Template:Networking rutos manual bacnet: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==General Configuration== | ==General Configuration== | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_bacnet_general_configuration_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable BBMD</td> | <td>Enable BBMD</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off | <span style="color:blue">on</span>; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>Enables BACnet broadcast management function.</td> | <td>Enables BACnet broadcast management function.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>BBMD interface</td> | <td><span style="color:blue">BBMD port</span></td> | ||
<td>integer [1..65535]; default: <b>47809</b></td> | |||
<td>BACnet broadcast management devices port.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">BBMD interface</span></td> | |||
<td>network interface; default: <b>eth0</b></td> | <td>network interface; default: <b>eth0</b></td> | ||
<td>Specifies interface for BBMD function. IP address of this interface should be reachable from WAN.</td> | <td>Specifies interface for BBMD function. IP address of this interface should be reachable from WAN.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Allow Remote Access</td> | <td><span style="color:blue">Allow Remote Access</span></td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>Creates port forward firewall rule to make application port in LAN reachable from selected BBMD interface.</td> | <td>Creates port forward firewall rule to make application port in LAN reachable from selected BBMD interface.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Force gateway</td> | <td><span style="color:blue">Force gateway</span></td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off | <span style="color:red">on</span>; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>Adds configured gateway IP address and port to BBMD packages sent.</td> | <td>Adds configured gateway IP address and port to BBMD packages sent.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Gateway address</td> | <td><span style="color:red">Gateway address</span></td> | ||
<td>ip4; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>ip4; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Gateway IP address.</td> | <td>Gateway IP address.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Gateway port</td> | <td><span style="color:red">Gateway port</span></td> | ||
<td>integer [1..65535]; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>integer [1..65535]; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Gateway port number.</td> | <td>Gateway port number.</td> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 74: | ||
Communications in BACnet over IP (<b>BIP</b>) rely upon the protocol rules of IP and Ethernet. | Communications in BACnet over IP (<b>BIP</b>) rely upon the protocol rules of IP and Ethernet. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_bacnet_bip_configuration_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 83: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Network ID</td> | ||
<td>integer [1..65535]; default: <b>1</b></td> | |||
<td>Unique identifier for the BACnet/IP subnet within the entire BACnet internetwork.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Port</td> | |||
<td>integer [1..65535]; default: <b>47808</b></td> | <td>integer [1..65535]; default: <b>47808</b></td> | ||
<td>BIP | <td>This specifies the port number used by BACnet/IP devices for communication..</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Device</td> | |||
<td>interface; default: <b>br-lan</b></td> | |||
<td>Select the network device to be used for BACnet/IP communication.</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Actions</td> | |||
<td>-interactive button; default: <b>delete</b></td> | |||
<td>Deletes BIP configuration.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 88: | Line 108: | ||
<b>MSTP</b> is most commonly used to connect field devices to controllers / routers / control applications. The physical layer uses RS485 which allows up to 31 devices to be installed on a single network. | <b>MSTP</b> is most commonly used to connect field devices to controllers / routers / control applications. The physical layer uses RS485 which allows up to 31 devices to be installed on a single network. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_bacnet_mstp_configuration_v3.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 95: | Line 115: | ||
<th>Value</th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th>Description</th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Network ID</td> | |||
<td>integer [1..65535]; default: <b>2</b></td> | |||
<td>Unique identifier for the BACnet MSTP network.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
Revision as of 13:30, 3 October 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
BACnet is a communication protocol for building automation and control (BAC) networks that use the ASHRAE, ANSI, and ISO 16484-5 standards protocol.
This manual page provides an overview of the BACnet functionality in {{{name}}} devices.
Note: BACnet is additional software that can be installed from the System → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]] page.
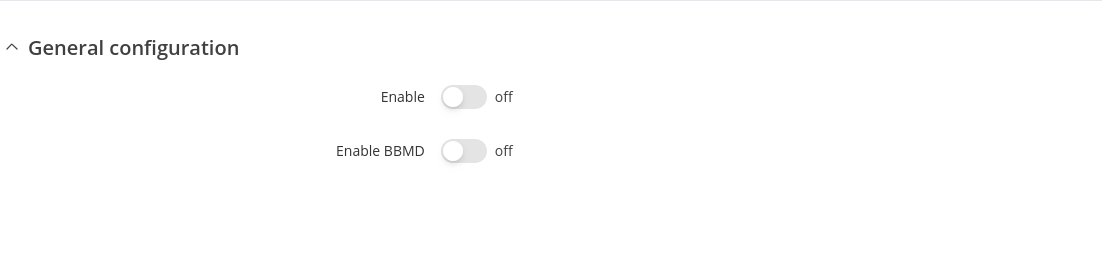
General Configuration
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enables BACnet router function. |
| Enable BBMD | off | on; default: off | Enables BACnet broadcast management function. |
| BBMD port | integer [1..65535]; default: 47809 | BACnet broadcast management devices port. |
| BBMD interface | network interface; default: eth0 | Specifies interface for BBMD function. IP address of this interface should be reachable from WAN. |
| Allow Remote Access | off | on; default: off | Creates port forward firewall rule to make application port in LAN reachable from selected BBMD interface. |
| Force gateway | off | on; default: off | Adds configured gateway IP address and port to BBMD packages sent. |
| Gateway address | ip4; default: none | Gateway IP address. |
| Gateway port | integer [1..65535]; default: none | Gateway port number. |
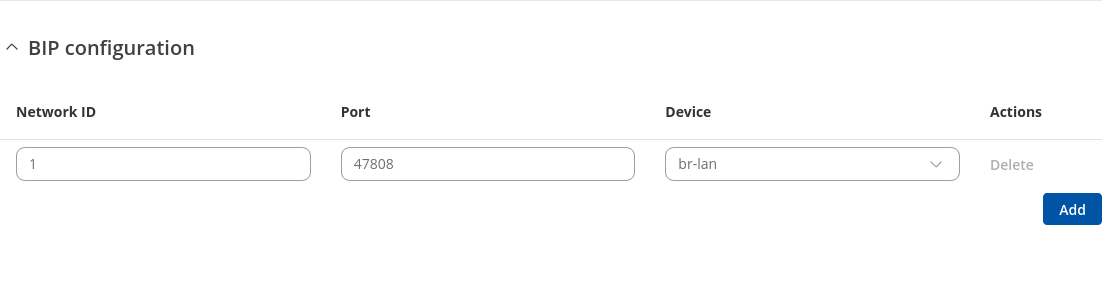
BIP Configuration
Communications in BACnet over IP (BIP) rely upon the protocol rules of IP and Ethernet.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Network ID | integer [1..65535]; default: 1 | Unique identifier for the BACnet/IP subnet within the entire BACnet internetwork. |
| Port | integer [1..65535]; default: 47808 | This specifies the port number used by BACnet/IP devices for communication.. |
| Device | interface; default: br-lan | Select the network device to be used for BACnet/IP communication. |
| Actions | -interactive button; default: delete | Deletes BIP configuration. |
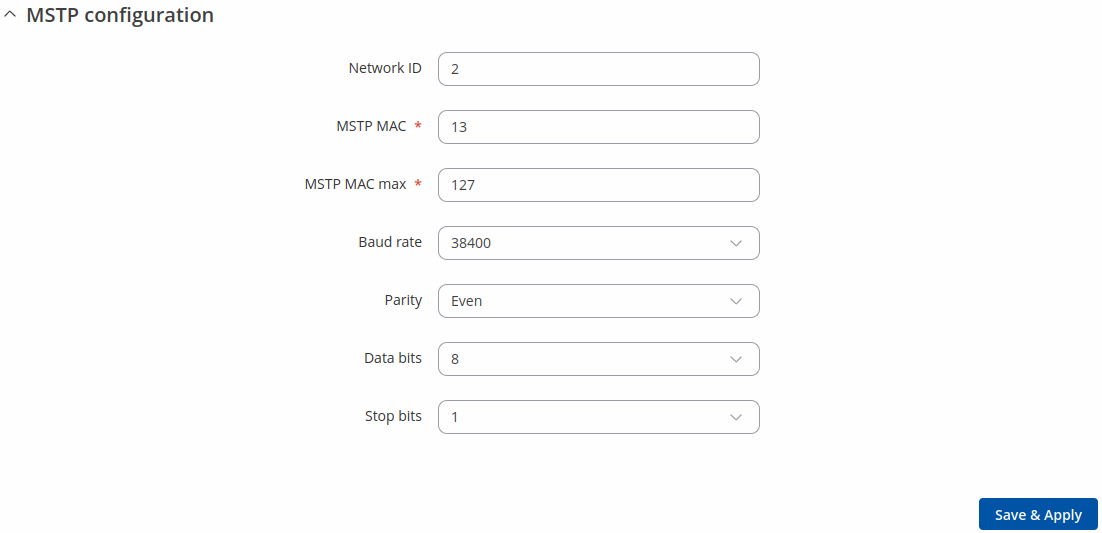
MSTP Configuration
MSTP is most commonly used to connect field devices to controllers / routers / control applications. The physical layer uses RS485 which allows up to 31 devices to be installed on a single network.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Network ID | integer [1..65535]; default: 2 | Unique identifier for the BACnet MSTP network. |
| MSTP MAC | integer [0..127]; default: 13 | Router MSTP MAC address. |
| MSTP MAC max | integer [1..127]; default: 127 | Maximum client address in the MSTP network. |
| Baud rate | 300 | 600 | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600 | 115200 | 230400; default: 38400 | Serial data transmission rate (in bits per second). |
| Parity | Even | Odd | Mark | Space | None; default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check.
|
| Data bits | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8; default: 8 | Number of data bits for each character. |
| Stop bits | 1 | 2; default: 1 | Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used.. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]]