RUT230 Mobile: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
! style="width: 250px; background: | ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | FIELD NAME | ||
! style="width: 250px; background: | ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | VALUE | ||
! style="width: | ! style="width: 579px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | DESCRIPTION | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Connection type | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Connection type | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | QMI {{!}} NCM {{!}} NDIS {{!}} PPP; Default: '''QMI''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | QMI {{!}} NCM {{!}} NDIS {{!}} PPP; Default: '''QMI''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Defines how the router's modem will establish a connection to the ISP (Internet Service Provider) | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Defines how the router's modem will establish a connection to the ISP (Internet Service Provider) | ||
'''PPP''' uses a dialling number to establish a data connection | '''PPP''' uses a dialling number to establish a data connection | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
'''NOTE''': PPP connection type exists on all RUT devices, but '''QMI''' does not. If you have a RUT device with a '''Telit''' modem, '''QMI''' will be replaced by '''NCM'''. If your RUT device contains a '''Huawei''' modem, you will see '''NDIS''' instead of '''QMI'''. '''QMI''' connection type is available on RUT devices that use a '''Quectel''' modem (which is the standard modem for most RUT devices) | '''NOTE''': PPP connection type exists on all RUT devices, but '''QMI''' does not. If you have a RUT device with a '''Telit''' modem, '''QMI''' will be replaced by '''NCM'''. If your RUT device contains a '''Huawei''' modem, you will see '''NDIS''' instead of '''QMI'''. '''QMI''' connection type is available on RUT devices that use a '''Quectel''' modem (which is the standard modem for most RUT devices) | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Mode | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Mode | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | NAT {{!}} Passthrough'''*'''; Default: '''NAT''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | NAT {{!}} Passthrough'''*'''; Default: '''NAT''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | '''NAT''' mode enables network address translation on the router | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | '''NAT''' mode enables network address translation on the router | ||
In '''Passthrough''' mode the router assigns its WAN IP address to another device. It is used instead of [[Network Address Translation]] (NAT) in order to make the router "transparent" in the communication process. | In '''Passthrough''' mode the router assigns its WAN IP address to another device. It is used instead of [[Network Address Translation]] (NAT) in order to make the router "transparent" in the communication process. | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | APN | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | APN | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | string; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | string; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | An Access Point Name (APN) is a gateway between a GSM, GPRS, 3G or 4G mobile network and another computer network | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | An Access Point Name (APN) is a gateway between a GSM, GPRS, 3G or 4G mobile network and another computer network | ||
'''NOTE''': an APN Network Identifier cannot start with any of the strings "rac", "lac", "sgsn" or "rnc", it cannot end in ".gprs" and it cannot take the value "*" | '''NOTE''': an APN Network Identifier cannot start with any of the strings "rac", "lac", "sgsn" or "rnc", it cannot end in ".gprs" and it cannot take the value "*" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | PIN number | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | PIN number | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | string; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | string; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | A personal identification number is a numeric password used to authenticate a user to a system | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | A personal identification number is a numeric password used to authenticate a user to a system | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Dialing number | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Dialing number | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | string; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | string; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | A Dialling number is used to establish a mobile PPP connection | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | A Dialling number is used to establish a mobile PPP connection | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | MTU | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | MTU | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | integer [0..1500]; Default: '''1500''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | integer [0..1500]; Default: '''1500''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) specifies the largest possible size of a data packet | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) specifies the largest possible size of a data packet | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Authentication method | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Authentication method | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | CHAP {{!}} PAP {{!}} None; Default: '''None''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | CHAP {{!}} PAP {{!}} None; Default: '''None''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | The Authentication method that your GSM carrier uses to authenticate new connections on its network | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | The Authentication method that your GSM carrier uses to authenticate new connections on its network | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Username | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Username | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | string; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | string; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | The | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | The Authentication method that your GSM carrier uses to authenticate new connections on its network | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Password | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Password | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | string; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | string; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | The password used to connect to your carrier’s network | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | The password used to connect to your carrier’s network | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Service mode | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Service mode | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | 2G only {{!}} 3G only {{!}} Automatic; Default: '''Automatic''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | 2G only {{!}} 3G only {{!}} Automatic; Default: '''Automatic''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Your service mode preference. If your local mobile network supports 2G and 3G you can specify to which type of network you wish to connect to, e.g., if you choose 2G only, the router will connect to a 2G network, so long as it is available, otherwise it will connect to a network that provides better connectivity. If you select Automatic, then the router will connect to the network that provides the best connectivity | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Your service mode preference. If your local mobile network supports 2G and 3G you can specify to which type of network you wish to connect to, e.g., if you choose 2G only, the router will connect to a 2G network, so long as it is available, otherwise it will connect to a network that provides better connectivity. If you select Automatic, then the router will connect to the network that provides the best connectivity | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Deny data roaming | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Deny data roaming | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | When enabled this function prevents the device from establishing mobile data connection while not in your home network | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | When enabled this function prevents the device from establishing mobile data connection while not in your home network | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Use IPv4 only | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Use IPv4 only | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''yes''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''yes''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | When enabled this function makes the device use only IPv4 settings when connecting to an operator | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | When enabled this function makes the device use only IPv4 settings when connecting to an operator | ||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="3" | Mobile Data On Demand | ! colspan="3" style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | <big>Mobile Data On Demand</big> | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Enable | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Enable | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Toggles Mobile Data On Demand ON or OFF. The Mobile Data On Demand function keeps the mobile data connection '''ON''' only when it is in use. | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Toggles Mobile Data On Demand ON or OFF. The Mobile Data On Demand function keeps the mobile data connection '''ON''' only when it is in use. | ||
'''NOTE:''' This function is only available whith PPP Connection type | '''NOTE:''' This function is only available whith PPP Connection type | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | No data timeout (sec) | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | No data timeout (sec) | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | integer [10..3600]; Default: '''10''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | integer [10..3600]; Default: '''10''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Mobile data connection will be terminated if no data is transferred during the timeout period specified in this field | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Mobile data connection will be terminated if no data is transferred during the timeout period specified in this field | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 09:59, 22 October 2018
Main Page > EOL Products > RUT230 > RUT230 Manual > RUT230 WebUI > RUT230 Network section > RUT230 MobileSummary
The Mobile section is used to configure SIM card parameters and mobile data limit. This chapter is an overview of RUT230 routers' Mobile section.
General
The General tab is used to configure SIM card parameters such as Service mode, Connection type, APN and more.
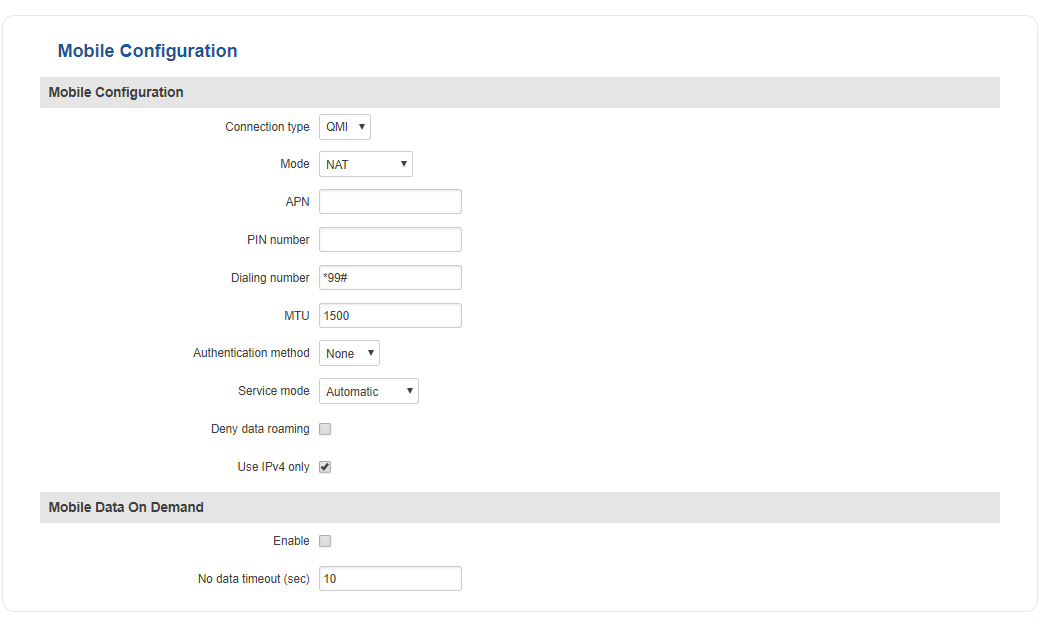
Mobile Configuration
The Mobile Configuration section is used to configure main SIM card parameters.
| FIELD NAME | VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Connection type | QMI | NCM | NDIS | PPP; Default: QMI | Defines how the router's modem will establish a connection to the ISP (Internet Service Provider)
PPP uses a dialling number to establish a data connection QMI does not use dialling or the PPP protocol to establish data connection and it is usually faster than PPP mode NOTE: PPP connection type exists on all RUT devices, but QMI does not. If you have a RUT device with a Telit modem, QMI will be replaced by NCM. If your RUT device contains a Huawei modem, you will see NDIS instead of QMI. QMI connection type is available on RUT devices that use a Quectel modem (which is the standard modem for most RUT devices) |
| Mode | NAT | Passthrough*; Default: NAT | NAT mode enables network address translation on the router
In Passthrough mode the router assigns its WAN IP address to another device. It is used instead of Network Address Translation (NAT) in order to make the router "transparent" in the communication process. |
| APN | string; Default: " " | An Access Point Name (APN) is a gateway between a GSM, GPRS, 3G or 4G mobile network and another computer network
NOTE: an APN Network Identifier cannot start with any of the strings "rac", "lac", "sgsn" or "rnc", it cannot end in ".gprs" and it cannot take the value "*" |
| PIN number | string; Default: " " | A personal identification number is a numeric password used to authenticate a user to a system |
| Dialing number | string; Default: " " | A Dialling number is used to establish a mobile PPP connection |
| MTU | integer [0..1500]; Default: 1500 | MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) specifies the largest possible size of a data packet |
| Authentication method | CHAP | PAP | None; Default: None | The Authentication method that your GSM carrier uses to authenticate new connections on its network |
| Username | string; Default: " " | The Authentication method that your GSM carrier uses to authenticate new connections on its network |
| Password | string; Default: " " | The password used to connect to your carrier’s network |
| Service mode | 2G only | 3G only | Automatic; Default: Automatic | Your service mode preference. If your local mobile network supports 2G and 3G you can specify to which type of network you wish to connect to, e.g., if you choose 2G only, the router will connect to a 2G network, so long as it is available, otherwise it will connect to a network that provides better connectivity. If you select Automatic, then the router will connect to the network that provides the best connectivity |
| Deny data roaming | yes | no; Default: no | When enabled this function prevents the device from establishing mobile data connection while not in your home network |
| Use IPv4 only | yes | no; Default: yes | When enabled this function makes the device use only IPv4 settings when connecting to an operator |
| Mobile Data On Demand | ||
| Enable | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles Mobile Data On Demand ON or OFF. The Mobile Data On Demand function keeps the mobile data connection ON only when it is in use.
NOTE: This function is only available whith PPP Connection type |
| No data timeout (sec) | integer [10..3600]; Default: 10 | Mobile data connection will be terminated if no data is transferred during the timeout period specified in this field |
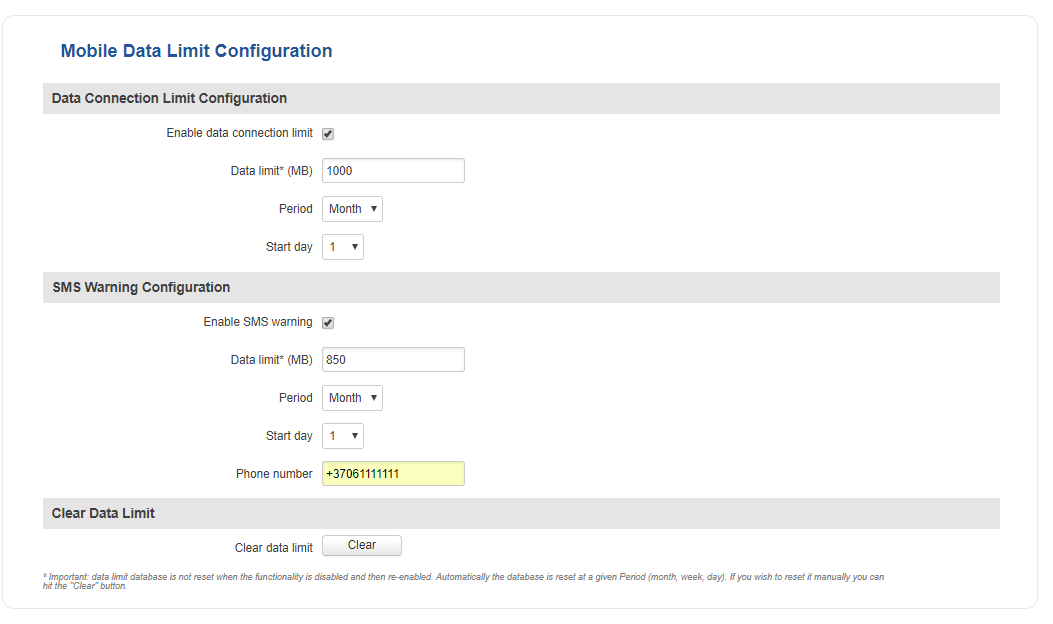
Mobile Data Limit
The Mobile Data Limit window provides you with the ability to set a data limit for your SIM card in order to protect yourself from unwanted data charges.
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data Connection Limit Configuration | ||
| Enable data connection limit | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles data limit ON or OFF |
| Data limit* (MB) | integer; Default: " " | The received data limit. After reaching the specified data limit, the router will kill your current mobile data connection |
| Period | Month | Week | Day; Default: Month | Period for which the data limit applies to |
| Start day | Start hour | day [1..31] | day [Monday..Sunday] | hour [1..24]; Default: day 1 | Data limit counting start time. For example, if the selected Period is Month and Start day is 5, every month on the fifth day the data limit counter will reset and start counting the data limit over again |
| SMS Warning Configuration | ||
| Enable SMS warning | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles SMS Warning ON or OFF. SMS Warning Configuration provides you with the ability to configure a rule that sends you an SMS message after the router reaches a specified amount of data. |
| Data limit* (MB) | integer; Default: " " | The received data limit. After reaching the specified data limit, the router will send out an SMS warning message to the specified phone number |
| Period | Month | Week | Day; Default: Month | Period for which the data limit applies to |
| Start day | Start hour | day [1..31] | day [Monday..Sunday] | hour [1..24]; Default: day 1 | Data limit counting start time. For example, if the selected Period is Month and Start day is 5, every month on the fifth day the data limit counter will reset and start counting the data limit over again |
| Phone number | phone number; Default: " " | Recipient's phone number |
*Your carrier's data usage accounting may differ. Teltonika is not liable should any accounting discrepancies occur
Clear Data Limit
The Clear Data Limit section contains only one button - the Clear data limit button, which resets the configured data limits.
Remember that the Clear data limit button doesn't clear the actual SIM used data counter, only the received data counters of the router!