Template:Networking rutos manual modbus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
You can create a maximum of 10 slave configurations. | You can create a maximum of 10 slave configurations. | ||
===Slave | ===Slave Device Configuration=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
The figure below is an example of the | The <b>Slave Device Configuration</b> section is used to configure the parameters or Modbus TCP slaves that the Master (this {{{name}}} device) will querying with requests. The figure below is an example of the Slave Device Configuration and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_modbus_modbus_tcp_master_slave_device_configuration.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
===Requests | ===Requests Configuration=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
A Modbus <b>request</b> is a way of obtaining data from Modbus slaves. The master sends a request to a slave specifying the function code to be performed. The slave then sends the requested data back to the Modbus master. You can create a maximum of 64 request configurations for each slave device. | A Modbus <b>request</b> is a way of obtaining data from Modbus slaves. The master sends a request to a slave specifying the function code to be performed. The slave then sends the requested data back to the Modbus master. You can create a maximum of 64 request configurations for each slave device. | ||
The | The Request Configuration list is empty by default. To add a new Request Configuration loon to the Add New Instance section. Enter a custom name into the 'Name' field and click the 'Add' button: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_modbus_modbus_tcp_master_requests_configuration_add_new_instance.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
The new Request Configuration should become visible in the list: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_modbus_modbus_tcp_master_requests_configuration.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 155: | Line 159: | ||
<td>Name</td> | <td>Name</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b>Unnamed</b></td> | <td>string; default: <b>Unnamed</b></td> | ||
<td>Request | <td>Name of this Request Configuration. Used for easier management purposes.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Data type</td> | <td>Data type</td> | ||
<td>8bit INT | 8bit UINT | 16bit INT, high byte first | 16bit INT, low byte first | 16bit UINT, high byte first | 16bit UINT, low byte first | 32bit float, Byte order 1,2,3,4 | 32bit float, Byte order 4,3,2,1 | 32bit float, Byte order 2,1,4,3 | 32bit float, Byte order 3,4,1,2; default: <b>16bit INT, high byte first</b></td> | <td>8bit INT | 8bit UINT | 16bit INT, high byte first | 16bit INT, low byte first | 16bit UINT, high byte first | 16bit UINT, low byte first | 32bit float, Byte order 1,2,3,4 | 32bit float, Byte order 4,3,2,1 | 32bit float, Byte order 2,1,4,3 | 32bit float, Byte order 3,4,1,2; default: <b>16bit INT, high byte first</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Defines how read data will be stored.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 191: | Line 195: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
After having configured a request, you should see a new 'Testing' section appear. It is used to check whether the configuration works correctly. Simply | <b>Additional note:</b>By default the newly added Request Configurations are turned off. You can use the on/off slider to the right of the Request Configuration to turn it on: | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_modbus_modbus_tcp_master_requests_configuration_on_off_slider.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
---- | |||
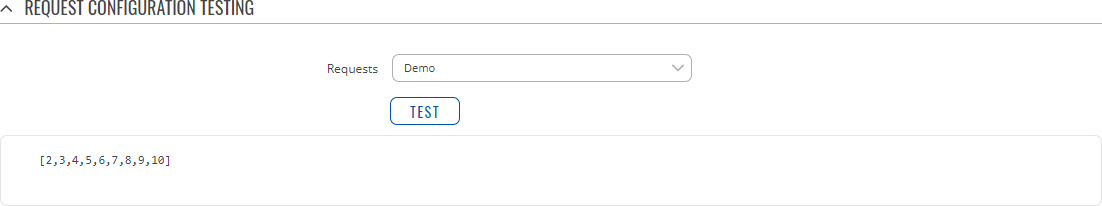
After having configured a request, you should see a new 'Request Configuration Testing' section appear. It is used to check whether the configuration works correctly. Simply click the 'Test' button and a response should appear in the box below. A successful response to a test may look something like this: | |||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_modbus_modbus_tcp_master_requests_configuration_testing.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
===Alarms Configuration=== | ===Alarms Configuration=== | ||
Revision as of 12:25, 25 August 2020
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
Modbus is a serial communications protocol. Simple and robust, it has become a de facto standard communication protocol and is now a commonly available means of connecting industrial electronic devices.
This manual page provides an overview of the Modbus functionality in {{{name}}} devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
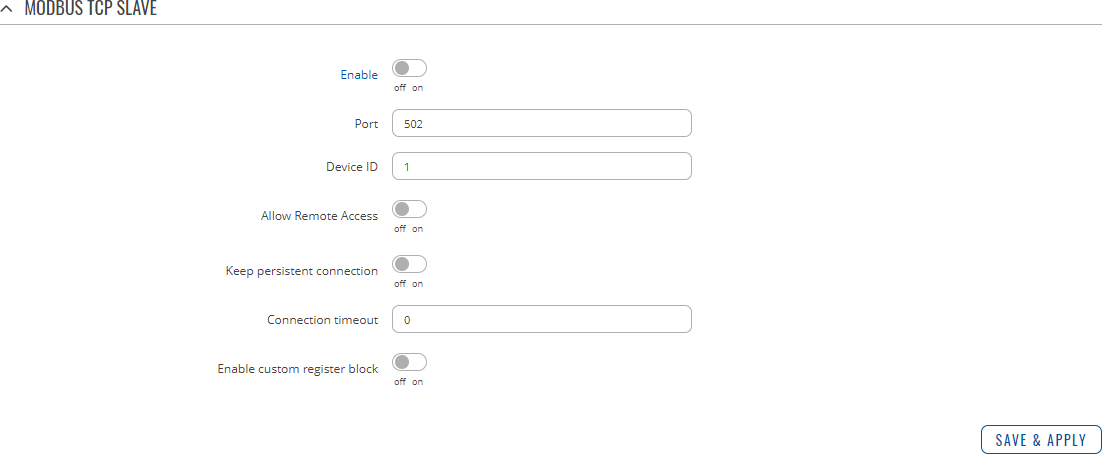
Modbus TCP slave
A Modbus TCP slave listens for connections from a master (client) and sends out a response or sets some system related parameter in accordance with the given query. This provides the user with the possibility to set or get system parameters.
The figure below is an example of the Modbus TCP window section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that window:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: none | Turns Modbus TCP on or off. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 502 | TCP port used for Modbus communications. |
| Device ID | integer [0..255]; default: 1 | The device's Modbus slave ID. When set to 0, it will respond to requests addressed to any ID. |
| Allow Remote Access | off | on; default: off | Allows remote Modbus connections by adding an exception to the device's firewall on the port specified in the field above. |
| Keep persistent connection | off | on; default: off | Allows keep the connection open after responding a Modbus TCP master request. |
| Connection timeout | integer; default: 0 | Sets TCP timeout in seconds after which the connection is forcefully closed. |
| Enable custom register block | off | on; default: off | Allows the usage of custom register block. |
Get Parameters
Modbus parameters are held within registers. Each register contains 2 bytes of information. For simplification, the number of registers for storing numbers is 2 (4 bytes), while the number of registers for storing text information is 16 (32 bytes).
The register numbers and corresponding system values are described in the table below:
| required value | register address | register number | number of registers | representation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| System uptime | 1 | 2 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| System hostname | 7 | 8 | 16 | Text |
| Router serial number | 39 | 40 | 16 | Text |
| LAN MAC address | 55 | 56 | 16 | Text |
| Router name | 71 | 72 | 16 | Text |
| Current WAN IP address | 139 | 140 | 2 | 8 bit unsigned integer |
| Digital non-isolated input | 324 | 325 | 1 | 16 bit unsigned integer |
| Digital open collector output | 325 | 326 | 1 | 16 bit unsigned integer |
| PIN 3 direction | 326 | 327 | 1 | 16 bit unsigned integer |
| PIN 4 direction | 327 | 328 | 1 | 16 bit unsigned integer |
| Unix timestamp | 364 | 365 | 2 | 32 bit unsigned integer |
| Local ISO time | 366 | 367 | 12 | Text |
| UTC time | 378 | 379 | 12 | Text |
| LAN IP | 394 | 395 | 2 | 8 bit unsigned integer |
Set Parameters
The Modbus daemon can also set some device parameters.
| value to set | register address | register number | register value | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hostname | 7 | 8 | Hostname (in decimal form) | Changes hostname |
| Device name | 71 | 72 | Device name (in decimal form) | Changes device name |
| Reboot | 206 | 207 | 1 | Reboots the router |
| Switch PIN 3 state | 324 | 325 | 1|0 | Toggles PIN 3 ON or OFF, when output is selected |
| Switch PIN 4 state | 325 | 326 | 1|0 | Toggles PIN 4 ON or OFF, when output is selected |
| Switch PIN 3 direction | 326 | 327 | 1|0 | Toggles PIN 3 direction between INPUT (0) or OUTPUT (1) |
| Switch PIN 4 direction | 327 | 328 | 1|0 | Toggles PIN 4 direction between INPUT (0) or OUTPUT (1) |
| Change LAN IP | 394 | 395 | IPv4 (in decimal form) | Changes device LAN IP |
Modbus TCP Master
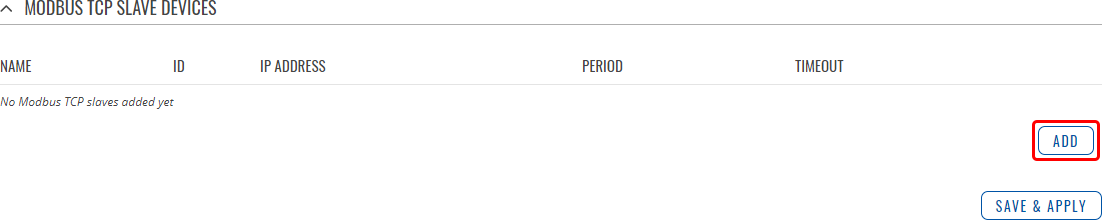
A Modbus Master device can request data from Modbus slaves. The Modbus TCP Master section is used to configure Modbus TCP slaves. By default, the slave list is empty. To add a new slave, click the 'Add' button
After clicking 'Add' you will be redirected to the newly added slave's configuration page.
You can create a maximum of 10 slave configurations.
Slave Device Configuration
The Slave Device Configuration section is used to configure the parameters or Modbus TCP slaves that the Master (this {{{name}}} device) will querying with requests. The figure below is an example of the Slave Device Configuration and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | off | on; default: off | Turns communication with the slave device on or off. |
| Name | string; default: none | Slave device's name, used for easier management purposes. |
| Slave ID | integer [0..255]; default: none | Slave ID. Each slave in a network is assigned a unique identifier ranging from 1 to 255. When the master requests data from a slave, the first byte it sends is the Slave ID. When set to 0, the slave will respond to requests addressed to any ID. |
| IP address | ip; default: none | Slave device's IP address. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Slave device's Modbus TCP port. |
| Period | integer [1..86400]; default: 60 | Interval at which requests are sent to the slave device. |
| Timeout | integer [1..30]; default: 5 | Maximum response wait time. |
Requests Configuration
A Modbus request is a way of obtaining data from Modbus slaves. The master sends a request to a slave specifying the function code to be performed. The slave then sends the requested data back to the Modbus master. You can create a maximum of 64 request configurations for each slave device.
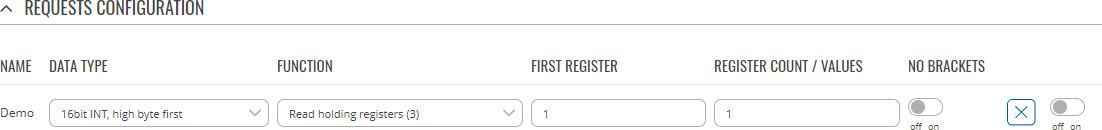
The Request Configuration list is empty by default. To add a new Request Configuration loon to the Add New Instance section. Enter a custom name into the 'Name' field and click the 'Add' button:
The new Request Configuration should become visible in the list:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: Unnamed | Name of this Request Configuration. Used for easier management purposes. |
| Data type | 8bit INT | 8bit UINT | 16bit INT, high byte first | 16bit INT, low byte first | 16bit UINT, high byte first | 16bit UINT, low byte first | 32bit float, Byte order 1,2,3,4 | 32bit float, Byte order 4,3,2,1 | 32bit float, Byte order 2,1,4,3 | 32bit float, Byte order 3,4,1,2; default: 16bit INT, high byte first | Defines how read data will be stored. |
| Function | Read coils (1) | Read input coils (2) | Read holding registers (3) | Read input registers (4) | Set single coil (5) | Set single coil register (6) | Set multiple coils (15) | Set multiple holding registers (16); default: Read holding registers (3) | Specifies the type of register being addressed by a Modbus request. |
| First Register | integer [0..65535]; default: 1 | First Modbus register from which data will be read. |
| Register Count / Values | integer [1..2000]; default: 1 | Number of Modbus registers that will be read during the request. |
| Enabled | off | on; default: off | Turns the request on or off. |
| Delete [ X ] | - (interactive button) | Deletes the request. |
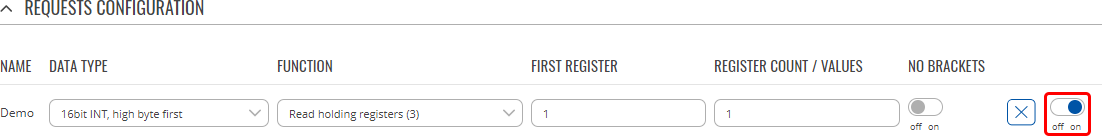
Additional note:By default the newly added Request Configurations are turned off. You can use the on/off slider to the right of the Request Configuration to turn it on:
After having configured a request, you should see a new 'Request Configuration Testing' section appear. It is used to check whether the configuration works correctly. Simply click the 'Test' button and a response should appear in the box below. A successful response to a test may look something like this:
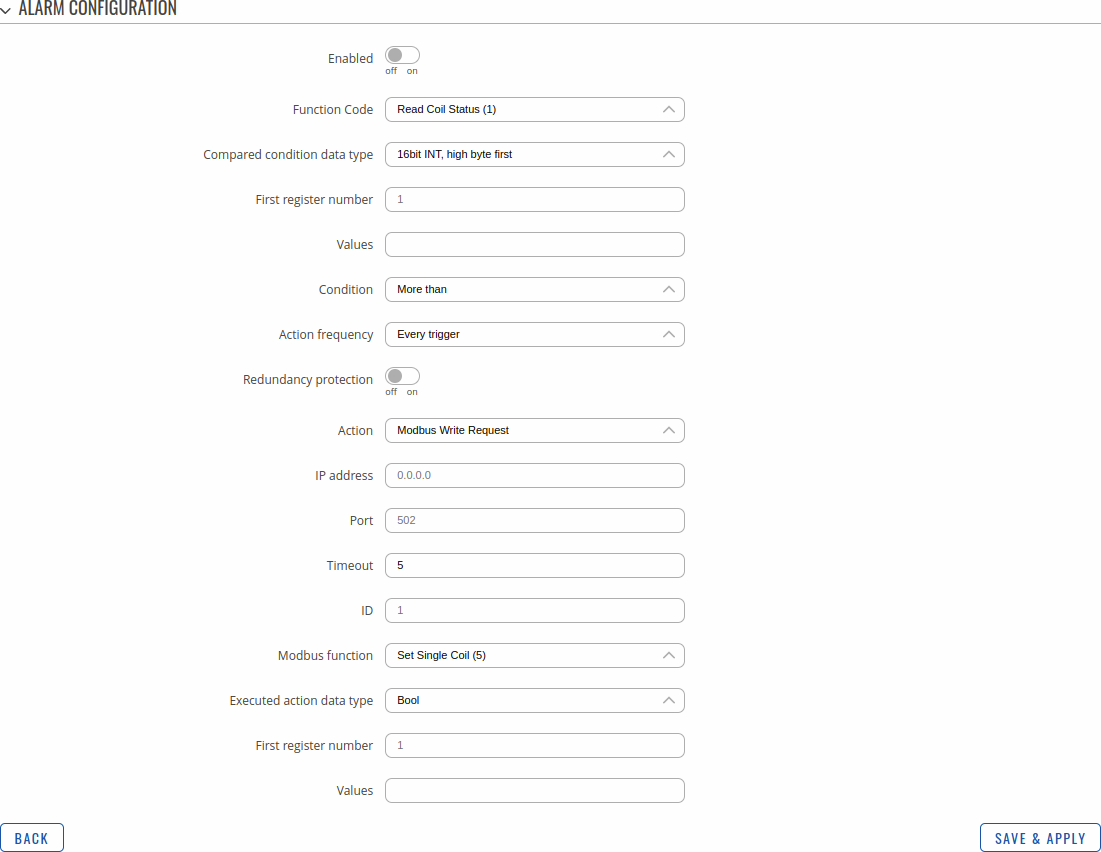
Alarms Configuration
Alarms are a way of setting up automated actions when some Modbus values meet user specified conditions. The figure below is an example of the Alarms Configuration list.
It is empty by default. So, to begin editing click the 'Add' button and you should be redirected to a page such as this:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enabled | off | on; default: off | Turns the alarm on or off. |
| Function code | Read Coil Status (1) | Read Input Status (2) | Read Holding Registers (3) | Read Input Registers (4); default: Read Coil Status (1) | Modbus function used for this alarm's Modbus request. |
| Register | integer [1..65536]; default: none | Number of the Modbus coil/input/holding-register/input-register to read from. |
| Condition | More than | Less than | Equal to | Not Equal to; default: Equal to | When a value is obtained it will be compared against the value specified in the following field. The comparison will be made in accordance with the condition specified in this field. |
| Value | various; default: none | The value against which the read data will be compared. |
| Value | integer [0..65535]; default: none | The value against which the read data will be compared. |
| Action frequency | Every trigger | First trigger; default: Every trigger | Describes how frequently the specified action will be taken. |
| Redundancy protection | off | on; default: off | Protection against executing a configured action too often. |
| Redundancy protection period | integer [1..86400]; default: none | Duration to activate redundancy protection for, measured in seconds. This field becomes visible only when 'Redundancy protection' is turned on. |
| Action | SMS | MODBUS Write Request; default: MODBUS Write Request | Action that will be taken if the condition is met. Possible actions:
|
| SMS: Message | string; default: none | SMS message text. |
| SMS: Phone number | phone number; default: none | Recipient's phone number. |
| MODBUS Write Request: IP address | ip | host; default: none | Modbus slave's IP address. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Port | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Modbus slave's port. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Timeout | integer [1..30]; default: 5 | Maximum time to wait for a response. |
| MODBUS Write Request: ID | integer [1..255]; default: none | Modbus slave ID. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Modbus function | Read Force Single Coil (5) | Preset Single Register (6) | Force Multiple Coils (15) | Force Multiple Registers (16); default: Force Single Coil (5) | A function code specifies the type of register being addressed by a Modbus request. |
| MODBUS Write Request: First register | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Begins reading from the register specified in this field. |
| MODBUS Write Request: Values | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Register/Coil values to be written (multiple values must be separated by space character). |
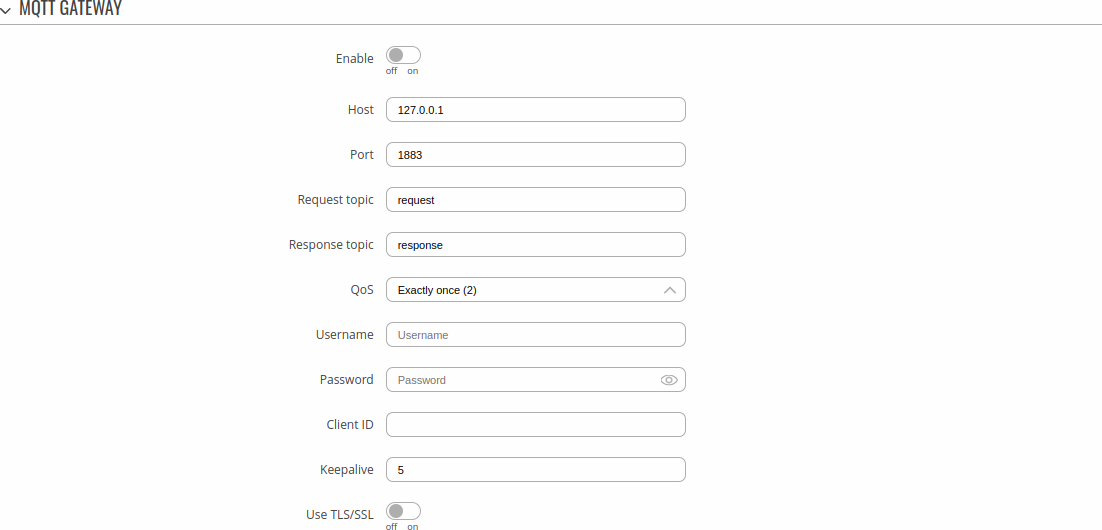
MQTT Gateway
The MQTT Gateway function is used to transfer Modbus data over MQTT. Refer to the table for information on MQTT gateway configuration fields.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns MQTT gateway on or off. |
| Host | ip | host; default: 127.0.0.1 | IP address or hostname of an MQTT broker. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 1883 | Port number of the MQTT broker. |
| Request topic | alphanumeric string; default: request | . |
| Response topic | alphanumeric string; default: response | . |
| Username | string; default: none | Username for authentication to the MQTT broker. |
| Password | string; default: none | Password for authentication to the MQTT broker. |
See also
Template:Networking device modbus see also
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]]