|
|
| (10 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| ==Summary==
| | {{Template:Networking_rut_manual_wireless |
| | | <!------------------------DEVICE-----------------------> |
| This chapter is an overview of the Wireless section of RUT routers.
| | | name = RUT850 |
| | | | series = RUT850 |
| ==Wireless Configuration==
| | }} |
| | |
| The '''Wireless configuration''' window provides you with the possibility to configure your wireless access points and wireless stations. The Wireless Station Mode will become active only when Wi-Fi is configured as an active WAN interface (either main or backup).
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Network wireless wireless configuration rut850.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| Above is the overview of the Wireless Configuration window. It displays active access points and stations. Here you can disable or enable your Wi-Fi interfaces, remove unwanted access points or stations or enter a configuration window for each Wi-Fi interface, where you can configure it more thoroughly.
| |
| | |
| ==Wireless Access Point==
| |
| | |
| The Wireless Access Point configuration window is used to make changes to different access points. It is divided into two main sections – device and interface. One is dedicated to configuring hardware parameters, the other – software. To access this window, simply click the '''Edit''' button next to the Wi-Fi interface that you wish to configure.
| |
| | |
| ===Device Configuration===
| |
| ----
| |
| The '''Device Configuration''' section is used for configuring Wi-Fi hardware parameters.
| |
| | |
| ====General Setup====
| |
| ----
| |
| The '''General Setup''' tab is used to select the wireless channel used by the Access Point.
| |
| | |
| Choose a WiFi channel according to the busyness of other channels. While RUT devices do not provide a function that lets you monitor the usage of nearby WiFi channels, you can download a free WiFi analyzer app on your phone, laptop or other WiFi device. In most countries there are 13 WiFi channels on the 2.4 GHz band (14 in Japan) to choose from. RUT routers' WiFi works on the 2.4 GHz band. A wireless 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi channel requires a signaling band roughly 22 MHz wide, radio frequencies of neighboring channels numbers significantly overlap each other. Many home networks utilize routers that by default run on channel 6 on the 2.4 GHz band. Neighboring Wi-Fi home networks that run over the same channel generate radio interference that can cause significant network performance slowdowns for users. Reconfiguring a network to run on a different wireless channel helps minimize these slowdowns. Therefore, pick a channel with no other active Access Points and preferably one that has no active Access Point on two adjacent channels on each side as well. If you don't feel like doing this, set the '''Channel''' field to '''Auto''' and the router will pick the least busy channel in your location automatically.
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Network wireless device configuration general setup rut850.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| ====Advanced Setup====
| |
| ----
| |
| The '''Advanced Setup''' tab is used to configure how the wireless Access Point will work from a hardware perspective.
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Network wireless device advanced.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable"
| |
| |+
| |
| ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | FIELD NAME
| |
| ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | VALUE
| |
| ! style="width: 579px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | DESCRIPTION
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Mode
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Auto {{!}} 802.11b {{!}} 802.11g {{!}} 802.11g+n; Default: '''802.11g+n'''
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Wireless protocol used. Different modes provide different wireless standard support which directly impacts the radio's throughput performance
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | HT mode
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | 20 MHz {{!}} 40 MHz 2nd channel above; Default: '''20 MHz'''
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | HT (High Throughput) mode allows you to specify channel width. 40 MHz bandwidth provides better performance but it overlaps 4 adjacent channels on each side, therefore, it might overlap with many other Access Points working in those channels. If that is the case, the router will switch back to 20 MHz mode automatically to reduce interference. 40 MHz is only available if the selected channel is not '''Auto'''
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Country code
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | country code; Default: '''0 - World'''
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | SO/IEC 3166 alpha2 country codes as defined in ISO 3166-1 standard
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Transmit power
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | 100 % {{!}} 80 % {{!}} 60 % {{!}} 40 % {{!}} 20 %; Default: '''100 %'''
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | WiFi signal power. Use lower power to reduce the router's CPU usage
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Fragmentation threshold
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | integer [256..2346]; Default: " "
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | The smallest packet size that can be fragmented and transmitted by multiple frames. In areas were interference is a problem, setting a lower fragment threshold might help reduce the probability of unsuccessful packet transfers, thus increasing speed
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | RTS/CTS threshold
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | integer [0..2347]; Default: " "
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to Send) are mechanisms, used to reduce frame collisions introduced by the hidden node problem. It can help resolve problems arising when several access points are in the same area, contending
| |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| ===Interface Configuration===
| |
| ----
| |
| The '''Interface Configuration''' section is used to configure wireless Access Points from the software perspective.
| |
| | |
| ====General Setup====
| |
| ----
| |
| The '''General Setup''' tab contains only two options. '''SSID''' is the name of your Wi-Fi interface. When other Wi-Fi capable computers or devices scan the area for Wi-Fi networks they will see your network with this name. '''Hide SSID''' is used to make your Access Point invisible to other devices. To use a hidden WiFi Access Point, first un-hide it, connect your device to it, then hide it again.
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Network wireless interface general.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| ====Wireless Security====
| |
| ----
| |
| The '''Wireless Security''' tab is used to determine what kind of encryption your WLAN will use. You can choose between different types of '''WEP''' (Wireless Encryption Protocol) or '''WPA''' (Wi-Fi Protected Access.) '''WPA''' provides better security because it uses improved data encryption through the temporal key integrity protocol (TKIP) but not all devices support '''WPA''' and will work only with '''WEP''' type of encryption.
| |
| | |
| =====WEP=====
| |
| ----
| |
| [[Image:Network wireless interface security wep.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable"
| |
| |+
| |
| ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | FIELD NAME
| |
| ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | VALUE
| |
| ! style="width: 579px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | DESCRIPTION
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Encryption*
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | No encryption {{!}} WEP Open System {{!}} WEP shared key; Default: '''No encryption'''
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | The type of WiFi encryption used. Configurations for both '''WEP Open System''' and '''WEP shared key''' are identical
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Used key slot
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Key #1 {{!}} Key #2 {{!}} Key #3 {{!}} Key #4; Default: '''Key #1'''
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Specifies which key is used for authentication
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Key #1 {{!}} Key #2 {{!}} Key #3 {{!}} Key #4
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | string; Default: " "
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | A 10 symbol custom key used for authentication
| |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| =====WPA=====
| |
| ----
| |
| [[Image:Network wireless interface security wpa.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable" | |
| |+
| |
| ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | FIELD NAME
| |
| ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | VALUE
| |
| ! style="width: 579px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | DESCRIPTION | |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Encryption*
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | No encryption {{!}} WPA-PSK {{!}} WPA2-PSK {{!}} WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK mixed mode; Default: '''No encryption'''
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | The type of WiFi encryption used. Configurations for both '''WEP Open System''' and '''WEP shared key''' are identical
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Cipher
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Auto {{!}} Force CCMP (AES) {{!}} Force TKIP {{!}} Force TKIP and CCMP (AES); Default: '''Auto'''
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | An algorithm for performing encryption or decryption
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Key
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | string; Default: " "
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | A custom passphrase used for authentication (at least 8 characters long)
| |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| ====MAC Filter====
| |
| ---- | |
| The '''MAC Filter''' tab is used for setting up rules that allow or exclude devices with specified MAC addresses from connecting to your Wi-Fi network.
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Network wireless interface mac.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable"
| |
| |+
| |
| ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | FIELD NAME
| |
| ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | VALUE
| |
| ! style="width: 579px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | DESCRIPTION
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | MAC address filter
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Disable {{!}} Allow listed only {{!}} Allow all except listed; Default: '''Disable'''
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | '''Allow listed only''' – only allows devices with MAC addresses specified in the MAC list to connect to your WiFi network
| |
| '''Allow all except listed''' - blocks devices with MAC addresses specified in the MAC list from connecting to your WiFi network
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | MAC
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | mac; Default: " "
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | List of MAC addresses to be included or excluded from connecting to your WiFi network
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Key
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | string; Default: " "
| |
| | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | A custom passphrase used for authentication (at least 8 characters long)
| |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| ====Advanced Settings====
| |
| ---- | |
| [[Image:Network wireless interface advanced.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| {| class="wikitable"
| |
| |+
| |
| ! style="width: 250px; background: black; color: white;" | Field name
| |
| ! style="width: 250px; background: black; color: white;" | Value
| |
| ! style="width: 1200px; background: black; color: white;" | Description
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Separate clients
| |
| | style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no'''
| |
| | style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Prevents Wi-Fi clients from communicating with each other on the same subnet
| |
| |-
| |
| ! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Increase TTL packet size
| |
| | style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no'''
| |
| | style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Increase TTL packet size for incoming packets
| |
| |-
| |
| |}
| |
| | |
| ==Wireless Station==
| |
| | |
| RUT955 can also work as a Wi-Fi client. Configuring client mode is nearly identical to AP, except for the fact that most of the options are dictated by the wireless access point that the router is connecting to. Changing them can result in an interrupted connection to that AP.
| |
| | |
| In addition to standard options you can also click the '''Scan''' button to rescan the surrounding area and attempt to connect to a new wireless access point.
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Network wireless wireless station scan rut850.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| | |
| After which you will be redirected to the window shown below.
| |
| | |
| | |
| [[Image:Network wireless station step2.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| | |
| Pressing '''Start scan''' will initiate a scan for available Wi-Fi Access Points in the area. After the scan finishes, you will see a list of these Access points. Choose one according to your liking and press the '''Join Network''' button next to it.
| |
| | |
| | |
| [[Image:Network wireless station step3.PNG]]
| |
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
The Wireless page is used to configure and manage WiFi Access Points (AP) and WiFi Stations (STA). RUT850 devices support 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11b/g/n and 802.11e_WMM wireless technologies.
This user manual page provides an overview of the Wireless page in RUT850 devices.
Wireless Access Points
The Wireless Access Points section displays existing WiFi access point (AP) configurations. By default there is one active WiFi AP.
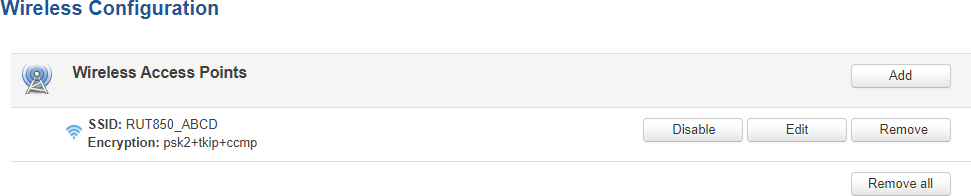
Its SSID consists of a combination of the device's name and the last 4 symbols of the WiFi MAC address (for example, RUT850_ABCD). which is enabled by default. The default password is unique to each device and can be found on the bottom engraving:

You can create more WiFi APs from this section with the 'Add' button or you can make modifications to the existing AP by clicking the 'Edit' button next to it:
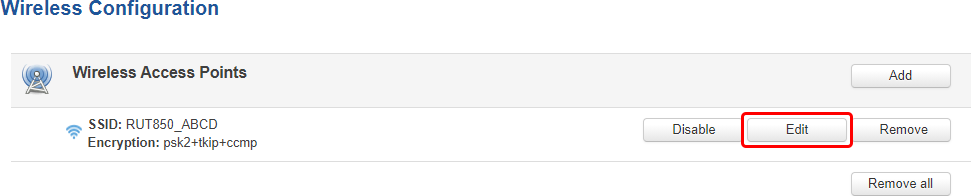
After clicking 'Edit' you will be redirected to the configuration page of the wireless AP.
Device Configuration
The Device Configuration section is used to configure hardware related parameters of the WiFi radio.
General Setup
The General Setup section is used to turn an Access Point on or off and to select the wireless channel used by the WiFi radio.
In some cases choosing a WiFi channel manually can improve overall WiFi performance. You can download a free WiFi analyzer app on your phone, laptop or other WiFi device and scan the surrounding WiFi networks to see which channels are most and least populated. Choose a WiFi channel that overlaps with the lowest number of other channels. Choosing WiFi channels that are far apart from each other may also prove to increase performance when using more than one AP on the device.
Alternatively, leave channel selection set as 'Auto'. This way your device will pick the WiFi channel automatically.
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings section is used to configure the hardware operating settings of the WiFi radio. The settings available in this section are mostly used to find the best WiFi performance conditions.
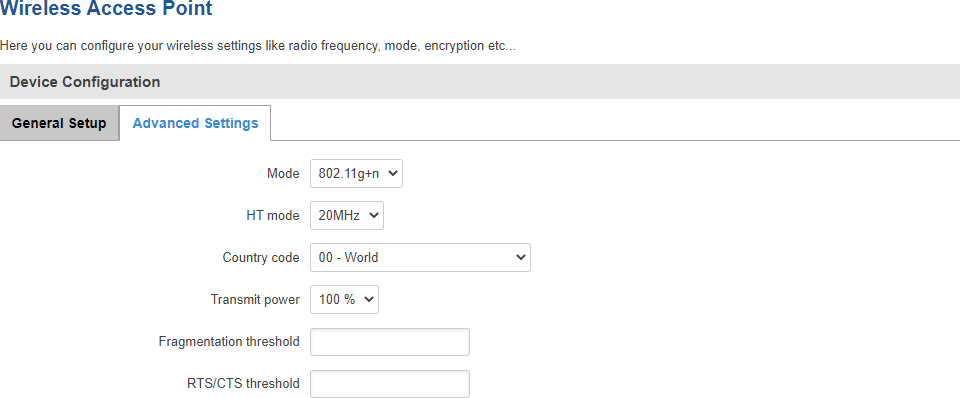
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Mode |
Auto | 802.11b | 802.11g | 802.11g+n; default: 802.11g+n |
Selects the wireless protocol. Different modes provide different wireless standard support which directly impacts the radio's throughput performance. |
| HT mode |
20MHz | 40MHz 2nd channel below | 40MHz 2nd channel above; default: 20MHz |
HT (High Throughput) mode specifies WiFi channel bandwidth. 40 MHz bandwidth provides better performance but it overlaps with 4 adjacent channels on each side. Therefore, it might overlap with many other Access Points operating at similar frequencies. If that is the case, the router will switch back to 20 MHz mode automatically to reduce interference.
40 MHz is only available when the WiFi Channel is selected manually in the General Setup section. |
| Country code |
country code; default: 00 - World |
SO/IEC 3166 alpha2 country codes as defined in the ISO 3166-1 standard. |
| Transmit power |
100 % | 80 % | 60 % | 40 % | 20 %; default: 100 % |
WiFi signal power. Use lower power to reduce the device's CPU usage, but lower wireless performance. |
| Fragmentation threshold |
integer [256..2346]; default: none |
The smallest packet size that can be fragmented and transmitted in multiple frames. In areas were interference is a problem, setting a lower fragment threshold might help reduce the probability of unsuccessful packet transfers, thus increasing speed. |
| RTS/CTS threshold |
integer [0..2347]; default: none |
RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to Send) are mechanisms used to reduce frame collisions introduced by the hidden node problem. It can help resolve issues arising when several access points are in the same area, contending. |
Interface Configuration
The Interface Configuration section is used to configuring software related parameters of the WiFi AP.
General Setup
The General Setup section is used to set SSID related settings. An SSID is the name of a WiFi AP. When other WiFi capable computers or devices scan the area for WiFi networks they will see your network with this name.
The 'Hide SSID' option is used to make your Access Point invisible to other devices. To use a hidden WiFi Access Point, first un-hide it, connect your device to it, then hide it again.
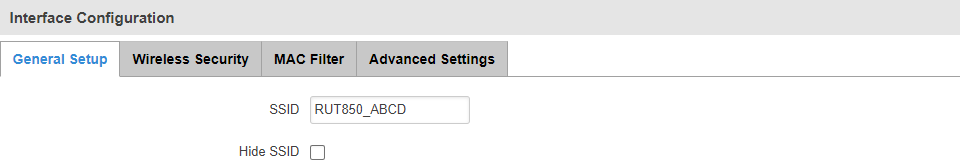
Wireless Security
The Wireless Security section is used to set the authentication settings for the WiFi AP.
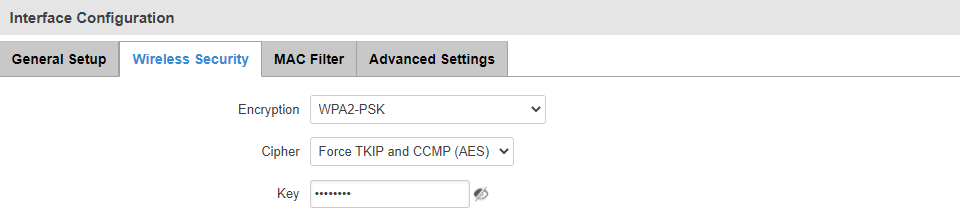
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Encryption |
No encryption | WPA-PSK | WPA2-PSK | WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK mixed mode | WPA-EAP* | WPA2-EAP*; default: WPA2-PSK |
The type of WiFi encryption used. PSK uses a pre-shared key for authentication while EAP uses a RADIUS server. |
| Cipher |
Auto | Force CCMP (AES) | Force TKIP | Force TKIP and CCMP (AES); default: Force TKIP and CCMP (AES) |
Selects an algorithm for performing encryption and decryption. |
| Key |
string; default: none |
Pre-shared key, a custom passphrase used for user authentication (at least 8 characters long). |
* The "EAP" (Extensible Authentication Protocol) are for using a RADIUS server for authentication instead of a pre-shared key. The configuration layout for these selections is distinct from PSK.
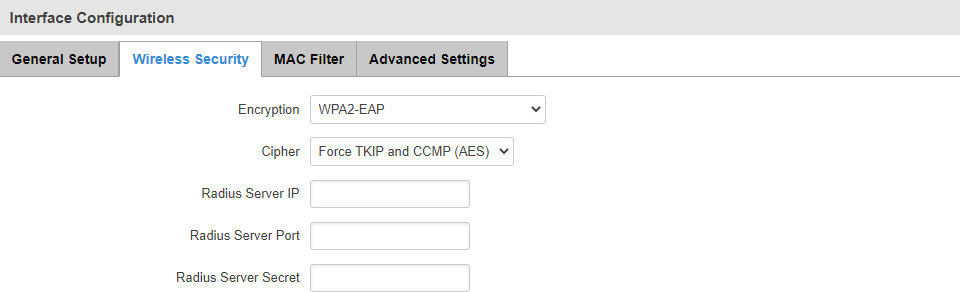
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Encryption |
No encryption | WPA-PSK | WPA2-PSK | WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK mixed mode | WPA-EAP* | WPA2-EAP*; default: WPA2-PSK |
The type of WiFi encryption used. PSK uses a pre-shared key for authentication while EAP uses a RADIUS server. |
| Cipher |
Auto | Force CCMP (AES) | Force TKIP | Force TKIP and CCMP (AES); default: Force TKIP and CCMP (AES) |
Selects an algorithm for performing encryption and decryption. |
| Radius Server IP |
host | ip; default: none |
RADIUS server's IP address or hostname. |
| Radius Server Port |
integer [0..65535]; default: none |
The port number used for connection to the RADIUS server. |
| Radius Server Secret |
string; default: none |
A case-sensitive shared secret used for authentication on both RADIUS devices. |
MAC Filter
The MAC Filter section is used for setting up rules that allow or exclude listed devices (based on MAC address) from connecting to your WiFi network.
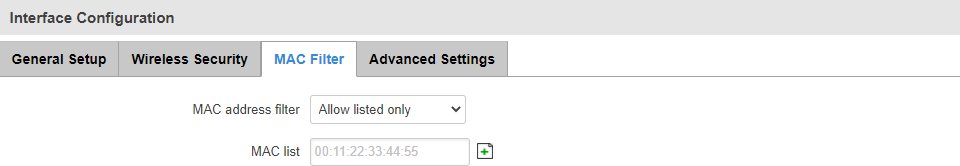
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| MAC address filter |
Disable | Allow listed only | Allow all except listed; default: Disable |
Defines how MAC filtering is done.
- Disable - allows all devices to connect to the WiFi network.
- Allow listed only - allows devices with MAC addresses specified in the MAC list to connect to the WiFi network.
- Allow all except listed - blocks devices with MAC addresses specified in the MAC list from connecting to your WiFi network.
|
| MAC |
mac; default: none |
List of MAC addresses to be included or excluded from connecting to your WiFi network. |
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings section can be used to set the following parameters:
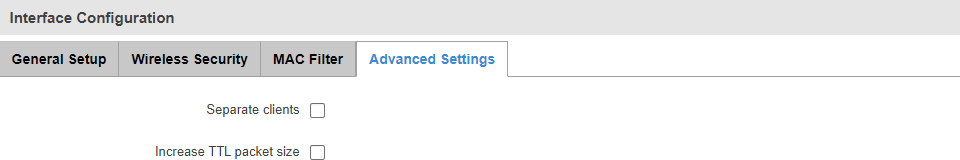
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Separate clients |
yes | no; default: no |
Prevents WiFi clients from communicating with each other on the WiFi network. |
| Increase TTL packet size |
yes | no; default: no |
Increases TTL packet size for incoming packets. |
Wireless Station
The RUT850 device can also operate as a WiFi Station (client) to obtain an Internet connection from another WiFi AP.
In order to configure the device as a Wireless Station, go to the Network → WAN page and set WiFi to either Main WAN or WAN Failover. Then click the 'Scan' button to initiate a scan for available nearby WiFi access points.
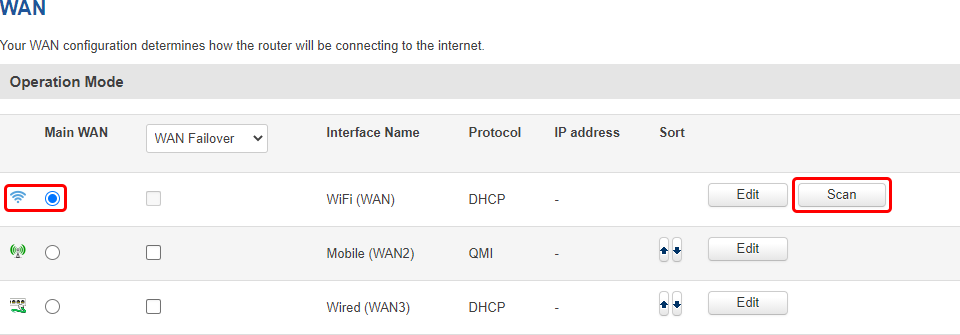
The scan should take up to 10 seconds and display a list of available WiFi access points at the end of the process. Pick an access point to connect to and click 'Join Network'.
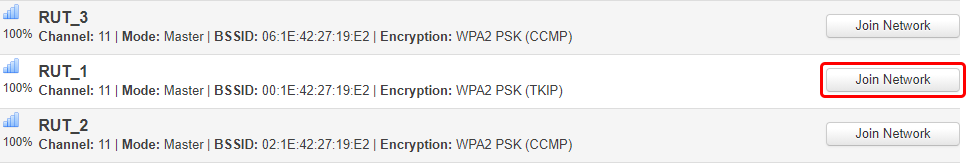
If the selected access point is secured, enter the password (WPA passphrase) in the next window and click 'Save' to finish the process.
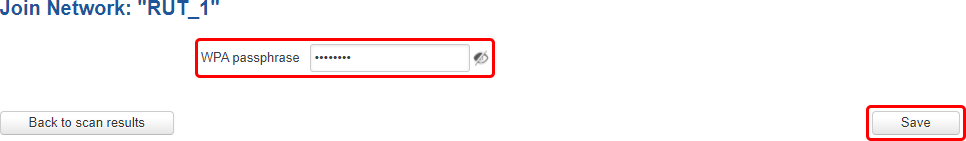
The newly connected access points should be displayed in the Network → Wireless page.
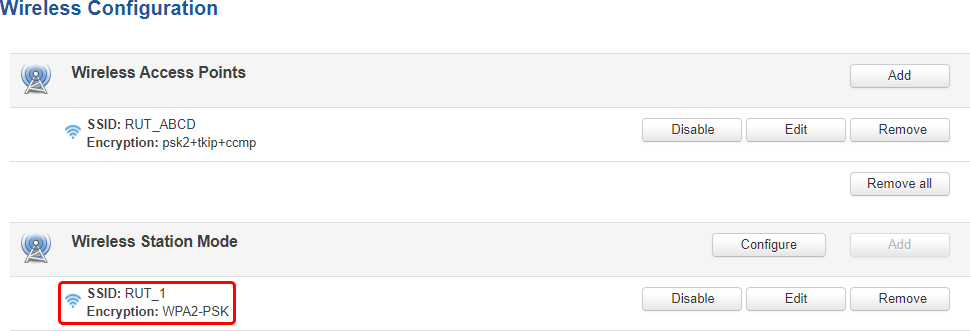
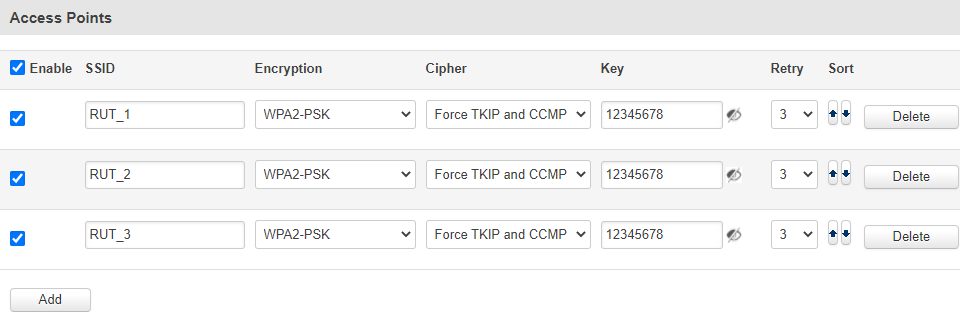
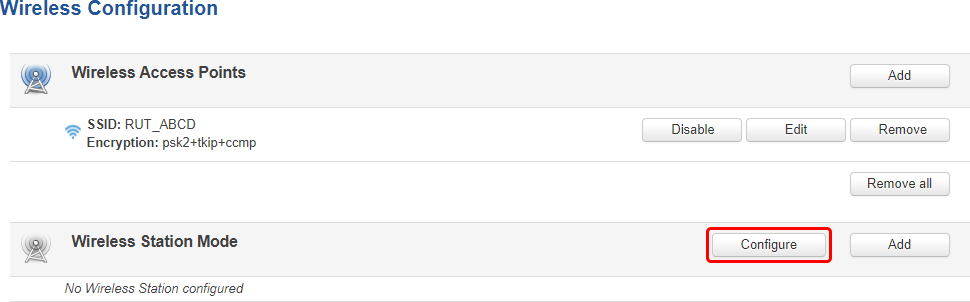
Multiple Access Points
You can also configure access to multiple wireless access points from one page. To enter multiple access point configuration, click the 'Configure' button next to Wireless Station Mode.
After this you should be redirected to a page that looks like this:
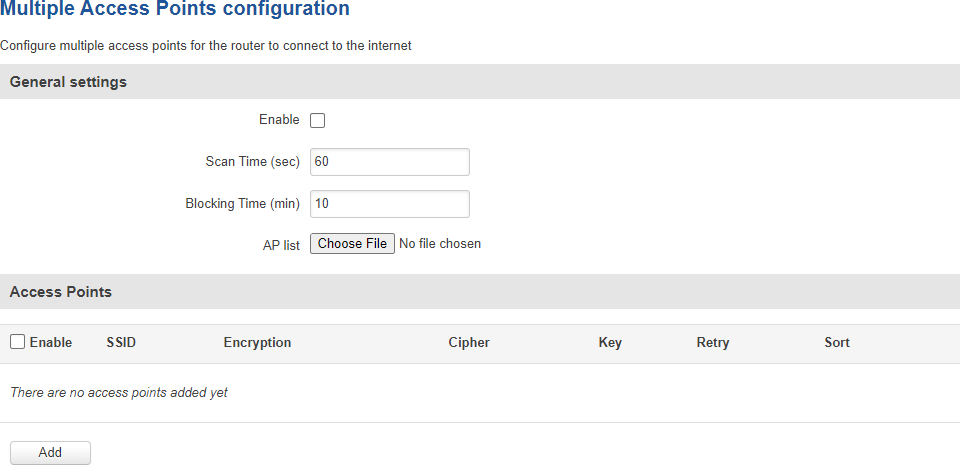
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Enable |
yes | no; default: no |
Turns multiple access point configuration on or off. |
| Scan Time (sec) |
integer (30+); default: 60 |
Frequency (in seconds) of scans for WiFi access point availability. |
| Blocking Time (min) |
integer (1+); default: 10 |
The amount time (in minutes) after which the device will no longer attempt to connect to an access point after the number of unsuccessful retries is exceeded. |
| AP list |
- (interactive button) |
Uploads a list of access point configurations. |
You can either configure multiple access points from this page of the WebUI or you can upload a file with a list of access point configurations. The file should contains WIFi access point configuration options and values, which should be defined as option: value (for example, ssid: home_wifi). The SSID is mandatory, while other optional options are:
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Enable |
1 | 0 |
State of an access point configuration.
|
| SSID |
string |
SSID of an access point. |
| Encryption |
none | psk | psk2 | psk-mixed |
The type of WiFi encryption used by an access point. |
| Cipher |
auto | ccmp | tkip | ccmp+tkip |
Algorithm for performing encryption and decryption. |
| Key |
string |
Pre-shared key, a custom passphrase used for user authentication (at least 8 characters long). |
| Retry |
integer [1..10] |
Defines the number of times this device will attempt to connect to an access point before moving to another configuration in the list. |
Option names in the file should be provided in lower case letters. AP list file example:
ssid: RUT_1
enable: 1
encryption: psk2
cipher: tkip+ccmp
key: 12345678
retry: 3
ssid: RUT_2
enable: 1
encryption: psk2
cipher: tkip+ccmp
key: 12345678
retry: 3
ssid: RUT_3
enable: 1
encryption: psk2
cipher: tkip+ccmp
key: 12345678
retry: 3
Once uploaded, the contents of the file should become visible in the Access Points list: