Private and Public IP Addresses: Difference between revisions
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
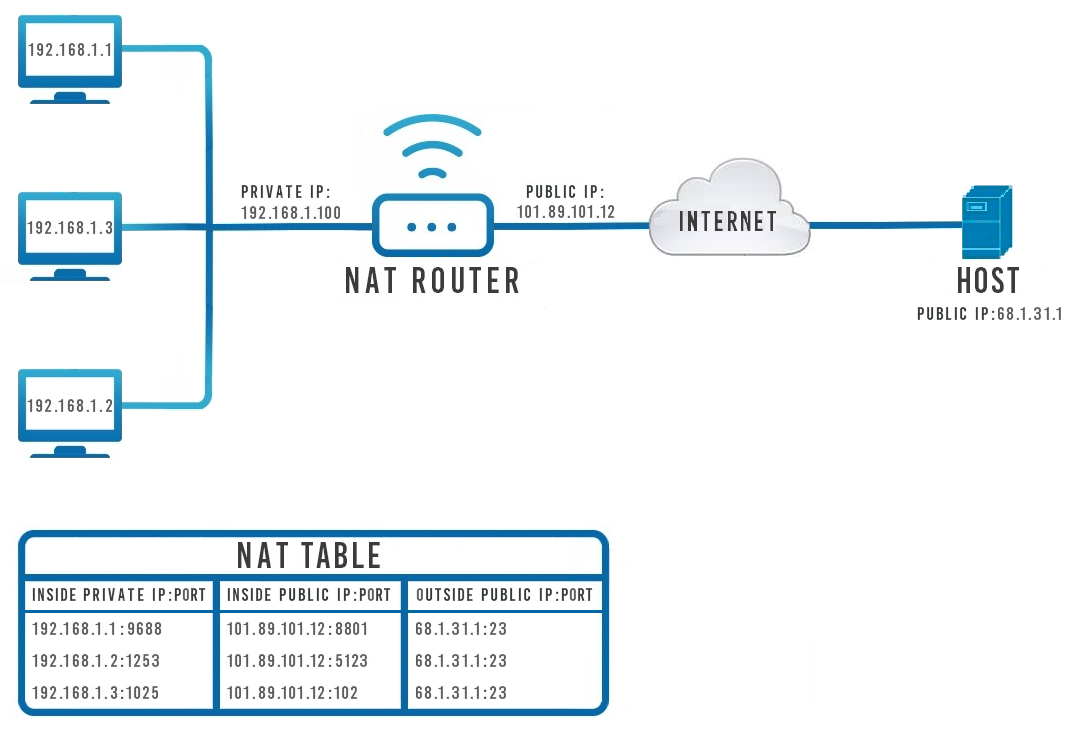
'''IP masquerading''' is a technique that hides an entire IP address space, usually consisting of private IP addresses, behind a single IP address in another, usually public address space. The address that has to be hidden is changed into a single (public) IP address as "new" source address of the outgoing IP packet so it appears as originating not from the hidden host but from the routing device itself: | '''IP masquerading''' is a technique that hides an entire IP address space, usually consisting of private IP addresses, behind a single IP address in another, usually public address space. The address that has to be hidden is changed into a single (public) IP address as "new" source address of the outgoing IP packet so it appears as originating not from the hidden host but from the routing device itself: | ||
[[File:Private public ip 3.png]] | [[File:Private public ip 3 v2.png]] | ||
The scheme above roughly describes how devices with private IP addresses communicate with a remote host on the Internet (and ''vice versa'') with the help of NAT. Bellow the scheme is a depiction of a NAT mapping table. It illustrates how the router differentiates to which device in the local network to redirect incoming data packets. | The scheme above roughly describes how devices with private IP addresses communicate with a remote host on the Internet (and ''vice versa'') with the help of NAT. Bellow the scheme is a depiction of a NAT mapping table. It illustrates how the router differentiates to which device in the local network to redirect incoming data packets. | ||
Revision as of 07:39, 10 January 2018
Main Page > FAQ > Networking > Private and Public IP AddressesThe are two types of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses: Public and Private.
A router will typically have two types of network interfaces:
- An Internal Interface
- An external Interface
Each of these interfaces will have an IP address.
Public IP address
A Public IP address (External) is assigned to every device that connects to the Internet and each IP address is unique. Therefore, there cannot exist two device with the same public IP address. This addressing scheme makes it possible for the devices to “find each other” online and exchange information. A user has no control over the IP address (public) that is assigned to the device. The public IP address is assigned to the device by the Internet Service Provider as soon as the device is connected to the Internet.
A public IP address can be static, dynamic or shared.
Public static - some times called Dedicated means the IP address never changes.
Public dynamic - means the IP address can change from time-to-time (for example, when you lose connection and re-connect or the ISP might change the address periodically).
Public shared - in some cases, an ISP can assign a public IP address to a group of users, and then employ NAT to isolate their traffic.
Private IP address
Private IP address (Internal) is only used by devices communicating to each other on the same network. Devices with private IP addresses cannot connect to the Internet directly. Likewise, computers or other devices outside the local network cannot connect directly to a device with a private IP.
An IP address is considered private if the IP number falls within one of the IP address ranges reserved for private networks such as a Local Area Network (LAN). The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three blocks of the IP address space for private networks (local networks):
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (Total Addresses: 16,777,216)
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (Total Addresses: 1,048,576)
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 (Total Addresses: 65,536)
Network Address Translation
Network address translation (NAT) is a method of remapping one IP address space into another by modifying network address information in IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device. Or to put it in plain terms, NAT allows devices with private IP addresses to communicate with hosts via the internet using IP masquerading.
IP masquerading is a technique that hides an entire IP address space, usually consisting of private IP addresses, behind a single IP address in another, usually public address space. The address that has to be hidden is changed into a single (public) IP address as "new" source address of the outgoing IP packet so it appears as originating not from the hidden host but from the routing device itself:
The scheme above roughly describes how devices with private IP addresses communicate with a remote host on the Internet (and vice versa) with the help of NAT. Bellow the scheme is a depiction of a NAT mapping table. It illustrates how the router differentiates to which device in the local network to redirect incoming data packets.
IP Address Terminology
Static means the IP address never changes as long as you stay with the same provider or same server.
Dynamic means the IP address can change from time-to-time.
Public means the IP address can be reached via the Internet from any computer in the world.
Private means the IP address can only be reached by other devices on the same network.
Shared means other people besides you use your IP address for their connection.
Dedicated means no one else uses your IP address for their connection.
Class identifies the range of your IP address and the default subnet mask. Examples of IP classes:
- A class - 0 to 127 with default mask of 255.0.0.0
- B class - 128 to 191 with default mask of 255.255.0.0
- C class - 192 to 223 with default mask of 255.255.255.0
- D class - 224 to 247 (not currently used)
- E class - 248 to 255 (not currently used)
Frequently Asked Questions
How to obtain a static IP address?
If you prefer a static IP address, contact your service provider. Customers can sometimes obtain a static IP by subscribing to a special service plan and paying extra fees.
Can I setup remote access for my Teltonika router with a dynamic IP address?
Yes. You can use Dynamic DNS or RMS services.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a static IP address?
Advantages:
Convenient remote access – when you remotely connect to a router you need not worry about the IP address changing.
Static IP addresses are more stable for Internet use since they never change. In cases of a dynamic IP addresses, the Internet service provider may automatically change the address on a regular basis, as frequently as every few hours. This can cause a lapse in the connection.
Disadvantages:
Security – a router with a static IP address is much easier to track through the Internet. A Static IP Address could be a security risk as the IP address is constant, therefore, there is a greater chance of hacking.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a dynamic IP address?
Security – routers that have Dynamic IP addresses have a relatively lower security risk.
Remote Access – for permanent access to the router from a remote location you will need a DNS address service that can update your IP address regularly.