Template:Networking rutos manual input output: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (86 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: | {{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | ||
| | | series = {{{series}}} | ||
| series | | name = {{{name}}} | ||
| fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
}} | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT9 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} Input/Output (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT9XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i> | |||
<p style="color:red">Warning: From 7.0 version I/O parameters and controls have changed compared to {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT9XX}} and earlier legacy versions.</p>|}} | |||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT2 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} Input/Output (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT2XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i> | |||
<p style="color:red">Warning: From 7.1 version I/O parameters and controls have changed compared to {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT2XX}} and earlier legacy versions.</p>|}} | |||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 23: | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Physical characteristics and I/O pin mapping== | |||
= | |||
Electrical characteristics and I/O pin mapping information are presented below. | |||
{{Template:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_pinout | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| configurableio = {{{configurableio}}} | |||
| input_volts = {{{input_volts}}} | |||
}}{{#switch: {{{name}}} | |||
| TRB141 =<h3>Input/Output Connector Pinout</h3> | |||
---- | ---- | ||
[[File:Networking_trb141_manual_input_output_input_output_connector_pinout_v2.png]] | |||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li><b> | <li><b>DI<sub>1</sub></b> & <b>DI<sub>2</sub></b> - DRY/WET configurable inputs: | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>< | <li><b>WET</b>: 0-1.9 V is detected as logical "0"; 1.9-3.8 V is detected as logical "1"</li> | ||
<li>< | <li><b>DRY</b>: is detected as logical "0" when the input is shorted to GND; otherwise is detected as logical "1"</li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
<li><b> | <li><b>NC<sub>1</sub></b>, <b>C<sub>1</sub></b> & <b>NO<sub>1</sub></b> - Normally Closed, Common and Normally Open contacts of the internal Non-Latching Relay respectively.<br>Maximum relay ratings: 0.5 A at 60 VDC/70 VAC, 1 A at 30 VDC/VAC.</li> | ||
<li><b>NC<sub>2</sub></b>, <b>C<sub>2</sub></b> & <b>NO<sub>2</sub></b> - Normally Closed, Common and Normally Open contacts of the internal Latching Relay respectively.<br>Maximum relay ratings: 0.8 A at 70 VDC, 0.9 A at 70 VAC, 2 A at 30 VDC/VAC.</li> | |||
<li><b>A</b> - ADC input. Analog voltage range: 0-30 V. The input can be configured for 4-20 mA sensor protocol as current measurement (ACL) of 0-30 mA.</li> | |||
<li><b>l</b> and <b>⏚</b> - isolated input contacts. | |||
<ul> | |||
<li>0-7.3 V is detected as logical "0"</li> | |||
<li>7.3-71 V is detected as logical "1"</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
</li> | |||
<li><b>+</b> - a power output connected directly to gateway's power supply input pin. This Output can be used to power an external 4-20 mA current sensor.</li> | |||
<li><b>3.8</b> is a 3.8 V power output that can be used to power 1-Wire sensors.</li> | |||
<li><b>1W</b> - 1-Wire protocol input/output.</li> | |||
<li><b>⏚</b> - GND contact.</li> | |||
<li><b>''Note:''</b> input circuit components have tolerance of +-1%.</li> | |||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| | | RUT955|RUT956|RUT906 =<h3>Input/Output Connector Pinout</h3> | ||
| | |||
---- | ---- | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rut955_manual_input_output_input_output_connector_pinout_v3.png]] | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li><b> | <li><b>DI</b><sub>1</sub> and <b>⏚</b><sub>1</sub> - Digital input (dry type):</li> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li> | <li>0-1.2 V is detected as logical "1"</li> | ||
<li> | <li>1.8-3 V is detected as logical "0"</li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</li> | <li><b>DI</b><sub>2</sub> and <b>⏚</b><sub>2</sub> - Digital galvanically isolated input:</li> | ||
<ul> | |||
<li>0-4 V is detected as logical "0"</li> | |||
<li>9-30 V is detected as logical "1"</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<li><b>DO</b> and <b>⏚</b><sub>3</sub> - Galvanically isolated open collector (OC) output: 30 V, 250 mA.</li> | |||
<li><b>+V</b> and <b>⏚</b><sub>3</sub> - External VCC for <b>DO</b> (<30 V).</li> | |||
<li><b>C & NO</b> - Common and Normally Open contacts of the internal Non-Latching Relay respectively.<br>Maximum relay ratings: 4 A at 24 VDC, 4 A at 40 VAC.</li> | |||
<li><b>A</b> and <b>⏚</b><sub>1</sub> - ADC input. Analog voltage range: 0-24 V. The input can be configured for 4-20 mA sensor protocol as current measurement (ACL).<span class="asterisk">*</span></li> | |||
<li><b>⏚</b><sub>1</sub> - GND for <b>DI</b><sub>1</sub> and <b>A</b>.</li> | |||
<li><b>⏚</b><sub>2</sub> - GND for <b>DI</b><sub>2</sub>. | |||
<li><b>⏚</b><sub>3</sub> - GND for <b>DO</b> pins. | |||
<li><b>''Note:''</b> input circuit components have tolerance of +-1%.</li> | |||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
<span class="asterisk">*</span> The deviation from the actual input voltage and the voltage measured by the device is dependent on the input voltage value: | |||
* | |||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li> | <li>'''≥ 1.5 V''' - the deviation is about ± 10 % and gets lower when the input voltage increases towards 5 V</li> | ||
<li> | <li>'''≥ 5 V''' - the deviation does not exceed ± 3 %</li> | ||
<li> | <li>'''≥ 9 V''' - the deviation does not exceed ± 2 %</li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
<b>Additional note</b>: the deviation values specified above are applicable in temperatures of < 50 °C. Under higher temperatures the deviation values become considerably higher. | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 100: | Line 98: | ||
The <b>Status</b> page displays the current states of the device's input and output pins: | The <b>Status</b> page displays the current states of the device's input and output pins: | ||
{{# | {{#switch: {{{name}}} | ||
| TRB141 = [[File:Networking_trb141_manual_input_output_status_v5.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
| RUT955|RUT956|RUT906 = [[File:Networking_RUT955_manual_input_output_status_v4.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
| TRB245|TRB246|TRB255|TRB256 = [[File:Networking_trb2_manual_input_output_status_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
| [[File:Networking_{{lc:{{{series}}}}}_manual_input_output_status.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
}} | }} | ||
You can invert an Input pin by clicking the on/off slider under the "Inversion" column or switch the state of an Output pin by clicking the on/off slider under the "State" column. | You can invert an Input pin by clicking the on/off slider under the "Inversion" column or switch the state of an Output pin by clicking the on/off slider under the "State" column. | ||
User can <b> Rename </b> Input/Output interface by clicking on the "Edit" button. | |||
{{#switch: {{{name}}} | |||
| TRB141 = '''Note:''' When dry/wet input is not connected to anything - the state of level is undetermined. | |||
| #default =}} | |||
{{#switch: {{{name}}}|RUT955|RUT956|RUT906|TRB245|TRB246|TRB255|TRB141|TRB256 = | |||
'''Note:''' You can edit the adc/acl formula to customize values. | |||
Custom I/O status labels for "Analog input": | |||
[[File:Networking_manual_input_output_status_formula_adc0.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
Custom I/O status labels for "Analog current loop": | |||
[[File:Networking_manual_input_output_status_formula_acl0.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
| #default =}} | |||
===Status from command line=== | ===Status from command line=== | ||
| Line 111: | Line 126: | ||
You can also obtain the status of input and output pins via the command line (CLI or SSH). List of possible ubus values in {{{name}}} devices: | You can also obtain the status of input and output pins via the command line (CLI or SSH). List of possible ubus values in {{{name}}} devices: | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{name}}} | TRB141 | {{#switch: {{{series}}} | ||
| TRB1 ={{#ifeq:{{{name}}} | |||
| TRB141 | {{Template:Networking_trb141_manual_input_output_status}} | |||
| {{Template:Networking_{{lc:{{{series}}}}}_manual_input_output_status|name={{{name}}}}} | |||
}} | |||
| #default = {{Template:Networking_{{lc:{{{series}}}}}_manual_input_output_status|name={{{name}}}}} | |||
}} | |||
{{#switch: {{{name}}} | |||
| RUT300|RUT301|RUT360|TRB245|TRB246|TRB255|TRB140|TRB141|TRB142|TRB143|TRB145|TRB256|TRB160 = '''Note:''' Changes of configurable pin type from output to input (and reverse) could causes the issues where the specific type was set in configurations. Make sure that configurations do not contradict one another. | |||
| #default = | |||
}} | }} | ||
==Post/Get== | ==Post/Get== | ||
Enabling <b>Post/Get</b> provides the possibility to control the state of an output via HTTP POST/GET requests. The figure below is an example of the Auth Settings section of the Post/Get page. It is used to turn Post/Get on or off and to set authentication parameters. | Enabling <b>Post/Get</b> provides the possibility to control the state of an output via HTTP POST/GET requests. The figure below is an example of the Auth Settings section of the Post/Get page. It is used to turn Post/Get requests on or off and to set authentication parameters. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_post_get_auth_settings_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 130: | Line 153: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>off | <td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>Turns Post/Get on or off.</td> | <td>Turns Post/Get on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Access</td> | |||
<td>io_state {{!}} io_type {{!}} io_value {{!}} io_invert; default: <b>io_state, io_type, io_value, io_invert</b></td> | |||
<td>Accessible methods. It is considered that all methods are allowed if this list is empty.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 149: | Line 177: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
<b>Note:</b> password fields are required to enable POST/GET funcionallity. | |||
===Post/Get examples=== | ===Post/Get examples=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Use a web browser or any other compatible software to send HTTP POST/GET requests to the device. | |||
Below is a table containing syntax examples of this usage: | ====Setting==== | ||
---- | |||
Changing states of various I/O is possible using requests. Below is a table containing syntax examples of this usage: | |||
<table class="nd-othertables_2"> | <table class="nd-othertables_2"> | ||
| Line 161: | Line 193: | ||
<th style="width: 900px">POST/GET URL</th> | <th style="width: 900px">POST/GET URL</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Turn Output state to high</td> <!-- another ifeq to change ip subnet according to trb14x... --> | <td>Turn Output state to high</td> <!-- another ifeq to change ip subnet according to trb14x... --> | ||
<td><nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{# | <td><nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}.1/cgi-bin/<span style="color: #0054a6;"><b>io_state</b></span><nowiki>?username=user1&password=user1&pin=</nowiki>{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUTX|dout1|<dio0/dio1{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB2|TRB2M=/dio2}}>}}<span style="color: #0054a6;"><b><nowiki>&state=on</nowiki></b></span></td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Turn Output state to low after 5 seconds for 3 seconds</td> | <td>Turn Output state to low after 5 seconds for 3 seconds</td> | ||
<td><nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{# | <td><nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}.1/cgi-bin/<span style="color: #0054a6;"><b>io_state</b></span><nowiki>?username=user1&password=user1&pin=</nowiki>{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUTX|dout1|<dio0/dio1{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB2|TRB2M=/dio2}}>}}&state=on<span style="color: #0054a6;"><b><nowiki>&delay=5</nowiki></b></span><span style="color: #3232ff;"><b><nowiki>&time=3</nowiki></b></span></td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Check t_time parameter - time is set in miliseconds</td> | ||
<td><nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{# | <td><nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}.1/cgi-bin/<span style="color: #0054a6;"><b>io_state</b></span><nowiki>?username=user1&password=user1&pin=</nowiki>{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUTX|dout1|<dio0/dio1{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB2|TRB2M=/dio2}}>}}&state=on<span style="color: #0054a6;"><b><nowiki>&t_time=msec</nowiki></b></span><span style="color: #3232ff;"><b><nowiki>&time=5000</nowiki></b></span><span style="color: #3232ff;"><b><nowiki>&time=1000</nowiki></b></span></td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Invert input</td> | |||
<td><nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}.1/cgi-bin/io_invert?username=user1&password=user1&pin={{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUTX|din1|<dio0/dio1{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB2|TRB2M=/dio2}}>}}<span style="color: #0054a6;"><b><nowiki>&invert=<0/1> (0 - disable inversion/1 - enable inversion</nowiki></b></span></td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
{{#ifeq:{{{configurableio}}}|1| | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Change Configurable Input/Output with pin3 to Output</td> | |||
<td><nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}.1/cgi-bin/<span style="color: #0054a6;"><b>io_type</b></span><nowiki>?username=user1&password=user1&</nowiki><span style="color: #0054a6;"><b>pin=dio0</b></span><span style="color: #3232ff;"><b><nowiki>&type=out</nowiki></b></span></td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
}} | ||}} | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
<b>Overview</b>: | <b>Overview</b>: | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>192.168.{{# | <li>192.168.{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}.1 - device default LAN IP address; replace it in accordance with your own configuration.</li> | ||
{{#ifeq:{{{configurableio}}}|1|<li>io_state or | {{#ifeq:{{{configurableio}}}|1|<li>io_state,io_type or io_invert- allows you to change IO state, type or invert cofigurable input.</li>}} | ||
<li>username - login name from Post/Get configuration.</li> | <li>username - login name from Post/Get configuration.</li> | ||
<li>password- password from Post/Get configuration.</li> | <li>password- password from Post/Get configuration.</li> | ||
<li>state - turn Output on or off.</li> | <li>state - turn Output on or off.</li> | ||
{{#ifeq:{{{configurableio}}}|1|<li>type - turn Configurable Input/Output to Input or Output.</li>}} | {{#ifeq:{{{configurableio}}}|1|<li>type - turn Configurable Input/Output to Input or Output.</li>}} | ||
<li>invert - enables inversion on/off (only works with inputs).</li> | |||
<li>delay - defines a delay (in seconds) after which the specified action will be performed.</li> | <li>delay - defines a delay (in seconds) after which the specified action will be performed.</li> | ||
<li>time - defines a window of time during which the action will take place. For instance, if you post an <i>on</i> action while specifying <i>time=5</i>, the output will turn on and stay on for 5 seconds before turning off.</li> | <li>time - defines a window of time during which the action will take place. For instance, if you post an <i>on</i> action while specifying <i>time=5</i>, the output will turn on and stay on for 5 seconds before turning off.</li> | ||
| Line 205: | Line 238: | ||
<b>Examples:</b> | <b>Examples:</b> | ||
< | * <b>Switch output to High:</b> | ||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_state?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dout1&state=on</nowiki>" | |||
* <b>Switch output to Low after delay:</b> | |||
</ | curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_state?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dout1&state=off&delay=5</nowiki>" | ||
====Reading==== | |||
---- | |||
Getting the current state of various I/O is possible using requests. Usage is very similar to the examples above: | |||
<b>Examples:</b> | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{configurableio}}}|1|* {{#switch:{{{name}}}|TRB245|TRB246|TRB255|TRB256 = <b>Read state of Configurable Input/Output PIN2/PIN3/PIN4:</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dio0</nowiki>" | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dio1</nowiki>" | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dio2</nowiki>" | #default = <b>Read state of Configurable Input/Output PIN3/PIN4:</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dio0</nowiki>" | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dio1</nowiki>"}}| | |||
* <b>Read state of digital input/output:</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=din1</nowiki>" | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dout1</nowiki>"}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{analog}}}|1|* <b>Read state of analog input (in voltage mode):</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=adc0</nowiki>"|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{acl}}}|1|* <b>Read state of analog input (in current mode):</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=acl0</nowiki>"|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{dry}}}|1|* <b>Read state of Dry input PIN1:</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dwi0</nowiki>"|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{wet}}}|1|* <b>Read state of Wet input PIN2:</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dwi1</nowiki>"|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{isolated}}}|1|* <b>Read state of Isolated input:</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=iio</nowiki>"|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{onewire}}}|1|* <b>Read state of One Wire:</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=onewire</nowiki>"|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{relay}}}|1|* <b>Read state of Relay:</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=relay0</nowiki>"|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{latchingrelay}}}|1|* <b>Read state of Latching Relay:</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=relay1</nowiki>"|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{galvanic}}}|1|* <b>Read state of Galvanically isolated open collector output:</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dout2</nowiki>"|}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{digitalpassive}}}|1|* <b>Read state of Digital input (only for passive sensors):</b> | |||
curl -X GET "<nowiki>http://192.168.</nowiki>{{#switch:{{{series}}}|TRB1|TRB5|TRB16=2|#default=1}}<nowiki>.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=din2</nowiki>"|}} | |||
<b>Posible responses:</b> | |||
*<b>`io_value` for all pins</b> | |||
* Bad username or password | |||
* Pin does not exist | |||
*<b>`io_value` for din1, dout1, dio1/2/3</b> | |||
* 0 | |||
* 1{{#ifeq:{{{analog}}}|1| | |||
*<b>`io_value` for adc0</b> | |||
* float value|}}{{#ifeq:{{{acl}}}|1| | |||
*<b>`io_value` for acl0</b> | |||
* float value | |||
* Inactive|}}{{#ifeq:{{{dry}}}|1| | |||
*<b>`io_value` for dwi0</b> | |||
* Dry Shorted | |||
* Dry Open | |||
* Wet Low level | |||
* Wet High level|}}{{#ifeq:{{{wet}}}|1| | |||
*<b>`io_value` for dwi1</b> | |||
* Wet Low level | |||
* Wet High level | |||
* Dry Shorted | |||
* Dry Open|}}{{#ifeq:{{{isolated}}}|1| | |||
*<b>`io_value` for ii0</b> | |||
* 0 | |||
* 1|}}{{#ifeq:{{{onewire}}}|1| | |||
*<b>`io_value` for onewire</b> | |||
* 0 | |||
* 1|}}{{#ifeq:{{{relay}}}|1| | |||
*<b>`io_value` for relay0</b> | |||
* 0 | |||
* 1|}}{{#ifeq:{{{latchingrelay}}}|1| | |||
*<b>`io_value` for relay1</b> | |||
* 0 | |||
* 1|}}{{#ifeq:{{{galvanic}}}|1| | |||
*<b>`io_value` for dout2</b> | |||
* 0 | |||
* 1|}}{{#ifeq:{{{digitalpassive}}}|1| | |||
*<b>`io_value` for din2</b> | |||
* 0 | |||
* 1|}} | |||
==Scheduler== | ==Scheduler== | ||
The output <b>Scheduler</b> can be used to configure a timetable of when an output should be turned on or off, based on days of the week and hours of the day. | The output <b>Scheduler</b> can be used to configure a timetable of when an output should be turned on or off, based on days of the week or month and hours of the day. The General Configuration section is used to turn the Output Scheduler on or off. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_scheduler_general_configuration.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
The Scheduler is configured in the form of <b>Instances</b>. A Scheduler Instance defines a time interval during which the state of an output associated with the instance will be set to "High". The Output Scheduler Instances list is empty by default. Click the 'Add' button in order to create a new Scheduler Instance: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_scheduler_add_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
After this you should be redirected to the configuration page for the newly added Instance which should look similar to this: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_scheduler_instance_configuration_configurableio_{{{configurableio}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable</td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns the Scheduler Instance on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Pin</td> | |||
<td>output pin; default: <b>{{#ifeq:{{{configurableio}}}|1|Configurable Input/Output (3)|Output (4)}}</b></td> | |||
<td>Output pin. The state of the selected output will be set to "High" during the time interval defined in the fields below.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Interval Type</td> | |||
<td>Weekdays | <span style="color: red;">Month Days</span>; default: <b>Weekdays</b></td> | |||
<td>Selects the interval type for scheduler to use.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Start Day</td> | |||
<td>[Monday..Sunday] | [1..31]; default: <b>Monday | 1</b></td> | |||
<td>The day that marks the start of the time interval.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Start Time</td> | |||
<td>hh:mm ([00..23]:[00..59]); default: <b>12:00</b></td> | |||
<td>The hour and minute that mark the start of the time interval.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>End Day</td> | |||
<td>[Monday..Sunday] | [1..31]; default: <b>Tuesday | 1</b></td> | |||
<td>The day that marks the end of the time interval.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>End Time</td> | |||
<td>hh:mm ([00..23]:[00..59]); default: <b>12:00</b></td> | |||
<td>The hour and minute that mark the end of the time interval.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color: red;">Force Last Day</span></td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Forces intervals to accept last day of month as a valid option if selected day does not exist during ongoing month. This field becomes visible only when 'Interval Type' is set to <i>Month Days</i>.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
A Scheduler Instance will not work unless you turn both the the Scheduler service and the individual instance on: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_scheduler_on_off_slider_configurableio_{{{configurableio}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
==I/O Juggler== | ==I/O Juggler== | ||
| Line 226: | Line 390: | ||
The <b>I/O Juggler</b> is a feature that provides the possibility to create automated rules that perform certain actions based on Input state changes and other conditions. The operating sequence of I/O Juggler can be visualized as such: | The <b>I/O Juggler</b> is a feature that provides the possibility to create automated rules that perform certain actions based on Input state changes and other conditions. The operating sequence of I/O Juggler can be visualized as such: | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_scheme_condition_mobile_{{{mobile}}}.png]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_scheme_condition_mobile_{{{mobile}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
When an Input Trigger occurs, the Input check to see if user-specified conditions are also met. If so, it executes a user-specified action. | When an Input Trigger occurs, the Input check to see if user-specified conditions are also met. If so, it executes a user-specified action. | ||
| Line 329: | Line 493: | ||
Sends an email to specified recipients. Requires an existing email account configuration on the device. Email accounts can be configured in the System → Administration → Recipients → [[{{{name}}}_Administration#Email_Accounts|Email Accounts]] page. | Sends an email to specified recipients. Requires an existing email account configuration on the device. Email accounts can be configured in the System → Administration → Recipients → [[{{{name}}}_Administration#Email_Accounts|Email Accounts]] page. | ||
[[File: | {{#switch: {{{name}}} | ||
| RUTX12| RUTM12 = [[File:Networking rutos manual input output io juggler actions email rutx12 v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
| RUTX10 = [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_email_rutx10_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
| #default = [[File:Networking rutos manual input output io juggler actions email v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
}} | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 351: | Line 519: | ||
<td>positive integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>positive integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before the action is executed.</td> | <td>A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before the action is executed.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr>{{#switch: {{{name}}} | ||
| RUTX12| RUTM12 = | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Modem</td> | |||
<td>Primary modem {{!}} Secondary modem; default: <b>Primary modem</b></td> | |||
<td>Modem, which is used to get information from.</td> | |||
</tr>|}} | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Email account</td> | <td>Email account</td> | ||
| Line 363: | Line 537: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
====Type: Output==== | ====Type: Output==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 417: | Line 557: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Control</td> | <td>Control</td> | ||
<td>output; default: <b>{{#ifeq:{{{configurableio}}}|1|Configurable Input/Output ( | <td>output; default: <b>{{#ifeq:{{{configurableio}}}|1|Configurable Input/Output (3)|Output (4)}}</b></td> | ||
<td>Selects the output controlled by this Action.</td> | <td>Selects the output controlled by this Action.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 447: | Line 587: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
====HTTP==== | ====Type: HTTP==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Executes | Executes a HTTP POST/GET request. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_http_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 458: | Line 598: | ||
<th>Value</th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th>Description</th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 480: | Line 615: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Parameters</td> | <td>Alt. parameters mode</td> | ||
<td><span style="color:red">off</span> | <span style="color:blue">on</span>; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Choose a different way to pass parameters. If method is POST parameters are passed in request body. If method is GET parameters are passed throught the URL.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:red">Parameters</span></td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Parameters that are to be included the Post/Get request. Select a parameter (right drop-down box) and enter a custom name for it (left text box).</td> | <td>Parameters that are to be included the Post/Get request. Select a parameter (right drop-down box) and enter a custom name for it (left text box).</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">Text message</span></td> | |||
<td>default: <b>Device name - %rn; Time stamp - %ts</b></td> | |||
<td>Message to send.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Custom headers</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Allows to add custom headers to the HTTP requests.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Execution delay</td> | |||
<td>positive integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 490: | Line 645: | ||
Executes a custom, user-written shell script. | Executes a custom, user-written shell script. | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_script.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | {{#switch: {{{name}}} | ||
| RUTX10 = [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_script_rutx10_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
| #default = [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_script.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
}} | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 562: | Line 721: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
====Type: RMS==== | |||
---- | |||
Enables or disables RMS service. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_rms_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Execution delay</td> | |||
<td>positive integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable RMS</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b> </td> | |||
<td>Specifies whether RMS service will be enabled or disabled with this action.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
====Type: MQTT==== | |||
---- | |||
Executes a MQTT action. | |||
{{#switch: {{{name}}} | |||
| RUTX10 = [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_mqtt_rutx10_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
| #default = [[File:Networking rutos manual input output io juggler actions mqtt_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
}} | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Text message</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b> </td> | |||
<td>Below this field you can find special codes that begin with the '%' sign. Each code represents a piece information related to the status of the device. Include these codes in the Text message for dynamic information reports. | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Topic</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>The name of the topic that the broker will subscribe to.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Client ID</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Client ID to send with the data. If empty, a random client ID will be generated.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Hostname</td> | |||
<td>host | ip; default: <b>none</b> </td> | |||
<td>Broker’s IP address or hostname.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Port</td> | |||
<td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b>1883</b></td> | |||
<td>Broker's port number.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Keepalive</td> | |||
<td>positive integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>The number of seconds after which the broker should send a PING message to the client if no other messages have been exchanged in that time</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Qos</td> | |||
<td>At most once (0) | At least once (1) | Exactly once (2); default: <b>At most once (0)</b></td> | |||
<td>A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Username</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Username used for authentication to the Broker.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Password</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Password used for authentication to the Broker.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>TLS</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} <span style="color:blue">on</span>; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Select to enable TLS encryption.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">TLS Type</span></td> | |||
<td>Certificate based {{!}} Pre-Shared-Key based; default: <b>Certificate based</b></td> | |||
<td>Type of TLS encryption.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">Certificate based:</span>Allow insecure connection</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Allow not verifying server authenticity.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">Certificate based:</span>Certificate files from device</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Choose this option if you want to select certificate files from device.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">Certificate based:</span>CA file</td> | |||
<td>.crt file; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Upload CA file.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">Certificate based:</span>Certificate file</td> | |||
<td>.crt file; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>TLS client or server certificate file.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">Certificate based:</span>Key file</td> | |||
<td>.key file; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>TLS client or server key file.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">Pre-Shared-Key based:</span>Pre-Shared-Key</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>The pre-shared-key in hex format with no leading “0x”.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">Pre-Shared-Key based:</span>Identity</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Specify the Identity.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
{{#ifeq: {{{dualsim}}} | 1 | | {{#ifeq: {{{dualsim}}} | 1 | | ||
====Type: | ====Type: SIM switch==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Switches to using the specified SIM card. | Switches to using the specified SIM card. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_change_sim_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 584: | Line 879: | ||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>When set to 'on', switches to the opposite SIM card (the that is currently NOT in use). This can be used instead of selecting a specific SIM card to switch to.</td> | <td>When set to 'on', switches to the opposite SIM card (the that is currently NOT in use). This can be used instead of selecting a specific SIM card to switch to.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable primary option transfer</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Enables simd service to change primary card while switching sims </td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 589: | Line 889: | ||
<td>SIM1 {{!}} SIM2; default: <b>SIM1</b></td> | <td>SIM1 {{!}} SIM2; default: <b>SIM1</b></td> | ||
<td>Selects a SIM card to switch to. This field is visible only when the 'Flip' field is set to 'off'.</td> | <td>Selects a SIM card to switch to. This field is visible only when the 'Flip' field is set to 'off'.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
|}} | |||
{{#ifeq: {{{mobile}}} | 1 | | |||
====Type: SMS==== | |||
---- | |||
Sends an SMS message to specified recipients. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_sms.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Text message</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b> </td> | |||
<td>SMS body text. Below this field you can find special codes that begin with the '%' sign. Each code represents a piece information related to the status of the device. Include these codes in the Text message for dynamic information reports.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Execution delay</td> | |||
<td>positive integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before the action is executed.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Recipients</td> | |||
<td>Single number {{!}} Group; default: <b>Single number</b></td> | |||
<td>Defines whether the SMS message will be sent to a single number or multiple numbers included in a user-configured Phone group. Phone groups can be configured in the System → Administration → Recipients → [[{{{name}}}_Administration#Phone_Groups|Phone Groups]] page.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Recipient's phone number {{!}} Phone group</td> | |||
<td>phone number {{!}} phone group; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Phone number of a single recipient or a Phone group of multiple recipients. The name and selection type of this field depends on the value set in the 'Recipients' field.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
|}} | |||
{{#ifeq: {{{wifi}}} | 1 | | |||
====Type: WiFi==== | |||
---- | |||
Sends an SMS message to specified recipients. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_wifi_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Execution delay</td> | |||
<td>positive integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before the action is executed.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable WiFi</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Specifies whether all WiFi interfaces will be enabled/disabled with this action.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 619: | Line 979: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>I/O</td> | <td>I/O</td> | ||
<td>inputs/outputs; default: <b>Output( | <td>inputs/outputs; default: <b>Output(3)</b></td> | ||
<td>Specifies the I/O pin to which this Condition is listening to.</td> | <td>Specifies the I/O pin to which this Condition is listening to.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:46, 1 October 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
Inputs and outputs are used for monitoring and controlling a connected device or receiving signals from that device in order to trigger certain events.
This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the Input/Output section for {{{name}}} devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
Physical characteristics and I/O pin mapping
Electrical characteristics and I/O pin mapping information are presented below.
Power Socket Pinout
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_power_socket_pinout_configurableio_{{{configurableio}}}.png]]
- Power: {{{input_volts}}} VDC positive (+).
- Ground: negative/ground (-).
- Input: digital non-isolated input.
- logical low level: 0 - 5 V;
- logical high level: 8 - 30 V.
- Output: digital open collector (OC) output; 30 V, 300 mA.
Status
The Status page displays the current states of the device's input and output pins:
[[File:Networking_{{{series}}}_manual_input_output_status.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
You can invert an Input pin by clicking the on/off slider under the "Inversion" column or switch the state of an Output pin by clicking the on/off slider under the "State" column.
User can Rename Input/Output interface by clicking on the "Edit" button.
Status from command line
You can also obtain the status of input and output pins via the command line (CLI or SSH). List of possible ubus values in {{{name}}} devices:
{{Template:Networking_{{{series}}}_manual_input_output_status|name={{{name}}}}}
Post/Get
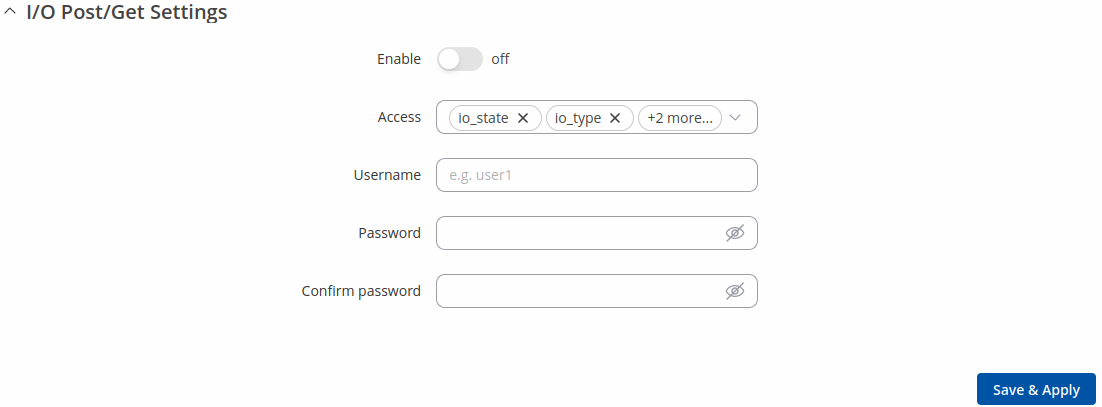
Enabling Post/Get provides the possibility to control the state of an output via HTTP POST/GET requests. The figure below is an example of the Auth Settings section of the Post/Get page. It is used to turn Post/Get requests on or off and to set authentication parameters.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns Post/Get on or off. |
| Access | io_state | io_type | io_value | io_invert; default: io_state, io_type, io_value, io_invert | Accessible methods. It is considered that all methods are allowed if this list is empty. |
| Username | string; default: none | Username used for authentication in POST/GET queries. |
| Password | string; default: none | Password used for authentication in POST/GET queries. |
| Confirm password | string; default: none | Repeat the password for confirmation. |
Note: password fields are required to enable POST/GET funcionallity.
Post/Get examples
Use a web browser or any other compatible software to send HTTP POST/GET requests to the device.
Setting
Changing states of various I/O is possible using requests. Below is a table containing syntax examples of this usage:
| Action | POST/GET URL |
|---|---|
| Turn Output state to high | http://192.168.1.1/cgi-bin/io_state?username=user1&password=user1&pin=<dio0/dio1>&state=on |
| Turn Output state to low after 5 seconds for 3 seconds | http://192.168.1.1/cgi-bin/io_state?username=user1&password=user1&pin=<dio0/dio1>&state=on&delay=5&time=3 |
| Check t_time parameter - time is set in miliseconds | http://192.168.1.1/cgi-bin/io_state?username=user1&password=user1&pin=<dio0/dio1>&state=on&t_time=msec&time=5000&time=1000 |
| Invert input | http://192.168.1.1/cgi-bin/io_invert?username=user1&password=user1&pin=<dio0/dio1>&invert=<0/1> (0 - disable inversion/1 - enable inversion |
Overview:
- 192.168.1.1 - device default LAN IP address; replace it in accordance with your own configuration.
- username - login name from Post/Get configuration.
- password- password from Post/Get configuration.
- state - turn Output on or off.
- invert - enables inversion on/off (only works with inputs).
- delay - defines a delay (in seconds) after which the specified action will be performed.
- time - defines a window of time during which the action will take place. For instance, if you post an on action while specifying time=5, the output will turn on and stay on for 5 seconds before turning off.
Delay and time parameters can be used together. For example, if delay is 10, time is 5, action is on, then 10 seconds after the execution of the command, the output will switch to on (or stay in on state if it was already that way), then after 5 more seconds it will switch to off state. In this case the overall command execution time is 15 seconds.
To use Post/Get via SSH instead of a browser, you may want to use the curl -X command. Simply add the same URL command in between quotes and specify the HTTP method.
Examples:
- Switch output to High:
curl -X GET "http://192.168.1.1/cgi-bin/io_state?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dout1&state=on"
- Switch output to Low after delay:
curl -X GET "http://192.168.1.1/cgi-bin/io_state?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dout1&state=off&delay=5"
Reading
Getting the current state of various I/O is possible using requests. Usage is very similar to the examples above:
Examples:
- Read state of digital input/output:
curl -X GET "http://192.168.1.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=din1" curl -X GET "http://192.168.1.1/cgi-bin/io_value?username=user1&password=user1&pin=dout1"
Posible responses:
- `io_value` for all pins
* Bad username or password * Pin does not exist
- `io_value` for din1, dout1, dio1/2/3
* 0 * 1
Scheduler
The output Scheduler can be used to configure a timetable of when an output should be turned on or off, based on days of the week or month and hours of the day. The General Configuration section is used to turn the Output Scheduler on or off.
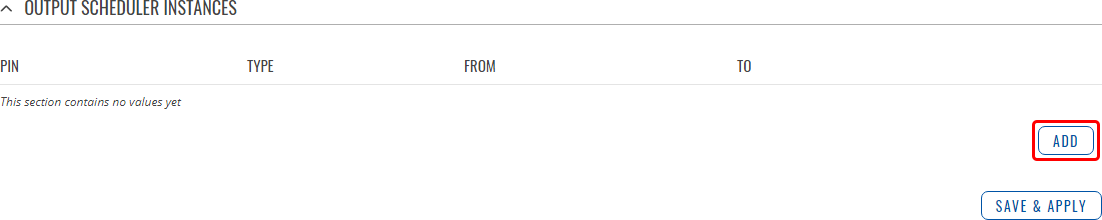
The Scheduler is configured in the form of Instances. A Scheduler Instance defines a time interval during which the state of an output associated with the instance will be set to "High". The Output Scheduler Instances list is empty by default. Click the 'Add' button in order to create a new Scheduler Instance:
After this you should be redirected to the configuration page for the newly added Instance which should look similar to this:
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_scheduler_instance_configuration_configurableio_{{{configurableio}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns the Scheduler Instance on or off. |
| Pin | output pin; default: Output (4) | Output pin. The state of the selected output will be set to "High" during the time interval defined in the fields below. |
| Interval Type | Weekdays | Month Days; default: Weekdays | Selects the interval type for scheduler to use. |
| Start Day | [Monday..Sunday] | [1..31]; default: Monday | 1 | The day that marks the start of the time interval. |
| Start Time | hh:mm ([00..23]:[00..59]); default: 12:00 | The hour and minute that mark the start of the time interval. |
| End Day | [Monday..Sunday] | [1..31]; default: Tuesday | 1 | The day that marks the end of the time interval. |
| End Time | hh:mm ([00..23]:[00..59]); default: 12:00 | The hour and minute that mark the end of the time interval. |
| Force Last Day | off | on; default: off | Forces intervals to accept last day of month as a valid option if selected day does not exist during ongoing month. This field becomes visible only when 'Interval Type' is set to Month Days. |
A Scheduler Instance will not work unless you turn both the the Scheduler service and the individual instance on:
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_scheduler_on_off_slider_configurableio_{{{configurableio}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
I/O Juggler
The I/O Juggler is a feature that provides the possibility to create automated rules that perform certain actions based on Input state changes and other conditions. The operating sequence of I/O Juggler can be visualized as such:
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_scheme_condition_mobile_{{{mobile}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
When an Input Trigger occurs, the Input check to see if user-specified conditions are also met. If so, it executes a user-specified action.
For example, if we configure the I/O Juggler like this:
- Trigger - input state rising.
- Condition - 8:00 AM - 5:00 PM.
- Action - send email.
The operating sequence would look like this:
- A connected device raises the input state.
- This {{{name}}} device checks whether the current time is between 8:00 AM and 5:00 PM.
- Yes - {{{name}}} sends an email.
- No - {{{name}}} doesn't send an email.
You can specify multiple actions and multiple conditions for any I/O Juggler rule. Selecting conditions is optional. If there are no set or configured I/O Juggler conditions, the operating sequence is as such:
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_scheme_mobile_{{{mobile}}}.png]]
General
The General section is used to Input Trigger rules, which can perform a specified user-configured action when the Input state changes and when certain other user-configured conditions are met (conditions are optional).
Before you can use the I/O Juggler, you must turn it on first (off by default). This can be done by setting the 'Enable' slider to "on":
Input
The Input is used to create Input Rules. An Input Rule is triggered by a user-specified input state change. When this trigger occurs, the device executes a specified command if certain specified conditions are met (conditions are optional).
The Input list is empty by default. To create a new Input Rule, look to the Add Input section at the bottom of the page; select an input and click the 'Add' button:
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_general_input_add_button_juggler_input_{{{juggler_input}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
After this you will be redirected to the configuration page for the newly added Rule, which should look similar to this:
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_general_input_configuration_juggler_input_{{{juggler_input}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | off | on; default: off | Changes current profile to specified one when action triggers. |
| Trigger interval | integer [0..99999999]; default: 1 | The shortest amount of time (in seconds) between two triggers. If the input is triggered more than once in a time period shorter than the value specified in this field, the device will react to the first trigger. |
| Trigger | Rising | Falling | Both; default: Rising | Input state change that will trigger this rule. |
| Add actions | i/o juggler action(s); default: none | Actions that will be executed by this rule when the specified trigger and conditions (optional) occur. |
| Add conditions | i/o juggler conditions; default: none | Conditions that have to be met for the rule to take action. Conditions are optional. |
Actions
The Actions section is used to manage and create new Actions that can be executed by the I/O Juggler Rules. The figure below is an example of the Actions section, which is empty by default.
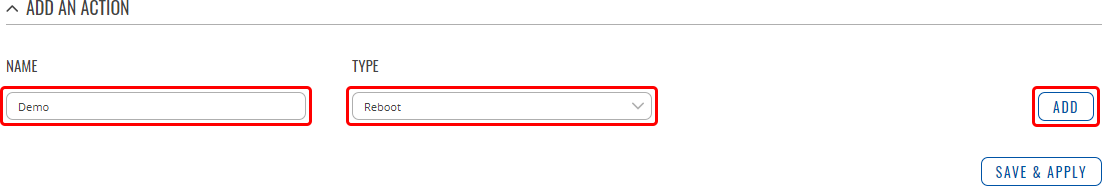
To create a new Action, look to the Add an Action section at the bottom of the page; enter a custom name, select an action type and click the 'Add' button:
After this you will be redirected to the configuration page for the newly added Action, which should look similar to this (example for action 'Type: Reboot'):
Action configuration depends on the selected action 'Type'. Each Action can have one or multiple user-defined Conditions assigned to it. Actions that have Conditions assigned to them are executed only if the Conditions are met (a trigger occurrence is not enough to set off these actions). Assigning to Actions is optional.
You will find descriptions of each different action Type described on the sections below.
Type: Email
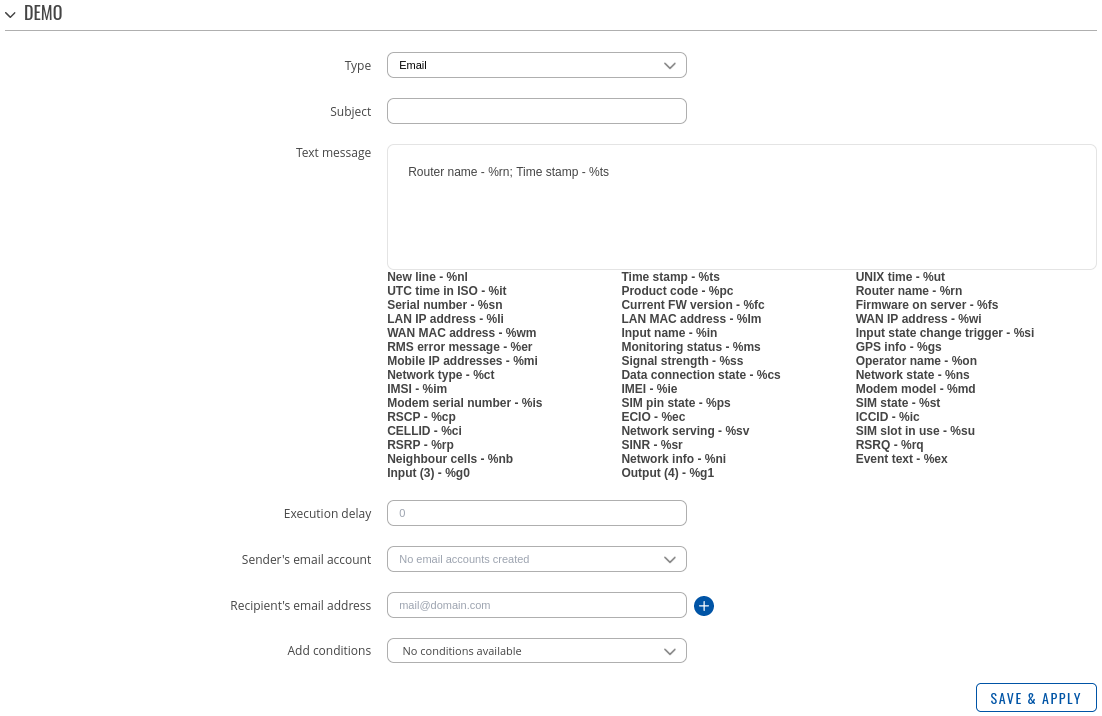
Sends an email to specified recipients. Requires an existing email account configuration on the device. Email accounts can be configured in the System → Administration → Recipients → [[{{{name}}}_Administration#Email_Accounts|Email Accounts]] page.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Subject | string; default: none | Subject of email. |
| Text message | string; default: none | Email body text. Below this field you can find special codes that begin with the '%' sign. Each code represents a piece information related to the status of the device. Include these codes in the Text message for dynamic information reports. |
| Execution delay | positive integer; default: none | A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before the action is executed. |
| Email account | email account; default: none | Email account used to send the email. Email accounts can be configured in the System → Administration → Recipients → [[{{{name}}}_Administration#Email_Accounts|Email Accounts]] page. |
| Recipient's email address | email; default: none | Email address(es) of the message's receiver(s). |
Type: Output
Changes the state of a selected output pin.
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_actions_output_configurableio_{{{configurableio}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Execution delay | positive integer; default: none | A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed. |
| Control | output; default: Output (4) | Selects the output controlled by this Action. |
| Revert | integer; default: 0 | After how many seconds the state will revert. If left as 0 or empty the state will not revert. |
| Maintain | off | on; default: on | When set to 'on', the output maintains its new state after reboot (the state is changed in the config file as well). |
| Invert | off | on; default: off | Inverts the state of the selected output, i.e., switches the output pin to a state that is opposite to its current one (high-to-low or low-to-high). This can be used instead of specifying a static state. |
| State copying | off | on; default: off | Copies the state from the selected input and applies it to the selected output. This can be used instead of specifying a static state. |
| State | High | Low; default: High | Specifies the state of the output pin that will be set by this Action. |
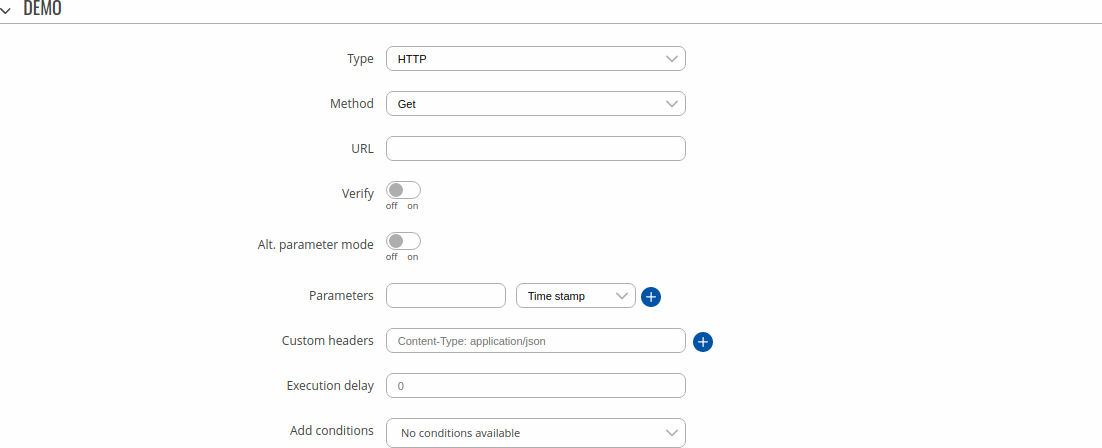
Type: HTTP
Executes a HTTP POST/GET request.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Get | Post; default: Get | HTTP method to be used by this Action. |
| URL | string; default: none | URL to send the HTTP Post/Get request to. |
| Verify | off | on; default: off | Verifies the validity of certificates; only used with HTTPS. |
| Alt. parameters mode | off | on; default: off | Choose a different way to pass parameters. If method is POST parameters are passed in request body. If method is GET parameters are passed throught the URL. |
| Parameters | string; default: none | Parameters that are to be included the Post/Get request. Select a parameter (right drop-down box) and enter a custom name for it (left text box). |
| Text message | default: Device name - %rn; Time stamp - %ts | Message to send. |
| Custom headers | string; default: none | Allows to add custom headers to the HTTP requests. |
| Execution delay | positive integer; default: none | A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed. |
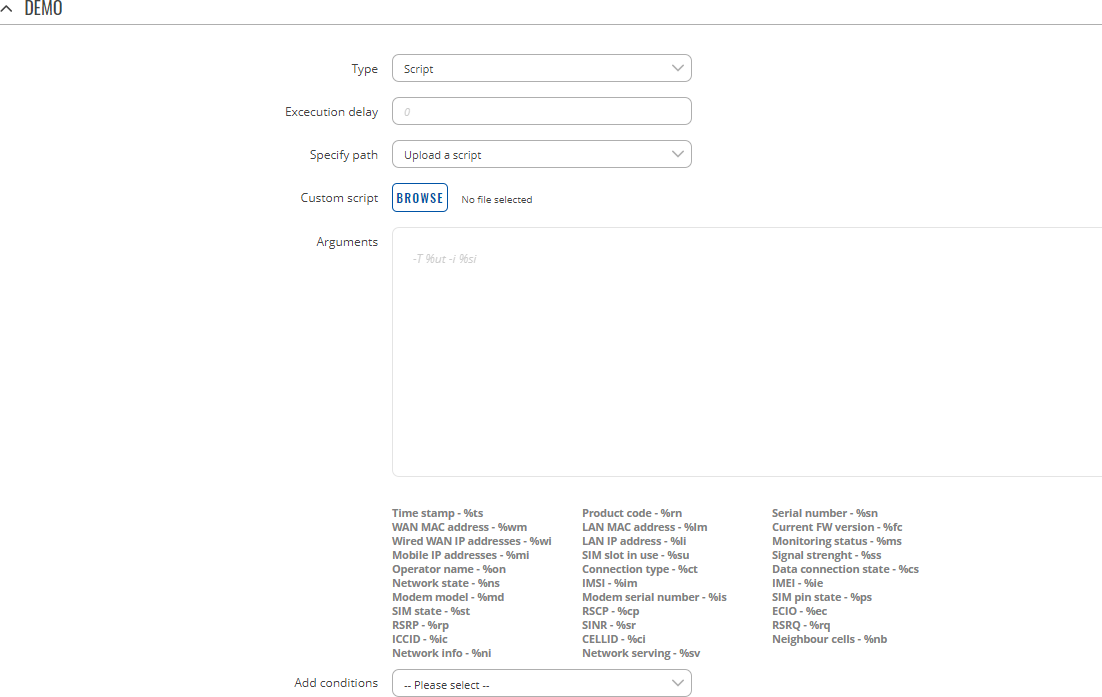
Type: Script
Executes a custom, user-written shell script.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Execution delay | positive integer; default: none | A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed. |
| Specify path | Upload a script |Specify path; default: Upload a script | Specifies whether the script should be uploaded from an external file or a path to an internal (on this device) script file should be specified. |
| Custom script | Script file | -(interactive button) | filepath | Shows file upload window on click or provides the possibility to specify a path to an internal script file. The name and selection type of this field depends on the value set in the 'Specify path' field. |
| Arguments | string; default: none | Optional arguments which can be provided for the script. You can include device information with values given below this input field. |
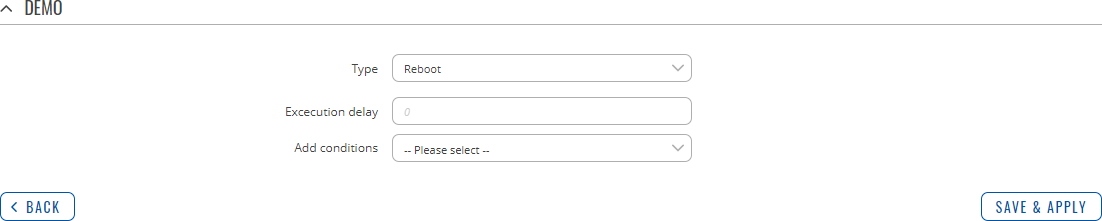
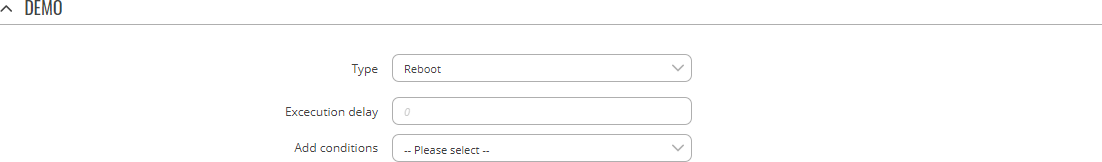
Type: Reboot
Reboots the device.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Execution delay | positive integer; default: none | A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed. |
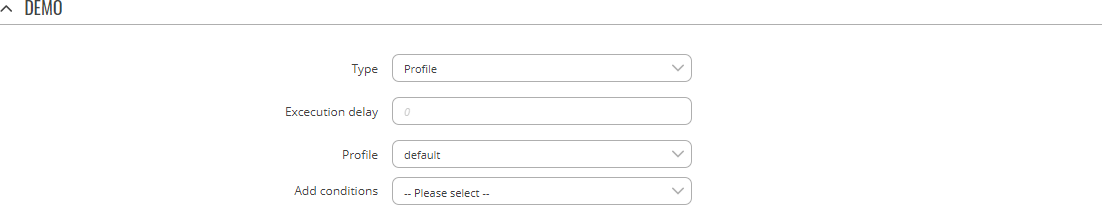
Type: Profile
Switches to using a specified Configuration Profile.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Execution delay | positive integer; default: none | A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed. |
| Profile | profile; default: default | Configuration Profile that will be applied by this Action. Configuration Profiles can be defined in the System → [[{{{name}}}_Profiles|Profiles]] page. |
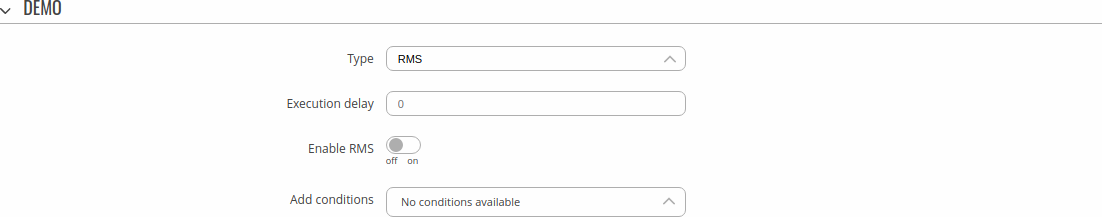
Type: RMS
Enables or disables RMS service.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Execution delay | positive integer; default: none | A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed. |
| Enable RMS | off | on; default: off | Specifies whether RMS service will be enabled or disabled with this action. |
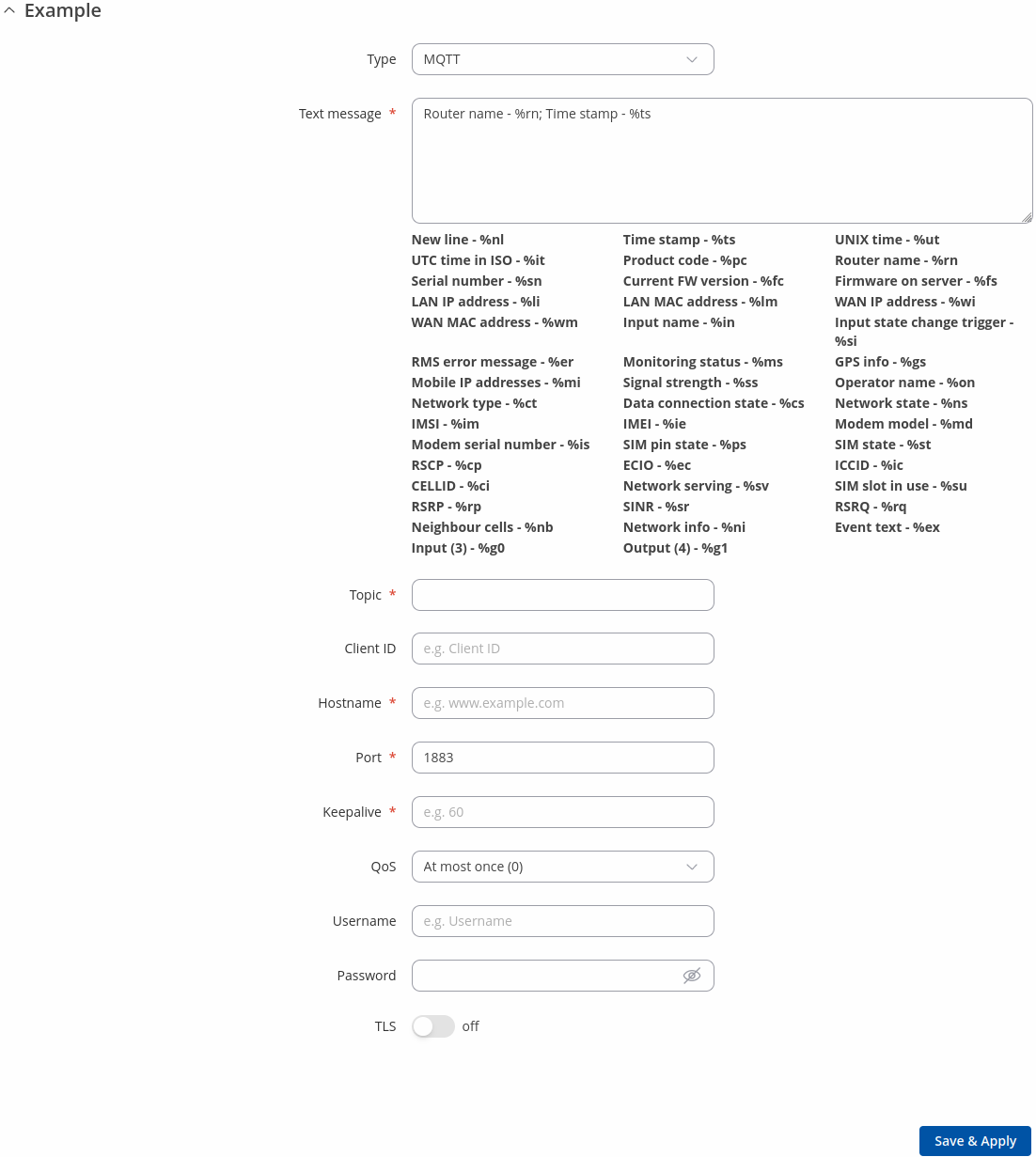
Type: MQTT
Executes a MQTT action.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Text message | string; default: none | Below this field you can find special codes that begin with the '%' sign. Each code represents a piece information related to the status of the device. Include these codes in the Text message for dynamic information reports. |
| Topic | string; default: none | The name of the topic that the broker will subscribe to. |
| Client ID | string; default: none | Client ID to send with the data. If empty, a random client ID will be generated. |
| Hostname | host | ip; default: none | Broker’s IP address or hostname. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 1883 | Broker's port number. |
| Keepalive | positive integer; default: none | The number of seconds after which the broker should send a PING message to the client if no other messages have been exchanged in that time |
| Qos | At most once (0) | At least once (1) | Exactly once (2); default: At most once (0) | A period of time (in seconds) which has to pass after a trigger event before this Action is executed. |
| Username | string; default: none | Username used for authentication to the Broker. |
| Password | string; default: none | Password used for authentication to the Broker. |
| TLS | off | on; default: off | Select to enable TLS encryption. |
| TLS Type | Certificate based | Pre-Shared-Key based; default: Certificate based | Type of TLS encryption. |
| Certificate based:Allow insecure connection | off | on; default: off | Allow not verifying server authenticity. |
| Certificate based:Certificate files from device | off | on; default: off | Choose this option if you want to select certificate files from device. |
| Certificate based:CA file | .crt file; default: none | Upload CA file. |
| Certificate based:Certificate file | .crt file; default: none | TLS client or server certificate file. |
| Certificate based:Key file | .key file; default: none | TLS client or server key file. |
| Pre-Shared-Key based:Pre-Shared-Key | string; default: none | The pre-shared-key in hex format with no leading “0x”. |
| Pre-Shared-Key based:Identity | string; default: none | Specify the Identity. |
Conditions
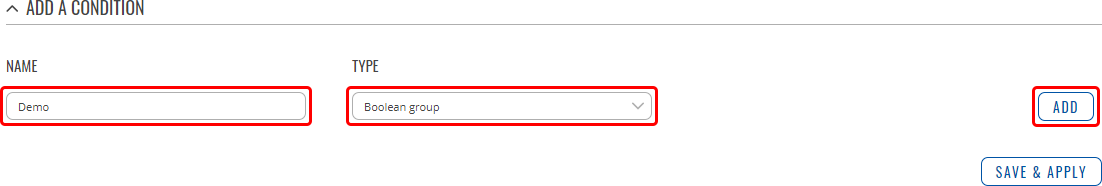
The Conditions section is used to manage and created Conditions for I/O Juggler Actions. The figure below is an example of the Conditions section, which is empty by default.
To create a new Condition, look to the Add a Condition section; enter a custom name, select the Type of the Condition and click the 'Add' button.
After this you should be redirected to the configuration page of the newly added Condition. You will find descriptions of each different Condition type described on the sections below.
Condition type: I/O
I/O Condition type tracks the state of a selected input or output pin and considers the Condition as MET if that pin is in a user-specified state.
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_input_output_io_juggler_conditions_io_configurableio_{{{configurableio}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| I/O | inputs/outputs; default: Output(3) | Specifies the I/O pin to which this Condition is listening to. |
| State | High | Low; default: High | Specifies in what state the pin has to be in in order for the Condition to be met. |
Condition type: Boolean group
Boolean Group will evaluate two or more existing conditions based on selected Boolean type. A Boolean Group condition will considered as MET based on the outcome of the evaluation performed along with one of the available Boolean types:
- AND - all selected conditions evaluate as TRUE.
- NAND - at least one selected condition evaluates as FALSE.
- OR - at least one selected condition evaluates as TRUE.
- NOR - none of the selected conditions evaluate as TRUE.
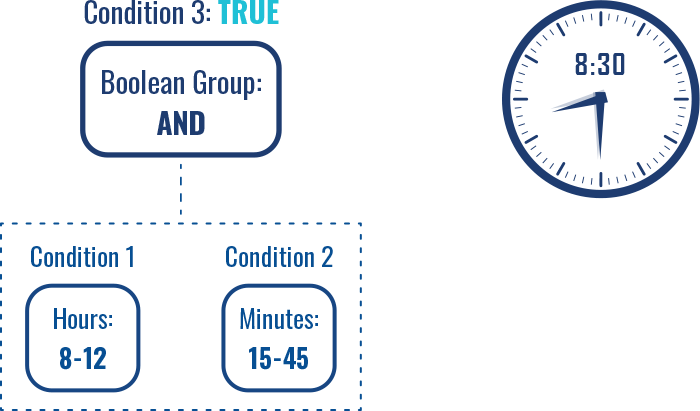
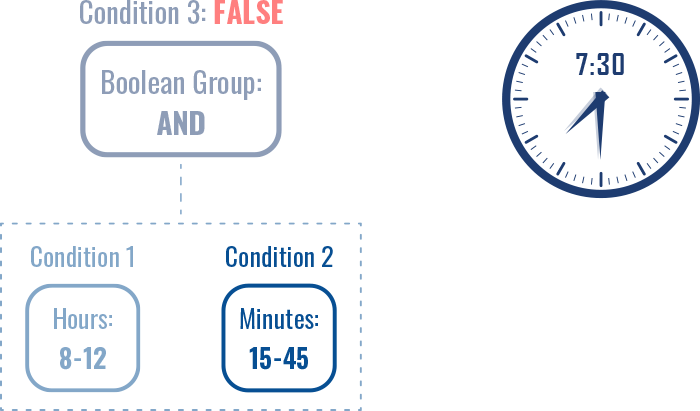
For example, if we have two time Conditions (hour and minute) and a third Condition of Boolean group: AND, both Conditions 1 & 2 have to be met for Condition 3 to be evaluated as TRUE.
In this case, if at least one condition is no longer met, the Boolean group: AND Condition is evaluated as FALSE.
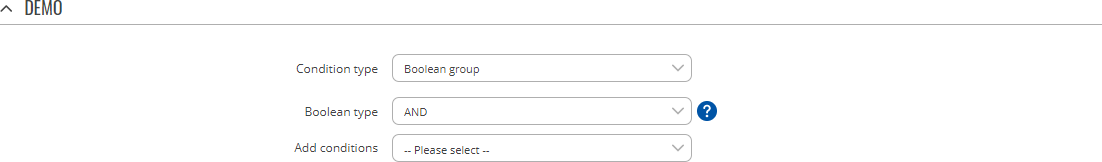
Below is an example of Condition type: Boolean group configuration.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Boolean type | AND | NAND | OR | NOR; default: AND | Type of boolean condition. |
| Add conditions | conditions; default: none | Specifies conditions which have to be met for action to occur. |
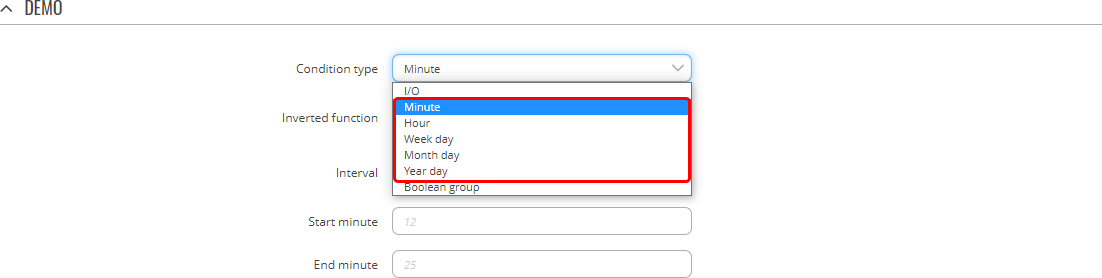
Condition types: Date/Time
Lastly, you can configure Conditions based on date and time. Date/time Conditions can be configured based on:
- Minute of the hour
- Hour of the day
- Day of the Week
- Day of the Month
- Day of the Year
Each type can be configured in two distinct ways:
- Specific time - configured as a single value which defines the exact time when the Condition is considered as TRUE. e.g.:
- Hour: 8
- Day of Month: 1
- Time interval - configured with a start and an end value which define a window of time during which the Condition is considered as TRUE. e.g.:
- Hours: 8-12
- Days of Month: 1-12
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]]