Template:Networking rut manual dynamic dns: Difference between revisions
Gytispieze (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Gytispieze (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "\{\{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_fw_disclosure (.*) (.*) (.*) (.*) (.*) \}\}" to "{{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | series = {{{series}}} | name = {{{name}}} | fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = {{{series}}} | name = {{{name}}} }} }}") |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: | {{Template: Networking_device_manual_fw_disclosure | ||
| | | series = {{{series}}} | ||
| name = {{{name}}} | |||
| fw_version ={{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | |||
| series = {{{series}}} | |||
| | | name = {{{name}}} | ||
}} | |||
}} | }} | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
Latest revision as of 11:30, 24 October 2023
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
Dynamic DNS (DDNS or DynDNS) is a method of automatically updating a name server in the Domain Name System (DNS). This is most often utilized when the end user has a dynamic IP address and wants to bind it to a static hostname.
The {{{name}}} device is compatible with many different third party DNS services that provide the possibility to create a custom hostname and bind it to an IP address. The DDNS service periodically updates the IP address information of the hostname, making sure that the device remains reachable via the same hostname even in cases when its IP address has changed.
This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the Dynamic DNS page for {{{name}}} devices.
Dynamic DNS Overview
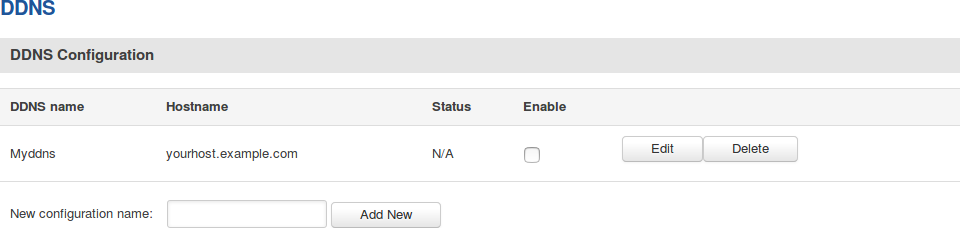
By default, an unconfigured DDNS instance will be present in the Dynamic DNS Overview page (the figure below is an example of this). You can create more DDNS instances by entering a New configuration name and clicking the Add New button or you can edit the existing instance since it is not operational by default.
Editing a DDNS instance
To configure a DDNS instance, click the Edit button located next to it.
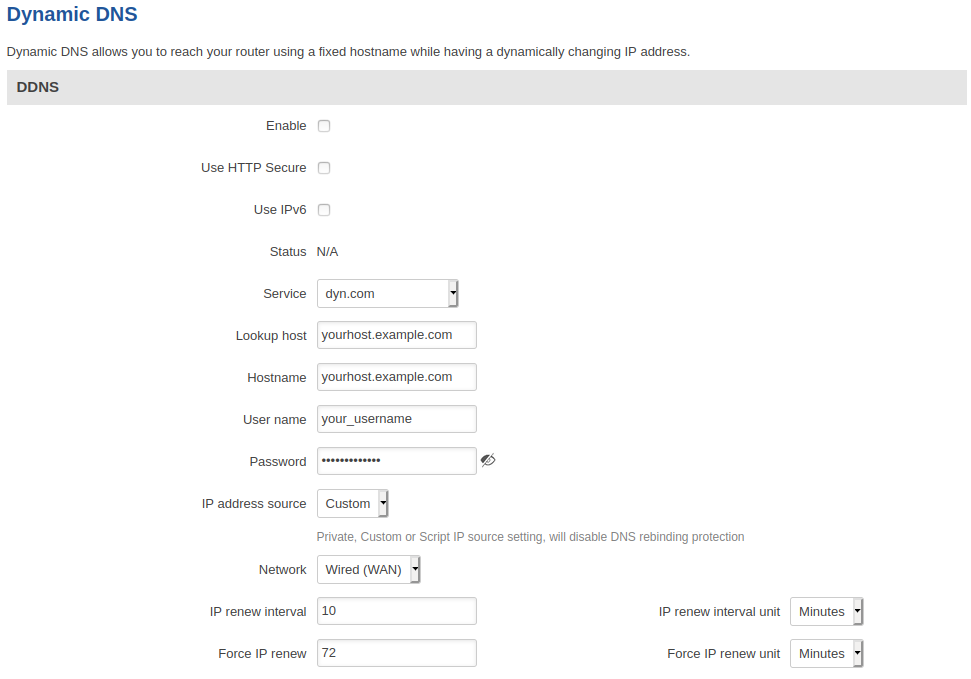
The figure below is an example of the edit page of the default DDNS instance called "Myddns" (already present in this device by default) and the table below provides information on the configuration fields contained in that page:
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; default: no | Turns the DDNS instance On or Off. |
| Use HTTP Secure | yes | no; default: no | Enables SSL data encryption. |
| Status | string; default: N/A | Data on the last status update of the DDNS instance. When status is shown as "N/A", it means that the device has not been able to establish a connection to the DDNS service provider. |
| Service | third party DNS service (chosen from list*) | -- custom --; default: dyn.com | Third party DNS service provider. |
| Lookup host | host; default: yourhost.example.com | Fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of your defined host. This is required to verify what the hostname's current IP address at DNS is (using nslookup/host command). |
| Hostname | host; default: yourhost.example.com | Hostname that will be linked with the IP address of this device. |
| Username | string; default: your_username | User name required to login to the third party DNS service; used to periodically login to your DNS service account and make necessary updates. |
| Password | string; default: your_password | Password required to login to the third party DNS service; used to periodically login to your DNS service account and make necessary updates. |
| IP address source | Custom | Public | Private | Script; default: Custom | Defines the source to read the system's IPv4-Address from, that will be sent to the DNS provider. So if, for example, your RUT has a Private IP (i.e., 10.140.56.57) on its WAN interface, then you can send this exact IP to DDNS server by selecting Private. |
| Custom: Network | LAN | WAN | WAN2 | WAN3 | PPP | PPP_USB ; default: WAN | Specifies which interface's IP address should be bound to the hostname. |
| Public: URL to detect | host; default: http://checkip.dyndns.com | URL which is used to get your device's public IP from. |
| Script: Script | string; default: none | User defined script your device which is used to get it's public IP from. |
| Script: Event Network | network interfaces; default: WAN | Network interface on which your script will be started. |
| IP renew interval | integer [5..600000]; default: 10 | Frequency at which the device will check whether it's IP address has changed. |
| IP renew interval unit | Minutes | Hours | Days; default: Minutes | Unit which is used in IP renew interval. |
| Force IP renew | integer [5..600000]; default: 72 | Frequency at which IP update requests are sent to the DNS provider. |
| Force IP renew unit | Minutes | Hours | Days; default: Minutes | Unit which is used in Force IP renew interval. |
| * SUPPORTED DNS SERVICES | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3322.org | able.or.kr | afraid.org-basicauth | afraid.org-keyauth | all-inkl.com | bind-nsupdate | binero.se | changeip.com |
| cloudflare.com-v4 | core-networks.de | ddns.com.br | ddnss.de | ddo.jp | desec.io | dhis.org | dnsdynamic.org |
| dnsexit.com | dnshome.de | dnsmadeeasy.com | dnsmax.com | dnsomatic.com | dnspark.com | do.de | domopoli.de |
| dtdns.com | duckdns.org | duiadns.net | dy.fi | dyn.com | dyndns.it | dyndns.org | dyndnss.net |
| dyns.net | dynsip.org | dynu.com | dynv6.com | easydns.com | editdns.net | goip.de | google.com |
| he.net | joker.com | loopia.se | mydns.jp | myonlineportal.net | mythic-beasts.com | namecheap.com | nettica.com |
| noip.com | no-ip.pl | now-dns.com | nsupdate.info | nubem.com | opendns.com | oray.com | ovh.com |
| regfish.de | schokokeks.org | secure.camera | selfhost.de | sitesolutions.com | spdns.de | spdyn.de | strato.com |
| system-ns.com | thatip.com | twodns.de | umedia.de | variomedia.de | xlhost.de | zerigo.com | zoneedit.com |
| zzzz.io | |||||||
See also
- Dynamic DNS configuration examples for specific providers:
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]]