Template:Networking rutos manual administration: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
The <b>General</b> section is used to set up some of device managerial parameters, such as changing device name. For more information on the General section, refer to figure and table below. | The <b>General</b> section is used to set up some of device managerial parameters, such as changing device name. For more information on the General section, refer to figure and table below. | ||
{{#switch:{{{series}}} | {{#switch:{{{series}}} | ||
| RUTX = [[File:Networking_rutx_manual_administration_general_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | | RUTX = [[File:Networking_rutx_manual_administration_general_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| | | TRB2XX = [[File:Networking_trb2_manual_administration_general_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| TRB14X = [[File:Networking_trb1_manual_administration_general_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | | TRB14X = [[File:Networking_trb1_manual_administration_general_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 429: | Line 429: | ||
| [[File:Networking_rutx11_manual_administration_overview_setup_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | | [[File:Networking_rutx11_manual_administration_overview_setup_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| | | TRB2XX = [[File:Networking_trb2_manual_administration_overview_setup_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| | | TRB14X = [[File:Networking_trb1_manual_administration_overview_setup_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| | | | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 09:49, 9 July 2020
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
This page is an overview of the Administration section of {{{name}}} devices.
General
The General section is used to set up some of device managerial parameters, such as changing device name. For more information on the General section, refer to figure and table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Device name | string; default: {{{name}}} | Device model name. |
| Hostname | string; default: Teltonika-{{{name}}}.com | Device hostname. This can be used for communication with other LAN hosts. |
| Mode | Basic | Advanced; default: Basic | Mode determines what options and configurations are shown. In Basic mode only the essential configurations are shown. In Advanced mode there is greater freedom to configure and access more options. |
| Min time | integer [0..60]; default: none | Minimum time (in seconds) the button needs to be held to perform an action. |
| Max time | integer [1..60]; default: none | Maximum time (in seconds) the button can be held to perform an action, after which no action will be performed. |
| Restore to factory defaults | -(interactive button) | Restores device to manufacturer's default settings. |
| Restore to user's defaults | -(interactive button) | Restores device to custom configuration set by the user. |
Users & recipients
The Users & recipients section is used to configure phone groups and email users.
Phone groups
The Phone groups section is used to manage groups of phone numbers.
Refer to the figure below for information on device Phone groups page.
File:Networking rutx manual administration phone groups v1.png
You can create a group by writing its name and clicking Add button. To configure group, choose group you want to configure from the list and click ![]() Edit button, located at the right side of it.
Edit button, located at the right side of it.
Modify phone group
File:Networking rutx manual administration phone groups setup v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Group name | string; default: none | Name of this phone numbers group. |
| Phone number | string; default: none | A phone number entry for this group. A phone number containing 0-9*+# characters is accepted. |
Email users
The Email users section is used to manage email configurations.
Refer to the figure below for information on device Email users page.
File:Networking rutx manual administration email users v1.png
You can create user by writing its name and clicking Add button. To configure email user, choose user you want to configure from the list and click ![]() Edit button, located at the right side of it.
Edit button, located at the right side of it.
Modify email user
File:Networking rutx manual administration email users setup v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Secure connection | off | on; default: off | Use if your SMTP server supports TLS or SSL encryption. |
| SMTP server | string; default: none | SMTP server name. |
| SMTP server port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | SMTP server port. |
| User name | string; default: none | Username used in authentication to SMTP server. |
| Password | string; default: none | Password used in authentication to SMTP server. |
| Sender's email address | string; default: none | Configured SMTP server's user's email address. |
Access Control
General
The Access Control page is used to manage remote and local access to device.
Important: turning on remote access leaves your device vulnerable to external attackers. Make sure you use a strong password.
SSH
File:Networking rutx manual administration access control general ssh v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable SSH access | off | on; default: on | Turns SSH access from the local network (LAN) on or off. |
| Remote SSH access | off | on; default: off | Turns SSH access from remote networks (WAN) on or off. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 22 | Selects which port to use for SSH access. |
WebUI
File:Networking rutx manual administration access control general webui v2.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable HTTP access | off | on; default: on | Turns HTTP access from the local network (LAN) to the device WebUI on or off. |
| Enable HTTPS access | off | on; default: on | Turns HTTPS access from the local network (LAN) to the device WebUI on or off. |
| Redirect to HTTPS | off | on; default: off | Redirects connection attempts from HTTP to HTTPS. |
| Enable remote HTTP access | off | on; default: off | Turns HTTP access from remote networks (WAN) to the device WebUI on or off. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 80 | Selects which port to use for HTTP access. |
| Enable remote HTTPS access | off | on; default: off | Turns HTTPS access from remote networks (WAN) to the device WebUI on or off. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 443 | Selects which port to use for HTTPS access. |
CLI
File:Networking rutx manual administration access control general cli v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable CLI | off | on; default: on | Turns CLI access from the local network (LAN) on or off. |
| Enable remote CLI | off | on; default: off | Turns CLI access from remote networks (WAN) on or off. |
| Port range | range of integers [0..65534]-[1..65535]; default: 4200-4220 | Selects which ports to use for CLI access. |
| Shell limit | integer [1..10]; default: 5 | Maximum number of active CLI connections. |
Security
File:Networking rutx manual administration access control security v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fail count | integer; default: 10 | An amount of times IP address can try to access SSH or WebUI before being blocked. |
| Blocked address | ip | IP address which was blocked due to reaching fail count limit. |
| Failed attempts | integer | Amount of times IP address tried to access SSH or WebUI after getting blocked. |
Troubleshoot
The Troubleshoot section is used to download various files that contain information used for troubleshooting the device. Refer to the figure and table below for information on the Troubleshoot page.
File:Networking rutx manual administration troubleshoot v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| System log | - (interactive button) | Displays the contents of the device system log file. The system log contains records of various system related events, such as starts/stops of various services, errors, reboots, etc. |
| Kernel log | - (interactive button) | Displays the contents of the device kernel log file. The kernel log contains records of various events related to the processes of the operating system (OS). |
| Troubleshoot file | - (interactive button) | Downloads the device Troubleshoot file. It contains the device configuration information, logs and some other files. When requesting support, it is recommended to always provide the device Troubleshoot file to Teltonika engineers for analysis. |
| TCP dump file | - (interactive button) | Downloads the device TCP dump file. TCP dump is a program used to capture packets moving through network interfaces. By default, the device does not store TCP dump information. You must enable TCP dump and save the changes before you can download the file. |
| Enable TCP dump* | off | on; default: off | Turns TCP dump packets capture on or off. |
* More on TCP dump in the next section.
TCP dump
TCP dump is a program used to capture packets moving through network interfaces. By default, the device does not store TCP dump information. You must enable TCP dump and save the changes before you can download the file.
If you enable TCP dump, you will notice additional configuration fields appear. Refer to the figure and table below for realted information.
File:Networking rutx manual administration troubleshoot tcp dump v3.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable TCP dump | off | on; default: off | Turns TCP dump packet capture on or off. |
| Select interface | network interface; default: br-lan | Only captures packets that move through the specified network interface. |
| Select protocol filter | all | icmp | tcp | udp | arp; default: All | Only captures packets that match the specified protocol. |
| Select packets direction | Incoming/Outgoing | Incoming | Outgoing; default: Incoming/Outgoing | Only captures packets coming from the specified direction. |
| Host | ip | host; default: none | Only captures packets related to the specified host. |
| Port | integer [0..65335]; default: none | Only captures packets related to the specified communication port. |
| Select storage | Internal storage | / ; default: Internal storage | Specifies where the TCP dump file will be stored. |
Diagnostics
The Diagnostics section is used to execute simple network diagnostic tests, including ping, traceroute and nslookup.
File:Networking rutx manual administration diagnostics v3.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Ping | Traceroute | Nslookup; default: Ping | Selects diagnostic method.
|
| Protocol | IPv4 | IPv6; default: IPv4 | Selects IP address family for diagnostic test. |
| Address | ip | host; default: none | IP address or hostname on which the diagnostic test will be performed. |
| Perform | -(interactive button) | Performs diagnostic test when clicked. |
Overview setup
The Overview setup section is used to select which widgets will be shown in the [[{{{name}}}_Overview]] window.
Certificates
The Certificates page is used for convenient TLS certificate and key generation and management. Generated files can be exported and used on other machines or locally on this device with functions that use TLS/SSL, such as [[{{{name}}} MQTT|MQTT]], [[{{{name}}} VPN#OpenVPN|OpenVPN]], [[{{{name}}} VPN#IPsec|IPsec]] and others.
Certificate Generation
The Certificate Generation tab provides the possibility to generate TLS certificates required for secure authentication and communication encryption used by some of the devices services.
There are five distinct generation methods (denoted by the selected 'File Type').
- Simple - generates and signs a set of 2048 bit certificate and key files that include:
- Certificate Authority (CA)
- Server certificate & key
- Client certificate & key
- DH Parameters
- CA - generates a Certificate Authority (CA) file. A CA is a type of certificate file that certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. In other words, it assures clients that they are connecting to a trusted server and vice versa.
- Server - generates a server certificate and key. A server certificate validates a server's identity to connecting clients, while a key is responsible for encryption.
- Client - generates a client certificate and key. A client certificate validates a client's identity to the server that it's connecting to, while a key is responsible for encryption.
- DH Parameters - generates a Diffie-Hellman (DH) parameters file. DH parameters are used in symmetric encryption to protect and define how OpenSSL key exchange is performed.
Generation Parameters
Generating each type of file (excluding 'Simple') requires setting some parameters. This section provides an overview for parameters used in TLS certificate generation.
Core parameters or simply parameters that apply to each file type are the size and common name of the generated file(s).
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Key Size | integer; default: 2048 | Generated key size in bits. Larger keys provide more security but take longer to generate. A 2048 bit is the preferred option. |
| Name (CN) | string; default: cert | Common Name (CN), aka Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is a parameter that defines the name of the certificate. It should be chosen with care as it is not only used for easier management. For example, the Common Name should typically hostname of the server. It may also be used to differentiate clients in order to apply client-specific settings. |
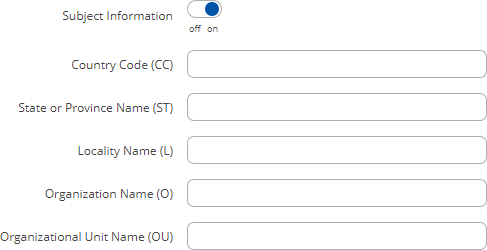
Subject information is not mandatory but can be used as user-friendly way to identify the ownership of certificate files by including such information as the owner's location and company name.
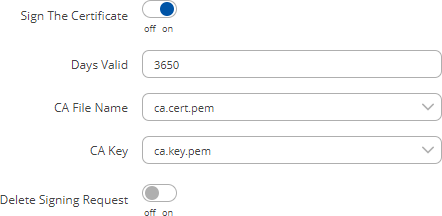
The Sign the certificate slider control whether the certificate will be signed automatically or manually after the generation is complete.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Days Valid | integer; default: 3650 | Length of the signature's validity. |
| CA File Name | filename; default: none | Selects which CA file will be used to sign the generated certificate. |
| CA key | filename; default: none | Selects which CA key file will be used to sign the generated certificate. |
| Delete Signing Request | off | on; default: off | Generation creates additional 'signing request' files (which appear under the Certificate Manager tab) that are later used to sign the generated certificates. When this option is set to 'on', the device deletes the signing request files after the signing process is complete. |
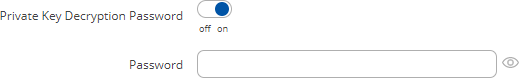
A Private Key Decryption Password is a parameter used to decrypt private keys protected by a password.
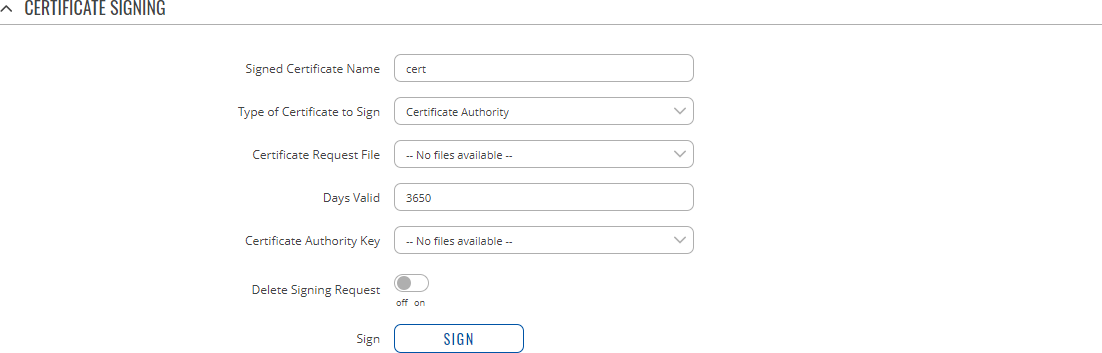
Certificate Signing
The Certificate Signing section is used to validate (sign) unsigned certificates.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Signed Certificate Name | string; default: cert | Name of the signed certificate. |
| Type of Certificate to Sign | Certificate Authority | Client Certificate | Server Certificate; default: Certificate Authority | Specifies what type of file will be signed. |
| Certificate Request File | file; default: none | Specifies the signing request file linked to the certificate. |
| Days Valid | integer; default: 3650 | Length of the signature's validity. |
| Certificate Authority File | filename; default: none | Selects which CA file will be used to sign the generated certificate. |
| Certificate Authority Key | filename; default: none | Selects which CA key file will be used to sign the generated certificate. |
| Delete Signing Request | off | on; default: off | Generation creates additional 'signing request' files (which appear under the Certificate Manager tab) that are later used to sign the generated certificates. When this option is set to 'on', the device deletes the signing request files after the signing process is complete. |
| Sign | - (interactive button) | Signs the certificate on click. |
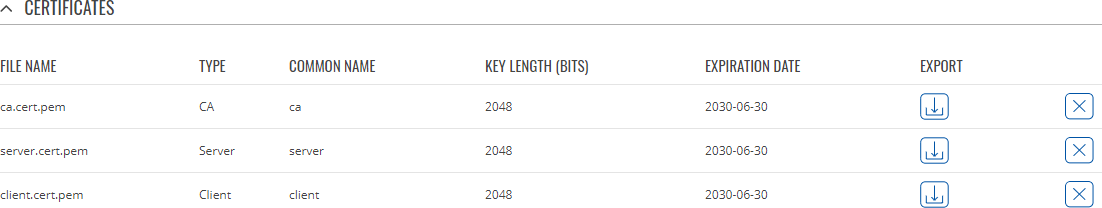
Certificate Manager
The Certificate Manager page displays information on all certificate and key files stored on the device and provides the possibility export these files for use on another machine or import files generated elsewhere.
Certificate Import
The Certificate Import section provides the possibility to import certificates and files generated on another machine. To upload such a file simply click 'Browse', locate the file on your computer and click 'Import'
Certificates, Keys & Requests
The Certificates, Keys and Requests section display files generated on or imported to the device along with the most important information related to them.
By default, the lists are empty. A set certificates generated using 'Simple' file type would look something like this:
The 'Export' buttons are used to download the files from the device onto your local machine. The 'X' buttons located to the right of each entry are used to delete related files.
Root CA
The Root CA section is used to add a root CA certificate file to the device. There is a default file already preloaded on the device which will be overwritten by any uploaded file. The certificates must be in .pem format, maximum file size is 300 KB. These certificates are only needed if you want to use HTTPS for your services and the default file should be sufficient in most cases.
File:Networking rutx manual administration root ca v2.png
Logging
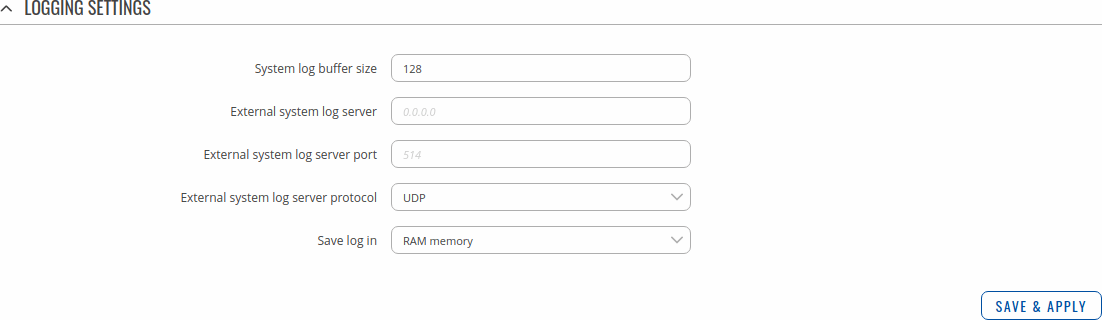
The Logging section is used to configure how and where the device stores system log data. The system log is a file that contains information on various system related events and is useful to engineers for troubleshooting the device.
Refer to the figure and table below for information on the device Logging page.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| System log buffer size | integer; default: 128 | System log buffer size in kibibytes (KiB). |
| External system log server | ip; default: none | IP address of an external server that will be used to store device logs. |
| External system log server port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | TCP/UDP port number of the external log server. |
| External system log server protocol | UDP | TCP; default: UDP | Communication protocol used by the external log server. |
| Save log in | RAM memory | Flash memory; default: RAM memory | Specifies which type of memory to use for storing system logs. |
Unsaved changes
The Unsaved changes section is used to see and apply or revert all unsaved changes.
File:Networking rutx manual administration unsaved changes v1.png
[[Category:{{{name}}} System section]]