|
|
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| ==Summary==
| | {{Template: Networking_rut_manual_load_balancing |
| | | <!------------------------DEVICE-----------------------> |
| Load balancing lets users create rules that divide traffic between different interfaces. This chapter is an Overview of the Load Balancing function in RUT routers.
| | | name = RUT240 |
| | | | series = RUT2XX |
| ==Policies==
| | }} |
| | |
| The '''Policies''' section contains Load Balancing policies. One default configuration named '''Balanced''' is already in place. You can edit this default policy or create a new custom one.
| |
| | |
| | |
| [[Image:Network load balancing policies.PNG|border]]
| |
| | |
| | |
| To configure a Policy, click the '''Edit''' button located next to it, after which you will be redirected to the Configuration window.
| |
| | |
| | |
| [[Image:Network load balancing policies configuration.PNG|border]]
| |
| | |
| | |
| As you can see from the image above, the configuration is very simple. You can assign ratio values to WAN interfaces. The ratio values represent a percentage of load that will go through an interface. For example, in the default configuration 3 parts of traffic will go through the Mobile interface and 2 parts will go through the Wired interface, which means roughly 60% (3/5) of data will be transferred through Mobile, 40% (2/5) through Wired. If the ratios would be different, say Mobile: 5, Wired: 10, then 33% (5/15) of data would be transferred through Mobile, and 66% (10/15) would go through Wired.
| |
| | |
| ==Rule==
| |
| | |
| The '''Rule''' section contains '''Load Balancing''' rules. One default rule named default_rule is already in place. You can edit it or create a new custom one.
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Networking rut manual load balancing rule.png|border]]
| |
| | |
| If you want to add a new rule, simply write a name, press '''Add''' button and then you will be redirected to the '''Configuration window'''. In order to configure an existing rule, click the '''Edit''' button located next to it, after which you will be redirected to the '''Configuration window'''.
| |
| | |
| [[Image:Networking rut manual load balancing rule edit.png|border]]
| |
| | |
| <table class="nd-mantable"> | |
| <tr>
| |
| <th>Field name</th>
| |
| <th>Value</th>
| |
| <th>Description</th>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Source address</td>
| |
| <td>Default: '''""'''</td>
| |
| <td>IP address from which data will be transmitted</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Source port</td>
| |
| <td>Default: '''""'''</td>
| |
| <td>Port that will be used for transmission</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Destination address</td>
| |
| <td>Default: '''0.0.0.0/0'''</td>
| |
| <td>Matches outgoing traffic to this IP or range of IPs only</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Destination port</td>
| |
| <td>Default: '''""'''</td>
| |
| <td>Port that will be used for transmission at the destination</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Protocol</td>
| |
| <td>Default: '''all'''</td>
| |
| <td>Specifies to which protocol the rule should apply. All vailable options are presented in the table below</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>Policy assigned</td>
| |
| <td>Default: '''balanced'''</td>
| |
| <td>Defines to which policy the rule should be assigned</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| | |
| </table>
| |
| | |
| Protocol options:
| |
| | |
| <table class="nd-othertables">
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <th width="250">Option name</th>
| |
| <th width="250">Port</th>
| |
| <th width="250">Protocol</th>
| |
| <th width="400">Description</th>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ip</td>
| |
| <td>0</td>
| |
| <td>IP</td>
| |
| <td>Internet protocol, pseudo protocol number</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>#hopopt</td>
| |
| <td>0</td>
| |
| <td>HOPOT</td>
| |
| <td>IPv6 Hop-by-Hop Option</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>icmp</td>
| |
| <td>1</td>
| |
| <td>ICMP</td>
| |
| <td>Internet control message protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>igmp</td>
| |
| <td>2</td>
| |
| <td>IGMP</td>
| |
| <td>Internet Group Management</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ggp</td>
| |
| <td>3</td>
| |
| <td>GGP</td>
| |
| <td>Gateway-gateway protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ipencap</td>
| |
| <td>4</td>
| |
| <td>IP-ENCAP</td>
| |
| <td>IP encapsulated in IP (officially ``IP'')</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>st</td>
| |
| <td>5</td>
| |
| <td>ST</td>
| |
| <td>ST datagram mode</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>tcp</td>
| |
| <td>6</td>
| |
| <td>TCP</td>
| |
| <td>Transmission control protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>egp</td>
| |
| <td>8</td>
| |
| <td>EGP</td>
| |
| <td>Exterior gateway protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>igp</td>
| |
| <td>9</td>
| |
| <td>IGP</td>
| |
| <td>Any private interior gateway</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>pup</td>
| |
| <td>12</td>
| |
| <td>PUP</td>
| |
| <td>PARC universal packet protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>udp</td>
| |
| <td>17</td>
| |
| <td>UDP</td>
| |
| <td>User datagram protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>hmp</td>
| |
| <td>20</td>
| |
| <td>HMP</td>
| |
| <td>Host monitoring protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>xns-idp</td>
| |
| <td>22</td>
| |
| <td>XNS-IDP</td>
| |
| <td>Xerox NS IDP</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>rdp</td>
| |
| <td>27</td>
| |
| <td>RDP</td>
| |
| <td>Reliable datagram protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>iso-tp4</td>
| |
| <td>29</td>
| |
| <td>ISO-TP4</td>
| |
| <td>ISO Transport Protocol class 4</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>xtp</td>
| |
| <td>36</td>
| |
| <td>XTP</td>
| |
| <td>Xpress Transfer Protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ddp</td>
| |
| <td>37</td>
| |
| <td>DDP</td>
| |
| <td>Datagram Delivery Protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>idpr-cmtp</td>
| |
| <td>38</td>
| |
| <td>IDPR-CMTP</td>
| |
| <td>IDPR Control Message Transport</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ipv6</td>
| |
| <td>41</td>
| |
| <td>IPv6</td>
| |
| <td>Internet Protocol, version 6</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ipv6-route</td>
| |
| <td>43</td>
| |
| <td>IPv6-Route</td>
| |
| <td>Routing Header for IPv6</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ipv6-frag</td>
| |
| <td>44</td>
| |
| <td>IPv6-Frag</td>
| |
| <td>Fragment Header for IPv6</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>idrp</td>
| |
| <td>45</td>
| |
| <td>IDRP</td>
| |
| <td>Inter-Domain Routing Protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>rsvp</td>
| |
| <td>46</td>
| |
| <td>RSVP</td>
| |
| <td>Reservation Protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>gre</td>
| |
| <td>47</td>
| |
| <td>GRE</td>
| |
| <td>General Routing Encapsulation</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>esp</td>
| |
| <td>50</td>
| |
| <td>IPSEC-ESP</td>
| |
| <td>Encap Security Payload</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ah</td>
| |
| <td>51</td>
| |
| <td>IPSEC-AH</td>
| |
| <td>Authentication Header</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>skip</td>
| |
| <td>57</td>
| |
| <td>SKIP</td>
| |
| <td>SKIP</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ipv6-icmp</td>
| |
| <td>58</td>
| |
| <td>IPv6-ICMP</td>
| |
| <td>ICMP for IPv6</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ipv6-nonxt 59</td>
| |
| <td>59</td>
| |
| <td>IPv6-NoNxt</td>
| |
| <td>No Next Header for IPv6</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ipv6-opts</td>
| |
| <td>60</td>
| |
| <td>IPv6-Opts</td>
| |
| <td>Destination Options for IPv6</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>rspf</td>
| |
| <td>73</td>
| |
| <td>RSPF CPHB</td>
| |
| <td>Radio Shortest Path First</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>vmtp</td>
| |
| <td>81</td>
| |
| <td>VMTP</td>
| |
| <td>Versatile Message Transport</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>eigrp</td>
| |
| <td>88</td>
| |
| <td>EIGRP</td>
| |
| <td>Enhanced Interior Routing Protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ospf</td>
| |
| <td>89</td>
| |
| <td>OSPFIGP</td>
| |
| <td>Open Shortest Path First IGP</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ax.25</td>
| |
| <td>93</td>
| |
| <td>AX.25</td>
| |
| <td>AX.25 frames</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ipip</td>
| |
| <td>94</td>
| |
| <td>IPIP</td>
| |
| <td>IP-within-IP Encapsulation Protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>etherip</td>
| |
| <td>97</td>
| |
| <td>ETHERIP</td>
| |
| <td>Ethernet-within-IP Encapsulation</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>encap</td>
| |
| <td>98</td>
| |
| <td>ENCAP</td>
| |
| <td>Yet Another IP encapsulation</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>#</td>
| |
| <td>99</td>
| |
| <td>-</td>
| |
| <td>Any private encryption scheme</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>pim</td>
| |
| <td>103</td>
| |
| <td>PIM</td>
| |
| <td>Protocol Independent Multicast</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>ipcomp</td>
| |
| <td>108</td>
| |
| <td>IPCOMP</td>
| |
| <td>IP Payload Compression Protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>vrrp</td>
| |
| <td>112</td>
| |
| <td>VRRP</td>
| |
| <td>Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>l2tp</td>
| |
| <td>115</td>
| |
| <td>L2TP</td>
| |
| <td>Layer Two Tunneling Protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>isis</td>
| |
| <td>124</td>
| |
| <td>ISIS</td>
| |
| <td>IS-IS over IPv4</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>sctp</td>
| |
| <td>132</td>
| |
| <td>SCTP</td>
| |
| <td>Stream Control Transmission Protocol</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| <tr>
| |
| <td>fc</td>
| |
| <td>133</td>
| |
| <td>FC</td>
| |
| <td>Fibre Channel</td>
| |
| </tr>
| |
| | |
| </table>
| |
| | |
| [[Category:RUT240 WebUI]]
| |
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version RUT2XX_R_00.01.14.7.
Summary
Load Balancing provides the possibility create policies and rules that divide traffic between different interfaces.
This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the Load Balancing page for RUT240 devices.
Policies
The Policies section contains Load Balancing policies. One default policy named Balanced is already in place. You can edit this default policy or create a new custom policy.
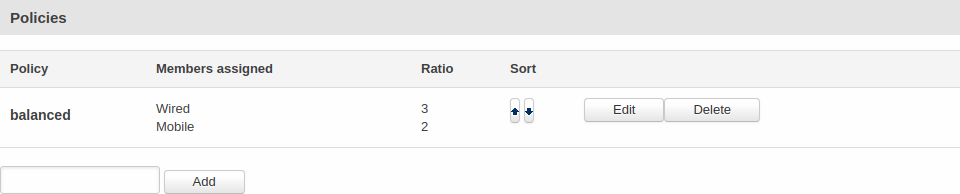
To configure a Policy, click the Edit button located next to it, after which you will be redirected to the Configuration window.
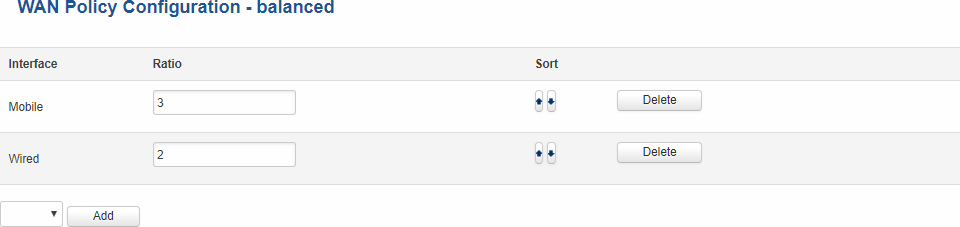
As you can see from the image above, the configuration is very simple. You can assign
ratio values to WAN interfaces. The ratio values represent a percentage of load that
will go through an interface. For example, in the default configuration 3 parts of
traffic will go through the Mobile interface and 2 parts will go through the Wired
interface, which means roughly 60% (3/5) of data will be transferred through Mobile,
40% (2/5) through Wired. If the ratios would be different, say Mobile: 5, Wired: 10, then
33% (5/15) of data would be transferred through Mobile, and 66% (10/15) would go through Wired.
Rules
The Rules section contains Load Balancing rules. One default rule named
default_rule is already in place. You can edit this default rule or create a new custom rule.
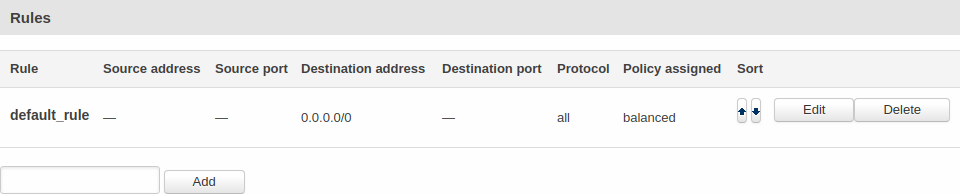
To configure a rule, click the Edit button located next to it, after which you will be redirected to the Configuration window.
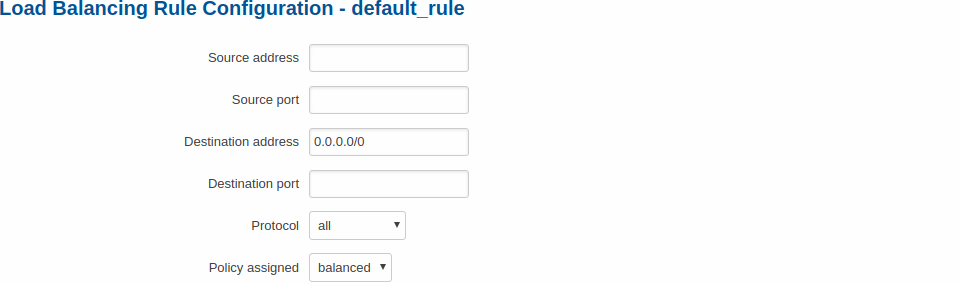
| field name |
value |
description |
| Source address |
ip; Default: none |
Source IP address. Can be specified in CIDR notation (eg "192.168.1.0/24" without quotes). |
| Source port |
number; Default: none |
Source port number. May be entered as a single or multiple ports (eg "21" or "80,443" without quotes). |
| Destination address |
ip; Default: 0.0.0.0/0 |
Destination IP address. Can be specified in CIDR notation (eg "192.168.1.0/24" without quotes). |
| Destination port |
number; Default: none |
Destination port number. May be entered as a single or multiple ports (eg "21" or "80,443" without quotes). |
| Protocol |
all | ip | #hopopt | icmp | igmp | ggp | ipencap | st | tcp | egp | igp | pup | udp | hmp | xns | rdp | iso | xtp | ddp | idpr | ipv6 | ipv6 | ipv6 | idrp | rsvp | gre | esp | ah | skip | ipv6 | ipv6 | ipv6 | rspf | vmtp | eigrp | ospf | ax | ipip | etherip | encap | pim | ipcomp | vrrp | l2tp | isis | sctp | fc; Default: all |
Which protocol to use. |
| Policy assigned |
policies; Default: balanced |
Policy to use for this rule. |




