Template:Networking rutos manual usb tools: Difference between revisions
| (46 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: | {{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | ||
| | | series = {{{series}}} | ||
| series | | name = {{{name}}} | ||
| fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
}} | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT9 |<br><i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} USB Tools (legacy WebUI)|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT9XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i>|}} | |||
==Summary== | |||
The <b>USB Tools</b> page is used to manage services related to the device's USB connector. | |||
This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the USB Tools page in {{{name}}} devices. | |||
{{Template:Networking_rutos_manual_basic_advanced_webui_disclaimer | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
}} | |||
==General== | |||
The <b>General</b> section is used to manage global USB settings. It consists of two subsections: | |||
===USB Mount Settings=== | |||
---- | |||
The <b>USB Mount Settings</b> section is used to set the transfer type (synchronous or asynchronous) for the USB device. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_general_usb_mount_settings.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
== | Synchronous ensures that all changes to the according filesystem are immediately flushed to disk. <b><u>Enabling this will drastically lower the life expectancy of your USB device.</u></b> | ||
===Mounted File Systems=== | |||
---- | |||
The <b>Mounted File Systems</b> list displays USB mass storage devices (MSD) currently attached to this device. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_general_mounted_file_systems_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | |||
<tr> | |||
<th>Field</th> | |||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Device</td> | |||
<td>filepath; default: <b>/dev/sd*</b></td> | |||
<td>The filesystem of the attached USB MSD.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Mount Point</td> | |||
<td>filepath; default: <b>/mnt/sd*</b></td> | |||
<td>The root directory of the mounted filesystem.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Available</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Displays available storage information for a mounted USB MSD.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Used</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Displays used storage information for a mounted USB MSD.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>In Use</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Indicates whether a USB MSD is currently in use by some device service or not.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
The <b>Format</b> button can be used to format the attached device, and the <b>Unmount</b> button next to each entry in the list is used to unmount an attached USB device. Please make sure to unmount a USB device before physically detaching it from the {{{name}}}. | |||
The <b> | The <b>Refresh</b> is used to refresh the information in the Mounted File Systems list. If you attach a new USB device and cannot see it in the list, try clicking the 'Refresh' button. | ||
'''Note:''' Usb with NTFS partition is supported in read-only mode. | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{printer}}}|0|| | |||
==Printer Server== | ==Printer Server== | ||
The <b>Printer Server</b> feature provides the possibility to configure access to a printer that is connected to the USB port of the device. The 'Add' button lets you add and manage additional printers. To configure a printer instance, click the Edit button located next to it: | The <b>Printer Server</b> feature provides the possibility to configure access to a printer that is connected to the USB port of the device. After the printer is connected to the device's USB port and configured, it can be utilized by users in the local network (LAN, WiFi) or remotely. | ||
The 'Add' button lets you add and manage additional printers. To configure a printer instance, click the Edit button located next to it: | |||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_printer_server_printer_server.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 92: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>off | <td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>Turns printer support on or off.</td> | <td>Turns USB printer support on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Device</td> | <td>Device</td> | ||
<td> | <td>filepath; default: <b>/dev/usb/lp0</b></td> | ||
<td>Printer's device file.</td> | <td>Printer's device file.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 107: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Bidirectional mode</td> | <td>Bidirectional mode</td> | ||
<td>off | <td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>on</b></td> | ||
<td>Turns bidirectional mode on or off.</td> | <td>Turns bidirectional mode on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|RUTM||For step-by-step instructions on how to use a printer with {{{name}}}, <b>[[How to set up a USB printer (Windows, {{{name}}})|click here]].</b>|}} | |||
}} | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{shares}}}|0|| | |||
==Network Shares== | |||
The <b>Network Shares</b> section is used to manage Network-attached storage (NAS) such as USB drives and hard drives. The {{{name}}} device supports the following file system architectures: | |||
<ul> | |||
<li>FAT</li> | |||
<li>FAT32</li> | |||
<li>exFAT</li> | |||
<li>NTFS</li> | |||
<li>ext2</li> | |||
<li>ext3</li> | |||
<li>ext4</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
{{#switch:{{{series}}} | |||
|#default=|RUTX|RUTM|RUTC= | |||
<u><b>Note:</b> Network Shares is additional software that can be installed from the <b>System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]]</b> page.</u>}} | |||
===General Settings=== | |||
---- | |||
The <b>General</b> section is used to set up <b>Samba</b> - a software solution for using the Server Message Block (SMB) networking protocol, which provides shared file access between nodes on a computer network. Refer to the figures and table below for more information about Samba configuration. | |||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_network_shares_general_samba_general_settings_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th>Field</th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns Samba on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Hostname</td> | |||
<td> | <td>string; default: <b>Router_share</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Name of the Samba server.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Description</td> | |||
<td> | <td>string; default: <b>Router share</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Short description about the Same server.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Workgroup</td> | |||
<td> | <td>string; default: <b>WORKGROUP</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Name of the server's workgroup.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Share home-directories</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>on</b></td> | |||
<td>Allows system users to reach their home directories via network shares.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Interfaces</td> | |||
<td> | <td>lan; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Bind samba server to specified interfaces </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Insert custom configuration to config</td> | |||
<td> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Insert custom line to configuration file.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
=== | ===Shared Directories=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
<b> | The <b>Shared Directories</b> section is used to configure access to the device's files and directories, including USB storage drives. The list of Shared Directories is empty by default; click the 'Add' button in order to create a new configuration: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_network_shares_general_shared_directories_add_button_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
The newly added Shared Directory configuration should look similar to this: | |||
The | |||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_network_shares_general_shared_directories_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th>Field</th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th>Value</th> | |||
<th>Description</th> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Name</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | |||
<td>Name of a shared directory.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Path</td> | |||
<td> | <td>filepath; default: <b>No mount point</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Path to a shared directory. To share an entire drive, choose an automatically generated path from this drop-down box (for example, /mnt/sda1). To share a specific directory on the drive, specify the full path to that directory (for example, /mnt/sda1/shared/video).</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Allowed users</td> | |||
<td> | <td>samba user(s); default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Samba user(s) that are permitted to access a Shared Directory. Users can be created from the Users menu tab.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Read-only</td> | |||
<td> | <td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Makes a Shared Directory read-only, which means the directory can only be accessed to view and read files (not write).</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Browseable</td> | |||
<td> | <td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>on</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Makes a Shared Directory browsable; i.e., visible in shared directory network discovery.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Allow guests</td> | |||
<td>off {{!}} on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns guest access on or off. Guest access allows anonymous connections to a Shared Directory.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Actions</td> | |||
<td> | <td>Delete; default: <b>Delete</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Deletes a Shared Directory configuration.</td> | ||
<td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
To connect to the router's SAMBA server from Windows, specify the address in this format: | |||
\\smb_server_address\share_name | |||
Replace <i>smb_server_address</i> with the IP address of this device or SAMBA share hostname; replace <i>share_name</i> with the name of the "share" (as specified in the 'Name' field). For example: | |||
<i> | |||
\\192.168.1.1\my_share | |||
\\Router_share\johns_files | |||
</i> | |||
=== | ===Users=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
The <b> | The <b>Users</b> section is used to create Samba users that can be granted access to Shared Directories. To add a new user, enter a custom username, password and click the 'Add' button. | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_network_shares_users_add_button_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
The newly added User should appear in the Users list. To change the password of a Samba User, click the 'Edit' button located next to it: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_network_shares_users_edit_button_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
This will redirect you to the Settings page for that User which should look similar to this: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_network_shares_users_user_settings_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
}} | |||
==DLNA== | |||
The <b>Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA)</b> standard provides the possibility to stream media files from local storage to DLNA-capable devices such as computers, Smart TVs, tablets, etc. | |||
This page is used to configure the DLNA service on the device. When the DLNA service is enabled, the device listens for incoming connections on the specified network interface and port number. Clients connecting to that port number on that interface will be granted access to the media files residing in the specified directories. | |||
DLNA devices use Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) to discover and communicate with each other on a network. To access the DLNA server hosted on this device you will need a DLNA-capable application. If you're using your phone or other mobile device, simply search for DLNA in the device's application store. On Linux and Windows computers you can use applications capable of playing network media streams (such as VLC). Smart TVs and similar devices may have DLNA support built-in by default. | |||
File format types supported by the DLNA service on this device: | |||
<ul> | |||
<li>Audio - WMA, WAV, MP3, FLAC</li> | |||
<li>Image - JPEG</li> | |||
<li>Video - WMV, MTS, MP4, MKV, MOV</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<u><b>Note:</b> DLNA is additional software that can be installed from the <b>System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]]</b> page.</u> | |||
[[File: | ===General Settings=== | ||
---- | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlna_general_settings_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 199: | Line 287: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td> | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns the DLNA service on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Port</td> | <td>Port</td> | ||
<td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b> | <td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b>8200</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>DLNA service listening port.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Friendly name</td> | |||
<td>string; default: <b>Teltonika DLNA Server</b></td> | |||
<td>The name of this server as it will be displayed to clients.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Root container</td> | |||
<td>Standard container | Browse directory | Music | Video | Pictures; default: <b>Standard container</b></td> | |||
<td>Specifies which type of files will be made available in DLNA file sharing. | |||
<ul> | |||
<li><b>Standard container</b> - allows browsing the shared media directory but also organizes files by type (music, video, pictures).</li> | |||
<li><b>Browse directory</b> - allows browsing the shared media directory .</li> | |||
<li><b>Music, Video, Pictures</b> - only shares the files of the specified type.</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Media directories</td> | |||
<td>filepath(s); default: <b>/mnt</b></td> | |||
<td>A list of directories that will be scanned by the DLNA service and made available to clients. You can also specify what types of files should be displayed from the directy. Use 'A' for audio, 'V' for video, 'P' for images followed by a comma and the path to the directory. For example: | |||
<ul> | |||
<li><i>A,/mnt</i> - share only audio files from the <i>/mnt/sda1</i> directory.</li> | |||
<li><i>V,/mnt</i> - share only video files from the <i>/mnt/sda1</i> directory.</li> | |||
<li><i>P,/mnt</i> - share only image files from the <i>/mnt/sda1</i> directory.</li> | |||
</ul>Click the plus symbol to add more directories. | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Album art names</td> | |||
<td>filename(s); default: <b>Album.jpg</b></td> | |||
<td>Name of the file(s) to check when searching for album art images. Click the plus symbol to specify more file names.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
=== | ===Advanced Settings=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_dlna_advanced_settings_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
[[File: | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 243: | Line 341: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Interfaces</td> | ||
<td> | <td>network interface; default: <b>br-lan</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Network interface(s) on which this DLNA server will be hosted.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Enable notify</td> | ||
<td> | <td>off | on; default: <b>on</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns inotify on or off. Inotify is a Linux kernel subsystem that notices changes to the filesystem and reports on these changes to applications, in this case, the DLNA service.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable TIVO</td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Turn support for streaming .jpg and .mp3 files to a TiVo supporting HMO on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Strict to DLNA standard</td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Set this to strictly adhere to DLNA standards. Turning this on will allow server-side downscaling of very large JPEG images, which may hurt JPEG serving performance on (at least) Sony DLNA products.</td> | |||
<td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Notify interval</td> | |||
<td>integer; default: <b>900</b></td> | |||
<td>Notify interval in seconds.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]] | [[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:40, 4 October 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
The USB Tools page is used to manage services related to the device's USB connector.
This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the USB Tools page in {{{name}}} devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
General
The General section is used to manage global USB settings. It consists of two subsections:
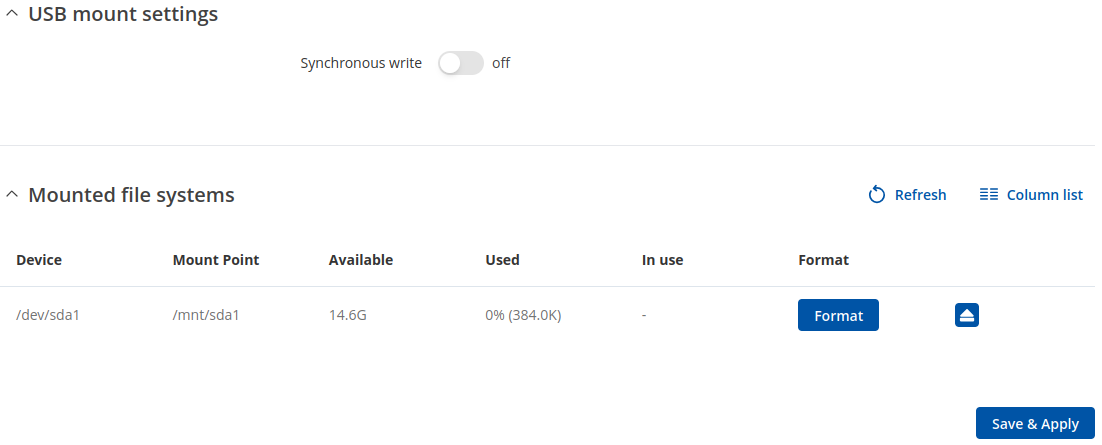
USB Mount Settings
The USB Mount Settings section is used to set the transfer type (synchronous or asynchronous) for the USB device.
Synchronous ensures that all changes to the according filesystem are immediately flushed to disk. Enabling this will drastically lower the life expectancy of your USB device.
Mounted File Systems
The Mounted File Systems list displays USB mass storage devices (MSD) currently attached to this device.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Device | filepath; default: /dev/sd* | The filesystem of the attached USB MSD. |
| Mount Point | filepath; default: /mnt/sd* | The root directory of the mounted filesystem. |
| Available | string; default: none | Displays available storage information for a mounted USB MSD. |
| Used | string; default: none | Displays used storage information for a mounted USB MSD. |
| In Use | string; default: none | Indicates whether a USB MSD is currently in use by some device service or not. |
The Format button can be used to format the attached device, and the Unmount button next to each entry in the list is used to unmount an attached USB device. Please make sure to unmount a USB device before physically detaching it from the {{{name}}}.
The Refresh is used to refresh the information in the Mounted File Systems list. If you attach a new USB device and cannot see it in the list, try clicking the 'Refresh' button.
Note: Usb with NTFS partition is supported in read-only mode.
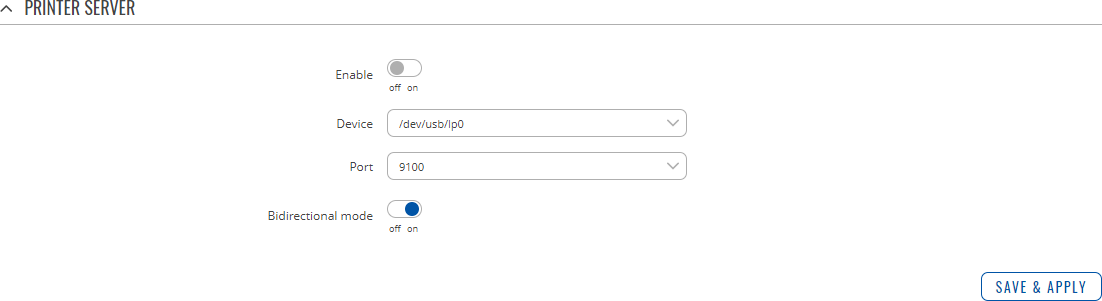
Printer Server
The Printer Server feature provides the possibility to configure access to a printer that is connected to the USB port of the device. After the printer is connected to the device's USB port and configured, it can be utilized by users in the local network (LAN, WiFi) or remotely.
The 'Add' button lets you add and manage additional printers. To configure a printer instance, click the Edit button located next to it:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns USB printer support on or off. |
| Device | filepath; default: /dev/usb/lp0 | Printer's device file. |
| Port | integer [9100..9109]; default: 9100 | Printer's TCP port. |
| Bidirectional mode | off | on; default: on | Turns bidirectional mode on or off. |
For step-by-step instructions on how to use a printer with {{{name}}}, [[How to set up a USB printer (Windows, {{{name}}})|click here]].
The Network Shares section is used to manage Network-attached storage (NAS) such as USB drives and hard drives. The {{{name}}} device supports the following file system architectures:
- FAT
- FAT32
- exFAT
- NTFS
- ext2
- ext3
- ext4
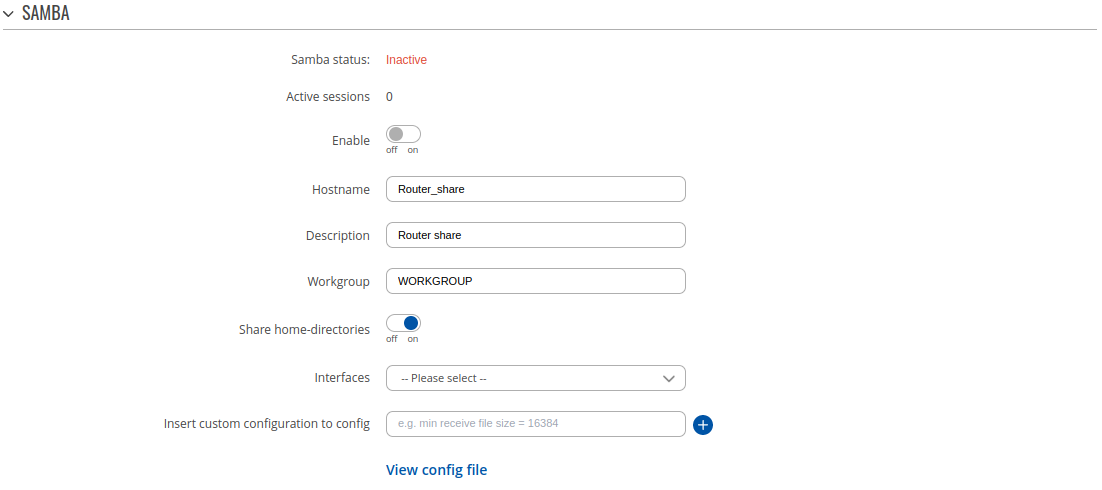
General Settings
The General section is used to set up Samba - a software solution for using the Server Message Block (SMB) networking protocol, which provides shared file access between nodes on a computer network. Refer to the figures and table below for more information about Samba configuration.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns Samba on or off. |
| Hostname | string; default: Router_share | Name of the Samba server. |
| Description | string; default: Router share | Short description about the Same server. |
| Workgroup | string; default: WORKGROUP | Name of the server's workgroup. |
| Share home-directories | off | on; default: on | Allows system users to reach their home directories via network shares. |
| Interfaces | lan; default: none | Bind samba server to specified interfaces |
| Insert custom configuration to config | string; default: none | Insert custom line to configuration file. |
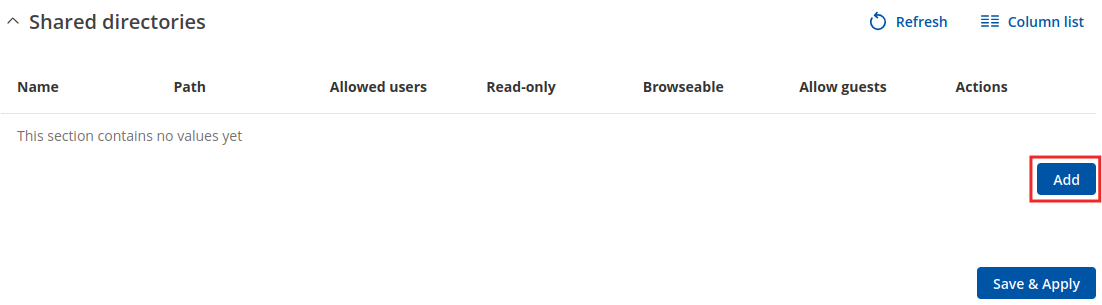
The Shared Directories section is used to configure access to the device's files and directories, including USB storage drives. The list of Shared Directories is empty by default; click the 'Add' button in order to create a new configuration:
The newly added Shared Directory configuration should look similar to this:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: none | Name of a shared directory. |
| Path | filepath; default: No mount point | Path to a shared directory. To share an entire drive, choose an automatically generated path from this drop-down box (for example, /mnt/sda1). To share a specific directory on the drive, specify the full path to that directory (for example, /mnt/sda1/shared/video). |
| Allowed users | samba user(s); default: none | Samba user(s) that are permitted to access a Shared Directory. Users can be created from the Users menu tab. |
| Read-only | off | on; default: off | Makes a Shared Directory read-only, which means the directory can only be accessed to view and read files (not write). |
| Browseable | off | on; default: on | Makes a Shared Directory browsable; i.e., visible in shared directory network discovery. |
| Allow guests | off | on; default: off | Turns guest access on or off. Guest access allows anonymous connections to a Shared Directory. |
| Actions | Delete; default: Delete | Deletes a Shared Directory configuration. |
To connect to the router's SAMBA server from Windows, specify the address in this format:
\\smb_server_address\share_name
Replace smb_server_address with the IP address of this device or SAMBA share hostname; replace share_name with the name of the "share" (as specified in the 'Name' field). For example:
\\192.168.1.1\my_share \\Router_share\johns_files
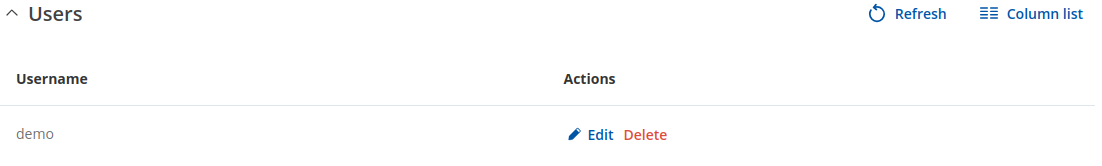
Users
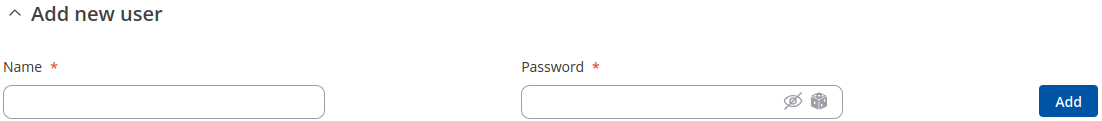
The Users section is used to create Samba users that can be granted access to Shared Directories. To add a new user, enter a custom username, password and click the 'Add' button.
The newly added User should appear in the Users list. To change the password of a Samba User, click the 'Edit' button located next to it:
This will redirect you to the Settings page for that User which should look similar to this:
DLNA
The Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA) standard provides the possibility to stream media files from local storage to DLNA-capable devices such as computers, Smart TVs, tablets, etc.
This page is used to configure the DLNA service on the device. When the DLNA service is enabled, the device listens for incoming connections on the specified network interface and port number. Clients connecting to that port number on that interface will be granted access to the media files residing in the specified directories.
DLNA devices use Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) to discover and communicate with each other on a network. To access the DLNA server hosted on this device you will need a DLNA-capable application. If you're using your phone or other mobile device, simply search for DLNA in the device's application store. On Linux and Windows computers you can use applications capable of playing network media streams (such as VLC). Smart TVs and similar devices may have DLNA support built-in by default.
File format types supported by the DLNA service on this device:
- Audio - WMA, WAV, MP3, FLAC
- Image - JPEG
- Video - WMV, MTS, MP4, MKV, MOV
Note: DLNA is additional software that can be installed from the System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]] page.
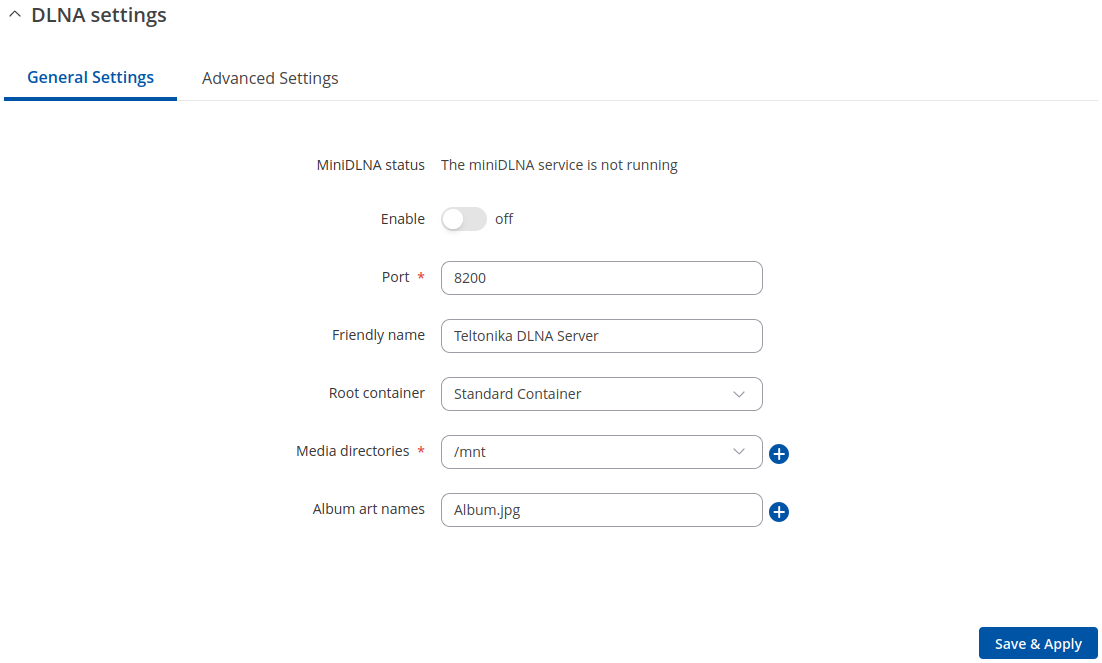
General Settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns the DLNA service on or off. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 8200 | DLNA service listening port. |
| Friendly name | string; default: Teltonika DLNA Server | The name of this server as it will be displayed to clients. |
| Root container | Standard container | Browse directory | Music | Video | Pictures; default: Standard container | Specifies which type of files will be made available in DLNA file sharing.
|
| Media directories | filepath(s); default: /mnt | A list of directories that will be scanned by the DLNA service and made available to clients. You can also specify what types of files should be displayed from the directy. Use 'A' for audio, 'V' for video, 'P' for images followed by a comma and the path to the directory. For example:
|
| Album art names | filename(s); default: Album.jpg | Name of the file(s) to check when searching for album art images. Click the plus symbol to specify more file names. |
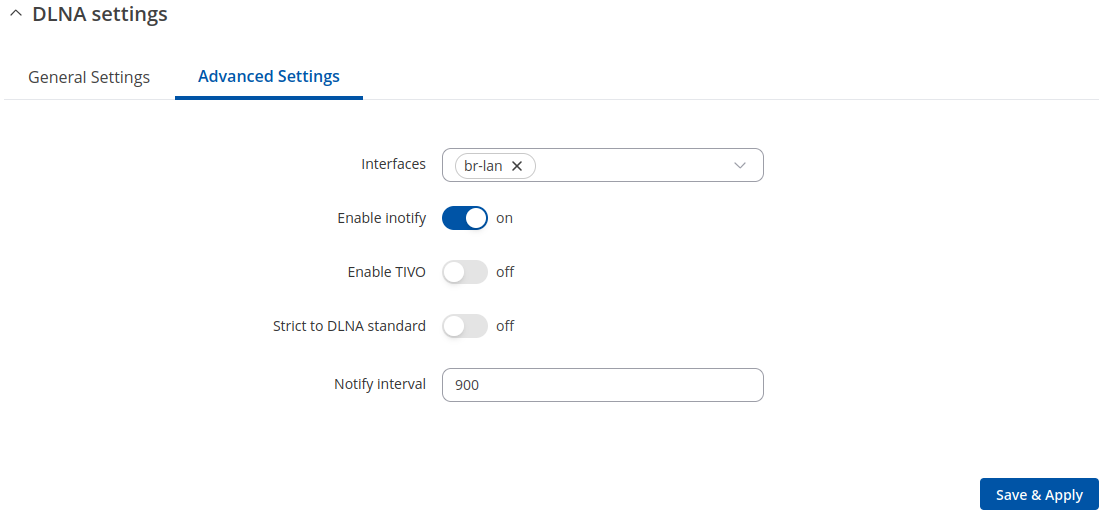
Advanced Settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Interfaces | network interface; default: br-lan | Network interface(s) on which this DLNA server will be hosted. |
| Enable notify | off | on; default: on | Turns inotify on or off. Inotify is a Linux kernel subsystem that notices changes to the filesystem and reports on these changes to applications, in this case, the DLNA service. |
| Enable TIVO | off | on; default: off | Turn support for streaming .jpg and .mp3 files to a TiVo supporting HMO on or off. |
| Strict to DLNA standard | off | on; default: off | Set this to strictly adhere to DLNA standards. Turning this on will allow server-side downscaling of very large JPEG images, which may hurt JPEG serving performance on (at least) Sony DLNA products. |
| Notify interval | integer; default: 900 | Notify interval in seconds. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]]