Template:Networking rutos manual lan: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (49 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: | {{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | ||
| | | series = {{{series}}} | ||
| series | | name = {{{name}}} | ||
| fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
}} | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT9 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} LAN (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT9XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i>|}} | |||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT2 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} LAN (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT2XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i>|}} | |||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
The <b>LAN</b> page is used to | The <b>LAN</b> page is used to create and set up local area network interfaces. | ||
This manual page provides an overview of the LAN windows in {{{name}}} devices. | This manual page provides an overview of the LAN windows in {{{name}}} devices. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 19: | ||
}} | }} | ||
==LAN | ==LAN== | ||
The <b>LAN | The <b>LAN</b> section displays LAN interfaces currently existing on this device. | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_lan_settings_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
If you hover mouse over the question mark [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wan_question_mark.png]] global IPv6 prefix assignment addresses will be displayed. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_lan_question_mark_info.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
The <b>Add New Instance</b> section is used to create additional network interfaces. To create a new interface, simply enter a custom name for it and click the 'Add' button. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_interfaces_add_interface_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
To begin configuring an interface, click the 'Edit' button on the right side of the interface: | To begin configuring an interface, click the 'Edit' button on the right side of the interface: | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_lan_begin_to_edit_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
=== | ===Interface configuration=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
The <b>General | ====General settings==== | ||
The <b>General Settings</b> section is used to configure the main parameters of LAN. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_lan_general_settings.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 49: | ||
<th>Value</th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th>Description</th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable</td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>on</b></td> | |||
<td>Enable interface</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Protocol</td> | |||
<td>Static | None; default: <b>Static</b></td> | |||
<td></td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>IPv4 address</td> | <td>IPv4 address</td> | ||
<td>ip4; default: <b> | <td>ip4; default: <b>192.168.1.1</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Your router's address on the network </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 55: | Line 70: | ||
<td>The IPv4 netmask of this interface. A <b>[[What is a Netmask?|netmask]]</b> is used to define how "large" a network is by specifying which part of the IP address denotes the network and which part denotes a device.</td> | <td>The IPv4 netmask of this interface. A <b>[[What is a Netmask?|netmask]]</b> is used to define how "large" a network is by specifying which part of the IP address denotes the network and which part denotes a device.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
{{#ifeq:{{{LAN_to_WAN}}}| 1 | | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{ | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>LAN to WAN </td> | <td>LAN to WAN </td> | ||
| Line 83: | Line 77: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
|}} | |}} | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
====IPV6 settings==== | |||
The <b>IPV6 settings</b> section is used to configure the IPv6 parameters of LAN. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_lan_ipv6_settings.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th>Field</th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | |||
<td>Delegate IPv6 prefixes</td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>on</b></td> | |||
<td>Enable downstream delegation of IPv6 prefixes available on this interface.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>IPv6 assignment length</td> | |||
<td>Disabled | 64 | Custom - integer [0..6]; default: <b>60</b></td> | |||
<td>Assign a part of given length of every public IPv6-prefix to this interface.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>IPv6 assignment hint</td> | |||
<td>A hexadecimal string of symbols: a-f, A-F and 0-9 is accepted; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Assign prefix parts using this hexadecimal subprefix ID for this interface.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | |||
<td>IPv6 suffix</td> | |||
<td>Allowed values: "eui64", "random", fixed value like "::1" or "::1:2"; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Optional. Allowed values: 'eui64', 'random', fixed value like '::1' or '::1:2'. When IPv6 prefix (like 'a:b:c:d::') is received from a delegating server, use the suffix (like '::1') to form the IPv6 address ('a:b:c:d::1') for the interface.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
====Advanced settings==== | |||
The <b>Advanced settings</b> section is used to configure the advanced parameters of LAN. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_lan_advanced_settings.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
[[File: | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th>Field</th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | |||
<td>Force link</td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>on</b></td> | |||
<td>Set interface properties regardless of the link carrier (If set, carrier sense events do not invoke hotplug handlers).</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Use gateway metric</td> | |||
<td>integer[0..4294967295]; default: <b>0</b></td> | |||
<td>The configuration by default generates a routing table entry. In this field you can alter the metric of that entry. Lower metric means higher priority.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Override MAC address</td> | |||
<td>Mac address of six groups of two hexadecimal digits are accepted. E.g. 00:23:45:67:89:AB; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Override MAC address of the interface. For example, your ISP (Internet Service Provider) gives you a static IP address and it might also bind it to your computers MAC address (i.e., that IP will only work with your computer but not with your router). In this field you can select your computer’s MAC address and fool the gateway in to thinking that it is communicating with your computer. You can select the MAC address of a currently connected computer, or use a custom one. When changing MAC address on LAN interface be careful to avoid MAC address collisions.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | |||
<td>Override MTU</td> | |||
<td>integer [98..65535]; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) – specifies the largest possible size of a data packet.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | |||
<td>IP4 table</td> | |||
<td>Value must be a valid unsigned integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>IPv4 routing table for routes of this interface.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
====Physical settings==== | |||
The <b>Physical settings</b> section is used to configure the physical parameters of LAN. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_lan_physical_settings.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
[[File: | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 214: | Line 157: | ||
<th>Value</th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th>Description</th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Bridge interfaces</td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>on</b></td> | |||
<td>Creates a bridge over specified interface(s).</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Enable STP</td> | ||
<td> | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Enables the Spanning Tree Protocol on this bridge.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable IGMP</td> | |||
<td> | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>Enables IGMP snooping on this bridge.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Interface</td> | |||
<td>network interface(s); default: <b>lan physical interface</b></td> | |||
<td>Physical interface name to assign to this section, list of interfaces if type bridge is set.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
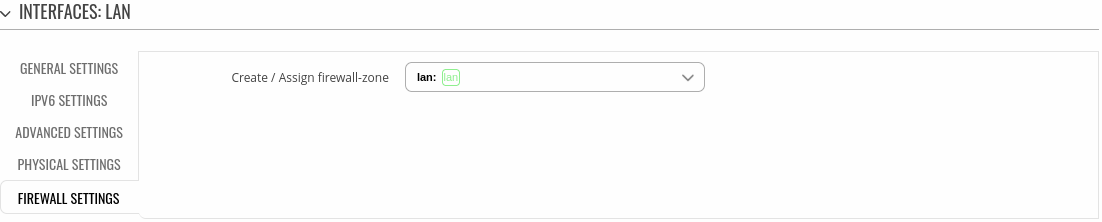
====Firewall settings==== | |||
The <b>Firewall settings</b> section is used to configure the firewall parameters of LAN. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_lan_firewall_settings.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
[[File: | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 243: | Line 190: | ||
<th>Description</th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | |||
<td> | <td>Create / Assign firewall-zone</td> | ||
<td> | <td>firewall zone; default: <b>lan</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Choose the firewall zone you want to assign to this interface. Select 'Unspecified' to remove the interface from the associated zone or define a new zone and attach the interface to it.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]] | [[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:30, 4 October 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
The LAN page is used to create and set up local area network interfaces.
This manual page provides an overview of the LAN windows in {{{name}}} devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
LAN
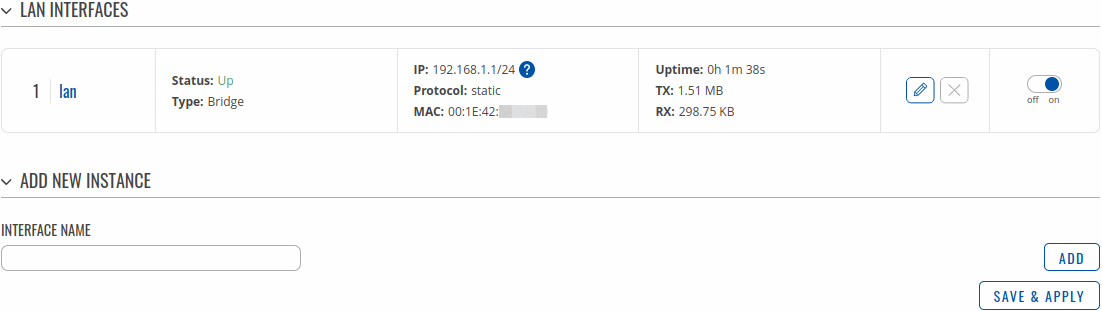
The LAN section displays LAN interfaces currently existing on this device.
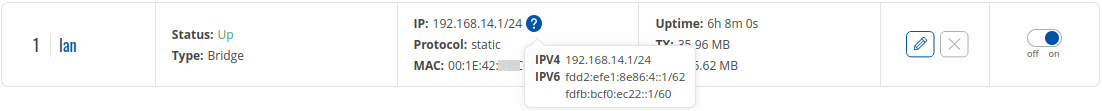
If you hover mouse over the question mark ![]() global IPv6 prefix assignment addresses will be displayed.
global IPv6 prefix assignment addresses will be displayed.
The Add New Instance section is used to create additional network interfaces. To create a new interface, simply enter a custom name for it and click the 'Add' button.
To begin configuring an interface, click the 'Edit' button on the right side of the interface:
Interface configuration
General settings
The General Settings section is used to configure the main parameters of LAN.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: on | Enable interface |
| Protocol | Static | None; default: Static | |
| IPv4 address | ip4; default: 192.168.1.1 | Your router's address on the network |
| IPv4 netmask | netmask; default: 255.255.255.0 | The IPv4 netmask of this interface. A netmask is used to define how "large" a network is by specifying which part of the IP address denotes the network and which part denotes a device. |
IPV6 settings
The IPV6 settings section is used to configure the IPv6 parameters of LAN.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Delegate IPv6 prefixes | off | on; default: on | Enable downstream delegation of IPv6 prefixes available on this interface. |
| IPv6 assignment length | Disabled | 64 | Custom - integer [0..6]; default: 60 | Assign a part of given length of every public IPv6-prefix to this interface. |
| IPv6 assignment hint | A hexadecimal string of symbols: a-f, A-F and 0-9 is accepted; default: none | Assign prefix parts using this hexadecimal subprefix ID for this interface. |
| IPv6 suffix | Allowed values: "eui64", "random", fixed value like "::1" or "::1:2"; default: none | Optional. Allowed values: 'eui64', 'random', fixed value like '::1' or '::1:2'. When IPv6 prefix (like 'a:b:c:d::') is received from a delegating server, use the suffix (like '::1') to form the IPv6 address ('a:b:c:d::1') for the interface. |
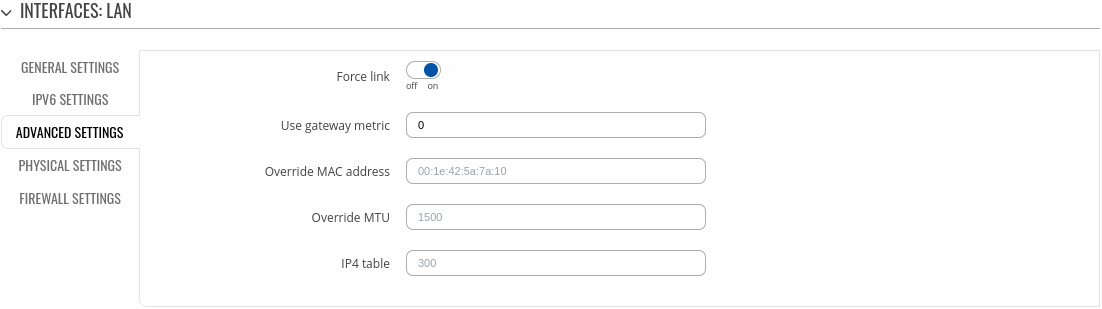
Advanced settings
The Advanced settings section is used to configure the advanced parameters of LAN.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Force link | off | on; default: on | Set interface properties regardless of the link carrier (If set, carrier sense events do not invoke hotplug handlers). |
| Use gateway metric | integer[0..4294967295]; default: 0 | The configuration by default generates a routing table entry. In this field you can alter the metric of that entry. Lower metric means higher priority. |
| Override MAC address | Mac address of six groups of two hexadecimal digits are accepted. E.g. 00:23:45:67:89:AB; default: none | Override MAC address of the interface. For example, your ISP (Internet Service Provider) gives you a static IP address and it might also bind it to your computers MAC address (i.e., that IP will only work with your computer but not with your router). In this field you can select your computer’s MAC address and fool the gateway in to thinking that it is communicating with your computer. You can select the MAC address of a currently connected computer, or use a custom one. When changing MAC address on LAN interface be careful to avoid MAC address collisions. |
| Override MTU | integer [98..65535]; default: none | Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) – specifies the largest possible size of a data packet. |
| IP4 table | Value must be a valid unsigned integer; default: none | IPv4 routing table for routes of this interface. |
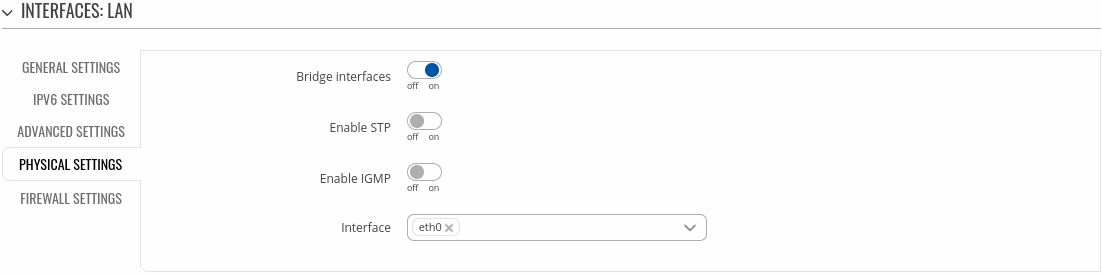
Physical settings
The Physical settings section is used to configure the physical parameters of LAN.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bridge interfaces | off | on; default: on | Creates a bridge over specified interface(s). |
| Enable STP | off | on; default: off | Enables the Spanning Tree Protocol on this bridge. |
| Enable IGMP | off | on; default: off | Enables IGMP snooping on this bridge. |
| Interface | network interface(s); default: lan physical interface | Physical interface name to assign to this section, list of interfaces if type bridge is set. |
Firewall settings
The Firewall settings section is used to configure the firewall parameters of LAN.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Create / Assign firewall-zone | firewall zone; default: lan | Choose the firewall zone you want to assign to this interface. Select 'Unspecified' to remove the interface from the associated zone or define a new zone and attach the interface to it. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]