Template:Netoworking rut configuration example cisco gre: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
[[File:Networking_rutxxx_configuration_example_rut_settings_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutxxx_configuration_example_rut_settings_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
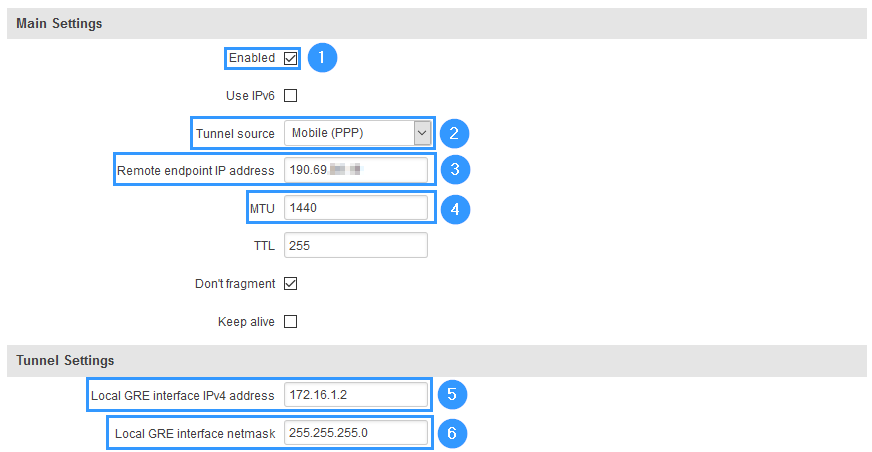
#'''Enable''' instance. | |||
#Select '''Tunnel source''' (select your WAN interface). | |||
#Enter '''Remote endpoint IP address''' (CISCO WAN IP). | |||
#Set '''MTU''' to '''1440'''. | |||
#Write '''Local GRE interface IP address''' (create GRE tunnel IP address or just use the same as in the example). | |||
#Write '''Local GRE interface netmask''' (create GRE tunnel netmask or just use the same as in the example) | |||
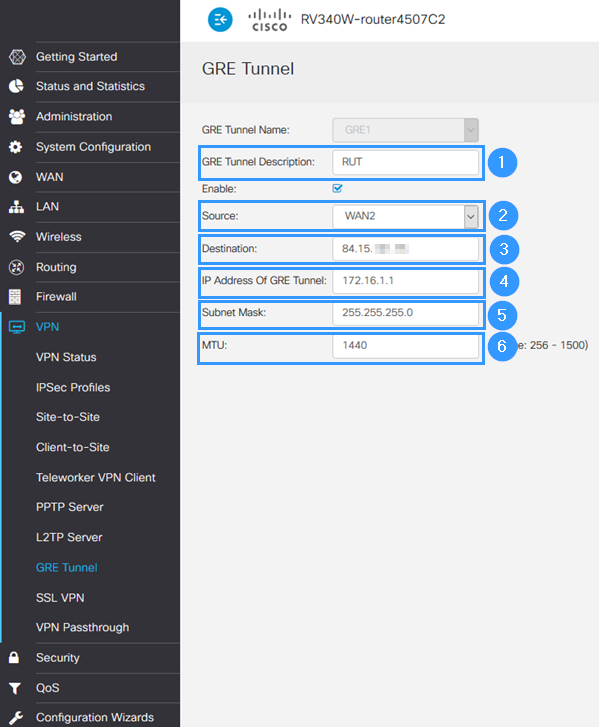
==Cisco configuration== | ==Cisco configuration== | ||
[[File:Networking_rutxxx_configuration_example_cisco_settings_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutxxx_configuration_example_cisco_settings_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 17 February 2020
Introduction
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a tunneling protocol that can encapsulate a wide variety of network layer protocols inside virtual point-to-point links over an Internet Protocol network.
This article provides an extensive configuration example with details on how to create a tunnel connection between two GRE Tunnel instances, one of which is configured on RUTxxx router and the second one on CISCO device.
Prerequisites
You will need:
- One RUTxxx router
- One Cisco router
- A PC to configure the routers
- Both routers must have a Public Static or Public Dynamic IP addresses
Configuration scheme
RUT configuration
- Enable instance.
- Select Tunnel source (select your WAN interface).
- Enter Remote endpoint IP address (CISCO WAN IP).
- Set MTU to 1440.
- Write Local GRE interface IP address (create GRE tunnel IP address or just use the same as in the example).
- Write Local GRE interface netmask (create GRE tunnel netmask or just use the same as in the example)