Template:Networking rutos manual usb tools: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
The 'Add' button lets you add and manage additional printers. To configure a printer instance, click the Edit button located next to it: | The 'Add' button lets you add and manage additional printers. To configure a printer instance, click the Edit button located next to it: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_printer_server_printer_server.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
The device's USB connector can also be used as a <b>serial port</b>. | The device's USB connector can also be used as a <b>serial port</b>. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_printer_server_usb_to_serial.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
<b>Console</b> mode requires no further configuration than the settings above and is used as a direct-access method to the device's shell interface. For this purpose you may want use such applications as PuTTY on Windows and microcom, minicom, picocom or similar applications on Linux. | <b>Console</b> mode requires no further configuration than the settings above and is used as a direct-access method to the device's shell interface. For this purpose you may want use such applications as PuTTY on Windows and microcom, minicom, picocom or similar applications on Linux. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_printer_server_usb_to_serial_console.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
===Over IP=== | ===Over IP=== | ||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
The <b>Over IP</b> serial type is used to manage serial connections over a TCP/IP network. | The <b>Over IP</b> serial type is used to manage serial connections over a TCP/IP network. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_printer_server_usb_to_serial_over_ip.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 192: | Line 192: | ||
The <b>Modbus gateway</b> serial type allows redirecting TCP data coming to a specified port to an RTU specified by the Slave ID. The Slave ID can be specified by the user or be obtained directly from the Modbus header. | The <b>Modbus gateway</b> serial type allows redirecting TCP data coming to a specified port to an RTU specified by the Slave ID. The Slave ID can be specified by the user or be obtained directly from the Modbus header. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_printer_server_usb_to_serial_modbus_gateway.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 236: | Line 236: | ||
<b>Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol (NTRIP)</b> is a protocol for streaming differential GPS (DGPS) data over the Internet in accordance with specification published by RTCM. | <b>Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol (NTRIP)</b> is a protocol for streaming differential GPS (DGPS) data over the Internet in accordance with specification published by RTCM. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_usb_tools_printer_server_usb_to_serial_ntrip_client.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
Revision as of 10:53, 21 August 2020
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
The USB Tools page is used to manage services related to the device's USB connector.
This manual page provides an overview of the USB Tools page in {{{name}}} devices.
Printer Server
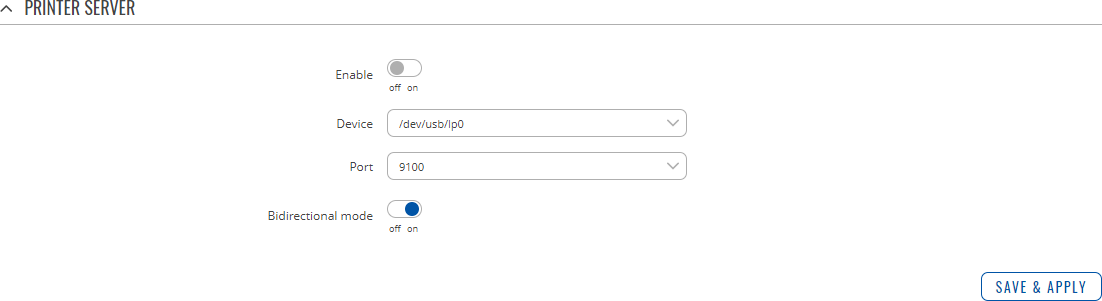
The Printer Server feature provides the possibility to configure access to a printer that is connected to the USB port of the device. After the printer is connected to the device's USB port and configured, it can be utilized by users in the local network (LAN, WiFi) or remotely.
The 'Add' button lets you add and manage additional printers. To configure a printer instance, click the Edit button located next to it:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns printer support on or off. |
| Device | file path; default: /dev/usb/lp0 | Printer's device file. |
| Port | integer [9100..9109]; default: 9100 | Printer's TCP port. |
| Bidirectional mode | off | on; default: on | Turns bidirectional mode on or off. |
PC and printer setup
For step-by-step instructions on how to use a printer with {{{name}}}, [[How to set up a USB printer (Windows, {{{name}}})|click here]]
USB to Serial
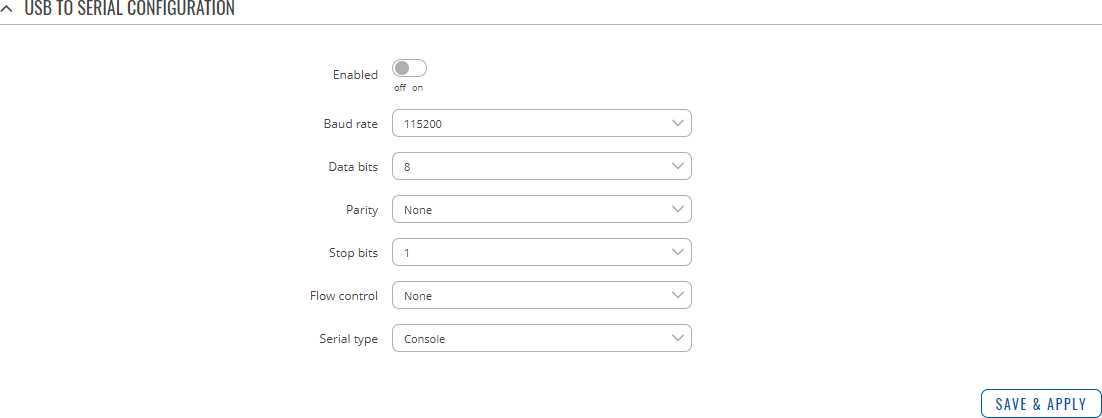
The device's USB connector can also be used as a serial port.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | off | on; default: off | Turns the USB to Serial service on or off. |
| Baud rate | 300 | 1200 | 2400 | 4800 | 9600 | 19200 | 38400 | 57600 | 115200; default: 115200 | Data rate for serial data transmission (in bits per second). |
| Data bits | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8; default: 8 | Number of data bits for each character |
| Parity | None | Odd | Even; default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check.
|
| Stop bits | 1 | 2; default: 1 | Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used. |
| Flow control | None | RTS/CTS | Xon/Xoff; default: None | In many circumstances a transmitter might be able to send data faster than the receiver is able to process it. To cope with this, serial lines often incorporate a "handshaking" method, usually distinguished between hardware and software handshaking.
|
| Serial type | Console | Over IP | Modbus gateway | NTRIP client; default: Console | Specifies the serial connection type. Look to the sections below for information on different USB to Serial type options. |
Console
Console mode requires no further configuration than the settings above and is used as a direct-access method to the device's shell interface. For this purpose you may want use such applications as PuTTY on Windows and microcom, minicom, picocom or similar applications on Linux.
Over IP
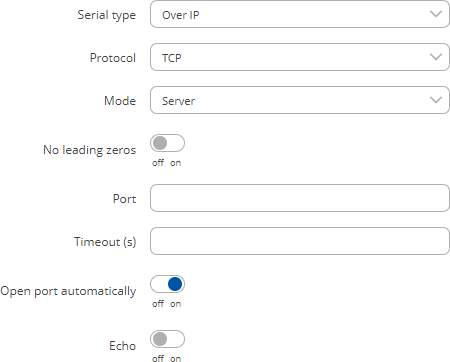
The Over IP serial type is used to manage serial connections over a TCP/IP network.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | TCP | UDP; default: TCP | Protocol used in the communication process. |
| Mode | Server | Client | Bidirect; default: Server | This device's role in the connection:
|
| No leading zeros | off | on; default: off | When checked, indicates that the first hex zeros should be skipped. |
| Server settings: Port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Internal port number used to listen for incoming connections. |
| Server settings: Timeout (s) | integer; default: none | Specifies an inactivity time limit (in second) after which an inactive clients is disconnected. |
| Server settings: Open port automatically | off | on; default: on | Automatically adds a traffic rule in the firewall configuration to open the required port for NTRIP communication. |
| Client settings: Server Address | ip | host; default: none | IP address or hostname of the server that this client will connect to. |
| Client settings: Port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Server's listening port number. |
| Client settings: Reconnect interval (s) | integer; default: none | Time period (in seconds) between reconnection attempts in case a connection fails. |
| Echo | off | on; default: off | Turn USB to serial echo on or off. |
Modbus gateway
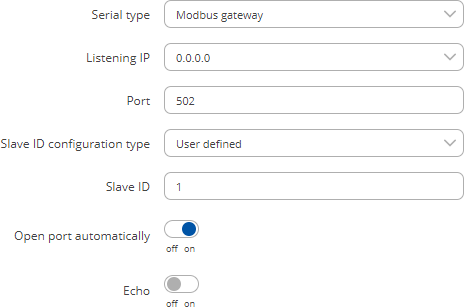
The Modbus gateway serial type allows redirecting TCP data coming to a specified port to an RTU specified by the Slave ID. The Slave ID can be specified by the user or be obtained directly from the Modbus header.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Listening IP | ip; default: 0.0.0.0 | IP address to listen for incoming connections. The default value (0.0.0.0) means that this device will listen for incoming connections on any interface or IP address. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 502 | Port number to listen for incoming connections. |
| Slave ID configuration type | User defined | Obtained from TCP; default: User defined |
Specifies whether slave IDs are user defined or automatically obtained from TCP. |
| Slave ID | Permitted slave IDs | integer | range of integers; default: 1 or 1-247 |
Specifies the slave ID of range of permitted slave IDs. The way this field is named and its function depends on the value of the Slave ID configuration field. A range of IDs can be specified by placing a hyphen (-) between two integer numbers. For example, if you permit slave IDs in the range of 10 to 20, you would specify it as: 10-20 You can also specify multiple values that are not connected in a range using commas (,). For example, to specify 6, 50 and 100 as permitted slave IDs, you would have to use: 6,50,100 |
| Open port automatically | off | on; default: on | Automatically adds a traffic rule in the firewall configuration to open the required port for serial communication. Caution: use with care if listening IP is left as the default value (0.0.0.0). Leaving it as such will leave the device open for remote connections on the specified port. |
| Echo | off | on; default: off | Turn USB to serial echo on or off. |
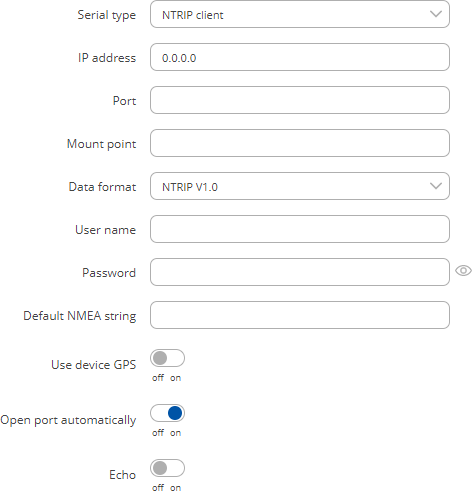
NTRIP client
Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol (NTRIP) is a protocol for streaming differential GPS (DGPS) data over the Internet in accordance with specification published by RTCM.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IP address | ip; default: 0.0.0.0 | IP address of an NTRIP server. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | TCP/UDP port used for NTRIP communication. |
| Mount point | file path | string; default: none | NTRIP mount point. |
| Data format | NTRIP V2.0 TCP/IP | NTRIP V2.0 RSTP/RTP | NTRIP V1.0 | Automatic detection | NTRIP V2.0 UDP; default: NTRIP V1.0 | Version of NTRIP protocol. |
| Username | string; default: none | User name for authentication to NTRIP server. |
| Password | string; default: none | Password for authentication to NTRIP server. |
| Default NMEA string | string; default: none | Optional NMEA string that will be used as the default value when initiating the connection to the NTRIP server (this value is only sent to the server if there is no NMEA from router's GPS device). |
| Use device GPS | off | on; default: off | Allows to obtain default NMEA string from the router's GPS device. Only works if GPS service is enabled and location fix is obtained at the time of NTRIP service start. |
| Open port automatically | off | on; default: on | Automatically adds a traffic rule in the firewall configuration to open the required port for serial communication. |
| Echo | off | on; default: off | Turn USB to serial echo on or off. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]]