Template:Networking tswos manual static routes: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
To add a new route and begin editing, simply click the 'Add' button. Refer to the table below for information on static route configuration fields. | To add a new route and begin editing, simply click the 'Add' button. Refer to the table below for information on static route configuration fields. | ||
[[File:Networking tswos manual static routes static ipv6 new | [[File:Networking tswos manual static routes static ipv6 new routes_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
Revision as of 14:49, 19 August 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Static Routes
Routes ensure that network traffic finds its path to a specified host or network, both in local and remote network scenarios. Static routes are simply fixed routing entries in the routing table(s).
This section provides the possibility to configure custom static routes.
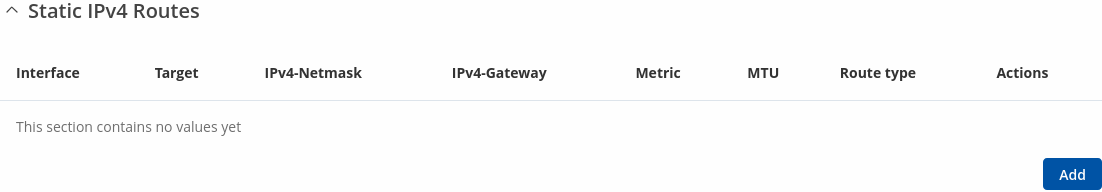
Static IPv4 Routes
The Static IPv4 Routes section displays a list of user defined static IPv4 routes and provides the possibility to add and configure new ones. The list is empty by default.
To add a new route and begin editing, simply click the 'Add' button. Refer to the table below for information on static route configuration fields.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | static | dhcp | dhcp6; default: static | The zone where the target network resides. |
| Target* | ip4; default: none | Destination network address. |
| IPv4-Netmask* | netmask; default: none | A netmask is used to divide an IP address into sub-networks (subnets). Combined together, the 'Netmask' and 'Target' values define the exact destination network or IP address to which this route applies. |
| IPv4-Gateway | ip4; default: none | A gateway can be any machine in a network that is capable of serving as an access point to another network. Traffic that matches this route will be directed over the IP address specified in this field. |
| Metric | integer [0..4294967295]; default: none | The metric value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the lower metric is applied. |
| MTU | integer [68..9200]; default: 1500 | Sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
| Route Type | unicast | local | broadcast | multicast | unreachable | prohibit | backhole | anycast; default: unicast | Selects route type. Each type specifies a different behavior for the route:
|
| Actions | -(interactive button) | Deletes the configuration. |
*Additional notes on 'Target' & 'Netmask' fields:
You can define a rule that applies to a single IP like this:
- Target: some IP
- Netmask: 255.255.255.255
Furthermore, you can create target/netmask combinations that apply to a range of IPs. Refer to the table below for examples.
| Target | Netmask | Network range |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.2.0 | 255.255.255.240 | 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.2.15 |
| 192.168.2.240 | 255.255.255.240 | 192.168.2.240 - 192.168.2.255 |
| 192.168.2.161 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.55.255 |
| 192.168.0.0 | 255.255.0.0 | 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 |
| 192.168.2.161 | 255.255.255.255 | 192.168.2.161 |
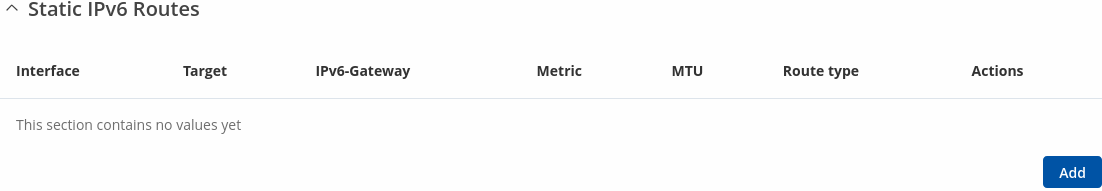
Static IPv6 Routes
The Static IPv6 Routes section displays a list of user defined static IPv6 routes and provides the possibility to add and configure new ones. The list is empty by default.
To add a new route and begin editing, simply click the 'Add' button. Refer to the table below for information on static route configuration fields.
File:Networking tswos manual static routes static ipv6 new routes v2.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | static | dhcp | dhcp6; default: static | The zone where the target network resides. |
| Target | ip6; default: none | Destination network address. |
| IPv6-Gateway | ip6; default: none | A gateway can be any machine in a network that is capable of serving as an access point to another network. Traffic that matches this route will be directed over the IP address specified in this field. |
| Metric | integer [0..4294967295]; default: none | The metric value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the lower metric is applied. |
| MTU | integer [68..9200]; default: 1500 | Sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
| Route Type | unicast | local | broadcast | multicast | unreachable | prohibit | backhole | anycast; default: unicast | Selects route type. Each type specifies a different behavior for the route:
|
| Actions | -(interactive button) | Deletes the configuration. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]