RUT850 VPN: Difference between revisions
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
! style="width: 250px; background: | ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | FIELD NAME | ||
! style="width: 250px; background: | ! style="width: 250px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | VALUE | ||
! style="width: | ! style="width: 579px; border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #0054A6; background: white; color: #0054A6; text-align: left;" | DESCRIPTION | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Enable | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Enable | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no'' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Enables the OpenVPN instance | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Enables the OpenVPN instance | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | TUN/TAP | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | TUN/TAP | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | TUN (tunnel) {{!}} TAP (bridged); Default: '''TUN (tunnel)''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | TUN (tunnel) {{!}} TAP (bridged); Default: '''TUN (tunnel)''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | OpenVPN interface type. '''TUN''' is most often in typical VPN connections, however, '''TAP''' is required in some Ethernet bridging configurations | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | OpenVPN interface type. '''TUN''' is most often in typical VPN connections, however, '''TAP''' is required in some Ethernet bridging configurations | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Protocol | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Protocol | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | UDP {{!}} TCP; Default: '''UDP''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | UDP {{!}} TCP; Default: '''UDP''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | The transfer protocol used by the OpenVPN connection. '''TCP''' is connection oriented – once a connection is established, data can be sent bidirectionally. '''UDP''' is a simpler, connectionless Internet protocol. '''UDP''' is usually faster but '''TCP''' has more security features. Choose the connection protocol according to your needs. | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | The transfer protocol used by the OpenVPN connection. '''TCP''' is connection oriented – once a connection is established, data can be sent bidirectionally. '''UDP''' is a simpler, connectionless Internet protocol. '''UDP''' is usually faster but '''TCP''' has more security features. Choose the connection protocol according to your needs. | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Port | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Port | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | integer [0..65535]; Default: '''1194''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | integer [0..65535]; Default: '''1194''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | TCP/UDP Port number for both local and remote endpoints (make sure that the chosen port is allowed by firewall) | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | TCP/UDP Port number for both local and remote endpoints (make sure that the chosen port is allowed by firewall) | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | LZO | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | LZO | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | With LZO compression, your VPN connection will generate less network traffic. However, enabling this causes a higher CPU load. Use it carefully with a high traffic rate or low CPU resources | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | With LZO compression, your VPN connection will generate less network traffic. However, enabling this causes a higher CPU load. Use it carefully with a high traffic rate or low CPU resources | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Encryption | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Encryption | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | DES-CBC 64 {{!}} RC2-CBC 128 {{!}} DES-EDE-CBC 128 {{!}} DES-EDE3-CBC 192 {{!}} DESX-CBC 192 {{!}} BF-CBC 128 {{!}} RC2-40-CBC 40 {{!}} CAST5-CBC 128 {{!}} RC2-40CBC 40 {{!}} CAST5-CBC 128 {{!}} RC2-64-CBC 64{{!}} AES-128-CBC 128 {{!}} AES-192-CBC 192 {{!}} AES-256-CBC 256 {{!}} none; Default: '''BF-CBC 128''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | DES-CBC 64 {{!}} RC2-CBC 128 {{!}} DES-EDE-CBC 128 {{!}} DES-EDE3-CBC 192 {{!}} DESX-CBC 192 {{!}} BF-CBC 128 {{!}} RC2-40-CBC 40 {{!}} CAST5-CBC 128 {{!}} RC2-40CBC 40 {{!}} CAST5-CBC 128 {{!}} RC2-64-CBC 64{{!}} AES-128-CBC 128 {{!}} AES-192-CBC 192 {{!}} AES-256-CBC 256 {{!}} none; Default: '''BF-CBC 128''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Packet encryption algorithm | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Packet encryption algorithm | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Authentication | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Authentication | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | TLS {{!}} Static Key {{!}} Password {{!}} TLS/Password; Default: '''TLS''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | TLS'''*''' {{!}} Static Key {{!}} Password {{!}} TLS/Password; Default: '''TLS''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Authentication mode, used to secure data sessions. | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Authentication mode, used to secure data sessions. | ||
'''Static key''' is a secret key used for server–client authentication. | '''Static key''' is a secret key used for server–client authentication. | ||
| Line 184: | Line 184: | ||
'''TLS/Password''' uses both TLS and Password authentication | '''TLS/Password''' uses both TLS and Password authentication | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | TLS cipher | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | TLS cipher | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | all {{!}} DHE+RSA {{!}} custom; Default: '''all''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | all {{!}} DHE+RSA {{!}} custom; Default: '''all''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Packet encryption algorithm cipher | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Packet encryption algorithm cipher | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Client to client | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Client to client | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Enables client to client communication in the Virtual network. In order for Client to client to work, the TLS Clients section most be utilized | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Enables client to client communication in the Virtual network. In order for Client to client to work, the TLS Clients section most be utilized | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Keep alive | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Keep alive | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | integer *space* integer; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | integer *space* integer; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Defines two time intervals: one is used to periodically send ICMP request to the OpenVPN server, the other defines a time window, which is used to restart the OpenVPN service, if no ICMP response is received during the window time slice. | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Defines two time intervals: one is used to periodically send ICMP request to the OpenVPN server, the other defines a time window, which is used to restart the OpenVPN service, if no ICMP response is received during the window time slice. | ||
'''Example:''' 10 60 | '''Example:''' 10 60 | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Virtual network IP address | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Virtual network IP address | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | ip; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | ip; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | IP address of the Virtual network, e.g., '''10.0.8.0''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | IP address of the Virtual network, e.g., '''10.0.8.0''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Virtual network IP netmask | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Virtual network IP netmask | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | ip; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | ip; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Subnet mask of the Virtual network | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Subnet mask of the Virtual network | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Push option | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Push option | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | string; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | string; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Push options are a way to “push” user defined routes to connecting clients’ routing tables. In the example above, the server will push the route of 192.168.1.0 network with the 255.255.255.0 netmask to connecting clients. Therefore, the client will be able to reach devices in the 192.168.1.0 network. This is useful when a client needs to reach devices located in the OpenVPN server’s LAN. | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Push options are a way to “push” user defined routes to connecting clients’ routing tables. In the example above, the server will push the route of 192.168.1.0 network with the 255.255.255.0 netmask to connecting clients. Therefore, the client will be able to reach devices in the 192.168.1.0 network. This is useful when a client needs to reach devices located in the OpenVPN server’s LAN. | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Allow duplicate certificates | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Allow duplicate certificates | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no''' | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | yes {{!}} no; Default: '''no''' | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | If checked, the server allows clients to connect with identical certificates | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | If checked, the server allows clients to connect with identical certificates | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Certificate authority | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Certificate authority | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | .ca file; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | .ca file; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Certificate authority is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Certificate authority is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Server certificate | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Server certificate | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | .crt file; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | .crt file; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Server certificate is a type of digital certificate that is used to identify the OpenVPN server | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Server certificate is a type of digital certificate that is used to identify the OpenVPN server | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Server key | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Server key | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | .key file; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | .key file; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Authenticates clients to the server | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Authenticates clients to the server | ||
|- | |- | ||
! style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | Diffie Hellman parameters | ! style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | Diffie Hellman parameters | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | .pem file; Default: " " | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | .pem file; Default: " " | ||
| style="text-align: left; vertical-align: top;" | DH parameters define how OpenSSL performs the Diffie-Hellman (DH) key-exchange. | | style="border: 1px solid white; border-bottom: 2px solid #E8E8E8; text-align: left; vertical-align: top; background: white;" | DH parameters define how OpenSSL performs the Diffie-Hellman (DH) key-exchange. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 26 October 2018
Main Page > EOL Products > RUT850 > RUT850 Manual > RUT850 WebUI > RUT850 Services section > RUT850 VPNSummary
Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a method for secure data transfer through unsafe public networks. This page is an overview of RUT850 routers' VPN service.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is an open-source software application that implements virtual private network (VPN) techniques for creating secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections in routed or bridged configurations and remote access facilities. This section is an overview of the OpenVPN section of RUT routers. For a more in depth guide refer to our OpenVPN configuration examples page.
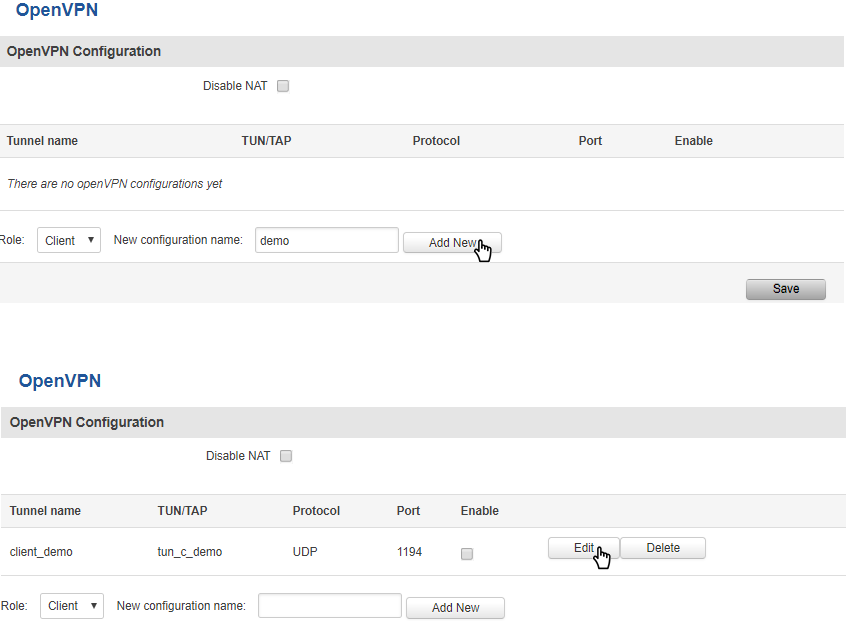
The default OpenVPN Configuration list is empty, so you have to define your own configuration to establish any sort of OpenVPN connection. OpenVPN configurations can have one of two roles: client or server. Let’s start with an OpenVPN client. To create it, enter the desired instance name in the New configuration name field, select the instance’s role from the Role list and press the Add New button.
Once you’ve added a new OpenVPN instance there is no need to press the Save button, since the Add New button both creates and saves the new instance. By default the instance will be disabled and unconfigured. In order to establish an OpenVPN connection you must Enable your instance, enter an OpenVPN server address, choose an authentication method and a few other things, all of which can be configured in the Settings window, which can reached by pressing the Edit button next to your OpenVPN instance (as shown in the figure above).
OpenVPN Client
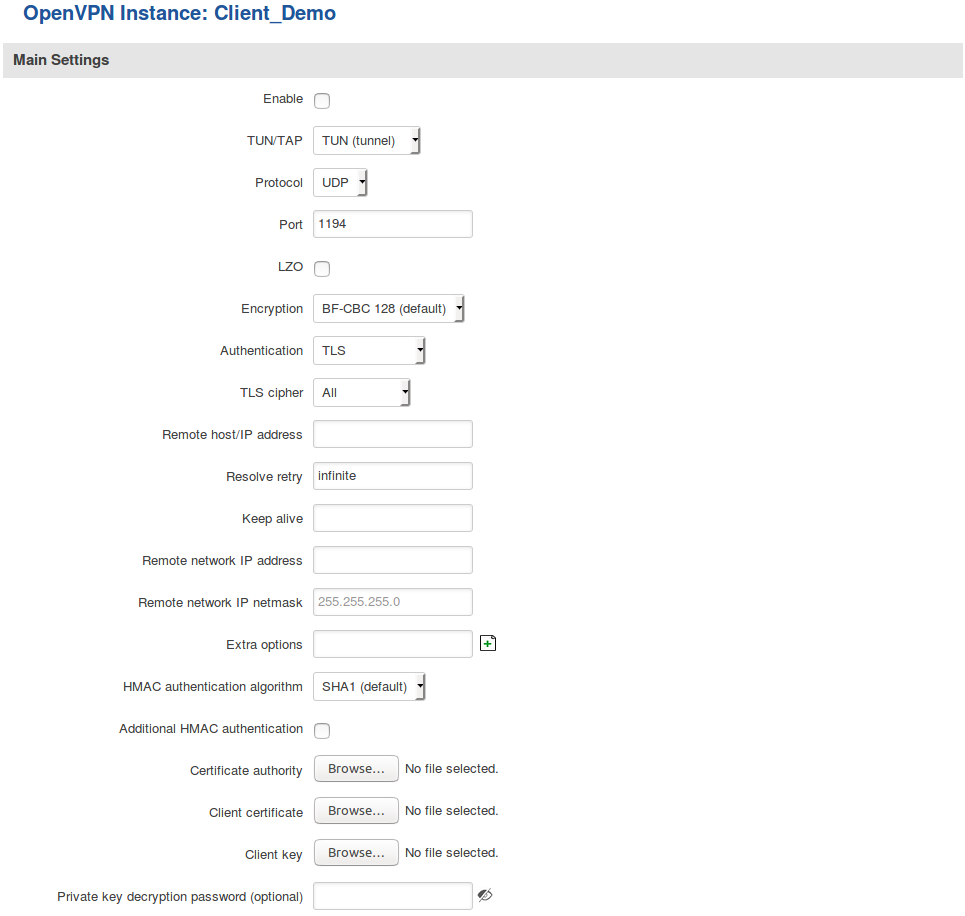
This section is overview of OpenVPN Client configuration.
The figure above is an example of a configured OpenVPN Client instance that uses the UDP protocol and TLS/Password authentication. Comprehensible explanations on how to configure each field are presented in the table below.
| FIELD NAME | VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; Default: no | Enables the OpenVPN instance |
| TUN/TAP | TUN (tunnel) | TAP (bridged); Default: TUN (tunnel) | OpenVPN interface type. TUN is most often in typical VPN connections, however, TAP is required in some Ethernet bridging configurations |
| Protocol | UDP | TCP; Default: UDP | The transfer protocol used by the OpenVPN connection. TCP is connection oriented – once a connection is established, data can be sent bidirectionally. UDP is a simpler, connectionless Internet protocol. UDP is usually faster but TCP has more security features. Choose the connection protocol according to your needs. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; Default: 1194 | TCP/UDP Port number for both local and remote endpoints (make sure that the chosen port is allowed by firewall) |
| LZO | yes | no; Default: no | With LZO compression, your VPN connection will generate less network traffic. However, enabling this causes a higher CPU load. Use it carefully with a high traffic rate or low CPU resources |
| Encryption | DES-CBC 64 | RC2-CBC 128 | DES-EDE-CBC 128 | DES-EDE3-CBC 192 | DESX-CBC 192 | BF-CBC 128 | RC2-40-CBC 40 | CAST5-CBC 128 | RC2-40CBC 40 | CAST5-CBC 128 | RC2-64-CBC 64| AES-128-CBC 128 | AES-192-CBC 192 | AES-256-CBC 256 | none; Default: BF-CBC 128 | Packet encryption algorithm |
| Authentication | TLS | Static Key | Password | TLS/Password; Default: TLS | Authentication mode, used to secure data sessions.
Static key is a secret key used for server–client authentication. TLS authentication mode uses X.509 type certificates: Certificate Authority (CA), Client certificate, Client key. All mentioned certificates can be generated using OpenVPN or Open SSL utilities on any type of host machine. Password is a simple username/password based authentication where the owner of the OpenVPN server provides the login data. TLS/Password uses both TLS and Password authentication |
| TLS cipher | all | DHE+RSA | custom; Default: all | Packet encryption algorithm cipher |
| Remote host / IP address | ip; Default: " " | IP address or hostname of an OpenVPN server |
| Resolve retry | integer | infinite; Default: infinite | Time in seconds to resolve server hostname periodically in case of first resolve failure before generating service exception |
| Keep alive | integer *space* integer; Default: " " | Defines two time intervals: one is used to periodically send ICMP request to the OpenVPN server, the other defines a time window, which is used to restart the OpenVPN service, if no ICMP response is received during the window time slice.
Example: 10 60 |
| Remote network IP address | ip; Default: " " | LAN IP address of the remote network (server) |
| Remote network IP netmask | ip; Default: " " | LAN IP subnet mask of the remote network (server) |
| Username | string; Default: " " | User name used for authentication |
| Password | string; Default: " " | Password name used for authentication |
| Extra options | string; Default: " " | Extra options to be used by the OpenVPN instance |
| HMAC authentication algorithm | none | SHA1 | SHA256 | SHA384 | SHA512; Default: SHA1 | HMAC authentication algorithm type |
| Additional HMAC authentication | yes | no; Default: no | An additional layer of HMAC authentication on top of the TLS control channel to protect against DoS attacks |
| Certificate authority | .ca file; Default: " " | Certificate authority is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate |
| Client certificate | .crt file; Default: " " | Client certificate is a type of digital certificate that is used by client systems to make authenticated requests to a remote server. Client certificates play a key role in many mutual authentication designs, providing strong assurances of a requester's identity |
| Client key | .key file; Default: " " | Authenticates the client to the server and establishes precisely who they are |
| Private key decryption password (optional) | string; Default: " " | Decrypts server private key password. Use only if server's .key file is encrypted with a password |
After setting any of these parameters press the Save button or else the changes will not be applied. Some of the selected parameters will be shown in the configuration list table. You should also be aware of the fact that the router will launch a separate OpenVPN service for every configuration entry (if it is defined as active at the time, of course) so the router has the ability to act as server and client at the same time.
OpenVPN Server
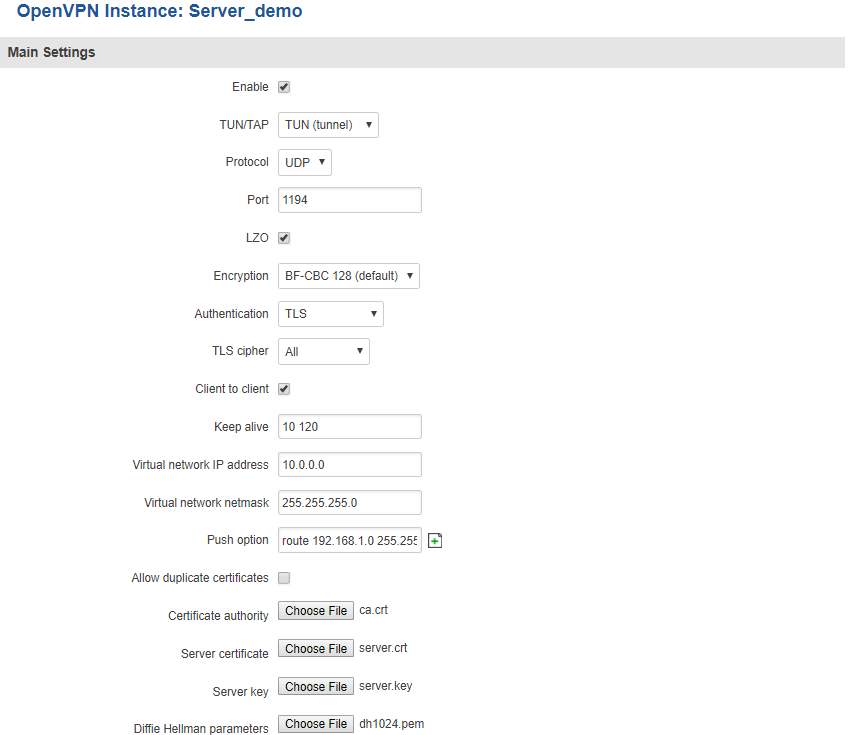
This section is overview of OpenVPN Client configuration.
The figure above is an exampled of a configured OpenVPN Server instance that uses the UDP protocol and TLS authentication. As you can see, the configuration is similar to OpenVPN Client but with a few key differences. Comprehensible explanations on how to configure each field are presented in the table below.
| FIELD NAME | VALUE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; Default: 'no | Enables the OpenVPN instance |
| TUN/TAP | TUN (tunnel) | TAP (bridged); Default: TUN (tunnel) | OpenVPN interface type. TUN is most often in typical VPN connections, however, TAP is required in some Ethernet bridging configurations |
| Protocol | UDP | TCP; Default: UDP | The transfer protocol used by the OpenVPN connection. TCP is connection oriented – once a connection is established, data can be sent bidirectionally. UDP is a simpler, connectionless Internet protocol. UDP is usually faster but TCP has more security features. Choose the connection protocol according to your needs. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; Default: 1194 | TCP/UDP Port number for both local and remote endpoints (make sure that the chosen port is allowed by firewall) |
| LZO | yes | no; Default: no | With LZO compression, your VPN connection will generate less network traffic. However, enabling this causes a higher CPU load. Use it carefully with a high traffic rate or low CPU resources |
| Encryption | DES-CBC 64 | RC2-CBC 128 | DES-EDE-CBC 128 | DES-EDE3-CBC 192 | DESX-CBC 192 | BF-CBC 128 | RC2-40-CBC 40 | CAST5-CBC 128 | RC2-40CBC 40 | CAST5-CBC 128 | RC2-64-CBC 64| AES-128-CBC 128 | AES-192-CBC 192 | AES-256-CBC 256 | none; Default: BF-CBC 128 | Packet encryption algorithm |
| Authentication | TLS* | Static Key | Password | TLS/Password; Default: TLS | Authentication mode, used to secure data sessions.
Static key is a secret key used for server–client authentication. TLS authentication mode uses X.509 type certificates: Certificate Authority (CA), Client certificate, Client key. All mentioned certificates can be generated using OpenVPN or Open SSL utilities on any type of host machine. Password is a simple username/password based authentication where the owner of the OpenVPN server provides the login data. TLS/Password uses both TLS and Password authentication |
| TLS cipher | all | DHE+RSA | custom; Default: all | Packet encryption algorithm cipher |
| Client to client | yes | no; Default: no | Enables client to client communication in the Virtual network. In order for Client to client to work, the TLS Clients section most be utilized |
| Keep alive | integer *space* integer; Default: " " | Defines two time intervals: one is used to periodically send ICMP request to the OpenVPN server, the other defines a time window, which is used to restart the OpenVPN service, if no ICMP response is received during the window time slice.
Example: 10 60 |
| Virtual network IP address | ip; Default: " " | IP address of the Virtual network, e.g., 10.0.8.0 |
| Virtual network IP netmask | ip; Default: " " | Subnet mask of the Virtual network |
| Push option | string; Default: " " | Push options are a way to “push” user defined routes to connecting clients’ routing tables. In the example above, the server will push the route of 192.168.1.0 network with the 255.255.255.0 netmask to connecting clients. Therefore, the client will be able to reach devices in the 192.168.1.0 network. This is useful when a client needs to reach devices located in the OpenVPN server’s LAN. |
| Allow duplicate certificates | yes | no; Default: no | If checked, the server allows clients to connect with identical certificates |
| Certificate authority | .ca file; Default: " " | Certificate authority is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate |
| Server certificate | .crt file; Default: " " | Server certificate is a type of digital certificate that is used to identify the OpenVPN server |
| Server key | .key file; Default: " " | Authenticates clients to the server |
| Diffie Hellman parameters | .pem file; Default: " " | DH parameters define how OpenSSL performs the Diffie-Hellman (DH) key-exchange. |
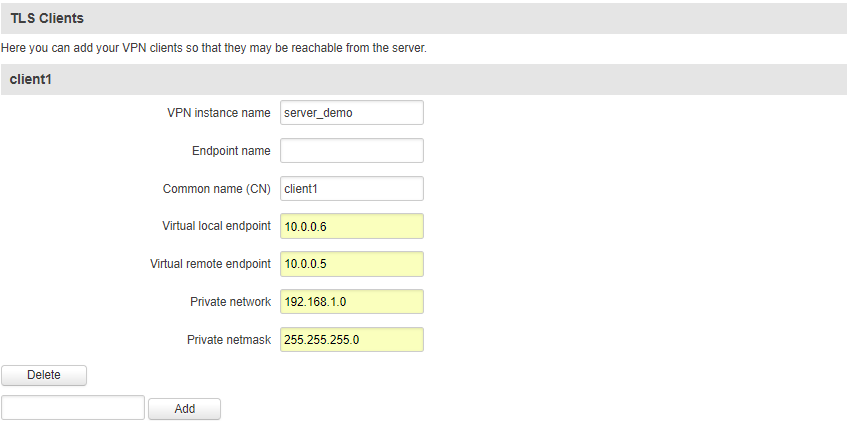
TLS Clients
TLS Clients is a way to more specifically differentiate clients by their Common Name (CN) found in the client certificate file. It can be used to assign specific VPN addresses to specific clients and bind them to their LAN addresses so that other device‘s in the client‘s LAN can be reached from the server or other clients.
The TLS Clients section can be found in the OpenVPN Server configuration window, provided that the OpenVPN server uses TLS or TLS/Password authentication methods. To create a new TLS client, type in the new client‘s name in the text field found bellow the TLS Clients tab and press the Add button.
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VPN instance name | string; Default: " " | With what VPN instance should the TLS Client be associated with |
| Endpoint name | string; Default: " " | Your endpoint name |
| Common name (CN) | string; Default: " " | Client’s Common Name (CN) found in the client’s certificate file |
| Virtual local endpoint | ip; Default: " " | Client’s virtual local address in the virtual network |
| Virtual remote endpoint | ip; Default: " " | Client’s virtual remote address in the virtual network |
| Private network | ip; Default: " " | Client’s private network (LAN) IP address |
| Private netmask | ip; Default: " " | Client’s private network (LAN) IP netmask |