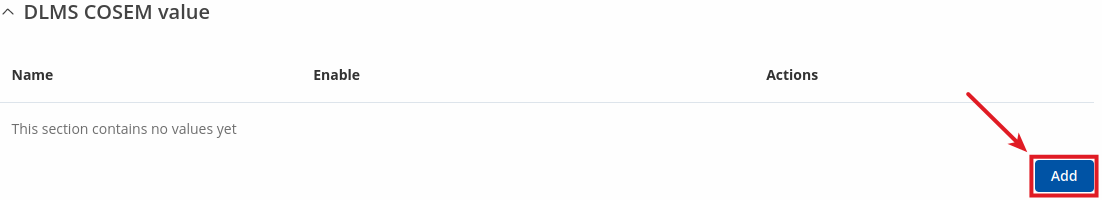Template:Networking rutos manual dlms: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_fw_disclosure | fw_version ={{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_latest_fw | series = {{{series}}} | name = {{{name}}} }} }} ==Summary...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: | {{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | ||
| fw_version ={{Template: | | series = {{{series}}} | ||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
| fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | | series = {{{series}}} | ||
| name = {{{name}}} | | name = {{{name}}} | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
This manual page provides an overview of the DLMS functionality in {{{name}}} devices. | This manual page provides an overview of the DLMS functionality in {{{name}}} devices. | ||
<b>Note:</b> DLMS is additional software that can be installed from the <b> | <b>Note:</b> DLMS is additional software that can be installed from the <b>System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]]</b> page. | ||
<b>Note:</b> The count of DLMS connections is limited to 30, physical devices - up to 30, space groups - up to 10, cosem objects - up to 20 in each group. | |||
==Main== | ==Main== | ||
The <b>Main</b> page is used to configure DLMS physical devices and Cosem Groups. | The <b>Main</b> page is used to configure DLMS physical devices and Cosem Groups. | ||
Notice the Global section config. It is used to outright turn the service off or on if any active configurations are present. | |||
[[File:Networking rutos manual dlms dlms physical devices global button v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
Clicking the Cog icon opens a modal window. The global configuration slider can be set and it's state saved. | |||
[[File:Networking rutos manual modbus modbus tcp client modbus tcp server devices global config modal v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
===DLMS Physical devices=== | ===DLMS Physical devices=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Interoperable devices in DLMS categorize as server (physical device) and client. Data collection device act as a client that supports system | Interoperable devices in DLMS categorize as server (physical device) and client. Data collection device act as a client that supports system | ||
dependent features, parameters, functions and classes requesting data from the server (physical device). In this structure, communication protocol stack is independent of application layer so both devices may communicate different media. To add a new physical device, | dependent features, parameters, functions and classes requesting data from the server (physical device). In this structure, communication protocol stack is independent of application layer so both devices may communicate different media. To add a new physical device, click the 'Add' button. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_physical_devices_add_button_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added physical device's configuration page. | After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added physical device's configuration page. | ||
| Line 49: | Line 41: | ||
The <b>DLMS Physical device configuration</b> section is used to configure the parameters of server (physical device). | The <b>DLMS Physical device configuration</b> section is used to configure the parameters of server (physical device). | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_physical_devices_configuration_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 61: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Name</td> | <td>Name</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Physical device name.</td> | <td>Physical device name.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Server address</td> | <td>Server address type</td> | ||
<td><span style="color:maroon">Default</span> {{!}} <span style="color:olive">Serial number</span>; default: <b>Default</b></td> | |||
<td>Select 'Default' for server address or 'Serial Number' for addressing by a specific serial number.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:maroon">Server address</span></td> | |||
<td>integer [0..255]; default: <b>1</b></td> | <td>integer [0..255]; default: <b>1</b></td> | ||
<td>DLMS device server address.</td> | <td>DLMS device server address.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:olive">Serial number</span></td> | |||
<td>unsigned integer; default: <b>1</b></td> | |||
<td>DLMS device serial number. Uses formula 'SN % 10000 + 1000'.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 89: | Line 91: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Access security</td> | <td>Access security</td> | ||
<td>none {{!}} <span style="color:red">Low</span> {{!}} <span style="color:red">High</span> {{!}} <span style="color:red">High MD5</span> {{!}} <span style="color:red">High SHA1</span> {{!}} <span style="color:blue">High GMAC</span>; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>none {{!}} <span style="color:red">Low</span> {{!}} <span style="color:red">High</span> {{!}} <span style="color:red">High MD5</span> {{!}} <span style="color:red">High SHA1</span> {{!}} <span style="color:blue">High GMAC</span> {{!}} <span style="color:red">HIGH SHA256</span>; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>DLMS device authentication type.</td> | <td>DLMS device authentication type.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 108: | Line 110: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:brown">Invocation counter OBIS code</span></td> | <td>Authentication/Encryption/Authentication encryption: <span style="color:brown">Invocation counter OBIS code</span></td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>DLMS device invocation counter OBIS code.</td> | <td>DLMS device invocation counter OBIS code.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:blue">Authentication key</span></td> | <td>Authentication/Authentication encryption: <span style="color:blue">Authentication key</span></td> | ||
<td>string (Length of the value must be 32); default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string (Length of the value must be 32); default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>DLMS device authentication key.</td> | <td>DLMS device authentication key.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:blue">Block cipher key</span></td> | <td>Encryption/Authentication encryption: <span style="color:blue">Block cipher key</span></td> | ||
<td>string (Length of the value must be 32); default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string (Length of the value must be 32); default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>DLMS device block cipher key.</td> | <td>DLMS device block cipher key.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:green">Dedicated key</span></td> | <td>Encryption/Authentication encryption: <span style="color:green">Dedicated key</span></td> | ||
<td>string (Length of the value must be 32); default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string (Length of the value must be 32); default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>DLMS device dedicated key.</td> | <td>DLMS device dedicated key.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Logical name referencing</td> | |||
<td>on {{!}} off; default: <b>on</b></td> | |||
<td>DLMS devices use Logical Names to reference and access specific data objects or attributes during communication. For example, when requesting data from a device, you might reference a specific Logical Name to retrieve the information.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 133: | Line 140: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
===Scan device parameters=== | |||
---- | |||
After successfully adding the 'DLMS physical devices' configuration, and if the DLMS server is available, you can initiate a <b>Device Parameters</b> scan, which will write the parameters locally next to the cosem value configuration. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_physical_devices_scan_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
===DLMS Cosem groups=== | ===DLMS Cosem groups=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
To add a new cosem group, | To add a new cosem group, click the 'Add' button. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_cosem_groups_add_button_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added cosem group's configuration page. | After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added cosem group's configuration page. | ||
| Line 146: | Line 160: | ||
The <b>DLMS Cosem group configuration</b> section is used to configure the parameters of cosem groups. | The <b>DLMS Cosem group configuration</b> section is used to configure the parameters of cosem groups. | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_cosem_groups_configuration.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_cosem_groups_configuration v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 161: | Line 175: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Name</td> | <td>Name</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>OBIS code group name.</td> | <td>OBIS code group name.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 178: | Line 192: | ||
====DLMS Cosem value==== | ====DLMS Cosem value==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
To add a new cosem value, | <b>Cosem value</b> is a specific value retrieved from a defined server (physical device). To add a new cosem value, click the 'Add' button. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_cosem_value_add_button_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added cosem value's configuration page. | After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added cosem value's configuration page. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_cosem_value_configuration_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 199: | Line 213: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Name</td> | <td>Name</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>COSEM option name.</td> | <td>COSEM option name.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 214: | Line 228: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>COSEM class id</td> | <td>COSEM class id</td> | ||
<td> | <td>DATA (ID: 1) {{!}} REGISTER (ID: 3) {{!}} EXTENDED REGISTER (ID: 4) {{!}} DEMAND REGISTER (ID: 5) {{!}} REGISTER ACTIVATION (ID: 6) {{!}} <span style="color:red">PROFILE GENERIC (ID: 7)</span> {{!}} CLOCK (ID: 8) {{!}} SCRIPT TABLE (ID: 9) {{!}} SPECIAL DAYS TABLE (ID: 11) {{!}} ASSOCIATION LOGICAL NAME (ID: 15) {{!}} SAP ASSIGNMENT (ID: 17) {{!}} IMAGE TRANSFER (ID: 18) {{!}} IEC LOCAL PORT SETUP (ID: 19) {{!}} ACTIVITY CALENDAR (ID: 20) {{!}} REGISTER MONITOR (ID: 21) {{!}} ACTION SCHEDULE (ID: 22) {{!}} IEC HDLC SETUP (ID: 23) {{!}} IEC TWISTED PAIR SETUP (ID: 24) {{!}} UTILITY TABLES (ID: 26) {{!}} MODEM CONFIGURATION (ID: 27) {{!}} AUTO ANSWER (ID: 28) {{!}} AUTO CONNECT (ID: 29) {{!}} PUSH SETUP (ID: 40) {{!}} TCP UDP SETUP (ID: 41) {{!}} IP4 SETUP (ID: 42) {{!}} MAC ADDRESS SETUP (ID: 43) {{!}} GPRS SETUP (ID: 45) {{!}} GSM DIAGNOSTIC (ID: 47) {{!}} IP6 SETUP (ID: 48) {{!}} COMPACT DATA (ID: 62) {{!}} SECURITY SETUP (ID: 64) {{!}} ARBITRATOR (ID: 68) {{!}} DISCONNECT CONTROL (ID: 70) {{!}} LIMITER (ID: 71); default: <b>DATA (ID: 1)</b></td> | ||
<td>OBIS code | <td>Object type for OBIS code.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:red">Entries</span></td> | |||
<td>interger [1..32767]; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>How many data objects to read.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
=====Device Parameters===== | |||
Parameters that are found after scan has finished. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_cosem_value_configuration_device_parameters_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
==Connections== | |||
The <b>Connections</b> page is used to configure DLMS connections. You can use either TCP or serial (depending on the router) connection to establish a connection between the physical device and the router. | |||
===General status=== | |||
---- | |||
This section displays DLMS general status information. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_connections_status.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
===DLMS Connections=== | |||
---- | |||
To add a new connection, click the 'Add' button. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_connections_add_button_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added connection's configuration page. | |||
====DLMS Connection configuration==== | |||
---- | |||
The <b>DLMS Connection configuration</b> section is used to configure the parameters of connections. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlms_dlms_connections_configuration_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Enables Cosem state.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Name</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>previously added connection name</b></td> | |||
<td>Name of DLMS connection configuration.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Connection type</td> | |||
<td>TCP {{#ifeq: {{{serial}}} | 1 | {{!}} <span style="color:red">Serial</span> |}}; default: <b>TCP</b></td> | |||
<td>DLMS connection type.</td> | |||
</tr>{{#ifeq: {{{serial}}} | 1 | | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:red">Serial device</span></td> | |||
<td>{{Template: Networking rutos manual serial ports| rs232={{{rs232}}}| rs485={{{rs485}}}| usb = {{{usb}}}}}; default: <b>{{Template: Networking rutos manual default serial port| rs232={{{rs232}}}| rs485={{{rs485}}}| usb = {{{usb}}}}}</b></td> | |||
<td>DLMS serial device.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Baud rate</td> | |||
<td>300 {{!}} 1200 {{!}} 2400 {{!}} 4800 {{!}} 9600 {{!}} 19200 {{!}} 38400 {{!}} 57600 {{!}} 115200{{#ifeq: {{{rs485}}} | 1 | {{!}} 230400 {{!}} 460800 {{!}} 921600 {{!}} 1000000 {{!}} 3000000|}}; default: <b>9600</b></td> | |||
<td>Serial data transmission rate (in bits per second).</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Data bits</td> | |||
<td>{{#ifeq:{{#expr: {{{rs232}}} or {{{usb}}}}} |1|{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|TRB2||5 {{!}} 6 {{!}}}} 7 {{!}} |}}8; default: <b>8</b></td> | |||
<td>Number of data bits for each character.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Stop bits</td> | |||
<td>1{{#ifeq:{{#expr: {{{rs232}}} or {{{usb}}}}} |1| {{!}} 2|}}; default: <b>1</b></td> | |||
<td>Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Parity</td> | |||
<td>Even {{!}} Odd{{#ifeq:{{#expr: {{{rs232}}} or {{{usb}}}}} |1| {{!}} Mark {{!}} Space|}} {{!}} None; default: <b>None</b></td> | |||
<td>In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check. | |||
<ul> | |||
<li><b>None</b> (<b>N</b>) - no parity method is used.</li> | |||
<li><b>Odd</b> (<b>O</b>) - the parity bit is set so that the number of "logical ones (1s)" has to be odd.</li> | |||
<li><b>Even</b> (<b>E</b>) - the parity bit is set so that the number of "logical ones (1s)" has to be even.</li>{{#ifeq:{{#expr: {{{rs232}}} or {{{usb}}}}} |1|<li><b>Space</b> (<b>s</b>) - the parity bit will always be a binary 0.</li> | |||
<li><b>Mark</b> (<b>M</b>) - the parity bit will always be a binary 1.</li>|}} | |||
</ul> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Flow control</td> | |||
<td>None {{#ifeq:{{#expr: {{{rs232}}} or {{{usb}}}}} |1| {{!}} RTS/CTS {{!}} Xon/Xoff|}}; default: <b>None</b></td> | |||
<td>In many circumstances a transmitter might be able to send data faster than the receiver is able to process it. To cope with this, serial lines often incorporate a "handshaking" method, usually distinguished between hardware and software handshaking. | |||
{{#ifeq:{{#expr: {{{rs232}}} or {{{usb}}}}} |1|<ul> | |||
<li><b>RTS/CTS</b> - hardware handshaking. RTS and CTS are turned OFF and ON from alternate ends to control data flow, for instance when a buffer is almost full.</li> | |||
<li><b>Xon/Xoff</b> - software handshaking. The Xon and Xoff characters are sent by the receiver to the sender to control when the sender will send data, i.e., these characters go in the opposite direction to the data being sent. The circuit starts in the "sending allowed" state. When the receiver's buffers approach capacity, the receiver sends the Xoff character to tell the sender to stop sending data. Later, after the receiver has emptied its buffers, it sends an Xon character to tell the sender to resume transmission.</li> | |||
</ul>|}} | |||
</td> | |||
</tr>{{#ifeq: {{{rs485}}} | 1 | | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">RS485:</span> Full Duplex</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Enables RS485 full duplex.</td> | |||
</tr>|}}}} | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>IP address</td> | |||
<td>ip; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>DLMS device IP address for TCP connection.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Port</td> | |||
<td>integer [1..65535]; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>DLMS device IP port for TCP connection.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Persistent</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Open TCP connection once and reuse it between requests.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]] | |||
Latest revision as of 07:22, 8 October 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
The DLMS / COSEM standard suite (IEC 62056 / EN 13757- 1) is the most widely accepted international utility meter data exchange standard. DLMS is the application layer protocol that transforms the data into messages and COSEM describes the general object model and can be used for all kinds of presentations.
This manual page provides an overview of the DLMS functionality in {{{name}}} devices.
Note: DLMS is additional software that can be installed from the System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]] page. Note: The count of DLMS connections is limited to 30, physical devices - up to 30, space groups - up to 10, cosem objects - up to 20 in each group.
Main
The Main page is used to configure DLMS physical devices and Cosem Groups.
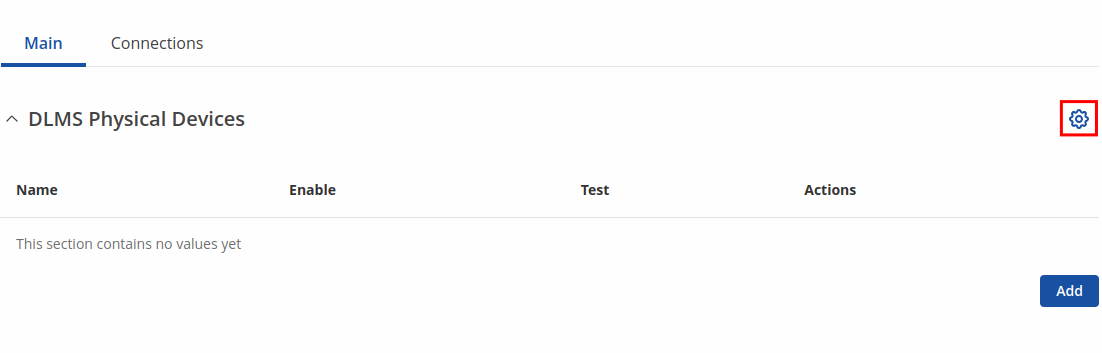
Notice the Global section config. It is used to outright turn the service off or on if any active configurations are present.
Clicking the Cog icon opens a modal window. The global configuration slider can be set and it's state saved.
DLMS Physical devices
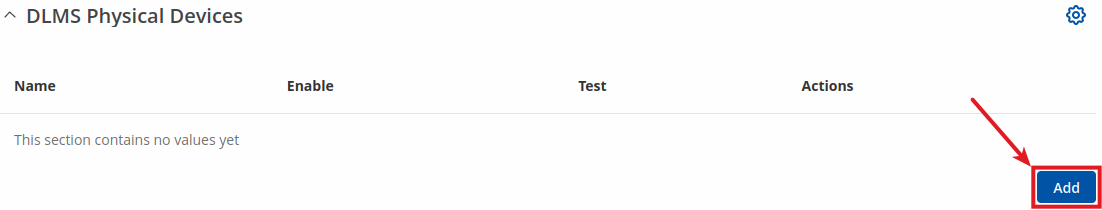
Interoperable devices in DLMS categorize as server (physical device) and client. Data collection device act as a client that supports system dependent features, parameters, functions and classes requesting data from the server (physical device). In this structure, communication protocol stack is independent of application layer so both devices may communicate different media. To add a new physical device, click the 'Add' button.
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added physical device's configuration page.
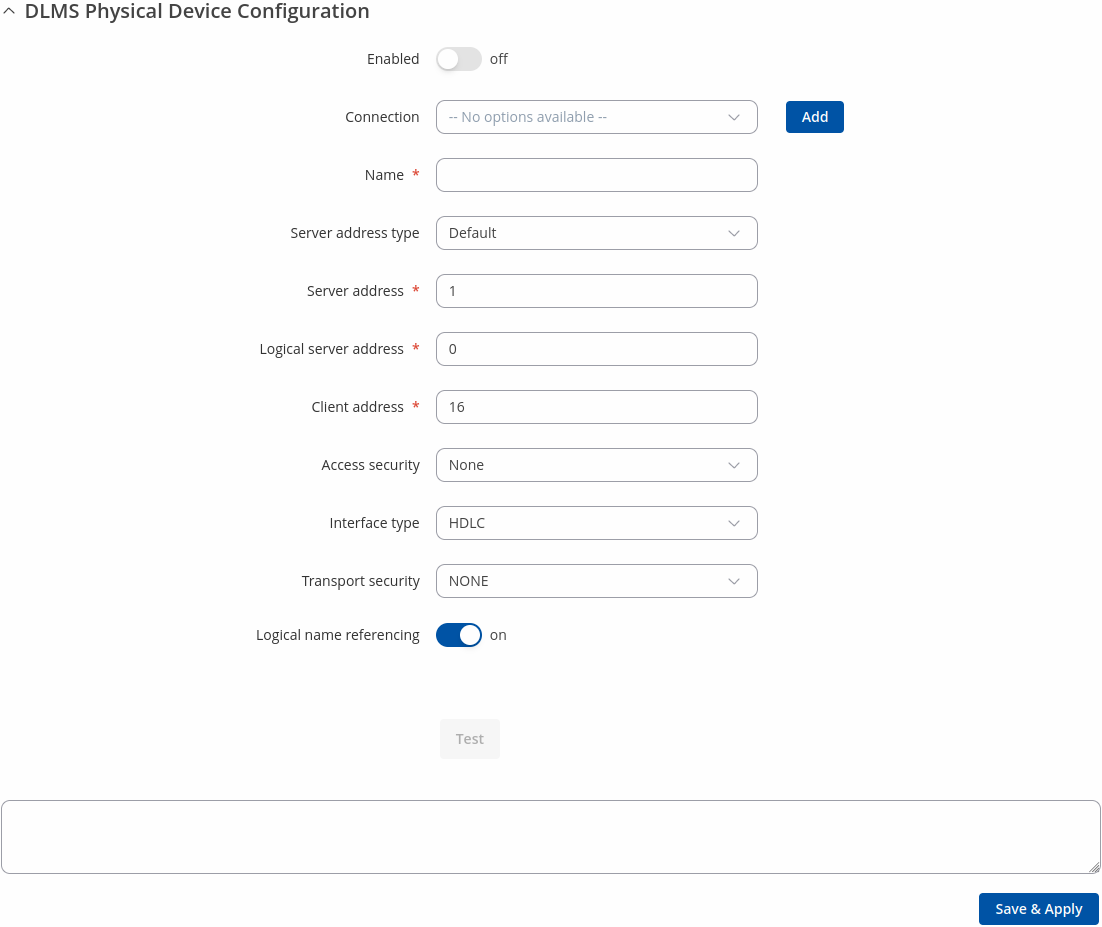
DLMS Physical device configuration
The DLMS Physical device configuration section is used to configure the parameters of server (physical device).
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enables specific physical device configuration. |
| Connection | empty ; default: none | DLMS connection. |
| Name | string; default: none | Physical device name. |
| Server address type | Default | Serial number; default: Default | Select 'Default' for server address or 'Serial Number' for addressing by a specific serial number. |
| Server address | integer [0..255]; default: 1 | DLMS device server address. |
| Serial number | unsigned integer; default: 1 | DLMS device serial number. Uses formula 'SN % 10000 + 1000'. |
| Logic server address | integer [0..255]; default: 0 | DLMS device logical server address. |
| Client address | integer [0..255]; default: 16 | DLMS device client address. |
| Access security | none | Low | High | High MD5 | High SHA1 | High GMAC | HIGH SHA256; default: none | DLMS device authentication type. |
| Password | string; default: none | DLMS device password if authentication is used. |
| Interface type | HDLC | WRAPPER; default: HDLC | DLMS device interface type. |
| Transport security | none | Authentication | Encryption | Authentication encryption; default: none | DLMS device message encryption. |
| Authentication/Encryption/Authentication encryption: Invocation counter OBIS code | string; default: none | DLMS device invocation counter OBIS code. |
| Authentication/Authentication encryption: Authentication key | string (Length of the value must be 32); default: none | DLMS device authentication key. |
| Encryption/Authentication encryption: Block cipher key | string (Length of the value must be 32); default: none | DLMS device block cipher key. |
| Encryption/Authentication encryption: Dedicated key | string (Length of the value must be 32); default: none | DLMS device dedicated key. |
| Logical name referencing | on | off; default: on | DLMS devices use Logical Names to reference and access specific data objects or attributes during communication. For example, when requesting data from a device, you might reference a specific Logical Name to retrieve the information. |
| Test | -(interactive button) | Test device configuration. |
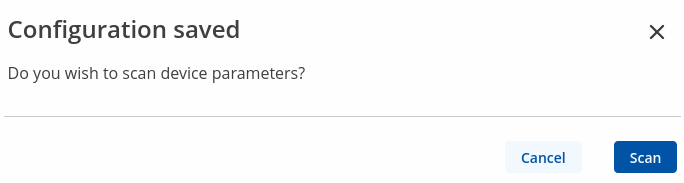
Scan device parameters
After successfully adding the 'DLMS physical devices' configuration, and if the DLMS server is available, you can initiate a Device Parameters scan, which will write the parameters locally next to the cosem value configuration.
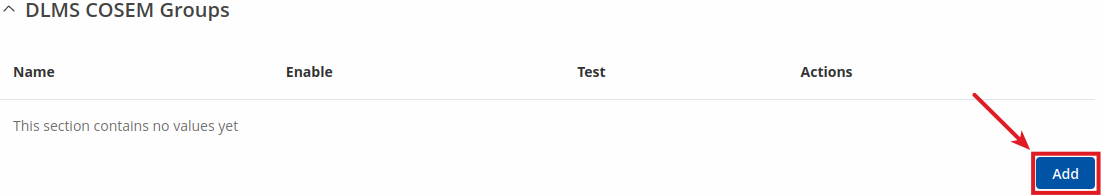
DLMS Cosem groups
To add a new cosem group, click the 'Add' button.
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added cosem group's configuration page.
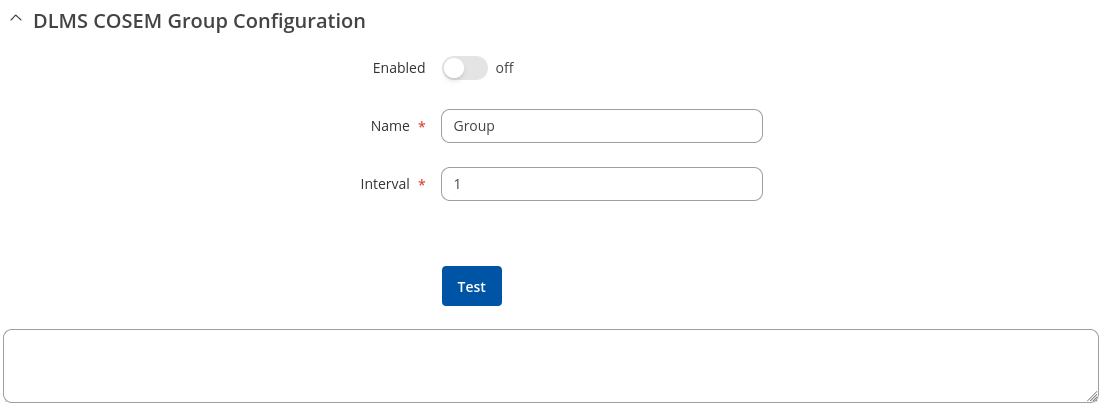
DLMS Cosem group configuration
The DLMS Cosem group configuration section is used to configure the parameters of cosem groups.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enables Cosem group. |
| Name | string; default: none | OBIS code group name. |
| Interval | integer [1..4294967295]; default: 1 | Interval for OBIS code reading (in seconds). |
| Test | -(interactive button) | Test cosem group. |
DLMS Cosem value
Cosem value is a specific value retrieved from a defined server (physical device). To add a new cosem value, click the 'Add' button.
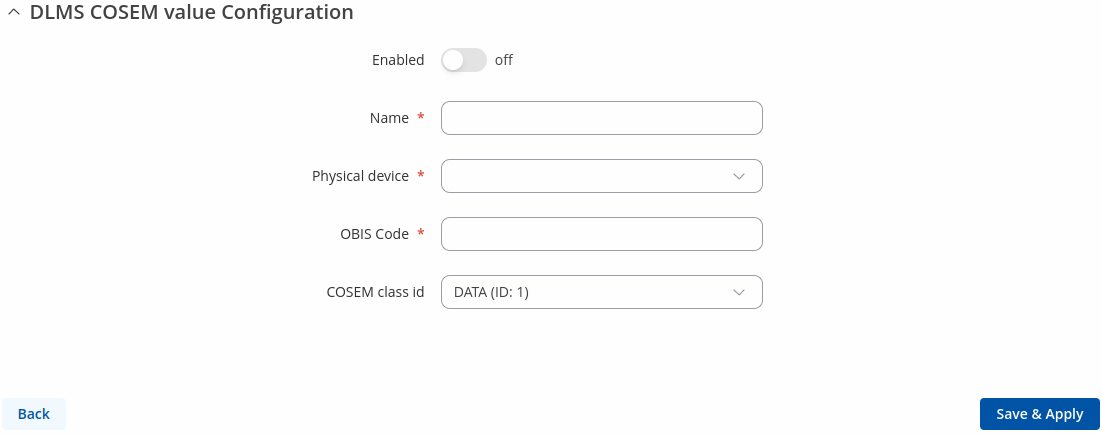
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added cosem value's configuration page.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enables Cosem state. |
| Name | string; default: none | COSEM option name. |
| Physical device | selection; default: none | Physical device to read from. |
| OBIS code | string; default: none | OBIS code value, actions are not executed, only properties are read. |
| COSEM class id | DATA (ID: 1) | REGISTER (ID: 3) | EXTENDED REGISTER (ID: 4) | DEMAND REGISTER (ID: 5) | REGISTER ACTIVATION (ID: 6) | PROFILE GENERIC (ID: 7) | CLOCK (ID: 8) | SCRIPT TABLE (ID: 9) | SPECIAL DAYS TABLE (ID: 11) | ASSOCIATION LOGICAL NAME (ID: 15) | SAP ASSIGNMENT (ID: 17) | IMAGE TRANSFER (ID: 18) | IEC LOCAL PORT SETUP (ID: 19) | ACTIVITY CALENDAR (ID: 20) | REGISTER MONITOR (ID: 21) | ACTION SCHEDULE (ID: 22) | IEC HDLC SETUP (ID: 23) | IEC TWISTED PAIR SETUP (ID: 24) | UTILITY TABLES (ID: 26) | MODEM CONFIGURATION (ID: 27) | AUTO ANSWER (ID: 28) | AUTO CONNECT (ID: 29) | PUSH SETUP (ID: 40) | TCP UDP SETUP (ID: 41) | IP4 SETUP (ID: 42) | MAC ADDRESS SETUP (ID: 43) | GPRS SETUP (ID: 45) | GSM DIAGNOSTIC (ID: 47) | IP6 SETUP (ID: 48) | COMPACT DATA (ID: 62) | SECURITY SETUP (ID: 64) | ARBITRATOR (ID: 68) | DISCONNECT CONTROL (ID: 70) | LIMITER (ID: 71); default: DATA (ID: 1) | Object type for OBIS code. |
| Entries | interger [1..32767]; default: none | How many data objects to read. |
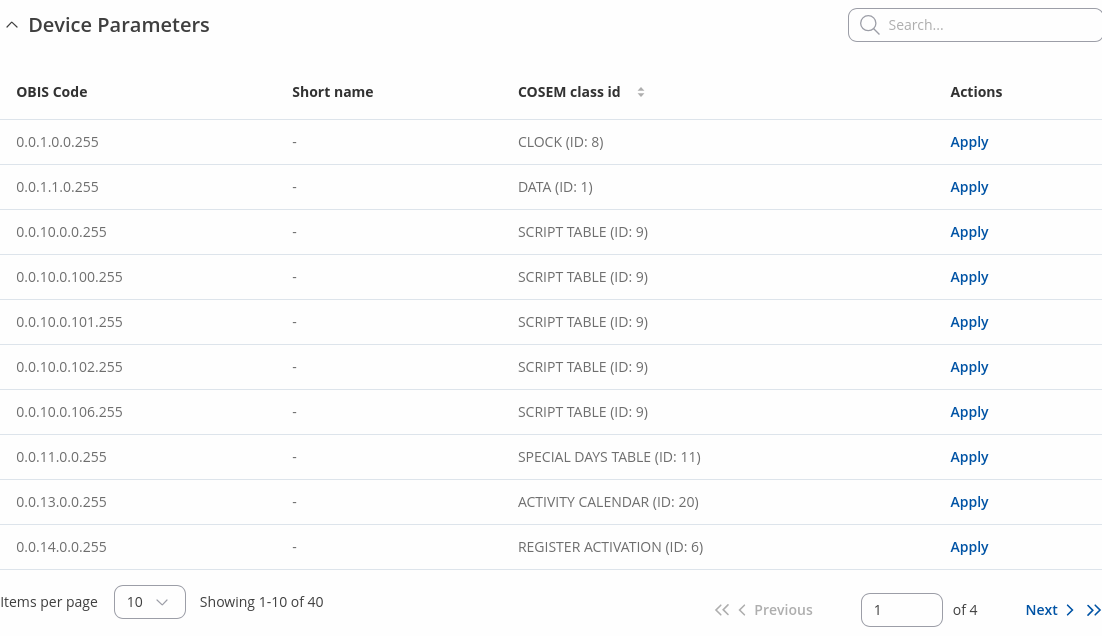
Device Parameters
Parameters that are found after scan has finished.
Connections
The Connections page is used to configure DLMS connections. You can use either TCP or serial (depending on the router) connection to establish a connection between the physical device and the router.
General status
This section displays DLMS general status information.
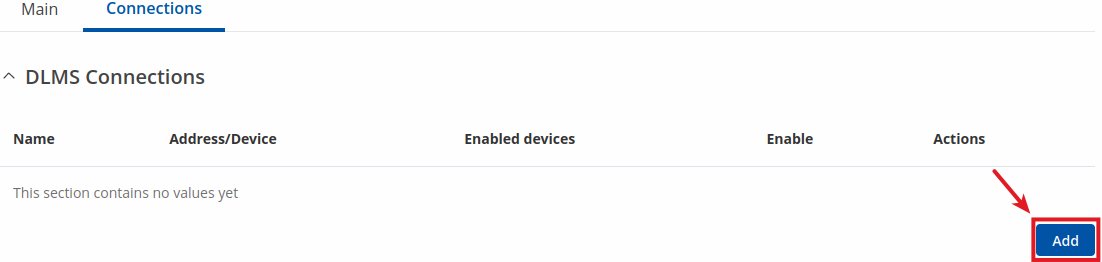
DLMS Connections
To add a new connection, click the 'Add' button.
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added connection's configuration page.
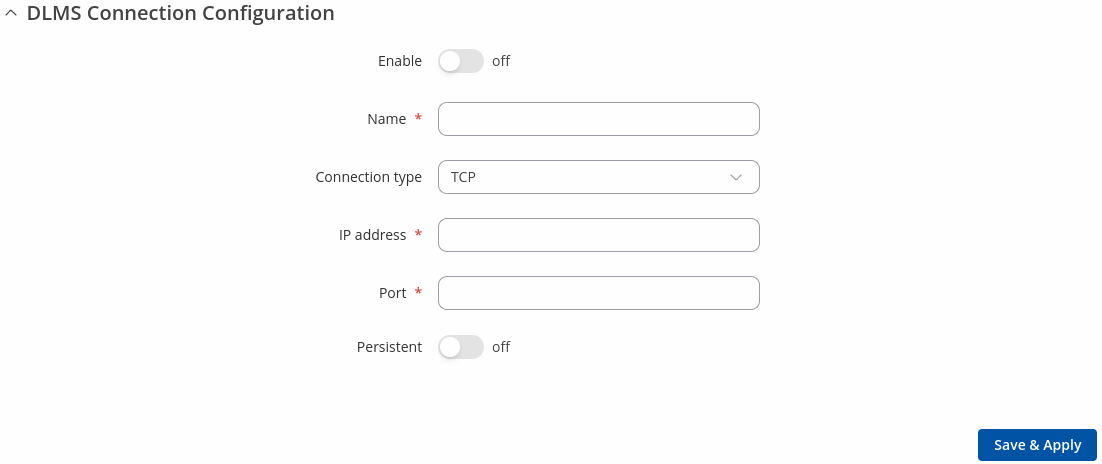
DLMS Connection configuration
The DLMS Connection configuration section is used to configure the parameters of connections.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enables Cosem state. |
| Name | string; default: previously added connection name | Name of DLMS connection configuration. |
| Connection type | TCP ; default: TCP | DLMS connection type. |
| IP address | ip; default: none | DLMS device IP address for TCP connection. |
| Port | integer [1..65535]; default: none | DLMS device IP port for TCP connection. |
| Persistent | off | on; default: off | Open TCP connection once and reuse it between requests. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]]