Template:Networking rutos manual devices: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<b>Virtual Extensible LAN</b> is a tunneling interface protocol (VXLAN), which allows VXLAN layer 2 virtualization over layer 3 network. VXLAN establishes a logical tunnel between the source and destination network devices, through which it uses MAC-in-UDP encapsulation for packets. In addition, it helps customer sites to configure layer2 VPN. | <b>Virtual Extensible LAN</b> is a tunneling interface protocol (VXLAN), which allows VXLAN layer 2 virtualization over layer 3 network. VXLAN establishes a logical tunnel between the source and destination network devices, through which it uses MAC-in-UDP encapsulation for packets. In addition, it helps customer sites to configure layer2 VPN. | ||
<b>Note:</b> VXLAN is additional software that can be installed from the <b>System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]]</b> page. | <b>Note:</b> VXLAN is additional software on some devices that can be installed from the <b>System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]]</b> page. | ||
===Device configuration (VXLAN)=== | ===Device configuration (VXLAN)=== | ||
| Line 123: | Line 119: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
{{# | {{#switch:{{{series}}}| RUTM | RUTC = | ||
==Bridge== | ==Bridge== | ||
A network <b>Bridge</b> is a computer networking device that creates a single, aggregate network from multiple communication networks or network segments. This function is called network bridging. Bridging is distinct from routing. Routing allows multiple networks to communicate independently and yet remain separate, whereas bridging connects two separate networks as if they were a single network. | A network <b>Bridge</b> is a computer networking device that creates a single, aggregate network from multiple communication networks or network segments. This function is called network bridging. Bridging is distinct from routing. Routing allows multiple networks to communicate independently and yet remain separate, whereas bridging connects two separate networks as if they were a single network. | ||
| Line 202: | Line 198: | ||
<td>Maximum expected arrival time of hello bridge protocol data units (BPDUs).</td> | <td>Maximum expected arrival time of hello bridge protocol data units (BPDUs).</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table>}} | ||
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]] | [[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:50, 20 February 2025
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
VXLAN
Virtual Extensible LAN is a tunneling interface protocol (VXLAN), which allows VXLAN layer 2 virtualization over layer 3 network. VXLAN establishes a logical tunnel between the source and destination network devices, through which it uses MAC-in-UDP encapsulation for packets. In addition, it helps customer sites to configure layer2 VPN.
Note: VXLAN is additional software on some devices that can be installed from the System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]] page.
Device configuration (VXLAN)
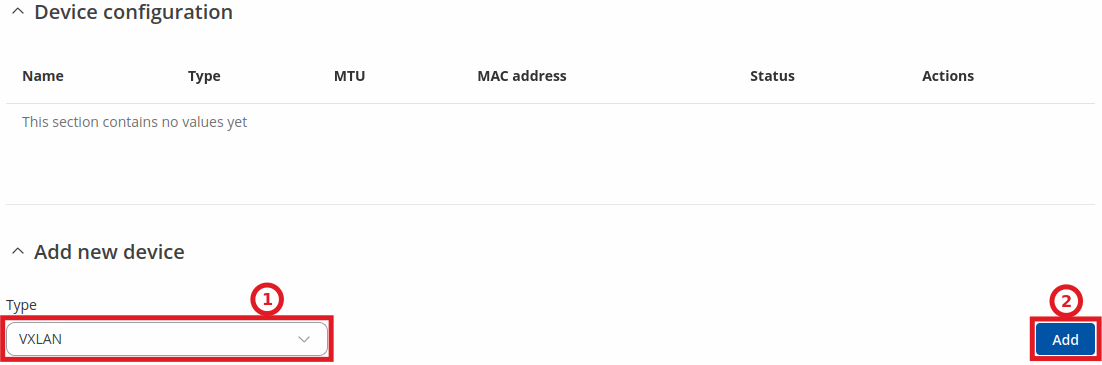
The Device configuration section is used to set up VXLAN devices.
To add a new device - select 'VXLAN' and click 'Add' button:
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added VXLAN device configuration page.
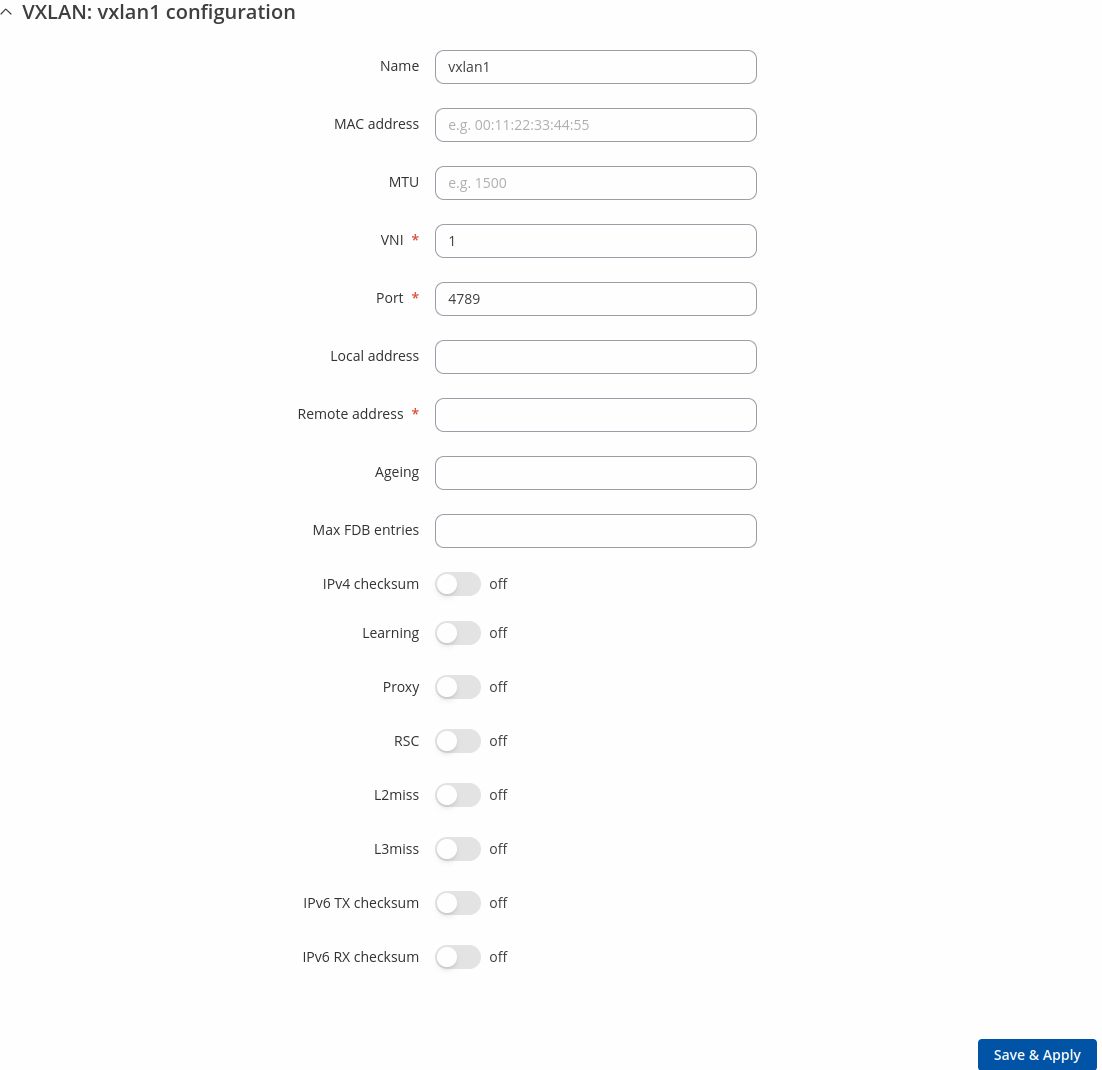
Configuration (VXLAN)
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: vxlan1 | Name of the device. |
| MAC address | mac; default: empty | Override MAC address of the device. If not set, the device's MAC address will be used. |
| MTU | integer [98..9000]; default: empty | Sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
| VNI | integer [1..16777215]; default: 1 | VXLAN network identifier. |
| PORT | integer [1..65535]; default: 4789 | VXLAN network identifier. |
| Local address | ip; default: none | Sets the local source IP address for VXLAN tunneling. |
| Remote address | ip; default: none | Specifies the multicast group or remote IP address used for VXLAN tunneling. |
| Ageing | integer [1..4294967295]; default: empty | Specifies the lifetime in seconds of FDB entries learnt by the kernel. |
| Max FDB entries | integer [1..4294967295]; default: empty | Specifies the maximum number of FDB entries. |
| IPv4 checksum | off | on; default: off | Specifies if UDP checksum is calculated for transmitted packets over IPv4. |
| Learning | off | on; default: off | Enables or disables MAC learning for VXLAN. |
| Proxy | off | on; default: off | Enables or disables ARP proxy for VXLAN. |
| RSC | off | on; default: off | Specifies if route short circuit is turned on. |
| L2miss | off | on; default: off | Specifies if netlink LLADDR miss notifications are generated. |
| L3miss | off | on; default: off | Specifies if netlink IP ADDR miss notifications are generated. |
| IPv6 TX checksum | off | on; default: off | Enables or disables UDP checksum calculation for transmitted packets over IPv6. |
| IPv6 RX checksum | off | on; default: off | Allow incoming UDP packets over IPv6 with zero checksum field. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]