Network Address Translation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
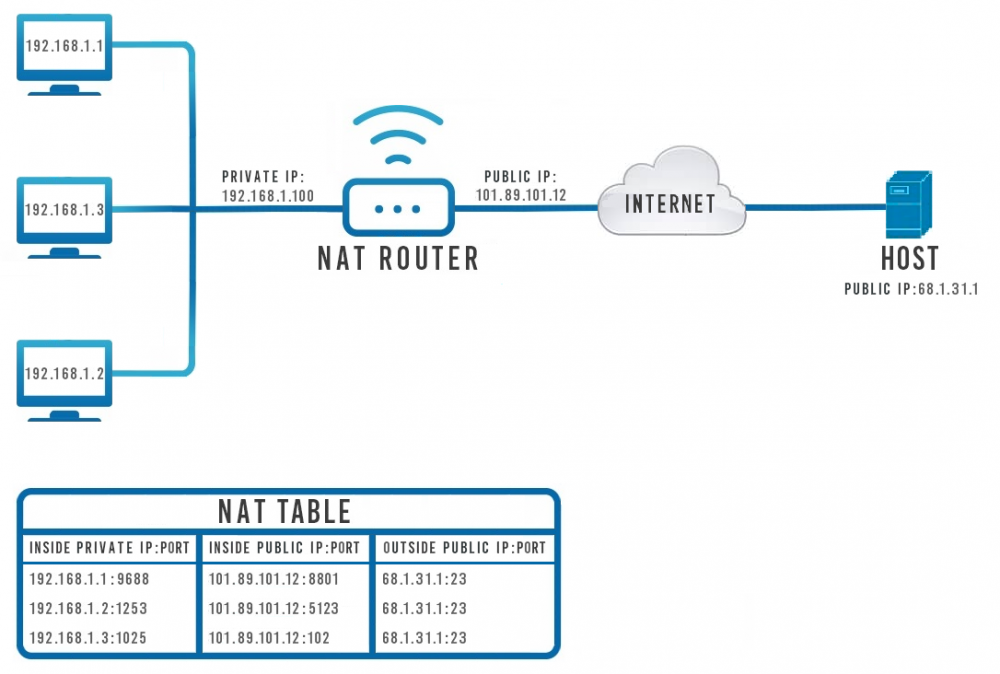
Lets say a user behind the computer with the IP address '''192.168.1.3''' wants to check a news site whose address is '''68.1.31.1'''. The computer generates a package containing its IP address, the destination IP address and the request to access website. The computer cannot send the packet through the Internet directly to the website's IP address as it would not receive any response. This is because the host would not know how to reach the computer's IP address of 192.168.1.3 since there might be thousands of devices using that same IP address at any given moment. | Lets say a user behind the computer with the IP address '''192.168.1.3''' wants to check a news site whose address is '''68.1.31.1'''. The computer generates a package containing its IP address, the destination IP address and the request to access website. The computer cannot send the packet through the Internet directly to the website's IP address as it would not receive any response. This is because the host would not know how to reach the computer's IP address of 192.168.1.3 since there might be thousands of devices using that same IP address at any given moment. | ||
This is where NAT comes in. Instead of sending the package directly to the host, it goes through the router who then changes the sender's IP address into its own Public IP Address:port, in this case '''101.89.101.12:8801'''.So now when the host receives the package it knows exactly where to send the response. It then generates a response package and sends it to 101.89.101.12:8801. The router then receives that response on the specific port and knows exactly where to re-route it - to '''192.168.1.3: | This is where NAT comes in. Instead of sending the package directly to the host, it goes through the router who then changes the sender's IP address into its own Public IP Address:port, in this case '''101.89.101.12:8801'''.So now when the host receives the package it knows exactly where to send the response. It then generates a response package and sends it to 101.89.101.12:8801. The router then receives that response on the specific port and knows exactly where to re-route it - to '''192.168.1.3:102''' | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
For more general information about IP addresses and their types visit our '''[[Private and Public IP Addresses]]''' wiki page. | For more general information about IP addresses and their types visit our '''[[Private and Public IP Addresses]]''' wiki page. | ||
[[Category:Networking]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:42, 10 June 2020
Main Page > FAQ > Networking > Network Address TranslationNetwork address translation (NAT) is a method of remapping one IP address space into another by modifying network address information in IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device. Or to put it in plain terms, NAT allows devices with private IP addresses to communicate with hosts via the internet using IP masquerading.
Why do we need NAT?
When the Internet was in its infancy and before IP addresses were first created, responsible engineers had to decide how long an IP address should be. Since data is exchanged through the Internet via data packets and every data packet has to contain the sender's and receiver's IP addresses, the length of an IP address would determine how large packets would be. A short IP address would mean smaller data packets but fewer possible IP addresses and vice versa.
32-bit length IP addresses were chosen and this is what we call IPv4 today. A 32-bit length means that there can be 232 or 4,294,967,296 distinct IP addresses which is not nearly enough to meet the demand of today's internet savvy society - with over 7 billion people in the world and countless more devices there is just no way that only 4.2 billion unique address would suffice. NAT solves this problem by applying a method that remaps one IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets. This way multiple devices can use one Public IP address to send and receive packets through the Internet.
How NAT works
NAT works by applying IP masquerading, which is a technique that hides an entire IP address space, usually consisting of private IP addresses, behind a single IP address in another, usually public address space. The address that has to be hidden is changed into a single (public) IP address as a "new" source address of the outgoing IP packet so it appears as originating not from the hidden host but from the routing device itself:
The scheme above roughly describes how devices with private IP addresses communicate with a remote host on the Internet (and vice versa) with the help of NAT. Bellow the scheme is a depiction of a NAT forwarding table. It illustrates how the router differentiates to which device in the local network to redirect incoming data packets. But lets go through the example step-by-step:
Lets say a user behind the computer with the IP address 192.168.1.3 wants to check a news site whose address is 68.1.31.1. The computer generates a package containing its IP address, the destination IP address and the request to access website. The computer cannot send the packet through the Internet directly to the website's IP address as it would not receive any response. This is because the host would not know how to reach the computer's IP address of 192.168.1.3 since there might be thousands of devices using that same IP address at any given moment.
This is where NAT comes in. Instead of sending the package directly to the host, it goes through the router who then changes the sender's IP address into its own Public IP Address:port, in this case 101.89.101.12:8801.So now when the host receives the package it knows exactly where to send the response. It then generates a response package and sends it to 101.89.101.12:8801. The router then receives that response on the specific port and knows exactly where to re-route it - to 192.168.1.3:102
See also
For more general information about IP addresses and their types visit our Private and Public IP Addresses wiki page.