Template:Networking manual Modbus serial RutOS: Difference between revisions
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{Template:Networking install Modbus serial RutOS}} | {{Template:Networking install Modbus serial RutOS}} | ||
==Configuring Modbus | ==Configuring Modbus serial slave device== | ||
In this example we are going to be using our Windows 10/11 OS computer as a slave. To do so you will need to install '''modRSsim''' application, which you can download [https://sourceforge.net/projects/modrssim2/ here]. | In this example we are going to be using our Windows 10/11 OS computer as a slave. To do so you will need to install '''modRSsim''' application, which you can download [https://sourceforge.net/projects/modrssim2/ here]. | ||
| Line 157: | Line 157: | ||
[[File:BeeceptorData1.png|border|class=tlt-border|]] | [[File:BeeceptorData1.png|border|class=tlt-border|]] | ||
== | ==Slave alarms== | ||
In order to setup the following configuration SIM card is required. | In order to setup the following configuration SIM card is required. | ||
Go back to '''Services → Modbus → Modbus Serial Client''' and press [[File:Networking edit button fw76 v1.png]] button on the previously created '''Modbus''' | Go back to '''Services → Modbus → Modbus Serial Client''' and press [[File:Networking edit button fw76 v1.png]] button on the previously created '''Modbus''' slave '''Device''' instance or create a new one. In the opened window scroll down to the bottom and in '''Alarms Configuration''' section press [[File:Add Button.png|60x90px]]. | ||
In Alarm Configuration apply the following changes: | In Alarm Configuration apply the following changes: | ||
| Line 186: | Line 186: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
Now go back to '''Modbus | Now go back to '''Modbus slave simulator''' and edit this window: | ||
[[File:Modbus serial rut955 14.png|border|class=tlt-border|1000x700px]] | [[File:Modbus serial rut955 14.png|border|class=tlt-border|1000x700px]] | ||
Revision as of 11:33, 29 August 2024
Summary
Modbus is a serial communications protocol originally published by Modicon (now Schneider Electric) in 1979 for use with its programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Modbus has become a de facto standard communication protocol and is now a commonly available means of connecting industrial electronic devices. The main reasons for the use of Modbus in the industrial environment are:
- developed with industrial applications in mind;
- openly published and royalty-free;
- easy to deploy and maintain;
- moves raw bits or words without placing many restrictions on vendors.
Modbus enables communication among many devices connected to the same network, for example, a system that measures temperature and humidity and communicates the results to a computer. Modbus is often used to connect a supervisory computer with a remote terminal unit (RTU) in supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. Many of the data types are named from its use in driving relays: a single-bit physical output is called a coil, and a single-bit physical input is called a discrete input or a contact.
This article provides a brief example on how to use Modbus serial to monitor a slave device, send data to server and how to configure slave alarms. To find more information about this feature visit RUT955 Modbus page.
Prerequisites
- One device with RS232 Serial port;
- Windows 10/11 OS computer;
- Beeceptor account and created Mock server;
- ModRSsim application;
- RS232 to USB cable.
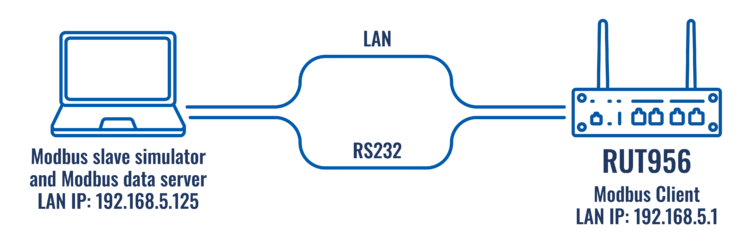
Topology
Installation
From FW version of RUT9_R_00.07.05 and newer Modbus Serial Client package is installed by default. To install it on older FW versions open device's WebUI, navigate to Services → Package manager → Packages and search for Modbus Serial Master and press + icon to install. After installation you should see a status Installed on this package.
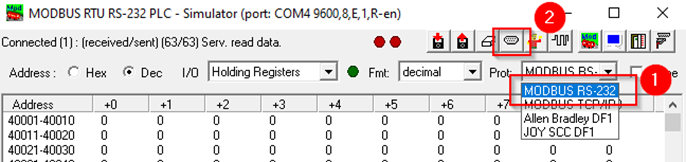
Configuring Modbus serial slave device
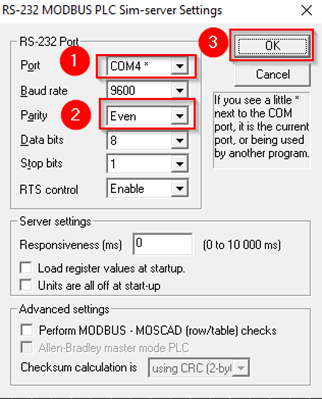
In this example we are going to be using our Windows 10/11 OS computer as a slave. To do so you will need to install modRSsim application, which you can download here.
When you are done with that, open the app and apply the following configuration.
 |
|
|---|---|
|
Configuring Modbus serial master
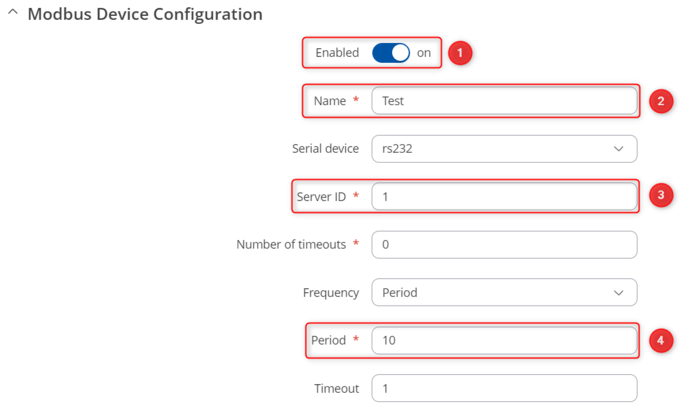
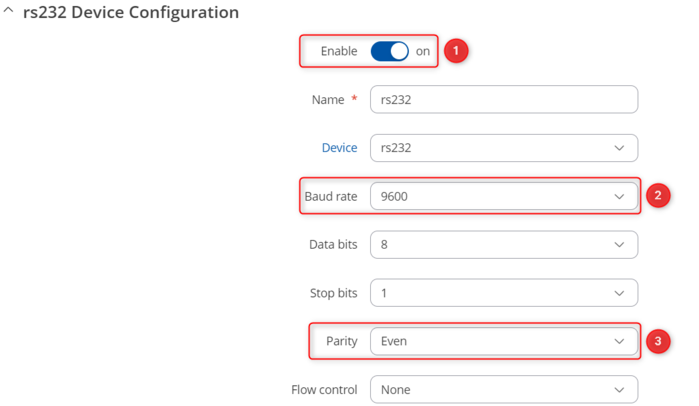
Open router’s WebUI, navigate to Services → Modbus → Modbus Serial Client and in Serial Device configuratio section add new instance by entering a name, selecting rs232 and pressing ![]() button. In the newly opened Device Configuration window configure everything as follows:
button. In the newly opened Device Configuration window configure everything as follows:
 |
|
|---|---|
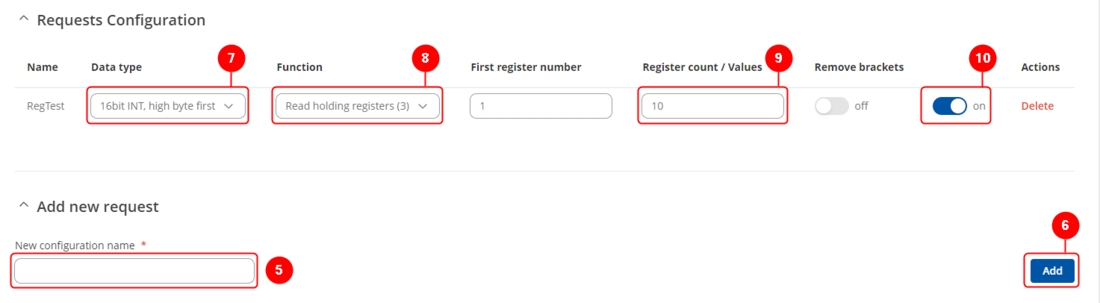
Now in Modbus Devices section create RS232 slave by writing a new instance name, selecting rs232 and pressing ![]() button. In the new window apply the following configuration:
button. In the new window apply the following configuration:
Modbus data to server
Creating server
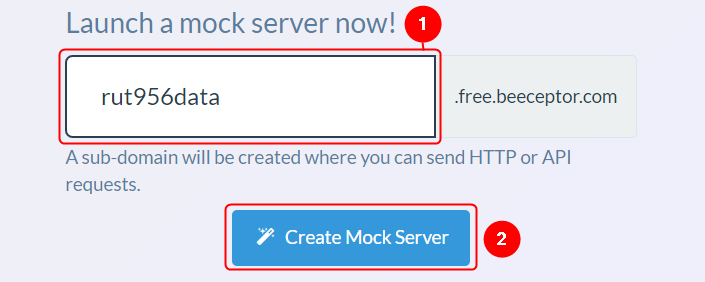
In order to test the functionality, you will need to set up a server.
There are many ways how you can create a server to which Modbus will send data to. In this example we are going to be using a Beeceptor's Mock server. If you don't have a Beeceptor account yet – create it or login via Google account.
 |
|
|---|---|
|
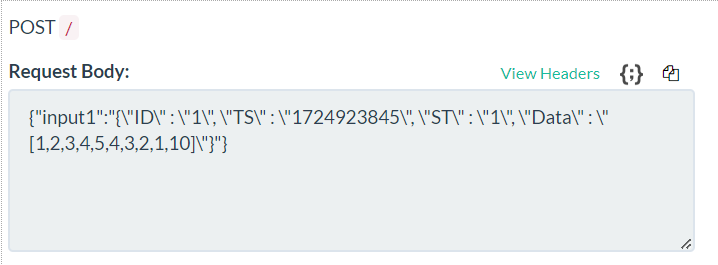
And that is it, now you will be able to see the data coming from Modbus to your created Beeceptor's server.
RUT Modbus data to server configuration
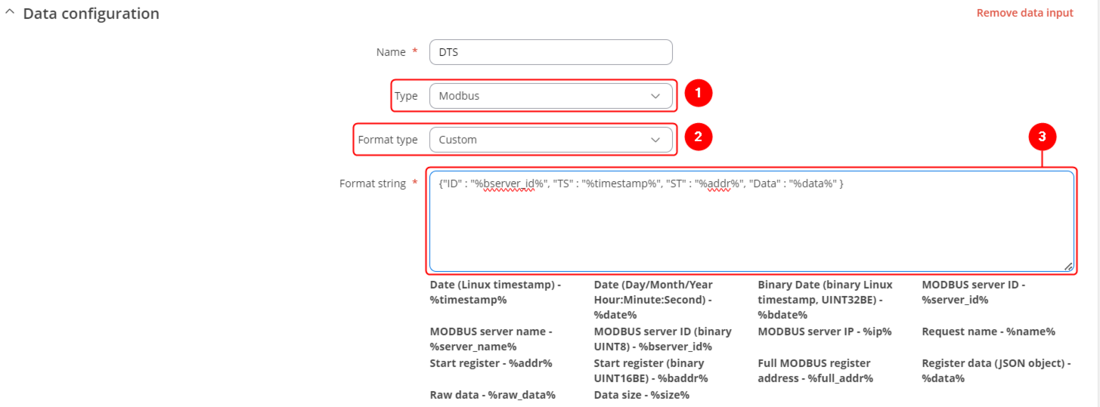
In order to setup your router to send Modbus data to server you will need to navigate to Services → Data to Server, create a "New collectiom name" and press ADD to add a new instance.
- Select Type: Modbus;
- Select Format Type: Custom;
- Enter desired format string;
- Leave other parameterms as it is and click on
 icon;
icon; - In the Collection configuration window leave the settings as default and click on
 button;
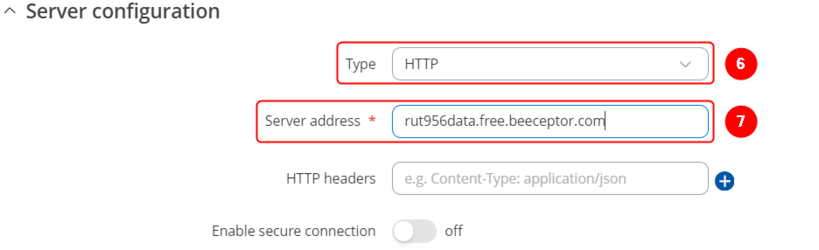
button; - In the Server configuration window select Type: HTTP;
- Enter Server address;
- Click
 ;
;
Receiving data
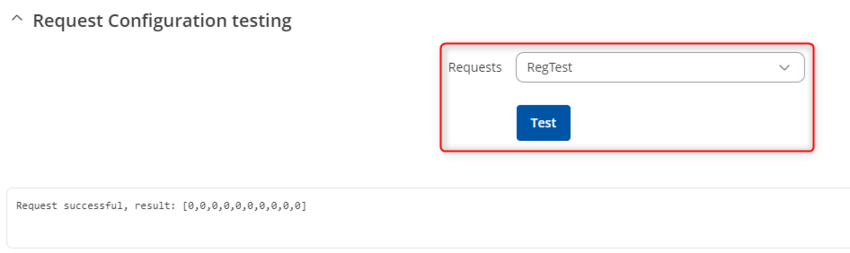
Open Beeceptor's window again, and after some time you should start receiving Modbus Data messages.
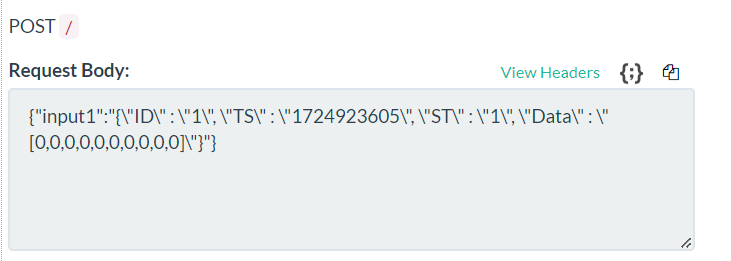
Try to change some data in the Modbus Slave simulator.
Received data should change.
Slave alarms
In order to setup the following configuration SIM card is required.
Go back to Services → Modbus → Modbus Serial Client and press ![]() button on the previously created Modbus slave Device instance or create a new one. In the opened window scroll down to the bottom and in Alarms Configuration section press
button on the previously created Modbus slave Device instance or create a new one. In the opened window scroll down to the bottom and in Alarms Configuration section press ![]() .
.
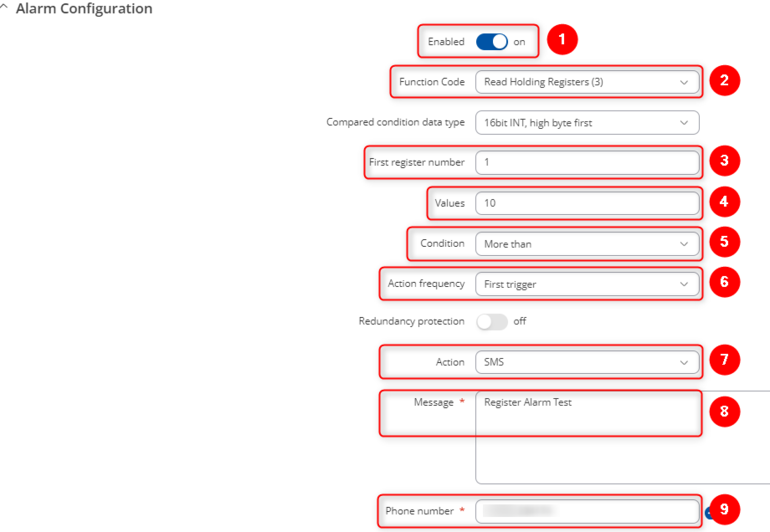
In Alarm Configuration apply the following changes:
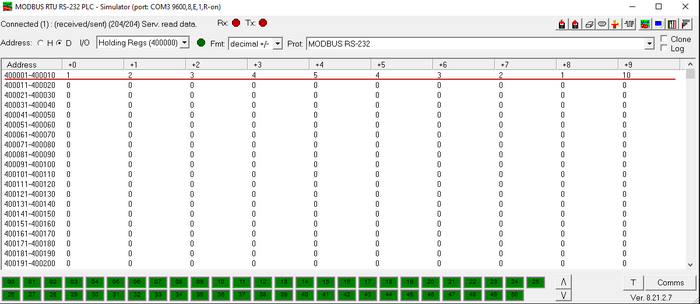
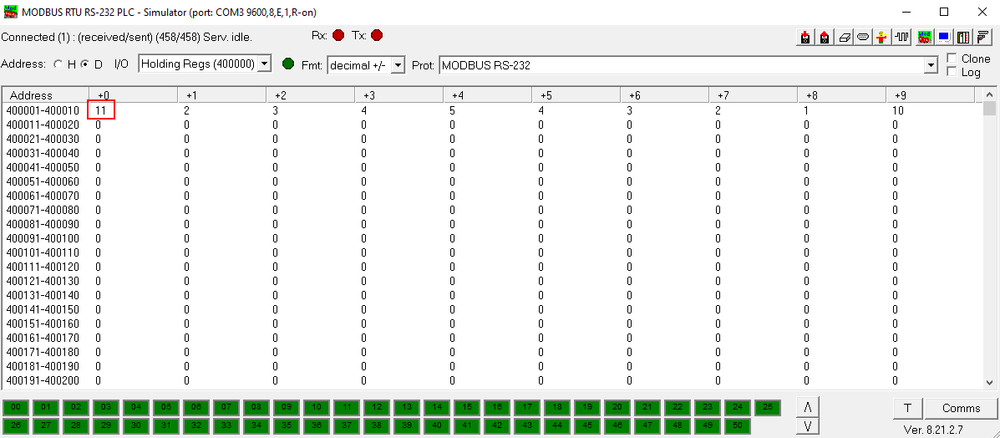
Now go back to Modbus slave simulator and edit this window:
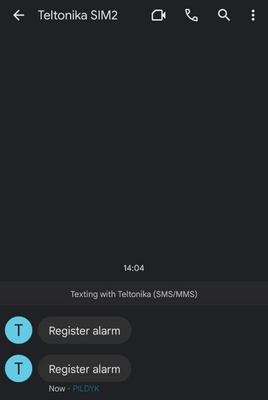
Change the value to anything below 10, you should not receive messages. Then change the value to anything above 10, you should start receiving messages.