Template:Networking rutos manual ip settings: Difference between revisions
Appearance
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
| fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT9 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} LAN (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT9XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i>|}} | |||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT2 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} LAN (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT2XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i>|}} | |||
==Network configuration== | ==Network configuration== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 54: | ||
<td>ip4; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>ip4; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>DNS server addresses that this interface will use. If left empty, DNS servers are assigned automatically. To see what DNS servers are currently used, you can check the contents of the <i>/tmp/resolv.conf.auto</i> file.</td> | <td>DNS server addresses that this interface will use. If left empty, DNS servers are assigned automatically. To see what DNS servers are currently used, you can check the contents of the <i>/tmp/resolv.conf.auto</i> file.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Management VLAN</td> | |||
<td>default {{!}} Add new; default: <b>default</b></td> | |||
<td>A management VLAN is the VLAN that is used to separate management and user data traffic for remotely manage, control, and monitor the devices in you network.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 51: | Line 66: | ||
The <b>DHCP</b> protocol is used to set up an interface which obtains its configuration parameters automatically via a DHCP lease. | The <b>DHCP</b> protocol is used to set up an interface which obtains its configuration parameters automatically via a DHCP lease. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_ipsettings_setup_dhcp_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Management VLAN</td> | |||
<td>default {{!}} Add new; default: <b>default</b></td> | |||
<td>A management VLAN is the VLAN that is used to separate management and user data traffic for remotely manage, control, and monitor the devices in you network.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable fallback IP</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>on</b></td> | |||
<td>The device will use the provided fallback IP address if the DHCP server is not reachable. If the fallback IP is not set, default IP address will be used instead (192.168.1.3).</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Fallback IP</td> | |||
<td>ip4; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>DHCP fallback IP.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
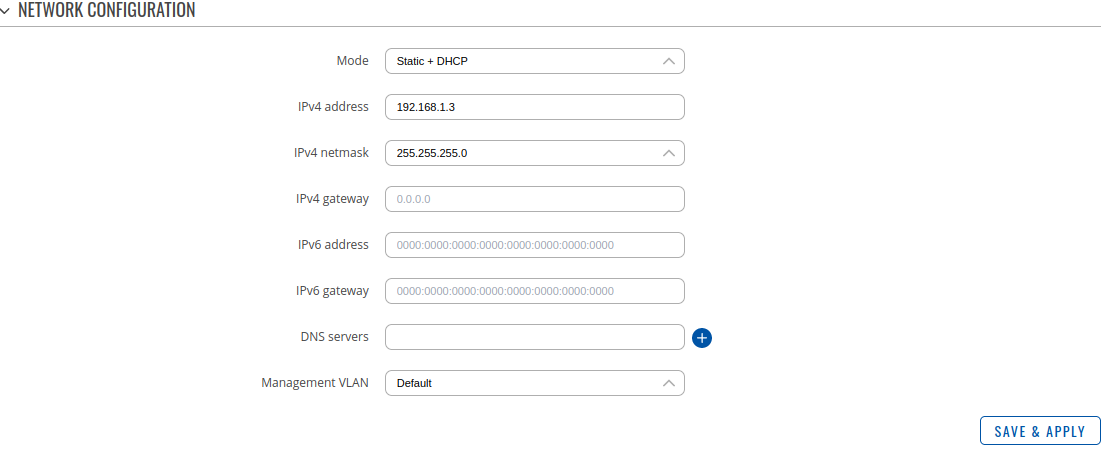
====Interface setup: Mode Static + DHCP==== | ====Interface setup: Mode Static + DHCP==== | ||
Latest revision as of 11:53, 22 November 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Network configuration
This section provides information on network interface configuration. There are three main modes of interface configuration:
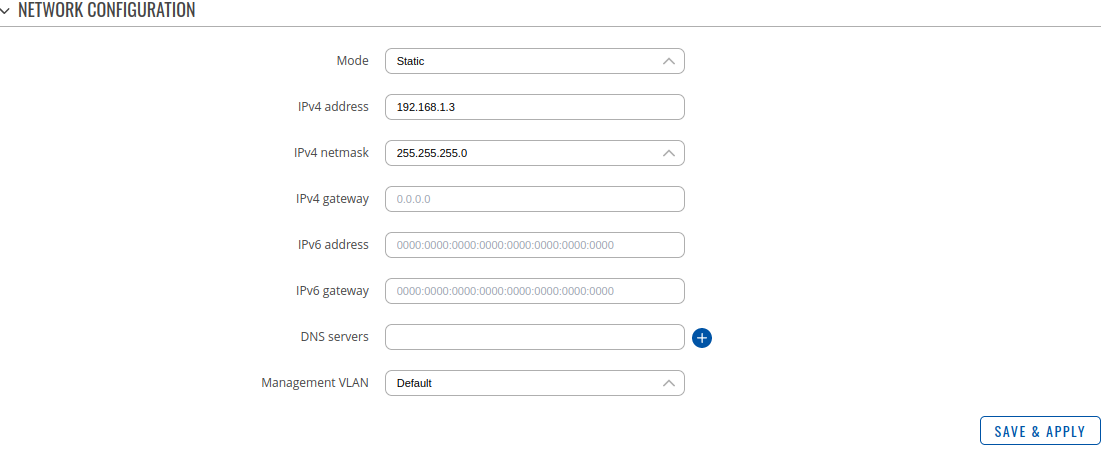
Interface setup: Mode Static
The static protocol uses a predefined manual configuration instead of obtaining parameters automatically via a DHCP lease.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IPv4 address | ip4; default[for LAN]: 192.168.1.3 | The IPv4 address interface of this interface. An IP address identifies a device on a network and allows it to communicate with other devices. |
| IPv4 netmask | netmask; default[for LAN]: 255.255.255.0 | The IPv4 netmask of this interface. A netmask is used to define how "large" a network is by specifying which part of the IP address denotes the network and which part denotes a device. |
| IPv4 gateway | ip4; default: none | The IPv4 gateway address used by this interface. An interface's default gateway is the default address through which all outgoing traffic is directed. |
| IPv6 address | ip6; default: none | The IPv6 address interface of this interface. An IP address identifies a device on a network and allows it to communicate with other devices. |
| IPv6 gateway | ip6; default: none | The IPv6 gateway address used by this interface. An interface's default gateway is the default address through which all outgoing traffic is directed. |
| DNS servers | ip4; default: none | DNS server addresses that this interface will use. If left empty, DNS servers are assigned automatically. To see what DNS servers are currently used, you can check the contents of the /tmp/resolv.conf.auto file. |
| Management VLAN | default | Add new; default: default | A management VLAN is the VLAN that is used to separate management and user data traffic for remotely manage, control, and monitor the devices in you network. |
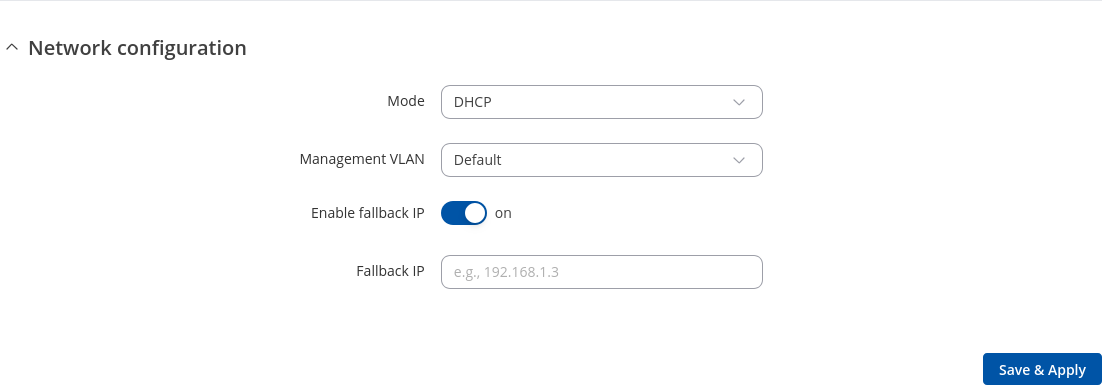
Interface setup: Mode DHCP
The DHCP protocol is used to set up an interface which obtains its configuration parameters automatically via a DHCP lease.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Management VLAN | default | Add new; default: default | A management VLAN is the VLAN that is used to separate management and user data traffic for remotely manage, control, and monitor the devices in you network. |
| Enable fallback IP | off | on; default: on | The device will use the provided fallback IP address if the DHCP server is not reachable. If the fallback IP is not set, default IP address will be used instead (192.168.1.3). |
| Fallback IP | ip4; default: none | DHCP fallback IP. |
Interface setup: Mode Static + DHCP
The Static + DHCP protocols are used simultaneously to obtain configuration parameters manually and automatically.
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]