Difference between revisions of "Template:Networking rutos manual network"
From Teltonika Networks Wiki
| (88 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| Line 14: | Line 4: | ||
The <b>Network</b> page contains information related to the device's networking. This chapter is an overview of the Network page in {{{name}}} devices. | The <b>Network</b> page contains information related to the device's networking. This chapter is an overview of the Network page in {{{name}}} devices. | ||
| − | {{Template: | + | {{Template: Networking_rutx_manual_fw_disclosure |
| − | | | + | | fw_version = RUTX_R_00.02.03 |
}} | }} | ||
| + | ==LAN== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This tab displays information about the device's local network(s). The figure below is an example of the '''Network''' window: | ||
| + | [[File:Networking_rutx_manual_network_lan_v1.png]] | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <table class="nd-othertables"> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th colspan="2">lan information</th> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td width="250">Name</td> | ||
| + | <td width="900">LAN interface name</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>IP address</td> | ||
| + | <td>IP address of the LAN interface</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Netmask</td> | ||
| + | <td>Netmask of the LAN interface. In a sense, a netmask specifies the size of a network. In other words, it indicates which part of the IP address denotes the network, and which denotes the device</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th colspan="2">dhcp leases</th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Hostname</td> | ||
| + | <td>Hostname of a LAN client</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>IP address</td> | ||
| + | <td>IP address of a LAN client</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>MAC address</td> | ||
| + | <td>MAC address of a LAN client</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Leasetime remaining</td> | ||
| + | <td>Remaining lease time for a DHCP client. Active DHCP lease holders will try to renew their DHCP leases after a half of the lease time passes. </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{mobile}}}|1| | {{#ifeq:{{{mobile}}}|1| | ||
| Line 22: | Line 54: | ||
The <b>Mobile</b> tab displays information about the mobile connection. The figure below is an example of the Mobile tab: | The <b>Mobile</b> tab displays information about the mobile connection. The figure below is an example of the Mobile tab: | ||
| − | + | [[File:Networking_rutx_manual_network_mobile_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 38: | Line 61: | ||
<th width="250">field name</th> | <th width="250">field name</th> | ||
<th width="900">description</th> | <th width="900">description</th> | ||
| + | </tr><tr><td>Sim card slot in use</td><td>Shows which sim card slot is currently in use</td></tr><tr> | ||
| + | <td>IMEI</td> | ||
| + | <td>The IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) is a unique 15 decimal digit number used to identify mobile modules. GSM network operators use the IMEI to identify devices in their networks</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>SIM card state</td> | <td>SIM card state</td> | ||
| Line 71: | Line 74: | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 102: | Line 101: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Cell ID</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>The ID of the cell that the modem is currently connected to</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Data connection state</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Indicates whether the device has a mobile data connection or not</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Connection type</td> |
| − | <td>Mobile | + | <td>Mobile connection connection type. Possible values are: |
| − | <ul> | + | <ul> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<li> <b>3G</b>: 3G (WCDMA), 3G (HSDPA), 3G (HSUPA), 3G (HSPA), 3G (HSPA+), 3G (DC-HSPA+), 3G (HSDPA+HSUPA), UMTS</li> | <li> <b>3G</b>: 3G (WCDMA), 3G (HSDPA), 3G (HSUPA), 3G (HSPA), 3G (HSPA+), 3G (DC-HSPA+), 3G (HSDPA+HSUPA), UMTS</li> | ||
| − | + | <li> <b>4G</b>: 4G (LTE)</li> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<li> <b>N/A</b> - not possible to determine at the moment</li> | <li> <b>N/A</b> - not possible to determine at the moment</li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| Line 132: | Line 119: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td>Carrier Aggregation</td> | + | <td>Signal strength</td> |
| − | + | <td>Received signal strength indicator (<b>[[RSSI]]</b>) measured in dBm. Values closer to 0 indicate a better signal strength</td> | |
| + | </tr><tr><td>Carrier Aggregation</td><td>LTE Advanced Carrier Aggregation, CA, is one of the key techniques used to enable the very high data rates of 4G to be achieved. | ||
By combining more than one carrier together, either in the same or different bands it is possible to increase the bandwidth available and in this way increase the capacity of the link. | By combining more than one carrier together, either in the same or different bands it is possible to increase the bandwidth available and in this way increase the capacity of the link. | ||
| − | </td> | + | </td> |
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Connected band</td> | ||
| + | <td>Currently used frequency band. For more information on supported frequency bands</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>RSRP</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Reference signal received power, measured in dBm. Values closer to 0 indicate better signal strength</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>RSRQ</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Reference signal received quality, measured in dB. Values closer to 0 indicate a better rate of information transfer</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>SINR</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio, measured in dB. Higher values indicate a better rate of information transfer</td> |
| − | </tr> | + | </tr> |
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Bytes received</td> |
<td>Amount of data received through the mobile interface</td> | <td>Amount of data received through the mobile interface</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Bytes sent</td> |
<td>Amount of data sent through the mobile interface</td> | <td>Amount of data sent through the mobile interface</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Restart Modem</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Restarts the devices module</td> |
| − | + | </tr></table> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | </tr> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{#ifeq:{{{wifi}}}|1| | ||
| + | ==Wireless== | ||
| + | [[File:Networking_rutx_manual_status_network_wireless.png]] | ||
<table class="nd-othertables"> | <table class="nd-othertables"> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th width="250">Field name</th> | <th width="250">Field name</th> | ||
| Line 356: | Line 167: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>SSID</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>The broadcasted SSID (Service Set Identifier) of the wireless network</td> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | < | + | <td>Wireless MAC</td> |
| − | < | + | <td>The MAC (Media Access Control) address of the access point radio</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Band</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>The band defines which frequency used </td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Signal</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>The signal quality between router's radio and some other device that is connected to the router</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Bit rate</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>The maximum possible physical throughput that the router's radio can handle. Bit rate will be shared between router and other possible devices which connect to local Access Point (AP) </td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Mode</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Connection mode. Can either be Access Point (AP) or Client. In AP mode others can connect to this router's wireless connection. In client mode router connects to other wireless networks</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Encryption</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>The type of WiFi encryption used</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Hostname</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Device's hostname</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>IP address</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Shows what IP address leased for device</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>MAC address</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Device's MAC (Media Access Control) address</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>Signal</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). Signal's strength measured in dBm</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td>RX rate</td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td>The rate at which packets are received from associated interface</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | < | + | <td>TX rate</td> |
| − | < | + | <td>The rate at which packets are sent to associated interface</td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | }} | ||
[[Category:{{{name}}} Status section]] | [[Category:{{{name}}} Status section]] | ||
Revision as of 10:58, 5 May 2020
Summary
The Network page contains information related to the device's networking. This chapter is an overview of the Network page in {{{name}}} devices.
The information in this page is updated in accordance with the RUTX_R_00.02.03 firmware version.
LAN
This tab displays information about the device's local network(s). The figure below is an example of the Network window:
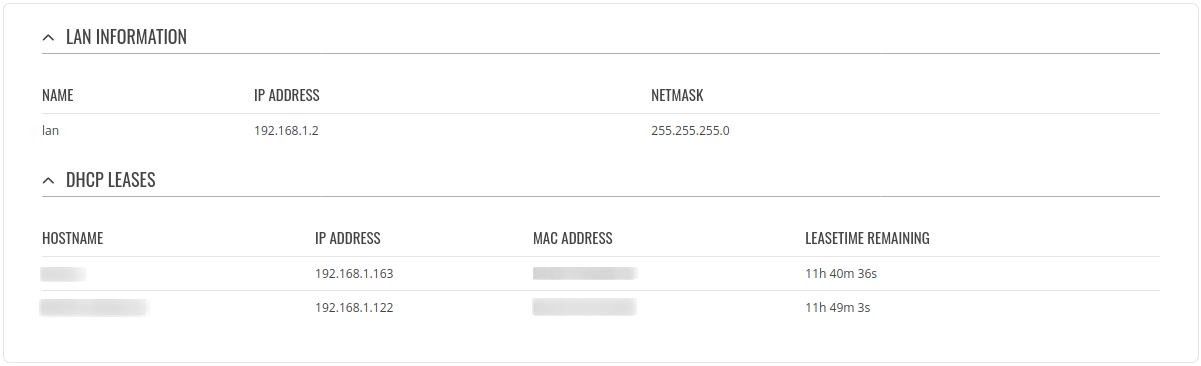
| lan information | |
|---|---|
| Name | LAN interface name |
| IP address | IP address of the LAN interface |
| Netmask | Netmask of the LAN interface. In a sense, a netmask specifies the size of a network. In other words, it indicates which part of the IP address denotes the network, and which denotes the device |
| dhcp leases | |
| Hostname | Hostname of a LAN client |
| IP address | IP address of a LAN client |
| MAC address | MAC address of a LAN client |
| Leasetime remaining | Remaining lease time for a DHCP client. Active DHCP lease holders will try to renew their DHCP leases after a half of the lease time passes. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Status section]]