SNMP configuration example: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
===RUT9xx=== | ===RUT9xx=== | ||
To setup SNMP first make sure that SNMP package is installed, more information here [[ | To setup SNMP first make sure that SNMP package is installed, more information here [[RUT956 Packages]] and [[RUT951_Package_Manager|RUT951 Packages]]. | ||
==OID codes== | ==OID codes== | ||
| Line 139: | Line 139: | ||
Press "Download" button to download MIB file. | Press "Download" button to download MIB file. | ||
[[File: | [[File:SNMP_config_example_7.8_5.png]] | ||
===Testing SNMP with MIB browser=== | ===Testing SNMP with MIB browser=== | ||
| Line 164: | Line 164: | ||
First enable SNMP Trap, then enter '''Host/IP''', Hots/IP is the SNMP manager, computer to which SNMP agent will send Trap messages. If router is connected to PC via ethernet cable, enter the IP address of the interface the router is connected to. You can use '''ipconfig''' command on windows, '''ifconfig''' on linux to find IP address of the interface to which router is connected. Next choose '''port''', preferably choose port number higher than '''1024''' so SNMP manager could establish connection without root/admin rights. If you choose to leave default port '''162''' make sure to launch SNMP manager with admin/root permissions. | First enable SNMP Trap, then enter '''Host/IP''', Hots/IP is the SNMP manager, computer to which SNMP agent will send Trap messages. If router is connected to PC via ethernet cable, enter the IP address of the interface the router is connected to. You can use '''ipconfig''' command on windows, '''ifconfig''' on linux to find IP address of the interface to which router is connected. Next choose '''port''', preferably choose port number higher than '''1024''' so SNMP manager could establish connection without root/admin rights. If you choose to leave default port '''162''' make sure to launch SNMP manager with admin/root permissions. | ||
[[File: | [[File:SNMP_config_example_7.8_1.png]] | ||
===Trap rules=== | ===Trap rules=== | ||
Trap rules describe on what event SNMP agent should send Trap messages. There are certain rules which can be set up using Teltonika WebUI depending on physical configuration of the device. | Trap rules describe on what event SNMP agent should send Trap messages. There are certain rules which can be set up using Teltonika WebUI depending on physical configuration of the device. | ||
====Events log==== | |||
---- | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Event</th> | ||
<th>Event subtype</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><b>Config change</b></td> | |||
<td>All | Specific config change; default: <b>all</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on changes to the device's configuration.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><b>Reboot</b></td> | |||
<td>All | From Web UI | From ping reboot | From reboot scheduler | From button | From SMS; default: <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on if the device was rebooted.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><b>Startup</b></td> | |||
<td>Device startup completed</td> | |||
<td>Informs on when the device is fully booted.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><b>GPS</b></td> | |||
<td>All | Entered geofence | Left geofence; default: <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on when the device has entered or left a user defined geofence zone.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><b>Mobile data</b></td> | |||
<td>All | Connected | Disconnected; default <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on changes to the state of the device's mobile connection.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><b>New DHCP client</b></td> | |||
<td>All | Connected from LAN | Connected from WiFi; default <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on new DHCP lease give outs.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><b>Ports state</b></td> | |||
<td>All | Link speed | Link state | Unplugged | Plugged in | Specific port; default: <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on Ethernet port state (plugged in or unplugged) or speed (100 Mbps or 1000 Mbps) changes.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><b>Reboot</b></td> | |||
<td>All | From button | From Input/Output | From Ping Reboot | From Reboot Scheduler | From WebUI | From SMS; default: <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs after device reboot occurrences.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><b>Signal strength</b></td> | |||
<td>All | - 121 dBm - 113 dBm | - 113 dBm - 98 dBm | - 98 dBm - 93 dBm | - 93 dBm - 75 dBm | - 75 dBm - 60 dBm | - 60 dBm - 50 dBm; default: <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on signal strength changes.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><b>SMS</b></td> | |||
<td>SMS received</td> | |||
<td>Informs on received SMS messages.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><b>SSH</b></td> | |||
<td>All | Successful authentication | Unsuccessful authentication; default: <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on successful or unsuccessful SSH login attempts.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><b>Topology state</b></td> | |||
<td>Topology changes</td> | |||
<td>Informs on changes to the device's network topology.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><b>WAN failover</b></td> | |||
<td>All | Switched to failover | Switched to main; default: <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on WAN failover occurrences.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><b>WebUI</b></td> | |||
<td>ALL | Successful authentication | Unsuccessful authentication; default: <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on successful or unsuccessful HTTP/HTTPS login attempts.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<table> | <td><b>New WiFi client</b></td> | ||
<td>All | Connected | Disconnected; default: <b>All</b></td> | |||
<td>Informs on new WiFi clients. Possible triggers are:</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
---- | ---- | ||
To create new rule chose action and press "Add" button, specify rule values and save | To create new rule chose action and press "Add" button, specify rule values and save: | ||
[[File:SNMP_config_example_7.8_2.png|1000px]] | |||
[[File: | |||
---- | ---- | ||
Modify the trap to your needs: | |||
[[File:SNMP_config_example_7.8_3.png|1000px]] | |||
[[File: | |||
---- | ---- | ||
New rule should appear in the main Trap window | New rule should appear in the main Trap rules window: | ||
[[File:SNMP_config_example_7.8_4.png|1000px]] | |||
[[File: | |||
---- | ---- | ||
====Testing Trap with MIB browser==== | ====Testing Trap with MIB browser==== | ||
| Line 240: | Line 277: | ||
===Testing Trap with Linux Terminal=== | ===Testing Trap with Linux Terminal=== | ||
To test Traps with Linux terminal extra configurations and packages are required. All information how to setup Trap listening service and how to test it can be found here [[Testing Trap With | To test Traps with Linux terminal extra configurations and packages are required. All information how to setup Trap listening service and how to test it can be found here [[Testing Trap With Linux Operating System]]. | ||
[[Category:SNMP]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:53, 13 August 2024
Main Page > General Information > Configuration Examples > SNMP > SNMP configuration exampleSummary
This chapter is a guide on configuring SNMP package to establish communication between devices.
SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) - is widely used in networking management for networking monitoring. SNMP uses MIB (Management Information Base) to organize management data in the form of variables, which describe the system configuration and status.
Trap
Traps are alert messages sent by SNMP agent to SNMP manager.
SNMP agent - Teltonika router. Device which sends Trap messages to the manager.
SNMP manager - device which listens for Trap messages from the agents.
Teltonika routers are able to send SNMP Trap messages to the manager on their own when they experience a problem or a situation described in the rules.
Preconditions
RUT9xx
To setup SNMP first make sure that SNMP package is installed, more information here RUT956 Packages and RUT951 Packages.
OID codes
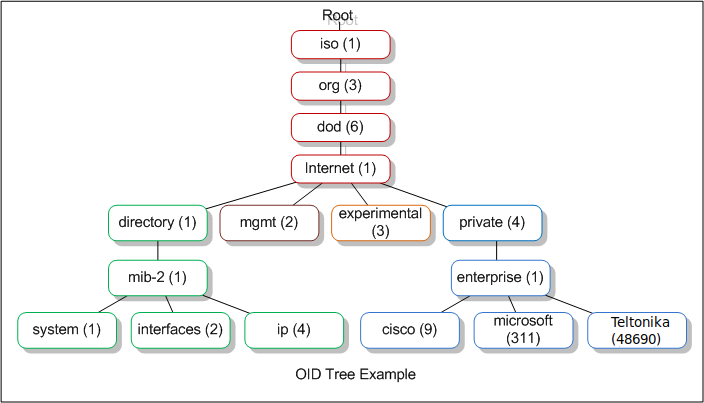
OID code (Object identifier code) - is an address used to identify devices and their status.
OID code is represented by the numbers in the boxes starting from "root".
| Number | Label | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | iso | ISO is the group that established the OID standard |
| 3 | org | An organization will be specified next |
| 6 | dod | The US Department of Defense (established the early internet) |
| 1 | internet | Communication will be via Internet/network |
| 4 | private | This is a device manufactured by a private entity |
| 1 | enterprise | The device manufacturer is classified as an enterprise |
| 48690 | Teltonika | Teltonika enterprise number |
To communicate with Teltonika router the start of the OID code, in this case, will be 1.3.6.1.4.1.48690.
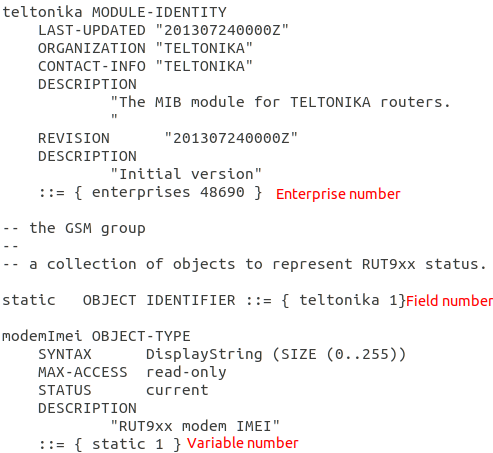
Every configuration or status variable has distinct OID code.
| Field | Number | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| static | 1 | Static router information (Router name, Modem Imei, Modem model etc.) |
| gsm | 2 | Sim card information (Sim State, Operator, Mobile IP etc.) |
| hotspot | 3 | Hotspot information (Hotspot ip, users etc.) |
| Trap | 4 | Trap messages (Information sent through trap messages) |
| rut9x5 | 5 | Input/Output information |
| gps | 6 | GPS information (Latitude, accuracy etc.) |
| ethernet | 7 | Information about router ports |
To access variable values, after enterprise number add field number and then specify variable number. For example: .1.3.6.1.4.1.48690.1.7.0 represents router name (48690.1.7.0: Enterprise (48690) - Teltonika, Field (1) - static, Variable (7.0) - routerName). All OID codes can be generated from MIB file, basic OID codes can be found here RUT955 SNMP#SNMP Variables list.
MIB File
MIB File can be used with MIB browsers for easier access to configuration and status information variables of the device. Download the MIB file and upload/load it in MIB browser. In this example iReasoning MIB browser was used only for testing purpose.
Generating OID code from MIB File
MIB File contains all OID codes. Line containing numbers needed for OID code can be identified by this marking "::=".
All that is left, is to add the numbers together. Example from given MIB File: 1.3.6.1.4.1.48690.1.1.0.
Important note: Do not forget to add .0 at the end of the generated OID code, except to Trap OID codes. Trap OID codes are only used by SNMP agent (router), using them in MIB browser or command line will not give any results.
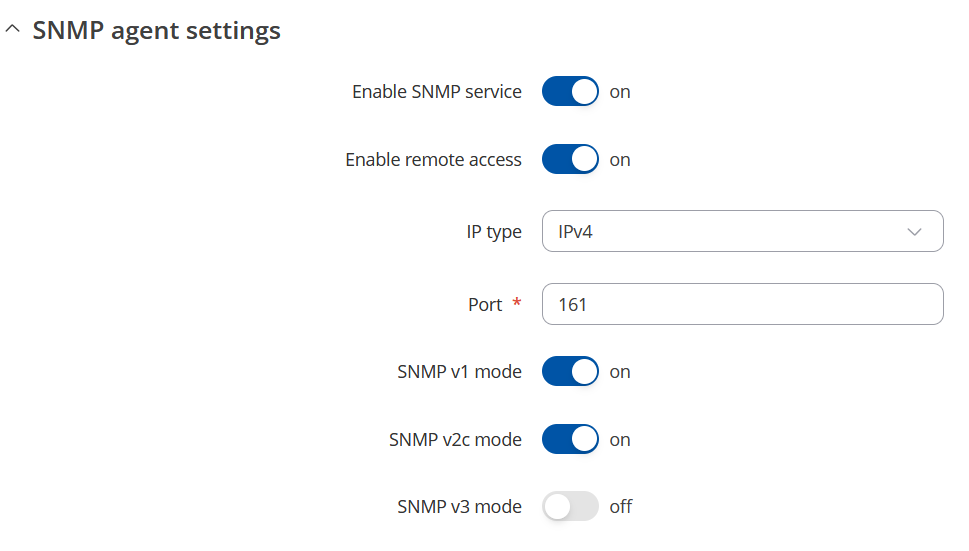
SNMP Configuration
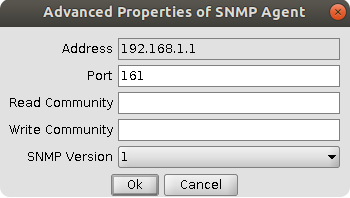
To configure SNMP, first enable SNMP service, leave or change the port, you can leave everything else as it is.
Press "Download" button to download MIB file.
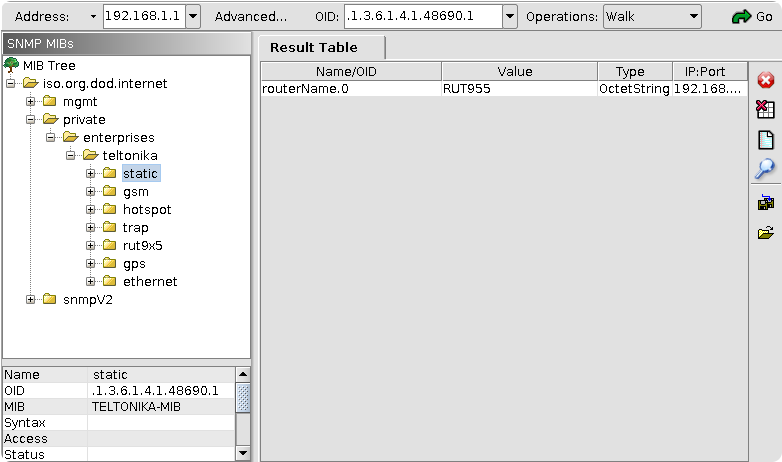
Testing SNMP with MIB browser
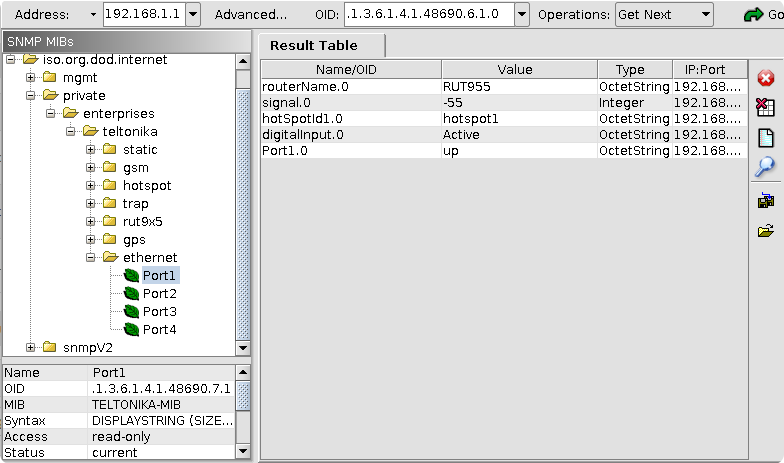
Use MIB browser to test if SNMP works. Make sure to use same port and IP address of the router in MIB browser. To enter port number in MIB browser press "Advanced" button (on the right of IP address field).
To upload/load MIB file press "File" in menu bar (top left side of the window) and press "Load MIBs", make sure to select the MIB file you downloaded from the WebUI. MIB browser lets you walk through all OID codes, or return a distinct variable value. To walk through all OID codes select "walk" in Operation tab (top left of the window). To iterate through OID codes manually, navigate to the desired folder on the left of the MIB browser window and select specific element (Double click). The value of the variable will be printed in the Result Table.
Testing SNMP with console command
We can use snmpget command to get information from router:
$ snmpget -c public -v 2c IP_address:port OID_code
Example:
$ snmpget -c public -v 2c 192.168.1.1:161 1.3.6.1.4.1.48690.1.7.0
Trap Configuration
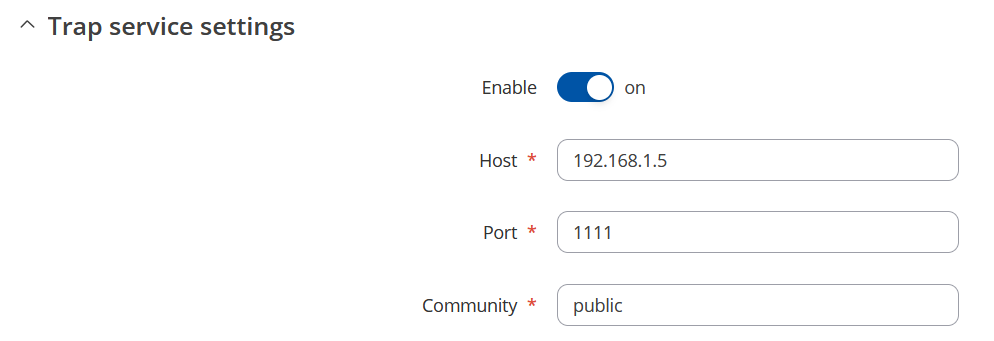
First enable SNMP Trap, then enter Host/IP, Hots/IP is the SNMP manager, computer to which SNMP agent will send Trap messages. If router is connected to PC via ethernet cable, enter the IP address of the interface the router is connected to. You can use ipconfig command on windows, ifconfig on linux to find IP address of the interface to which router is connected. Next choose port, preferably choose port number higher than 1024 so SNMP manager could establish connection without root/admin rights. If you choose to leave default port 162 make sure to launch SNMP manager with admin/root permissions.
Trap rules
Trap rules describe on what event SNMP agent should send Trap messages. There are certain rules which can be set up using Teltonika WebUI depending on physical configuration of the device.
Events log
| Event | Event subtype | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Config change | All | Specific config change; default: all | Informs on changes to the device's configuration. |
| Reboot | All | From Web UI | From ping reboot | From reboot scheduler | From button | From SMS; default: All | Informs on if the device was rebooted. |
| Startup | Device startup completed | Informs on when the device is fully booted. |
| GPS | All | Entered geofence | Left geofence; default: All | Informs on when the device has entered or left a user defined geofence zone. |
| Mobile data | All | Connected | Disconnected; default All | Informs on changes to the state of the device's mobile connection. |
| New DHCP client | All | Connected from LAN | Connected from WiFi; default All | Informs on new DHCP lease give outs. |
| Ports state | All | Link speed | Link state | Unplugged | Plugged in | Specific port; default: All | Informs on Ethernet port state (plugged in or unplugged) or speed (100 Mbps or 1000 Mbps) changes. |
| Reboot | All | From button | From Input/Output | From Ping Reboot | From Reboot Scheduler | From WebUI | From SMS; default: All | Informs after device reboot occurrences. |
| Signal strength | All | - 121 dBm - 113 dBm | - 113 dBm - 98 dBm | - 98 dBm - 93 dBm | - 93 dBm - 75 dBm | - 75 dBm - 60 dBm | - 60 dBm - 50 dBm; default: All | Informs on signal strength changes. |
| SMS | SMS received | Informs on received SMS messages. |
| SSH | All | Successful authentication | Unsuccessful authentication; default: All | Informs on successful or unsuccessful SSH login attempts. |
| Topology state | Topology changes | Informs on changes to the device's network topology. |
| WAN failover | All | Switched to failover | Switched to main; default: All | Informs on WAN failover occurrences. |
| WebUI | ALL | Successful authentication | Unsuccessful authentication; default: All | Informs on successful or unsuccessful HTTP/HTTPS login attempts. |
| New WiFi client | All | Connected | Disconnected; default: All | Informs on new WiFi clients. Possible triggers are: |
To create new rule chose action and press "Add" button, specify rule values and save:
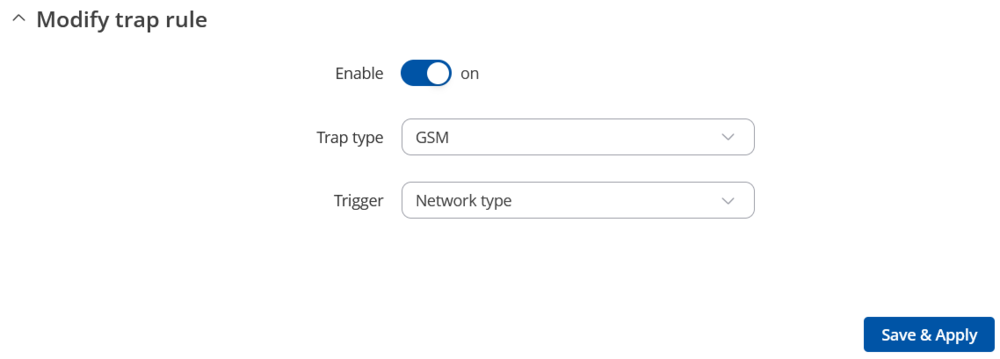
Modify the trap to your needs:
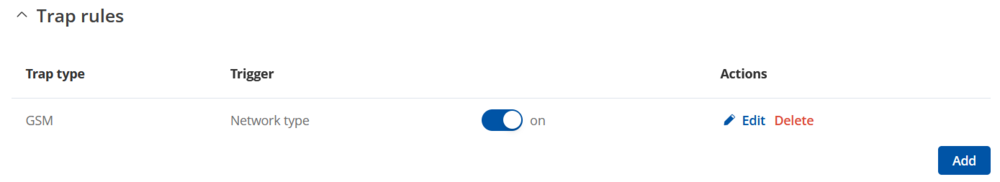
New rule should appear in the main Trap rules window:
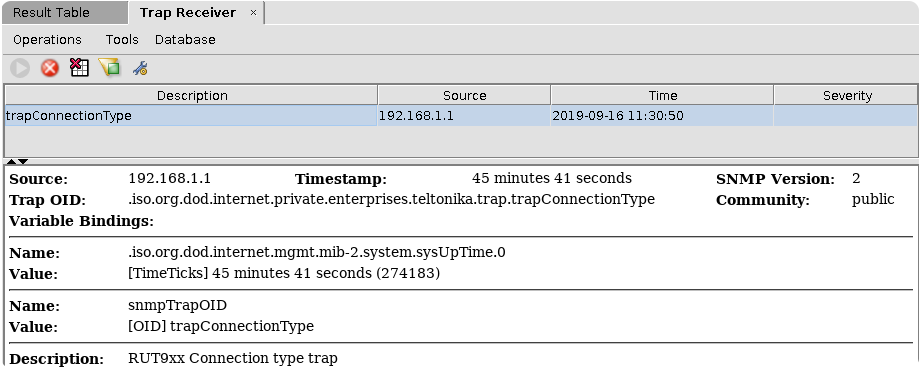
Testing Trap with MIB browser
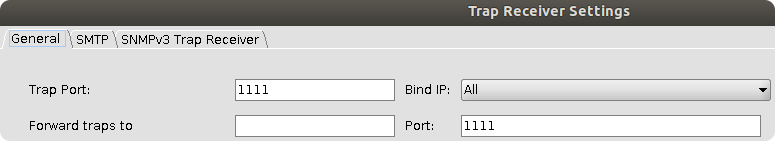
To test trap messages with MIB browser, open Trap receiver and configure the setting. Make sure to use the same port saved in WebUI configuration.
Note: Preferably open MIB browser with root/admin permissions.
To test "Connection type trap" reboot mobile modem. You can reboot modem through Status -> Network window. MIB browser should receive Trap message.
Testing Trap with Linux Terminal
To test Traps with Linux terminal extra configurations and packages are required. All information how to setup Trap listening service and how to test it can be found here Testing Trap With Linux Operating System.