TRB140 Static Routes: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Template: Networking_trb_manual_static_routes | ||
| name = TRB140 | | name = TRB140 | ||
| fw_version = TRB1400_R_00.01.05 | | fw_version = TRB1400_R_00.01.05 | ||
| | | file_routes = Networking_trb_manual_static_routes_v1.png | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:33, 25 November 2019
Summary
Static routes specify over which interface and gateway a certain host or network can be reached. This chapter is an overview of the Static Routes page in TRB140 gateways.
The information in this page is updated in accordance with the TRB1400_R_00.01.05 firmware version.123
Static routes
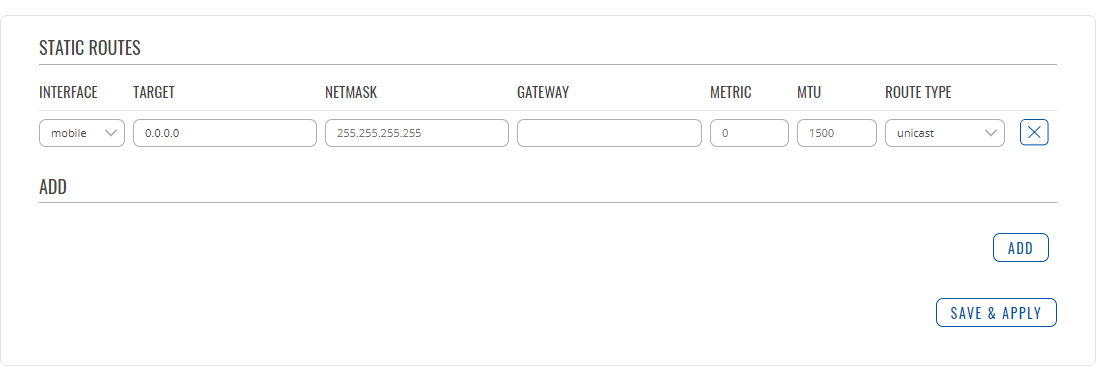
To find information on static route configuration, refer to the figure and table below:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | mobile | lan; default: mobile | The zone where the target network resides |
| Target* | ip4; default: 0.0.0.0 | The address of the destination network |
| Netmask* | netmask; default: 255.255.255.255 | A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies |
| Gateway | ip; default: none | Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule |
| Metric | integer; default: 0 | The metric value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the lower metric is applied. |
| MTU | integer [64..9000]; default: 1500 | Sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
| Route Type | unicast | local | broadcast | multicast | unreachable | prohibit | backhole | anycast | -- custom -- ; default: unicast | Selects route type. Each type specifies a different behavior for the route:
|
*Additional notes on Target & Netmask:
You can define a rule that applies to a single IP like this:
- Target: some IP
- Netmask: 255.255.255.255
Furthermore, you can define a rules that apply to a range of IPs. Refer to the table below for examples.
| Target | Netmask | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.2.0 | 255.255.255.240 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.2.15 range. |
| 192.168.2.240 | 255.255.255.240 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.240 - 192.168.2.255 range. |
| 192.168.2.161 | 255.255.255.0 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.55.255 range. |
| 192.168.0.0 | 255.255.0.0 | Applies to IPs in the 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 range. |
| 192.168.2.161 | 255.255.255.255 | Only applies to 192.168.2.161. |