Difference between revisions of "Active vs Passive PoE"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[File:Table.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | [[File:Table.png|border|class=tlt-border|center]] | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | Key Points:''' | ||
| + | *'''PoE''' (IEEE 802.3af): Provides up to 15.4 W of DC power. | ||
| + | *'''PoE+''' (IEEE 802.3at): Provides up to 30 W of DC power. | ||
| + | *'''PoE++''' (IEEE 802.3bt): Extends the power up to 60 W (Type 3) and up to 90 W (Type 4). | ||
| + | Each class within these standards specifies the maximum power that can be delivered to a powered device (PD), and the maximum power that can be drawn from the power sourcing equipment (PSE), ensuring compatibility and efficient power management across various devices and applications. | ||
Revision as of 08:57, 11 July 2024
Summary
This chapter is an overview of recommended use active and passive PoE
Note: The following recommendations apply to Teltonika devices
Active PoE
Active PoE (Power over Ethernet) refers to the technology that allows network cables to carry electrical power along with data to remote devices. This technology simplifies installation and reduces the need for separate power supplies and outlets for each device. Active PoE is standardized by the IEEE and comes in various classes, each specifying different power levels.
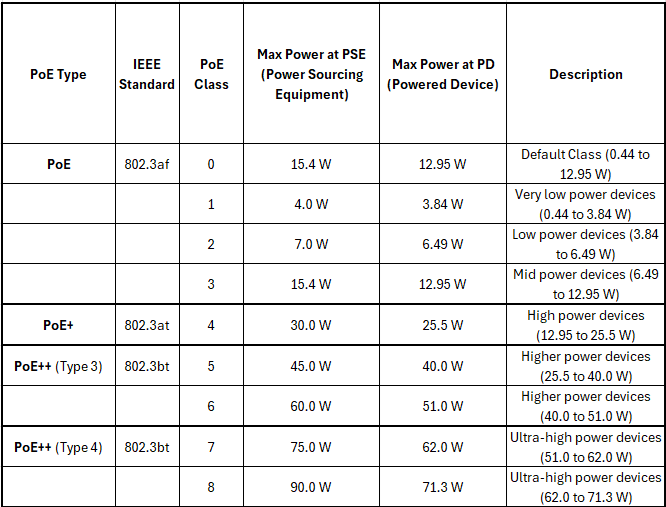
Here's a table outlining the different classes of Active PoE:
Key Points:
- PoE (IEEE 802.3af): Provides up to 15.4 W of DC power.
- PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at): Provides up to 30 W of DC power.
- PoE++ (IEEE 802.3bt): Extends the power up to 60 W (Type 3) and up to 90 W (Type 4).
Each class within these standards specifies the maximum power that can be delivered to a powered device (PD), and the maximum power that can be drawn from the power sourcing equipment (PSE), ensuring compatibility and efficient power management across various devices and applications.