||
==Spanning Tree Settings== | ==Spanning Tree Settings== | ||
[[File:Networking tswos manual spanning | [[File:Networking tswos manual spanning tree_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Mode</td> | <td>Mode</td> | ||
<td>Disabled | STP | RSTP; default: <b> | <td>Disabled | STP | <span style="color: red;">RSTP</span>; default: <b>RSTP</b></td> | ||
<td> STP - provides a single path between any two end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops. RSTP - detects network topologies to provide faster convergence of the spanning tree. Disabled - turns off spanning tree protocol. </td> | <td> STP - provides a single path between any two end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops. RSTP - detects network topologies to provide faster convergence of the spanning tree. Disabled - turns off spanning tree protocol. </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 52: | ||
<td>Integer [1..10]; default: <b>6</b></td> | <td>Integer [1..10]; default: <b>6</b></td> | ||
<td>The number or BPDUs that can be transmitted during every hello time period ranges from a minimum of one and a maximum of not more than defined value.</td> | <td>The number or BPDUs that can be transmitted during every hello time period ranges from a minimum of one and a maximum of not more than defined value.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color: red;">Max hops</span></td> | |||
<td>Integer [6..40]; default: <b>20</b></td> | |||
<td>Maximum number of bridge hops allowed in the network.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:53, 7 May 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that builds a loop-free logical topology for Ethernet networks. STP's primary function is to prevent loops in Ethernet networks. Ethernet loops can occur when there are redundant paths between network switches, and if not managed properly, they can lead to broadcast storms and network congestion. Spanning tree also allows a network design to include backup links providing fault tolerance if an active link fails.
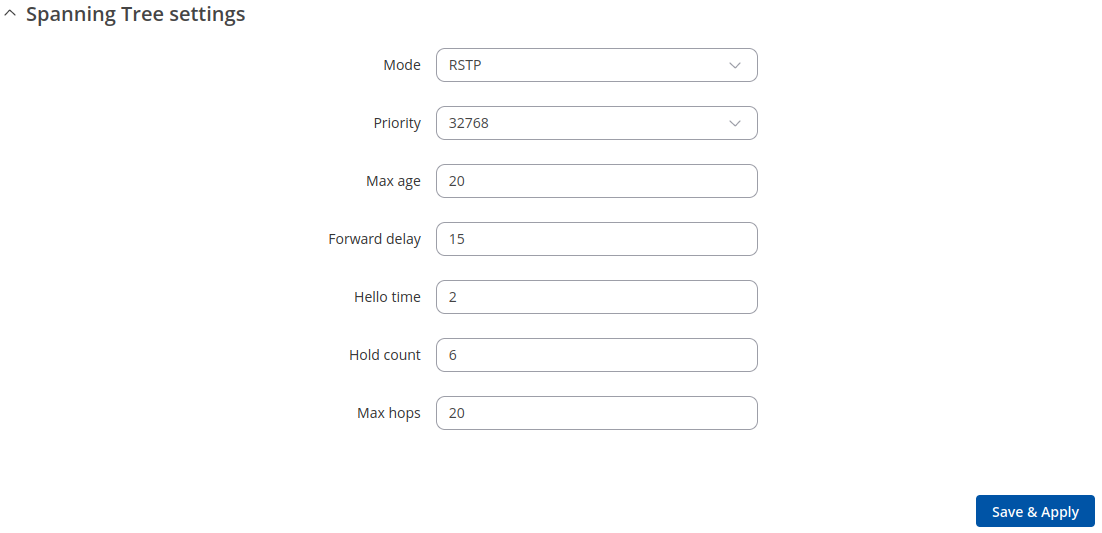
Spanning Tree Settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mode | Disabled | STP | RSTP; default: RSTP | STP - provides a single path between any two end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops. RSTP - detects network topologies to provide faster convergence of the spanning tree. Disabled - turns off spanning tree protocol. |
| Priority | Integer [0..61440]; default: 32768 | STP priority. The lower the number, the higher the priority. |
| Max age | Integer [6..40]; default: 20 | Maximum expected arrival time of hello bridge protocol data units (BPDUs). |
| Forward delay | Integer [4..30]; default: 15 | How long an STP bridge port remains in the listening and learning states before transitioning to the forwarding state. |
| Hello time | Integer [1..10]; default: 2 | Number of seconds between transmissions of configuration BPDUs. |
| Hold count | Integer [1..10]; default: 6 | The number or BPDUs that can be transmitted during every hello time period ranges from a minimum of one and a maximum of not more than defined value. |
| Max hops | Integer [6..40]; default: 20 | Maximum number of bridge hops allowed in the network. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]