Template:Networking tswos manual maintenance: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Type</td> | <td>Type</td> | ||
<td>Ping {{!}} <span style="color:olive">Wget</span>{{#switch:{{{name}}}|TSW202={{!}} <span style="color:blue">Port|#default=}}; default | <td>Ping {{!}} <span style="color:olive">Wget</span>{{#switch:{{{name}}}|TSW202= {{!}} <span style="color:blue">Port</span>|#default=}}; default: <b>Ping</b></td> | ||
<td>Method used for health checking. | <td>Method used for health checking. | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Action if no echo is received</td> | <td>Action if no echo is received</td> | ||
<td>Device reboot {{!}} None; default: <b>Device reboot</b></td> | <td>Device reboot {{!}} None{{#switch:{{{name}}}|TSW202 = {{!}} <span style="color:blue">Restart port</span>|#default=}}; default: <b>Device reboot</b></td> | ||
<td>Action that will be executed if there is no response after the specified amount of retries. If <b>None</b> is selected, only a message to syslog will be logged.</td> | <td>Action that will be executed if there is no response after the specified amount of retries. If <b>None</b> is selected, only a message to syslog will be logged.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
<td>host {{!}} ip; default: <b>8.8.8.8</b></td> | <td>host {{!}} ip; default: <b>8.8.8.8</b></td> | ||
<td>Hostname or IP address to which the Ping/Wget requests will be sent.</td> | <td>Hostname or IP address to which the Ping/Wget requests will be sent.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr>{{#switch:{{{name}}}|TSW202= | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:blue">Ping by</span></td> | <td><span style="color:blue">Ping by</span></td> | ||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
<td>port number and number of devices (unsigned integer); default: <b>Port1:1</b></td> | <td>port number and number of devices (unsigned integer); default: <b>Port1:1</b></td> | ||
<td>Port number and number of devices addresses to be pinged. (Number of devices connected must be less or equal to the actual number of connected devices to the port).</td> | <td>Port number and number of devices addresses to be pinged. (Number of devices connected must be less or equal to the actual number of connected devices to the port).</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr>|#default=}} | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 166: | Line 166: | ||
==Backup== | ==Backup== | ||
===Summary=== | ===Summary=== | ||
The <b>Backup</b> page is used to generate configuration backup files or upload existing ones to the device. This chapter is an overview of the Backup page in {{{name}}} devices. | The <b>Backup</b> page is used to generate configuration backup files or upload existing ones to the device. This chapter is an overview of the Backup page in {{{name}}} devices. | ||
===Create | ===Create backup=== | ||
The <b> | The <b>Backup configuration</b> section is used to generate and download a file which stores the current device configuration. The backup file can later be uploaded to the same device or another device of the same type (product codes must match). | ||
This section contains MD5, SHA256 checksum fields generated from latest downloaded backup file, 'Encrypt' option and the 'Download' button to generate and download the device configuration backup file. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_backup_create_backup.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{no_packages}}}|1|| | |||
<b><u>Important notes</u></b>: | |||
1. Password field is required if Encrypt is turned on and that's when the field appears. Password that will be used to encrypt Backup file. It will have to be provided when extracting formatted zip archive to gain access to a tar file. | |||
[[ | 2. If the device does not have an Internet connection when a Backup file is being loaded, <u>it will not reinstall software packages installed from Services → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]]</u>. You can add the package installation files to the Backup file manually, a {{{name}}} device will automatically install them when you load the Backup file even without a data connection. | ||
To embed a Backup file with package installation files, follow these steps: | |||
<ul> | |||
<li>Download the necessary software package installation files <b>[[{{{name}}} Package Downloads|from here]]</b></li> | |||
<li>Download a Backup file.</li> | |||
<li>Open the Backup file and create a new folder called <i>backup_packages</i> in the <i>/etc</i> directory.</li> | |||
<li>Add the necessary package files to <i>/etc/backup_packages</i></li> | |||
<li>Make sure files in <i>/etc/backup_packages</i> are fully extracted with the *.ipk extensions</li> | |||
</ul>}} | |||
===Upload backup=== | |||
The <b>Restore configuration</b> section is used to upload a configuration file that was taken from this device or another device of the same type. | The <b>Restore configuration</b> section is used to upload a configuration file that was taken from this device or another device of the same type. | ||
Turn on 'Encrypted' if backup file was previously encrypted and click the 'Browse' button to select a backup file from your computer and click the 'Upload archive' button to apply the selected configuration on to this device. | |||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_backup_upload_backup.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<b>Important notes</b>: | <b>Important notes</b>: | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>Password will be used when extracting formatted 7z or zip archive to gain access to a tar file.</li> | |||
<li>Backup files can be uploaded only if they are taken from an identical device (identical Product code (can be checked in the Status → [[{{{name}}} System|System]] page)) with identical or older firmware.</li> | <li>Backup files can be uploaded only if they are taken from an identical device (identical Product code (can be checked in the Status → [[{{{name}}} System|System]] page)) with identical or older firmware.</li> | ||
<li>It is important to remember that the backup file not only changes the device configuration, but also the password. If you are unsure of the backup file's password, you may want to reconsider uploading it because you may lose access to device.</li> | <li>It is important to remember that the backup file not only changes the device configuration, but also the password. If you are unsure of the backup file's password, you may want to reconsider uploading it because you may lose access to device.</li> | ||
| Line 201: | Line 211: | ||
====Backup Security Check==== | ====Backup Security Check==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
After uploading a backup file your device will calculate checksums for uploaded file and display them. If this backup file was the latest downloaded in your device then you can compare these checksums with the ones in your [[# | After uploading a backup file your device will calculate checksums for uploaded file and display them. If this backup file was the latest downloaded in your device then you can compare these checksums with the ones in your [[#Create backup|Create backup]] section to verify backup's integrity. | ||
If everything is in order click <b>Proceed</b> to restore configuration to backup. | If everything is in order click <b>Proceed</b> to restore configuration to backup. | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_backup_backup_security_check.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_backup_backup_security_check.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
==Troubleshoot== | ==Troubleshoot== | ||
| Line 238: | Line 222: | ||
The <b>Logging Settings</b> section is used to configure how and where the device stores system log data. The system log is a file that contains information on various system related events and is useful to engineers for troubleshooting the device. | The <b>Logging Settings</b> section is used to configure how and where the device stores system log data. The system log is a file that contains information on various system related events and is useful to engineers for troubleshooting the device. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_tswos_manual_maintenance_troubleshoot_logging_settings_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 254: | Line 238: | ||
<td>External system log server</td> | <td>External system log server</td> | ||
<td>ip; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>ip; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>IP address of an external server that will be used to store device logs | <td>IP address/host and port of an external server that will be used to store device logs.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 297: | Line 276: | ||
The <b>Troubleshoot</b> section is used to download various files that contain information used for troubleshooting the device. Refer to the figure and table below for information on the Troubleshoot page. | The <b>Troubleshoot</b> section is used to download various files that contain information used for troubleshooting the device. Refer to the figure and table below for information on the Troubleshoot page. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_tswos_manual_maintenance_troubleshoot_troubleshoot_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 314: | Line 293: | ||
<td>- (interactive button)</td> | <td>- (interactive button)</td> | ||
<td>Displays the contents of the device kernel log file. The kernel log contains records of various events related to the processes of the operating system (OS).</td> | <td>Displays the contents of the device kernel log file. The kernel log contains records of various events related to the processes of the operating system (OS).</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Encrypt</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} <span style="color:blue">on</span>; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Turn on AES 256 encryption and archive Troubleshoot file using zip format.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">Password</span></td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Password that will be used to encrypt Troubleshoot file. It will have to be provided when extracting formatted zip archive to gain access to a tar file.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 327: | Line 316: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable TCP dump</td> | <td>Enable TCP dump</td> | ||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off {{!}} <span style="color:green">on</span>; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>Turns TCP dump packets capture on or off.</td> | <td>Turns TCP dump packets capture on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
< | <td><span style="color:green">Select interface</span></td> | ||
<td>Any {{!}} br0.1; default: <b>Any</b></td> | |||
<td> | |||
<td>Only captures packets that move through the specified network interface.</td> | <td>Only captures packets that move through the specified network interface.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Select protocol filter</td> | <td><span style="color:green">Select protocol filter</span></td> | ||
<td>All {{!}} ICMP {{!}} TCP {{!}} UDP {{!}} ARP; default: <b>All</b></td> | <td>All {{!}} ICMP {{!}} TCP {{!}} UDP {{!}} ARP; default: <b>All</b></td> | ||
<td>Only captures packets that match the specified protocol.</td> | <td>Only captures packets that match the specified protocol.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Select packets direction</td> | <td><span style="color:green">Select packets direction</span></td> | ||
<td>Incoming/Outgoing {{!}} Incoming {{!}} Outgoing; default: <b>Incoming/Outgoing</b></td> | <td>Incoming/Outgoing {{!}} Incoming {{!}} Outgoing; default: <b>Incoming/Outgoing</b></td> | ||
<td>Only captures packets coming from the specified direction.</td> | <td>Only captures packets coming from the specified direction.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Host</td> | <td><span style="color:green">Host</span></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Domain names or IP; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Only captures packets related to the specified host.</td> | <td>Only captures packets related to the specified host.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Port</td> | <td><span style="color:green">Port</span></td> | ||
<td>integer [ | <td>integer [1..65535]; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Only captures packets related to the specified | <td>Only captures packets related to the specified port.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Select storage</td> | <td><span style="color:green">Select storage</span></td> | ||
<td>RAM memory; default: <b>RAM memory</b></td> | <td>RAM memory; default: <b>RAM memory</b></td> | ||
<td>Specifies where the TCP dump file will be stored.</td> | <td>Specifies where the TCP dump file will be stored.</td> | ||
| Line 435: | Line 403: | ||
[[File:Networking_tswos_manual_maintenance_cli.png]] | [[File:Networking_tswos_manual_maintenance_cli.png]] | ||
==Reset settings== | |||
===Reset settings=== | |||
The <b>Reset settings</b> page is used for restoring device's configuration. | |||
[[File:Networking_tswos_manual_backup_restore_default_settings.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Reset type</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>System settings</td> | |||
<td>-(single select)</td> | |||
<td>Resets all configuration except RMS data, mdcollect database, logs and PIN code.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Factory defaults</td> | |||
<td>-(single select)</td> | |||
<td>Resets device to factory configuration.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>User's default configuration<span class="asterisk">*</span></td> | |||
<td>-(single select)</td> | |||
<td>Resets device to user's default configuration.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<span class="asterisk">*</span>This button will be greyed out until you have created a <b>[[{{{name}}}_Maintenance#Create_user's_default_configuration|User's default configuration]]</b>. | |||
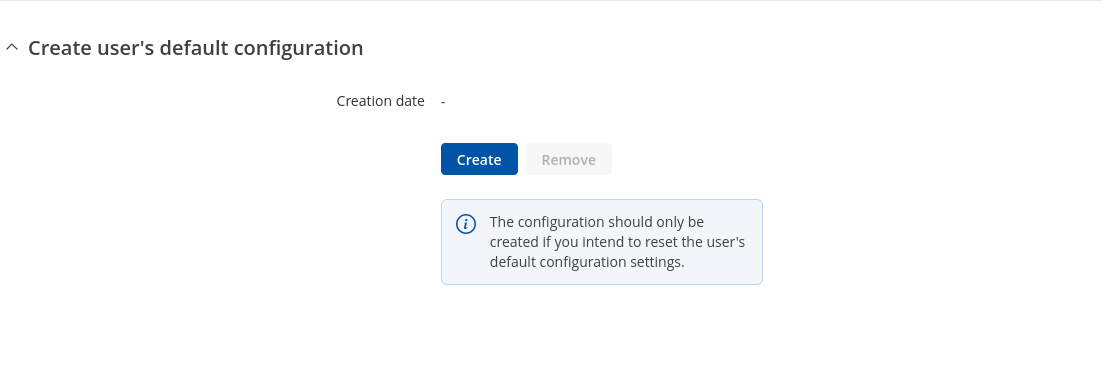
===Create user's default configuration=== | |||
The <b>Create user's default configuration</b> section is used to create or delete a file which stores current device configuration. The default configuration can later be loaded in [[{{{name}}}_Maintenance#Reset_settings|Reset settings]] page or via reset button. | |||
Click the 'Create' button to generate default configuration file from your current device configuration. | |||
[[File:Networking_tswos_manual_backup_create_default_configuration.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
[[Category:{{{name}}} System section]] | [[Category:{{{name}}} System section]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:04, 28 October 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
This page is an overview of the Maintenance section of {{{name}}} devices.
Auto Reboot
Summary
Various automatic device reboot scenarios can be configured in the Auto Reboot section. Automatic reboots can be used as a prophylactic or precautionary measure that ensures the device will self-correct some unexpected issues, especially related to connection downtime.
This chapter is an overview of the Auto Reboot section of {{{name}}} devices.
Ping/Wget Reboot
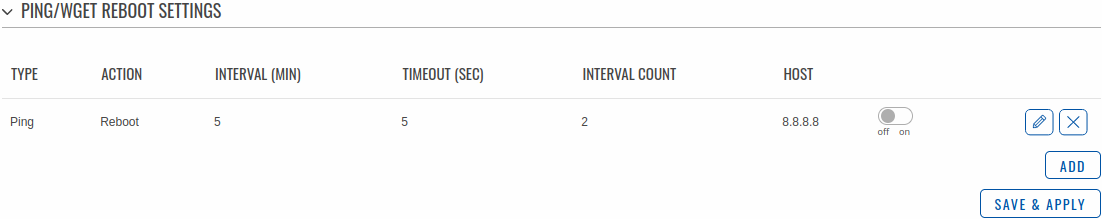
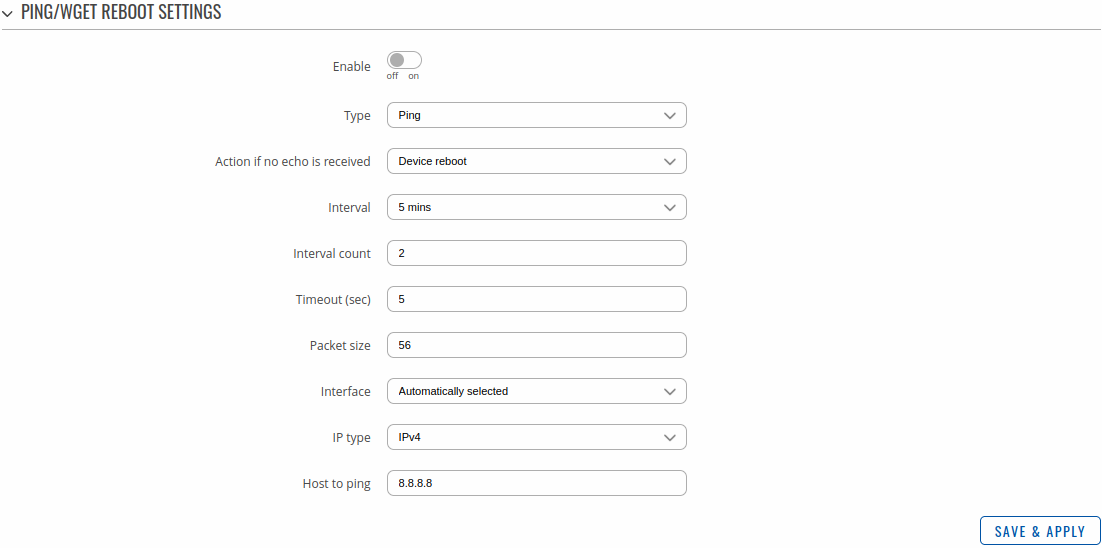
The Ping/Wget Reboot functions periodically send ICMP or Wget requests to a specified IP address or host and waits for a response. If no response is received, the device will attempt the same action a defined number of times at a defined frequency. If there is still no response, the device will execute the specified action (reboot, by default).
The Ping/Wget Reboot section contains one pre-configured rule by default:
To enable the default rule, use the off/on slider next to it. You can add more rules with the 'Add' button or delete them using the 'Delete' button. If you wish to customize a rule, click the button that looks like a pencil next to it.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns the rule on or off. |
| Type | Ping | Wget; default: Ping | Method used for health checking.
|
| Action if no echo is received | Device reboot | None; default: Device reboot | Action that will be executed if there is no response after the specified amount of retries. If None is selected, only a message to syslog will be logged. |
| Interval | 5 mins | 15 mins | 30 mins | 1 hour | 2 hours; default: 5 mins | The frequency at which ping/Wget requests are sent to the specified host. |
| Interval count | integer [1..9999]; default: 2 | Indicates how many additional times the device will try sending requests if the initial one fails. |
| Timeout (sec) | integer [1..9999]; default: 5 | Maximum response time. If no echo is received after the amount of time specified in this field has passed, the ping/wget request is considered to have failed. |
| URL | url; default: none | URL to which the wget requests will be sent. E.g. http://www.host.com |
| Packet size | integer [0..1000]; default: 56 | ICMP packet size in bytes. |
| Interface | Automatically selected; default: Automatically selected | Specifies through which interface the pings will be sent. If Automatically selected is set, the pings will go through the main WAN interface. |
| IP type | IPv4 | IPv6; default: IPv4 | IP address version of the host to ping. |
| Host to ping | host | ip; default: 8.8.8.8 | Hostname or IP address to which the Ping/Wget requests will be sent. |
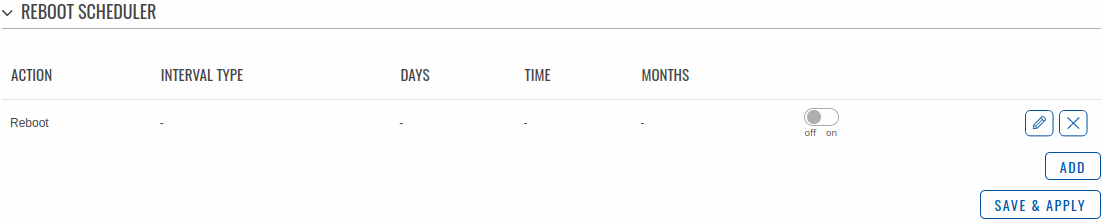
Reboot Scheduler
The Reboot Scheduler is a function that reboots the device at a specified time interval regardless of other circumstances. It can be used as a prophylactic measure, for example, to reboot the device once at the end of every day.
You can add more rules with the 'Add' button or delete them using the 'Delete' button. If you wish to customize a rule, click the button that looks like a pencil next to it.
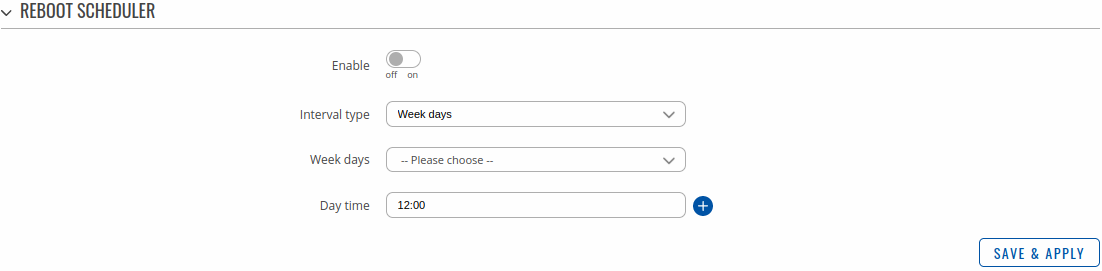
The figure below is an example of the Periodic Reboot configuration page and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that page:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns the rule on or off. |
| Interval type | Week days | Month days; default: Week days | Scheduler instance interval type. |
| Week days | Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday; default: Monday | Week day(s) when actions will be executed. This field becomes visible when Interval type is set to Week days. |
| Month day | integer [1..31]; default: 1 | Day of the month on which the reboot will occur. This field becomes visible when Interval type is set to Month days. |
| Month | month(s) [january..december]; default: none | The month(s) on which the reboot will occur. Leave empty to apply to all months. This field becomes visible when Interval type is set to Month days. |
| Day time | time [00:00..23:59]; default: none | Exact time of day the reboot will take place |
| Force last day | off | on; default: off | Forces intervals to accept last day of month as a valid option if selected day doesn't exist in the ongoing month. This field becomes visible when Interval type is set to Month days. |
Backup
Summary
The Backup page is used to generate configuration backup files or upload existing ones to the device. This chapter is an overview of the Backup page in {{{name}}} devices.
Create backup
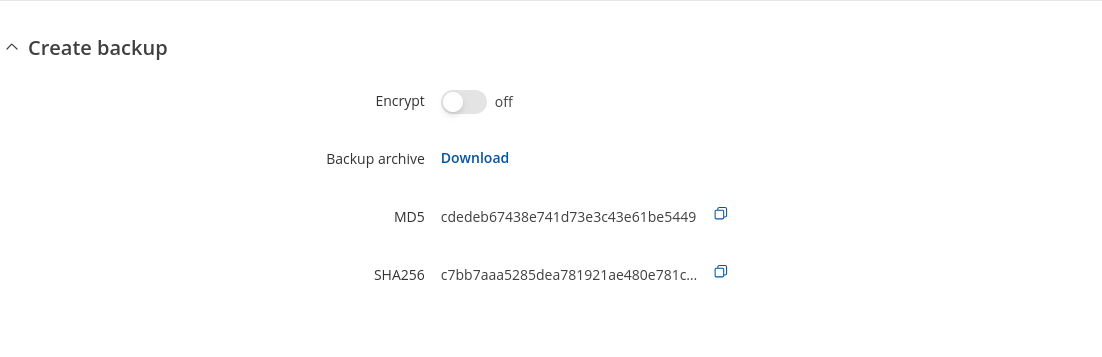
The Backup configuration section is used to generate and download a file which stores the current device configuration. The backup file can later be uploaded to the same device or another device of the same type (product codes must match).
This section contains MD5, SHA256 checksum fields generated from latest downloaded backup file, 'Encrypt' option and the 'Download' button to generate and download the device configuration backup file.
Important notes:
1. Password field is required if Encrypt is turned on and that's when the field appears. Password that will be used to encrypt Backup file. It will have to be provided when extracting formatted zip archive to gain access to a tar file.
2. If the device does not have an Internet connection when a Backup file is being loaded, it will not reinstall software packages installed from Services → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]]. You can add the package installation files to the Backup file manually, a {{{name}}} device will automatically install them when you load the Backup file even without a data connection.
To embed a Backup file with package installation files, follow these steps:
- Download the necessary software package installation files [[{{{name}}} Package Downloads|from here]]
- Download a Backup file.
- Open the Backup file and create a new folder called backup_packages in the /etc directory.
- Add the necessary package files to /etc/backup_packages
- Make sure files in /etc/backup_packages are fully extracted with the *.ipk extensions
Upload backup
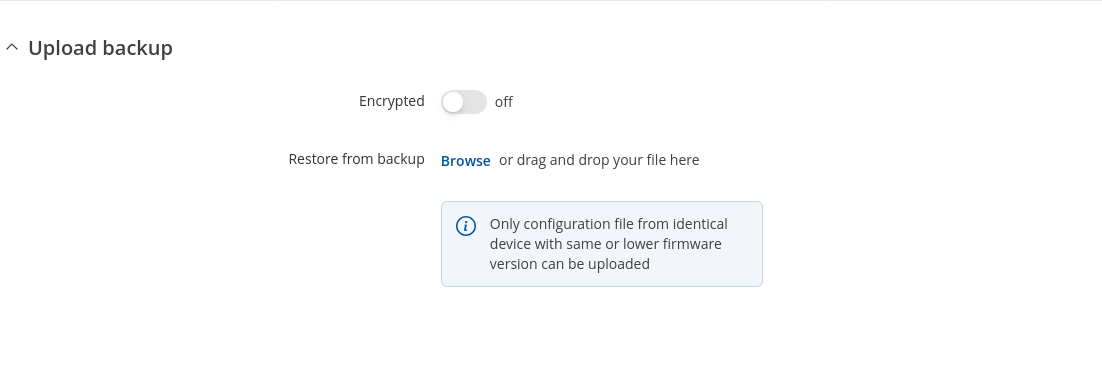
The Restore configuration section is used to upload a configuration file that was taken from this device or another device of the same type.
Turn on 'Encrypted' if backup file was previously encrypted and click the 'Browse' button to select a backup file from your computer and click the 'Upload archive' button to apply the selected configuration on to this device.
Important notes:
- Password will be used when extracting formatted 7z or zip archive to gain access to a tar file.
- Backup files can be uploaded only if they are taken from an identical device (identical Product code (can be checked in the Status → [[{{{name}}} System|System]] page)) with identical or older firmware.
- It is important to remember that the backup file not only changes the device configuration, but also the password. If you are unsure of the backup file's password, you may want to reconsider uploading it because you may lose access to device.
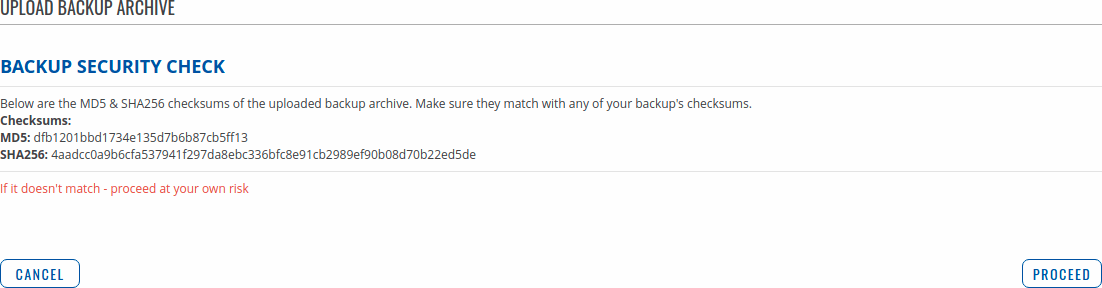
Backup Security Check
After uploading a backup file your device will calculate checksums for uploaded file and display them. If this backup file was the latest downloaded in your device then you can compare these checksums with the ones in your Create backup section to verify backup's integrity.
If everything is in order click Proceed to restore configuration to backup.
Troubleshoot
Logging Settings
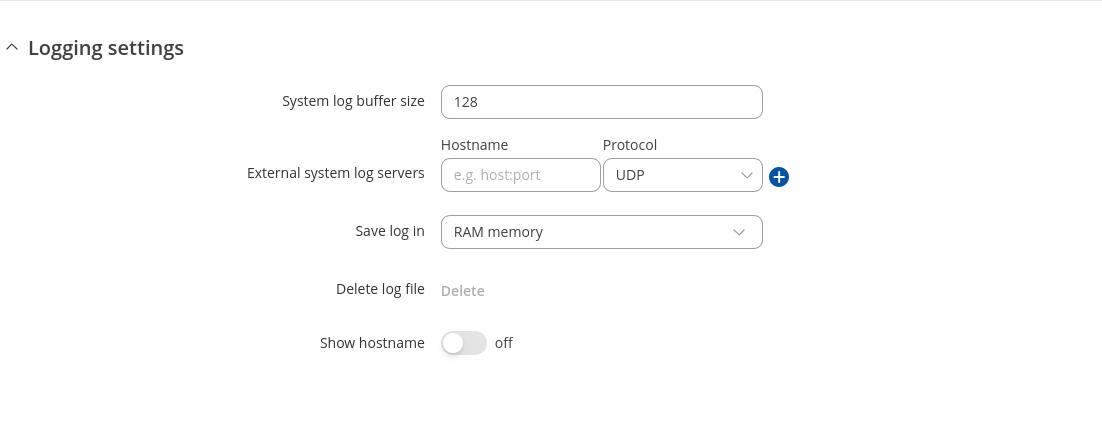
The Logging Settings section is used to configure how and where the device stores system log data. The system log is a file that contains information on various system related events and is useful to engineers for troubleshooting the device.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| System log buffer size | integer; default: 128 | System log buffer size in kibibytes (KiB). |
| External system log server | ip; default: none | IP address/host and port of an external server that will be used to store device logs. |
| External system log server protocol | UDP | TCP; default: UDP | Communication protocol used by the external log server. |
| Save log in | RAM memory | Flash memory; default: RAM memory | Specifies which type of memory to use for storing system logs. |
| System log file size | integer [10..500]; default: 200 | Maximum size (in kilobytes) of a log file. When threshold is reached, log rotation is performed. Can be set to value from 10kB to 500kB. Smaller the file, larger amount of old logs is saved. |
| Compress | off | on; default: off | Compress old rotated logs using GZ format. |
| Delete | - (interactive button) | Deletes log file from router. |
| Show hostname | off | on; default: off | Show hostname instead of IP address in syslog. |
Troubleshoot
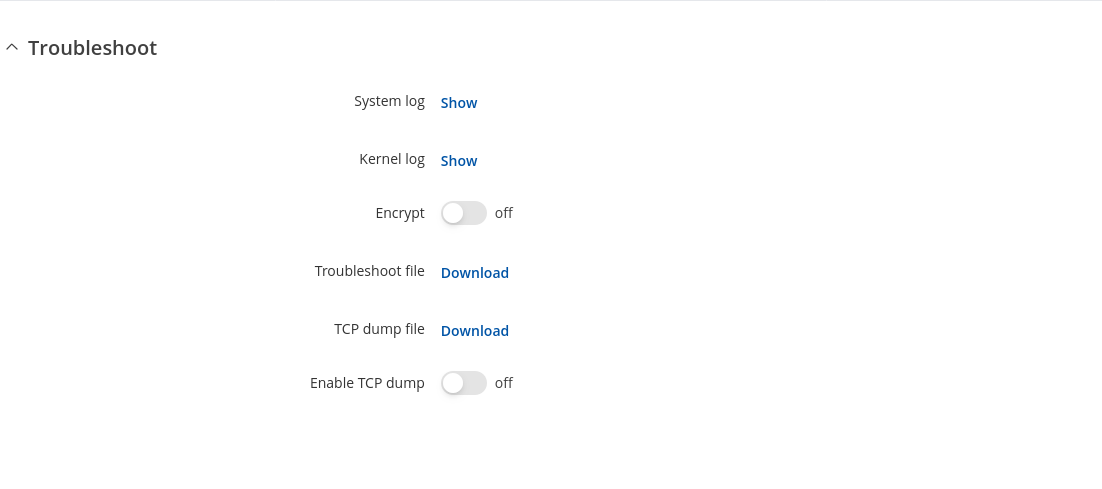
The Troubleshoot section is used to download various files that contain information used for troubleshooting the device. Refer to the figure and table below for information on the Troubleshoot page.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| System log | - (interactive button) | Displays the contents of the device system log file. The system log contains records of various system related events, such as starts/stops of various services, errors, reboots, etc. |
| Kernel log | - (interactive button) | Displays the contents of the device kernel log file. The kernel log contains records of various events related to the processes of the operating system (OS). |
| Encrypt | off | on; default: off | Turn on AES 256 encryption and archive Troubleshoot file using zip format. |
| Password | string; default: none | Password that will be used to encrypt Troubleshoot file. It will have to be provided when extracting formatted zip archive to gain access to a tar file. |
| Troubleshoot file | - (interactive button) | Downloads the device Troubleshoot file. It contains the device configuration information, logs and some other files. When requesting support, it is recommended to always provide the device Troubleshoot file to Teltonika engineers for analysis. |
| TCP dump file | - (interactive button) | Downloads the device TCP dump file. TCP dump is a program used to capture packets moving through network interfaces. By default, the device does not store TCP dump information. You must enable TCP dump and save the changes before you can download the file. |
| Enable TCP dump | off | on; default: off | Turns TCP dump packets capture on or off. |
| Select interface | Any | br0.1; default: Any | Only captures packets that move through the specified network interface. |
| Select protocol filter | All | ICMP | TCP | UDP | ARP; default: All | Only captures packets that match the specified protocol. |
| Select packets direction | Incoming/Outgoing | Incoming | Outgoing; default: Incoming/Outgoing | Only captures packets coming from the specified direction. |
| Host | Domain names or IP; default: none | Only captures packets related to the specified host. |
| Port | integer [1..65535]; default: none | Only captures packets related to the specified port. |
| Select storage | RAM memory; default: RAM memory | Specifies where the TCP dump file will be stored. |
Events Log
Summary
The Events Log page contains information on various device related events. This article is an overview of the Events Log page for {{{name}}} routers.
All Events
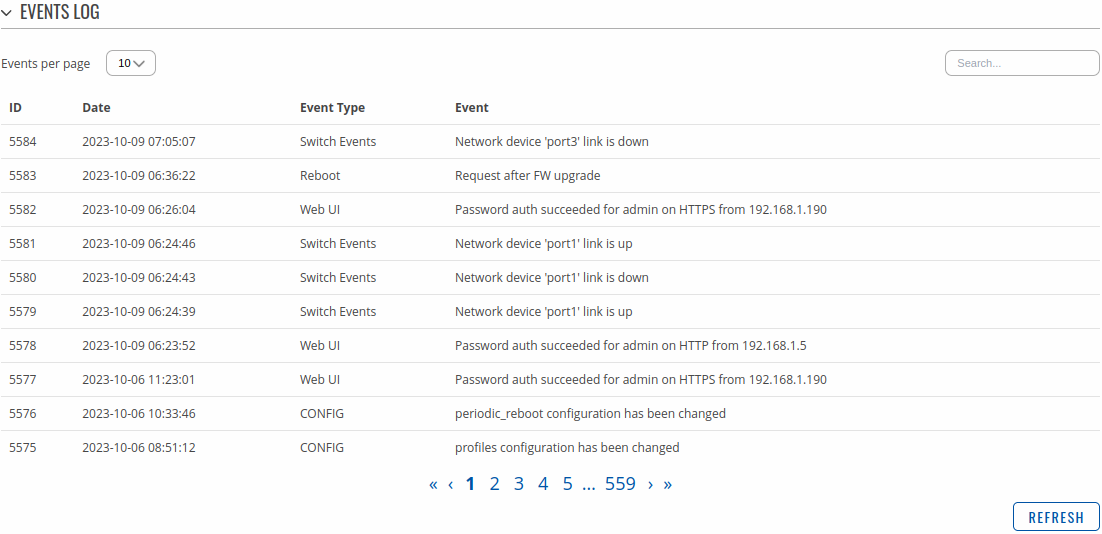
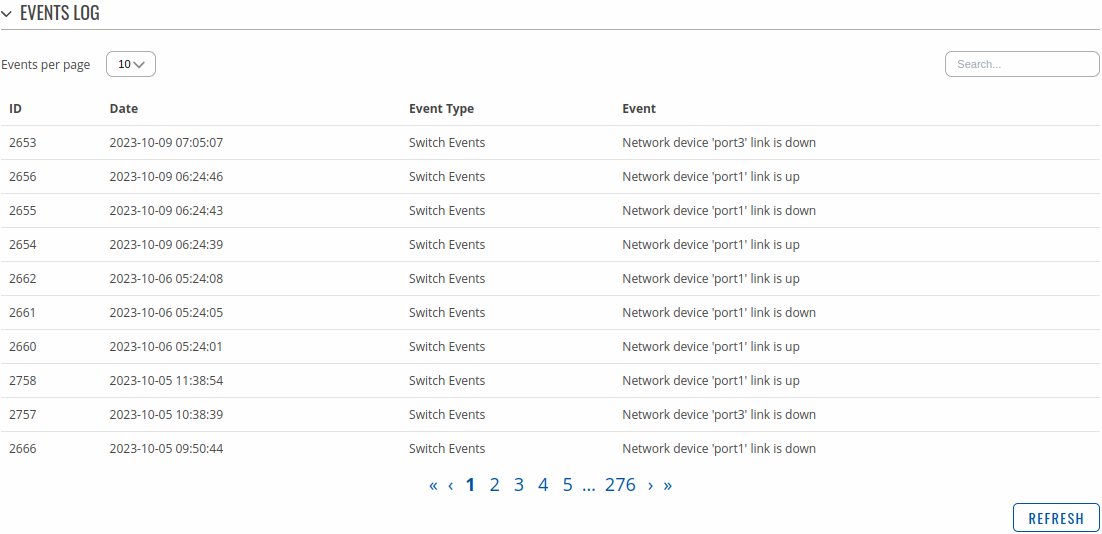
The All Events page contains a chronological list of various events related to the device. The figure below is an example of the Events Log section:
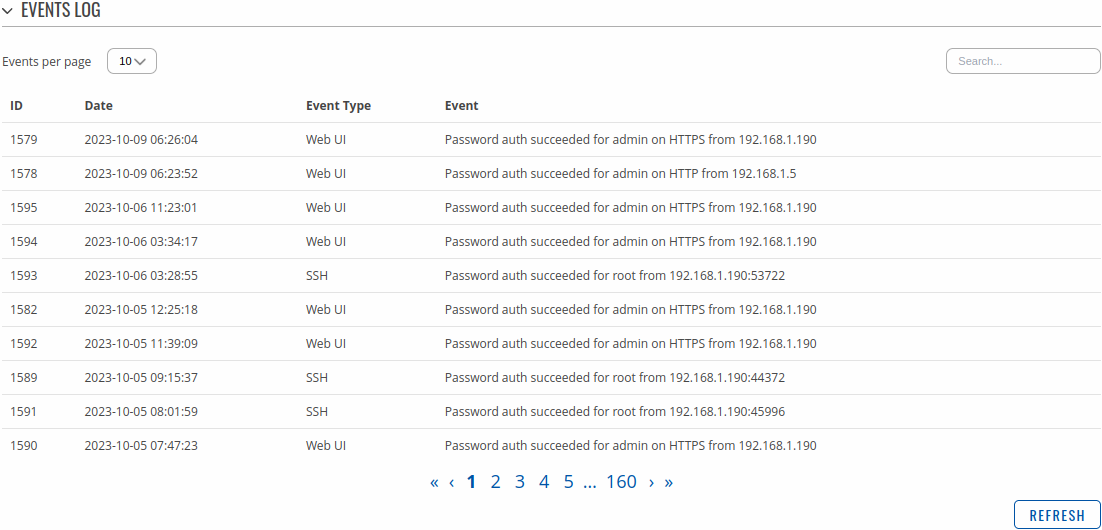
General Events
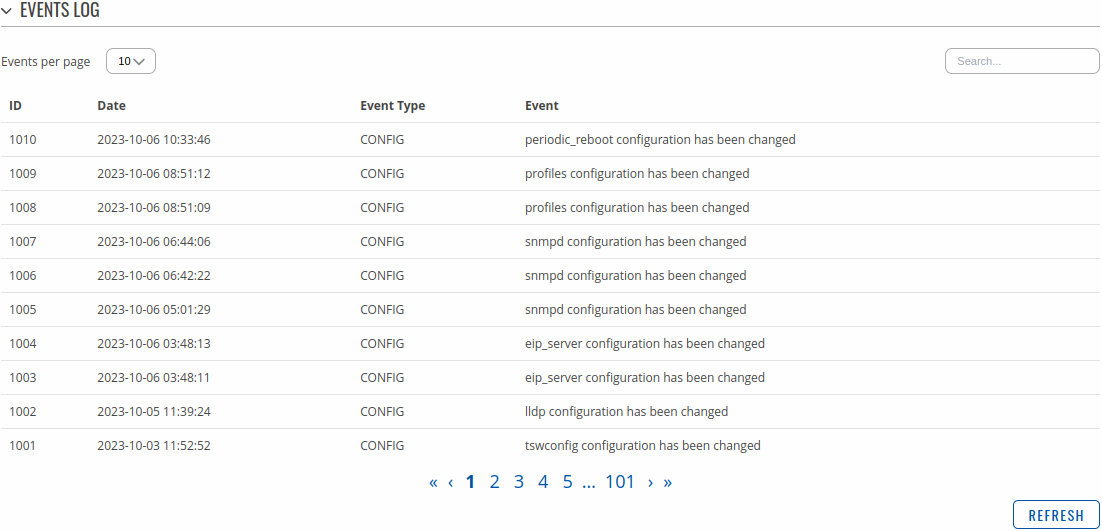
The General Events page contains a chronological list of general events related to the device. The figure below is an example of the Events Log section:
System Events
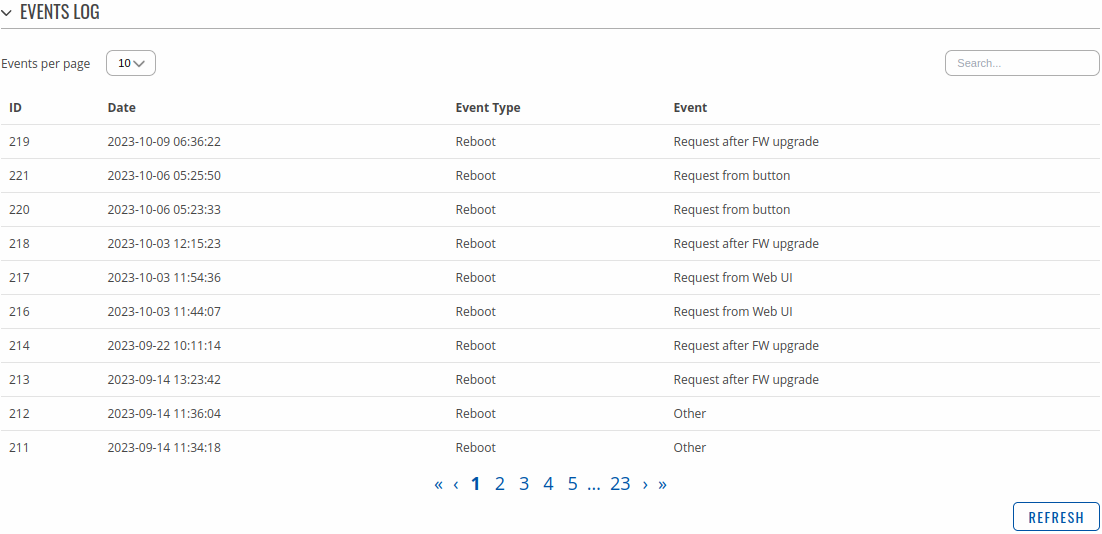
The System Events page contains a chronological list of system events related to the device. The figure below is an example of the Events Log section:
Network Events
The Netwrok Events page contains a chronological list of network events related to the device. The figure below is an example of the Events Log section:
Connections Events
The Connections Events page contains a chronological list of connections events related to the device. The figure below is an example of the Events Log section:
CLI
Summary
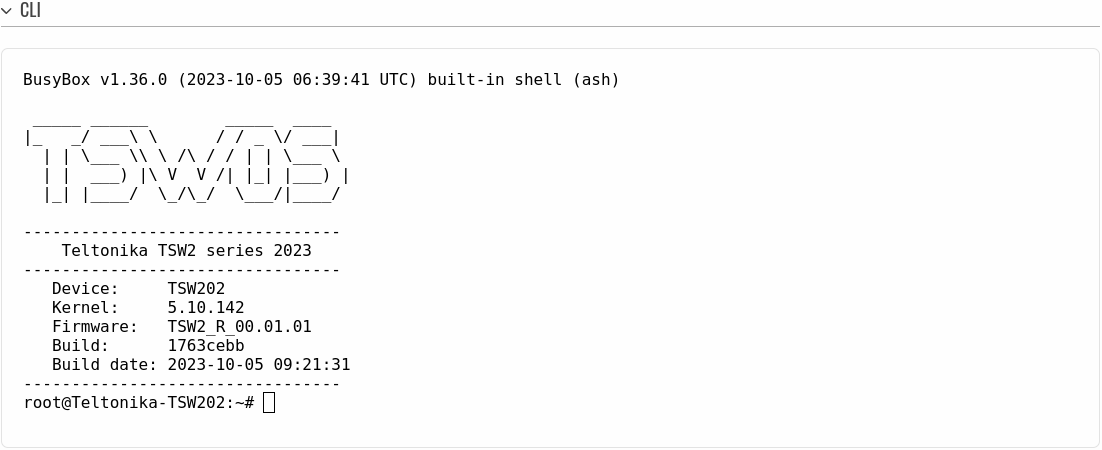
The CLI or Command-line interface functionality allows you to enter and execute Linux commands within the device. This manual page provides an overview of the CLI page in {{{name}}} devices.
CLI
The RutOS CLI is a console interface similar to the Linux Terminal program. Use the following credentials to log in:
- Username: root
- Password: device's password
If the login was successful, you should be greeted with a window similar to this:
Reset settings
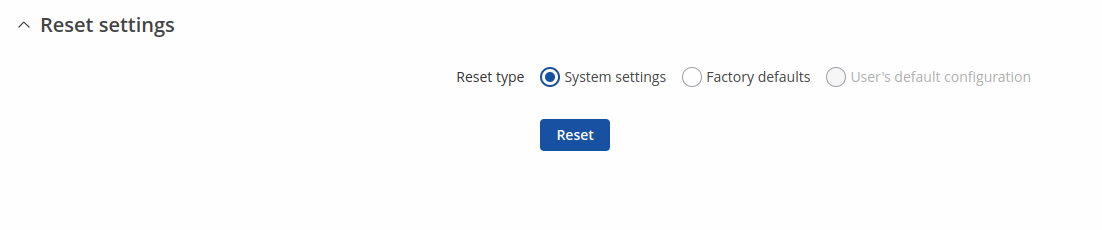
Reset settings
The Reset settings page is used for restoring device's configuration.
| Reset type | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| System settings | -(single select) | Resets all configuration except RMS data, mdcollect database, logs and PIN code. |
| Factory defaults | -(single select) | Resets device to factory configuration. |
| User's default configuration* | -(single select) | Resets device to user's default configuration. |
*This button will be greyed out until you have created a [[{{{name}}}_Maintenance#Create_user's_default_configuration|User's default configuration]].
Create user's default configuration
The Create user's default configuration section is used to create or delete a file which stores current device configuration. The default configuration can later be loaded in [[{{{name}}}_Maintenance#Reset_settings|Reset settings]] page or via reset button.
Click the 'Create' button to generate default configuration file from your current device configuration.
[[Category:{{{name}}} System section]]