|
|
| (23 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| ==Summary==
| | {{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_lan_rut2_rut9 |
| | | <!---------DEVICE DETAILS---------> |
| {{Template: webui_network_lan_summary}} | | | name = RUT240 |
| | | | series = RUT2 |
| ==Configuration==
| | <!-----------SEPARATORS-----------> |
| | | }} |
| ===General Setup===
| |
| ---- | |
| The General Setup tab provides you with the possibility to set the router's Private IP address, IP netmask and IP broadcast.
| |
| | |
| [[File:Network lan configuration general.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| <table class="nd-mantable">
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <th>field name</th>
| |
| <th>value</th>
| |
| <th>description</th>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>IP address</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: '''192.168.1.1'''</td>
| |
| <td>IP address that the device uses on the LAN network </td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>IP netmask</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: '''255.255.255.0'''</td>
| |
| <td>A netmask is used to define how “large" the LAN network is</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>IP broadcast</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>IP broadcasts are used by BOOTP and DHCP clients to find and send requests to their respective servers</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>IPv6 Address</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>Assigns an Ipv6 address for this interface. CIDR notation: address/prefix</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>IPv6 Prefix Length</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: <b>60</b></td>
| |
| <td>Delegates a prefix length for this interface</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>IPv6 Subprefix Hint</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>Hexadecimal hint to used in the IPv6 address prefix</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ULA Prefix</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>Prefix used for the Unique Local Address</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| | |
| </table>
| |
| | |
| ===Advanced Settings===
| |
| ---- | |
| LAN Configurations Advanced Settings tab contains some less frequently used, more complicated configurations, such as custom MTUs and network interface metric values.
| |
| | |
| [[File:Network lan configuration advanced.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| <table class="nd-mantable">
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <th>field name</th>
| |
| <th>value</th>
| |
| <th>description</th>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Accept router advertisements</td>
| |
| <td>yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no'''</td>
| |
| <td>Allows accepting router advertisements</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Override MTU</td>
| |
| <td>integer [0..1500]; Default: '''1500'''</td>
| |
| <td>MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) specifies the largest possible size of a data packet</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Use gateway metric</td>
| |
| <td>integer; Default: '''0'''</td>
| |
| <td>The LAN configuration generates an entry in the routing table. In this field you can alter the metric of that entry. Higher metric means higher priority</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Use WAN port as LAN</td>
| |
| <td>yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no'''</td>
| |
| <td>If this is enabled, the router's WAN port will act as if it were a LAN port. '''Works only if WAN is not set to wired'''</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| </table>
| |
| | |
| ==DHCP Server==
| |
| | |
| {{Template: webui_network_lan_dhcp_summary}}
| |
| | |
| ===General===
| |
| ---- | |
| {{Template: webui_network_lan_dhcp_general_setup}}
| |
| | |
| [[File:Network lan dhcpserver general.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| <table class="nd-mantable">
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <th>field name</th>
| |
| <th>value</th>
| |
| <th>description</th>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>DHCP</td>
| |
| <td>Enable {{!}} Disable {{!}} DHCP Relay; Default: '''Enable'''</td>
| |
| <td>Enables or disables DHCP Server. If DHCP Relay is selected, you will be prompted to enter an IP address of another DHCP server in your LAN. In this case, Whenever a new device connects to the router, the router will redirect any DHCP requests to the specified DHCP Server</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Start</td>
| |
| <td>integer [1..253]; Default: '''100'''</td>
| |
| <td>The starting IP address value. e.g., if your router’s LAN IP is 192.168.2.1 and your subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 that means that in your network a valid IP address has to be in the range of [192.168.2.0..192.168.2.254] (192.168.2.255 is a special unavailable address). If the Start value is set to 100 then the DHCP server will only lease out addresses starting from 192.168.2.100</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Limit</td>
| |
| <td>integer [1..4294967296]; Default: '''150'''</td>
| |
| <td>How many addresses the DHCP server can lease out. Continuing from the above example: if the start address is 192.168.2.100 and the server can lease out 150 (default limit value), availabe addresses will be from 192.168.2.100 to 192.168.2.249 (100 + 150 – 1 = 249; this is because the first address is inclusive)</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Lease time</td>
| |
| <td>time in 'h' (hours) or 'm' (minutes); Default: '''12h'''</td>
| |
| <td>he duration of an IP lease. Leased out addresses will expire after the amount of time specified in this field and the device that was using the lease will have to request a new DHCP lease. However, if the device stays connected, its lease will be renewed after half of the specified amount of time passes, e.g., if the lease time is 12 hours, then every 6 hours the device will send a request to the DHCP server asking to renew its lease<br>
| |
| Lease time can be set in '''hours''' ('''h''') or '''minutes''' ('''m'''). The minimal amount of time that can be specified is '''2min''' ('''2m''')</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| </table>
| |
| | |
| ===Advanced Settings===
| |
| ---- | |
| {{Template: webui_network_lan_dhcp_andvanced_settings}}
| |
| | |
| [[File:Network lan dhcpserver advanced.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| <table class="nd-mantable">
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <th>field name</th>
| |
| <th>value</th>
| |
| <th>description</th>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Dynamic DHCP</td>
| |
| <td>yes {{!}} no; Default: '''yes'''</td>
| |
| <td>Enables Dynamic allocation of client addresses. If this is disabled, only clients that have static IP leases will be served</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Enable DNS rebind protection</td>
| |
| <td>yes {{!}} no; Default: '''yes'''</td>
| |
| <td>Enables DNS rebind attack protection by discarding upstream RFC1918 responses (leave default unless necessary otherwise)</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Force</td>
| |
| <td>yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no'''</td>
| |
| <td>The DHCP force function ensures that the router will always start it’s DHCP server, even if there is another DHCP server already running in the router’s network. By default the router’s DHCP server will not start when it is connected to a network segment that already has a working DHCP server</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>IP netmask</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: '''255.255.255.0'''</td>
| |
| <td>Overrides your LAN netmask, thus making the DHCP server think that it’s serving a larger or smaller network than it actually is</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>DHCP Options</td>
| |
| <td>DHCP options; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>Additional options to be added to the DHCP server. For example with '26,1470' or 'option:mtu, 1470' you can assign an MTU value per DHCP. You can find more information on DHCP Options [https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc958941.aspx here] <br> You can add more options by clicking the plus symbol ([[Image:Services sms gateway auto reply plus symbol.PNG]]) located next to the field</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Force DHCP options</td>
| |
| <td>yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no'''</td>
| |
| <td>Forces DHCP option to be sent even if its not requested</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| </table>
| |
| | |
| ==Static Leases==
| |
| | |
| Static IP leases are used to reserve specific IP addresses for specific devices by binding them to their MAC address. This is useful when you have a stationary device connected to your network that you need to reach frequently, e.g., printer, IP phone, etc.
| |
| | |
| [[File:Network lan staticleases.PNG]]
| |
| | |
| <table class="nd-mantable">
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <th>field name</th>
| |
| <th>value</th>
| |
| <th>description</th>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Hostname</td>
| |
| <td>string; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>A custom name that will be linked with the device</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>MAC address</td>
| |
| <td>mac; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>Device’s MAC address</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>IP address</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>The desirable IP address that will be reserved for the specified device</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| </table>
| |
| | |
| ==IP Aliases==
| |
| | |
| IP Aliases are a way of defining or reaching a subnet that works in the same space as the regular network. This is useful if you need to reach the router that is located in the same network but in a different subnet. If you have a static IP configuration on your computer and don’t want to change it every time you need to reach a router in a different subnet, you can configure an IP alias in order to do so.
| |
| | |
| ===General setup===
| |
| ---- | |
| [[File:Network lan ip alias general.png]]
| |
| | |
| <table class="nd-mantable">
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <th>field name</th>
| |
| <th>value</th>
| |
| <th>description</th>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>IP address</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>An alternate IP address used to reach the router by a device(s) that resides in the router's LAN but has a different subnet</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Netmask</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: '''255.255.255.0'''</td>
| |
| <td>Netmask defines how "large" a network is</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| </table>
| |
| | |
| As you can see, the configuration is very similar to the static protocol; in the example above an IP address with a 99th subnet is defined. In this case, if some device has an IP in the 99th subnet (e.g., 192.168.99.xxx) and the subnet’s gateway metric is “higher” and the device is trying to reach the internet it will reroute it’s traffic not to the gateway that is defined in common configurations but through the one that is specified in IP aliases.
| |
| | |
| ===Advanced Settings===
| |
| ---- | |
| You may also define a broadcast address, a custom DNS server and Gateway for your IP Aliases in the Advanced Settings tab.
| |
| | |
| [[File:Network lan ip alias advanced.png]]
| |
| | |
| <table class="nd-mantable">
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <th>field name</th>
| |
| <th>value</th>
| |
| <th>description</th>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>IP Broadcast</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>IP broadcasts are used by BOOTP and DHCP clients to find and send requests to their respective servers</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>DNS</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>A separate DNS server to be used by the IP Alias address</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Gateway</td>
| |
| <td>ip; Default: " "</td>
| |
| <td>A gateway is a network node that connects two networks using different protocols together</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| </table>
| |
| | |
| ==Relayd==
| |
| | |
| '''Relayd''' is a daemon to relay and dynamically redirect incoming connections to a target host. Its main purpose in RUT routers is extending the wireless network. For example, when RUT is in STA (Wireless Station) mode, it can be used to bridge WAN and LAN interfaces to create a larger Wireless network. You can find a detailed example on how to use Relayd '''[[Relayd|here]]'''.
| |
| | |
| [[File:Network lan relayd.png]]
| |
| | |
| <table class="nd-mantable">
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <th>field name</th>
| |
| <th>value</th>
| |
| <th>description</th>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Enable</td>
| |
| <td>yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no'''</td>
| |
| <td>Toggles Relayd ON or OFF</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| </table>
| |
| | |
| [[Category:RUT240 WebUI]]
| |
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version RUT2_R_00.07.06.16.
Note: click here for the old style WebUI (FW version RUT2XX_R_00.01.14.7 and earlier) user manual page.
Summary
The LAN page is used to create and set up local area network interfaces.
This manual page provides an overview of the LAN windows in RUT240 devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.

LAN
The LAN section displays LAN interfaces currently existing on this device.
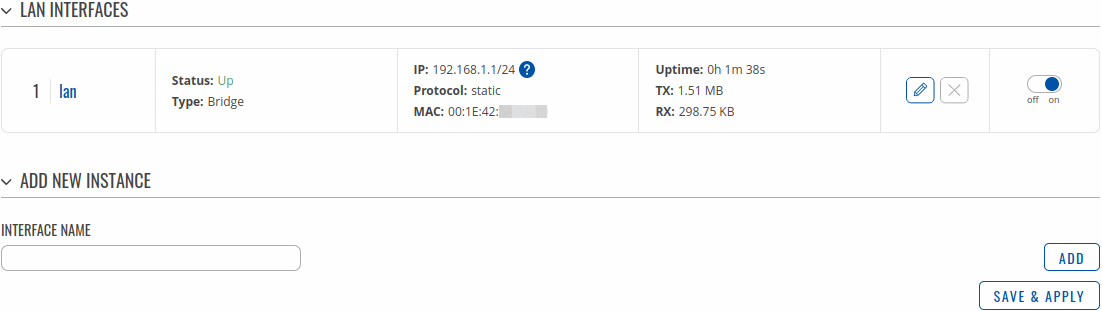
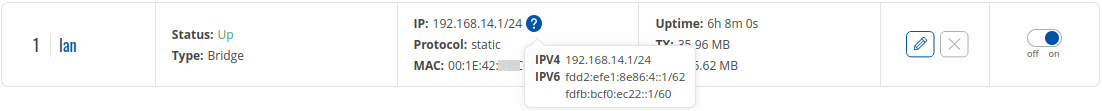
If you hover mouse over the question mark  global IPv6 prefix assignment addresses will be displayed.
global IPv6 prefix assignment addresses will be displayed.
The Add New Instance section is used to create additional network interfaces. To create a new interface, simply enter a custom name for it and click the 'Add' button.

To begin configuring an interface, click the 'Edit' button on the right side of the interface:

Interface configuration
General settings
The General Settings section is used to configure the main parameters of LAN.

| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Enable |
off | on; default: on |
Enable interface |
| Protocol |
Static | None; default: Static |
|
| IPv4 address |
ip4; default: 192.168.1.1 |
Your router's address on the network |
| IPv4 netmask |
netmask; default: 255.255.255.0 |
The IPv4 netmask of this interface. A netmask is used to define how "large" a network is by specifying which part of the IP address denotes the network and which part denotes a device. |
IPV6 settings
The IPV6 settings section is used to configure the IPv6 parameters of LAN.

| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Delegate IPv6 prefixes |
off | on; default: on |
Enable downstream delegation of IPv6 prefixes available on this interface. |
| IPv6 assignment length |
Disabled | 64 | Custom - integer [0..6]; default: 60 |
Assign a part of given length of every public IPv6-prefix to this interface. |
| IPv6 assignment hint |
A hexadecimal string of symbols: a-f, A-F and 0-9 is accepted; default: none |
Assign prefix parts using this hexadecimal subprefix ID for this interface. |
| IPv6 suffix |
Allowed values: "eui64", "random", fixed value like "::1" or "::1:2"; default: none |
Optional. Allowed values: 'eui64', 'random', fixed value like '::1' or '::1:2'. When IPv6 prefix (like 'a:b:c:d::') is received from a delegating server, use the suffix (like '::1') to form the IPv6 address ('a:b:c:d::1') for the interface. |
Advanced settings
The Advanced settings section is used to configure the advanced parameters of LAN.
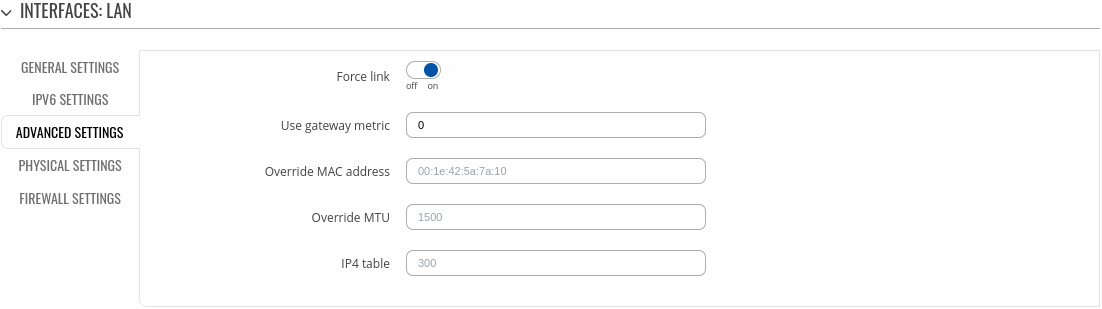
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Force link |
off | on; default: on |
Set interface properties regardless of the link carrier (If set, carrier sense events do not invoke hotplug handlers). |
| Use gateway metric |
integer [0..10000]; default: 0 |
The configuration by default generates a routing table entry. In this field you can alter the metric of that entry. Lower metric means higher priority. |
| Override MAC address |
Mac address of six groups of two hexadecimal digits are accepted. E.g. 00:23:45:67:89:AB; default: none |
Override MAC address of the interface. For example, your ISP (Internet Service Provider) gives you a static IP address and it might also bind it to your computers MAC address (i.e., that IP will only work with your computer but not with your router). In this field you can select your computer’s MAC address and fool the gateway in to thinking that it is communicating with your computer. You can select the MAC address of a currently connected computer, or use a custom one. When changing MAC address on LAN interface be careful to avoid MAC address collisions. |
| Override MTU |
integer [98..65535]; default: none |
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) – specifies the largest possible size of a data packet. |
| IP4 table |
Value must be a valid unsigned integer; default: none |
IPv4 routing table for routes of this interface. |
Physical settings
The Physical settings section is used to configure the physical parameters of LAN.
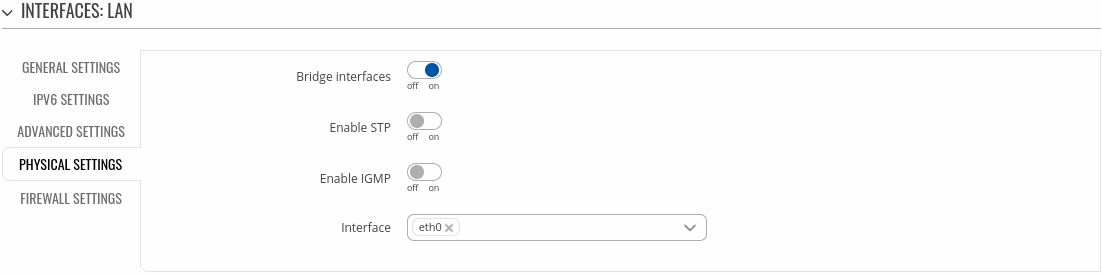
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Bridge interfaces |
off | on; default: on |
Creates a bridge over specified interface(s). |
| Enable STP |
off | on; default: off |
Enables the Spanning Tree Protocol on this bridge. |
| Enable IGMP |
off | on; default: off |
Enables IGMP snooping on this bridge. |
| Interface |
network interface(s); default: lan physical interface |
Physical interface name to assign to this section, list of interfaces if type bridge is set. |
Firewall settings
The Firewall settings section is used to configure the firewall parameters of LAN.
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Create / Assign firewall-zone |
firewall zone; default: lan |
Choose the firewall zone you want to assign to this interface. Select 'Unspecified' to remove the interface from the associated zone or define a new zone and attach the interface to it. |
DHCP server configuration
A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server is a service that can automatically configure the TCP/IP settings of any device that requests such a service. If you connect a device that has been configured to obtain an IP address automatically, the DHCP server will lease out an IP address from the available IP pool and the device will be able to communicate within the private network.
To make the DHCP Server section visible, set interface protocol to Static.
General setup
The General Setup section is used to set up the main operating parameters of the DHCP server.
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Enable DHCP |
Enable | Disable | Relay*; default: Enable |
Turns the DHCP server on or off or enables DHCP relay*.
If DHCP Relay* is selected, you will be prompted to enter an IP address of another DHCP server in your LAN. In this case, whenever a new machine connects to this device, it will redirect any DHCP requests to the specified DHCP Server. |
| Start IP |
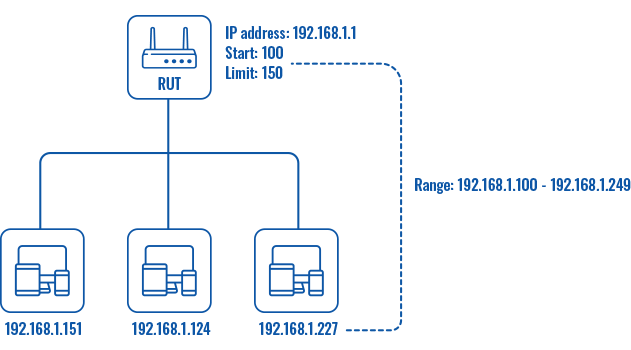
integer [1..255]; default: 100 |
The DHCP server's IP address range start value. |
| End IP |
integer [1..255]; default: 254 |
End IP, i.e., the last possible IP in the selected range for the DHCP server. |
| Lease time |
integer [1..999999]; default: 12integer [2..999999]*integer [120..999999]** |
A DHCP lease will expire after the amount of time specified in this field and the device that was using the lease will have to request a new one. However, if the device stays connected, its lease will be renewed after half of the specified amount of time passes (e.g., if lease time is 12 hours, then every 6 hours the device will ask the DHCP server to renew its lease).
The minimal amount of time that can be specified is 2 minutes.
*If selected Units is Minutes.
**If selected Units is seconds. |
| Units |
Hours | Minutes | Seconds; default: Hours |
Lease time measurement units. |
Advanced settings
Refer to the table below for information on the Advanced Settings section.
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Dynamic DHCP |
off | on; default: on |
Enables dynamic allocation of client addresses. If this is disabled, only clients that have static IP leases will be served. |
| Force |
off | on; default: off |
The DHCP force function ensures that the device will always start it’s DHCP server, even if there is another DHCP server already running in the its network. By default the device’s DHCP server will not start when it is connected to a network segment that already has a working DHCP server. |
| IPv4-Netmask |
netmask; default: none |
Sends a different netmask than the LAN netmask to DHCP clients. |
| Custom DHCP Options |
-(interactive button) |
Opens the edit window of DHCP options. |
| Force DHCP options |
off | on; default: off |
If enabled, DHCP options will be sent even if it's not requested. |
Custom DHCP options
Custom DHCP options are number and value pairs used to configure advanced DHCP functionality. It does not configure DHCP ipv6!. The DHCP options modal is used to 'Add', 'Delete', 'Save' multiple options.
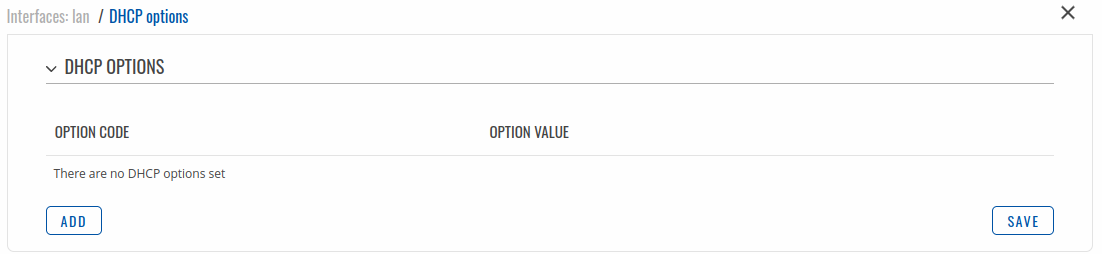
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Option code |
Custom | Time offset (2) | Router (3) | DNS (6) | Domain name (15) | NTP server (43); default: Time offset (2) |
Standartized DHCP option code. |
| Option value |
Custom | Time offset (2) - integer | Router (3)- IPv4 | DNS (6) - IPv4 | Domain name (15) - string | NTP server (43) - IPv4; default: empty |
Value that will be set for selected option. |
DHCP Server: IPv6 Settings
Refer to the table below for information on the IPv6 Settings section.
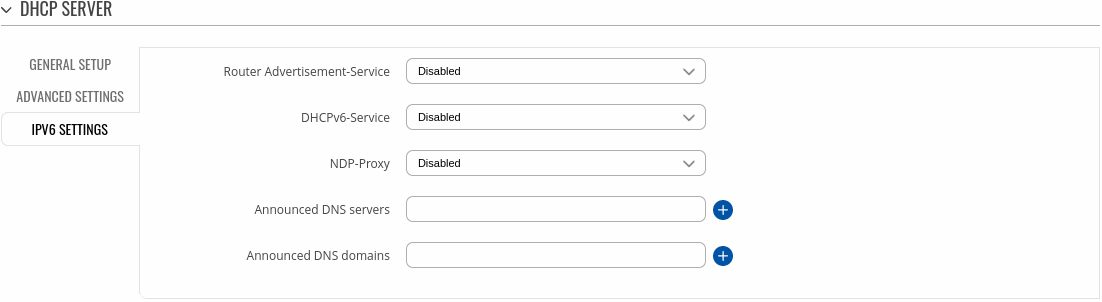
| Field |
Value |
Description |
| Router Advertisement Service |
Disabled | Relay mode | Server mode | Hybrid mode; default: Disabled |
Specifies whether router advertisements should be enabled (server mode), relayed or disabled. |
| DHCPv6 Service |
Disabled | Relay mode | Server mode | Hybrid mode; default: Disabled |
Specifies whether DHCPv6 server should be enabled (server), relayed (relay) or disabled (disabled). |
| NDP Proxy |
Disabled | Relay mode | Hybrid mode; default: Disabled |
Specifies whether NDP should be relayed or disabled. |
| Announced DNS server |
ip; default: none |
Supplements DHCP-assigned DNS server entries with ones specified in this field. |
| Announced DNS domains |
ip; default: none |
DNS domain handed out to DHCP clients. |
* When an interface is set to act as a DHCP Relay, it redirects all received DHCP request messages to another specified DHCP server:
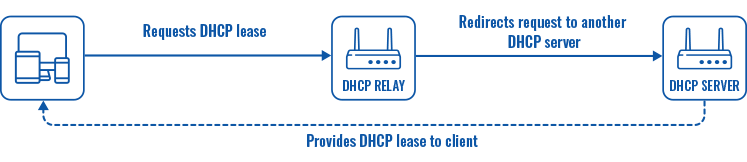
![]() global IPv6 prefix assignment addresses will be displayed.
global IPv6 prefix assignment addresses will be displayed.
















