Template:Networking rutos manual administration: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1,049: | Line 1,049: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
==Storage Memory Expansion== | |||
{{#ifeq:{{{usb}}}| 1 | | {{#ifeq:{{{usb}}}| 1 | | ||
===USB=== | ===USB=== | ||
Revision as of 13:14, 28 September 2023
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
This page is an overview of the Administration section of {{{name}}} devices.
General
The General section is used to set up some of device managerial parameters, such as changing device name. For more information on the General section, refer to figure and table below.
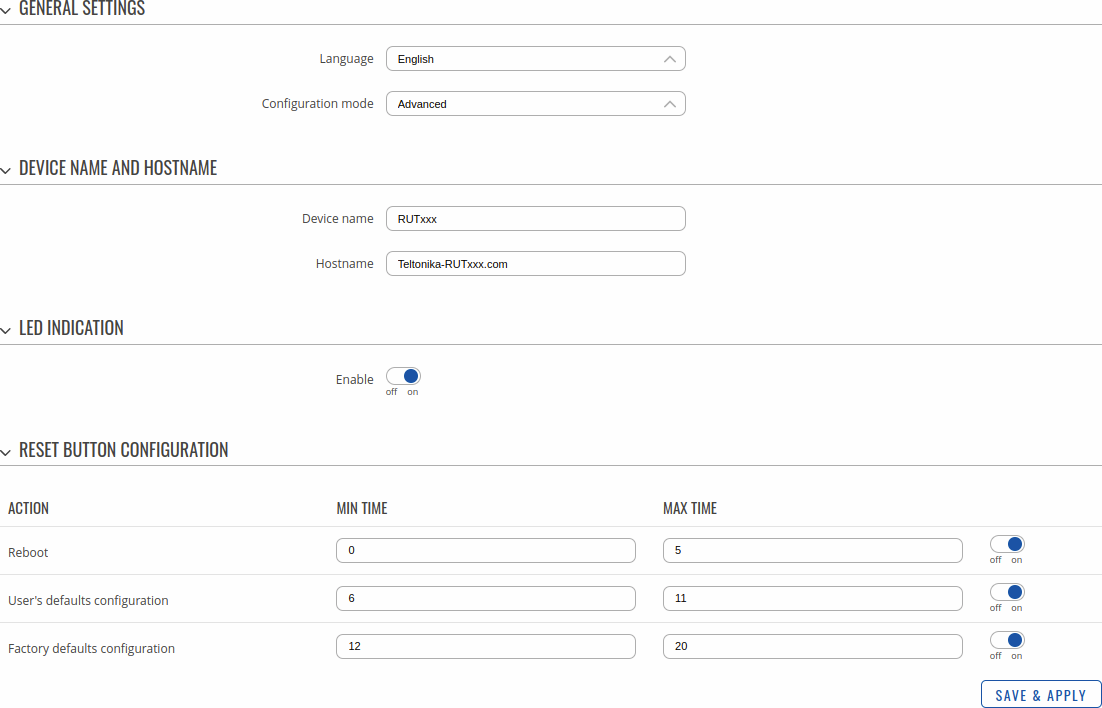
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| General Settings | ||
| Language | English | Turkish* | Spanish* | Portuguese* | German* | Japanese*; default: English | Changes the router's WebUI language. |
| Configuration Mode | Basic | Advanced; default: Basic | Mode determines what options and configurations are shown. In Basic mode only the essential configurations are shown. In Advanced mode there is greater freedom to configure and access more options. |
| Device name and hostname | ||
| Device name | string; default: {{{name}}} | Device model name. |
| Hostname | string; default: Teltonika-{{{name}}}.com | Device hostname. This can be used for communication with other LAN hosts. |
| LED Indication | ||
| Enable | off | on; default: on | Manages signal strength, LAN and connection status indication LEDs. |
| Reset Button Configuration | ||
| Min time | integer [0..60]; default: none | Minimum time (in seconds) the button needs to be held to perform an action. |
| Max time | integer [1..60]; default: none | Maximum time (in seconds) the button can be held to perform an action, after which no action will be performed. |
* Different language packages can be downloaded separately from the Services → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]] page.
Date & Time
Summary
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks. This chapter is an overview of the NTP section for {{{name}}} devices.
General
The Time Synchronization section lets you select time zone and synchronize the time.
The figure below is an example of the Time Synchronization section and the table below provides information about the fields contained in that section:
[[File:Networking_rutos_ntp_general_gps_{{{gps}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Current system time | time; default: none | Current local time of the device. |
| Sync with browser | -(interactive button) | Click to synchronize device time and time zone to browsers, if your device time or time zone is not correct. |
| Time zone | time zone; default: UTC | The device will sync time in accordance with the selected time zone. |
NTP
This section is used to configure NTP client, server and time servers.
Time Synchronization
This section is used to configure the device's time settings.
[[File:Networking_rutos_ntp_ntp_time_synchronization_{{{mobile}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable NTP Client | off | on; default: on | Turns NTP on or off. |
| Save time to flash | off | on; default: off | Saves last synchronized time to flash memory. |
| Force Servers | off | on; default: off | Forces unreliable NTP servers. |
| Update interval (in seconds) | integer; default: 86400 | How often the device will update the time. |
| Offset frequency | integer; default: 0 | Adjusts the minor drift of the clock so that it will run more accurately. |
| Count of time synchronizations | integer; default: none | The amount of times the device will perform time synchronizations. Leave empty in order to set to infinite. |
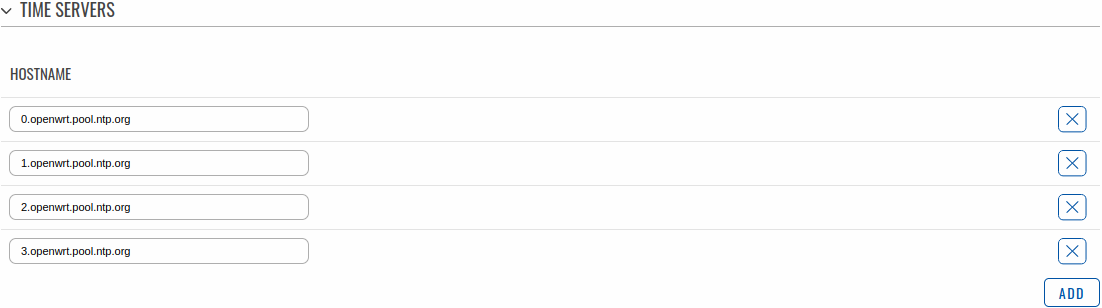
Time Servers
This section is used to specify which time servers the device will use for time synchronization. To add more time servers to the list, click the 'Add' button.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hostname | ip | url; default: 0.openwrt.pool.ntp.org | NTP servers that this device uses to sync time. |
NTP Server
The device can also act as an NTP Server, providing clock synchronization to other devices in the network. From this section you can turn this feature on or off:
NTPD
The NTPD program is an operating system daemon that synchronizes the system clock to remote NTP time servers or local reference clocks. NTPD includes the ability to use this to keep your clock in sync and will run more accurately than a clock on a device not running NTPD. NTPD will also use several servers to improve accuracy. It is a complete implementation of NTP version 4 defined by RFC-5905, but also retains compatible with version 3 defined by RFC-1305 and versions 1 and 2, defined by RFC-1059 and RFC-1119, respectively.
Note: PAM is additional software that can be installed from the Services → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]] page.
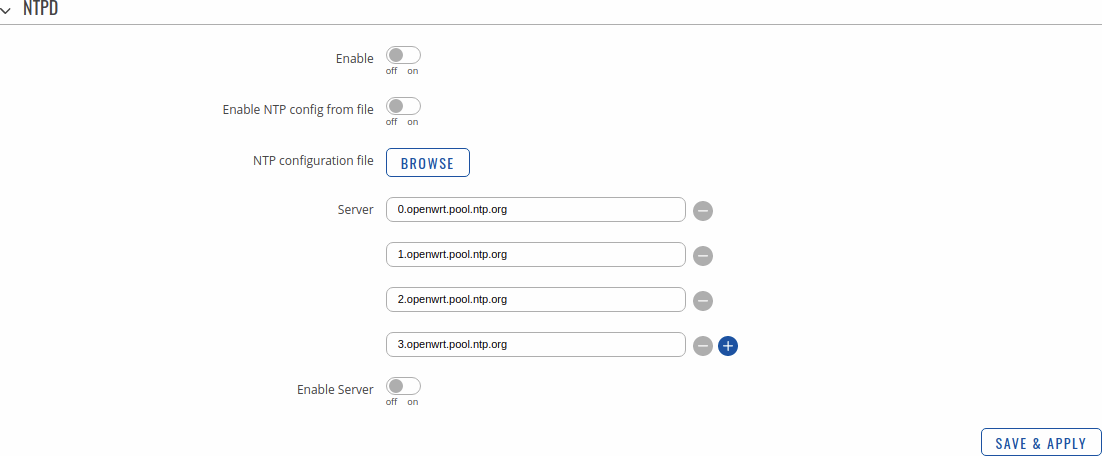
| Field | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enable NTPD | off
Access ControlGeneralThe Access Control page is used to manage remote and local access to device. Important: turning on remote access leaves your device vulnerable to external attackers. Make sure you use a strong password.

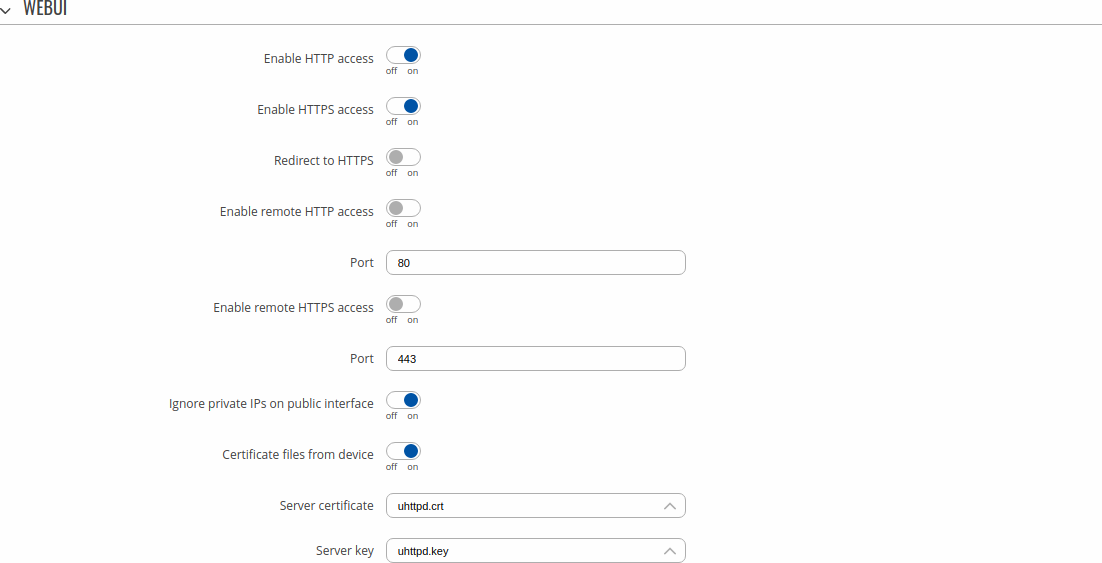
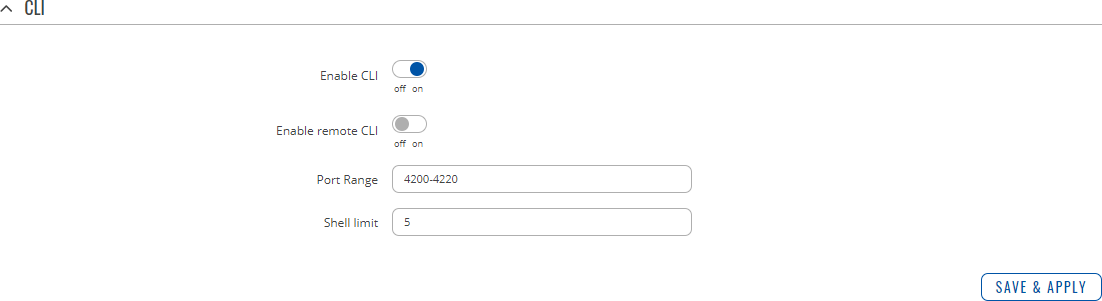
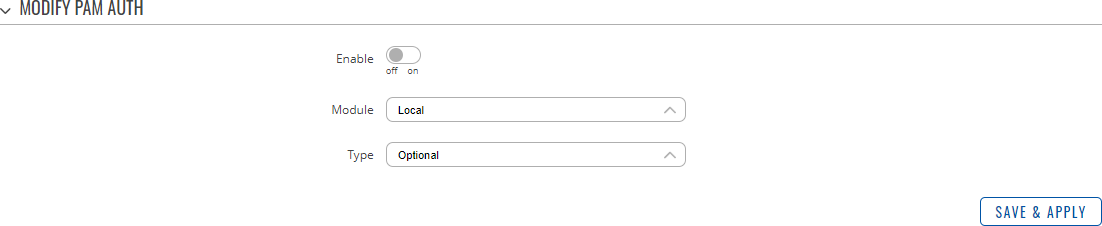
PAMNote: PAM is additional software that can be installed from the Services → [[{{{name}}} Package Manager|Package Manager]] page. Modify PAM Auth
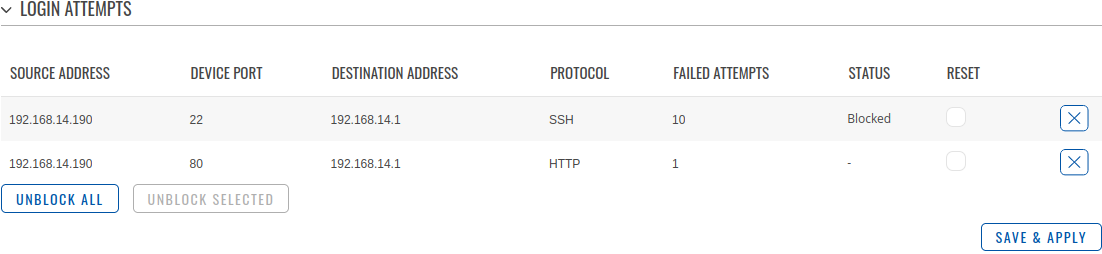
SecurityThe Security tab provides the possibility to enable/disable blocking IP's service and delete blocked devices from the list. IP Block Settings
Login Attempts
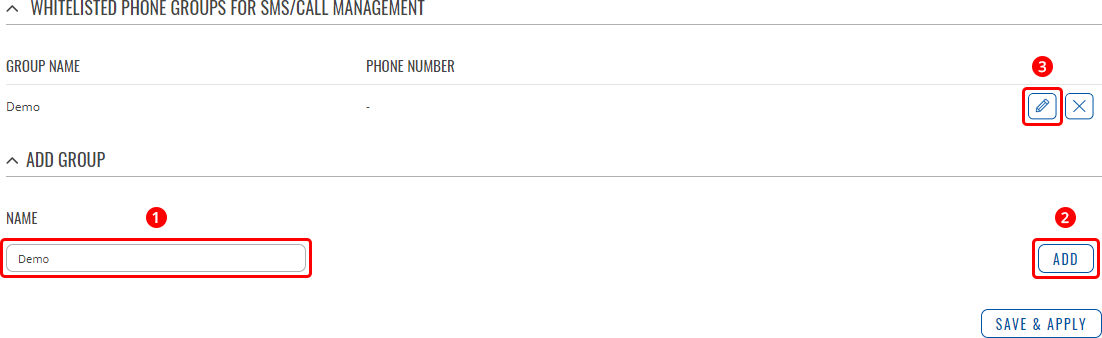
RecipientsThe Recipients section is used to configure phone groups and email users, which can later be used along with SMS or email related services, such as [[{{{name}}} Events Reporting|Events Reporting]]. Phone GroupsA Phone Group is a collection of phone numbers that can be used as the recipient in SMS & call related services instead of specifying every number individually. The phone group list is empty by default thus, you must first add at least one new group before you can add phone numbers to it. To create and begin editing a phone group, follow these steps:
After clicking 'Edit' you should be redirected to that phone group's configuration page where you can start adding phone numbers to it.
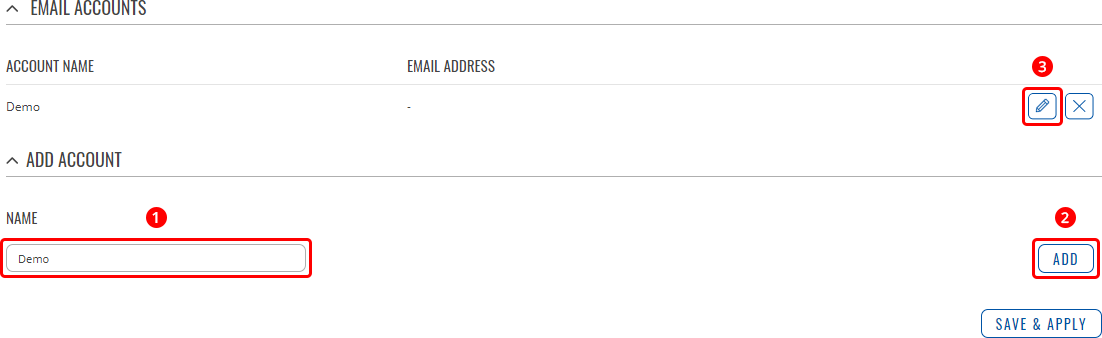
Email AccountsWhen email related services (such as [[{{{name}}} Events Reporting|Events Reporting]]) are used, the device logs in to the specified email account and reads the inbox (e.g., Email to SMS) or sends out a message (e.g., SMS to Email) depending on the configured service. In this context, an Email Account is an configuration instance that contains the necessary data required in order to log into an email account. The email accounts list is empty by default thus, you must first add at least one new account before you can configure it. To create and begin editing an email account, follow these steps:
After clicking 'Edit' you should be redirected to that email account's settings page where you can start configuring the account.
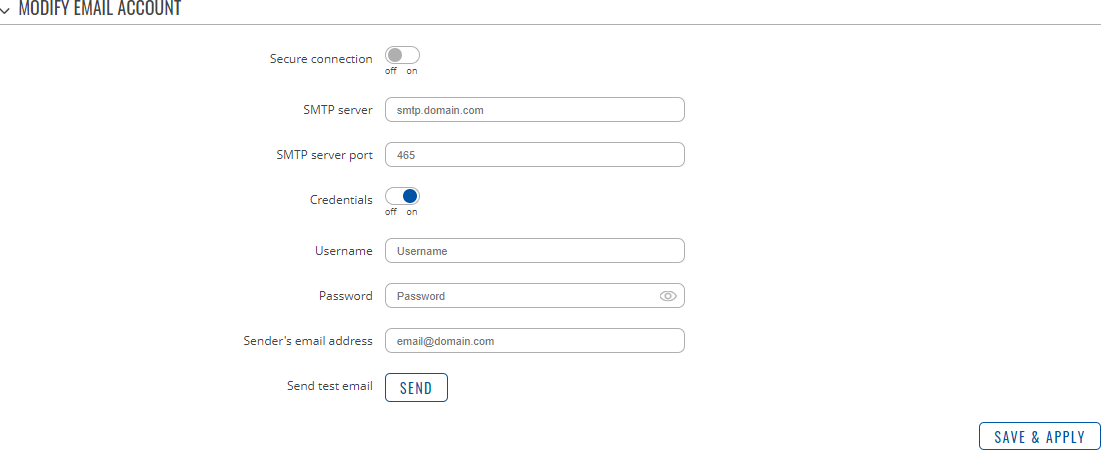
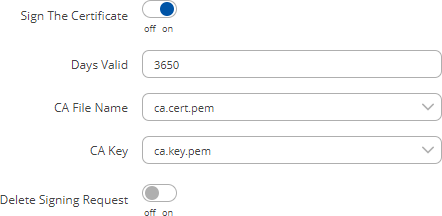
CertificatesThe Certificates page is used for convenient TLS certificate and key generation and management. Generated files can be exported and used on other machines or locally on this device with functions that use TLS/SSL, such as [[{{{name}}} MQTT|MQTT]], [[{{{name}}} VPN#OpenVPN|OpenVPN]], [[{{{name}}} VPN#IPsec|IPsec]] and others. Certificate GenerationThe Certificate Generation tab provides the possibility to generate TLS certificates required for secure authentication and communication encryption used by some of the devices services. There are five distinct generation methods (denoted by the selected 'File Type').
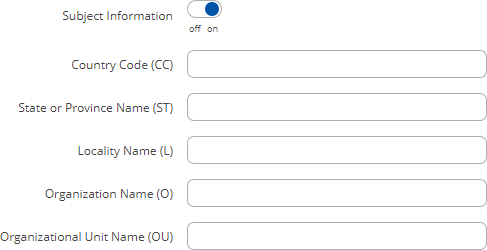
Generation ParametersGenerating each type of file (excluding 'Simple') requires setting some parameters. This section provides an overview for parameters used in TLS certificate generation. Core parameters or simply parameters that apply to each file type are the size and common name of the generated file(s).
Subject information is not mandatory but can be used as user-friendly way to identify the ownership of certificate files by including such information as the owner's location and company name. The Sign the certificate slider control whether the certificate will be signed automatically or manually after the generation is complete.
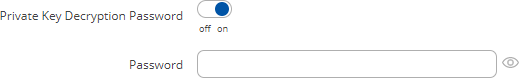
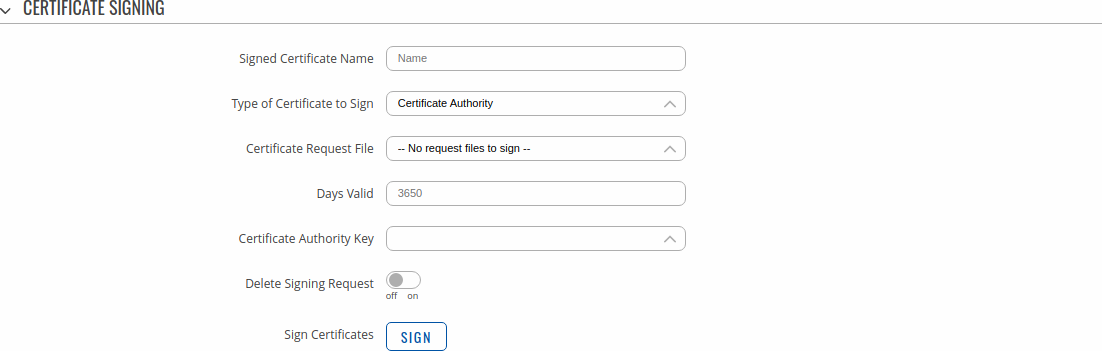
A Private Key Decryption Password is a parameter used to decrypt private keys protected by a password. Certificate SigningThe Certificate Signing section is used to validate (sign) unsigned certificates.
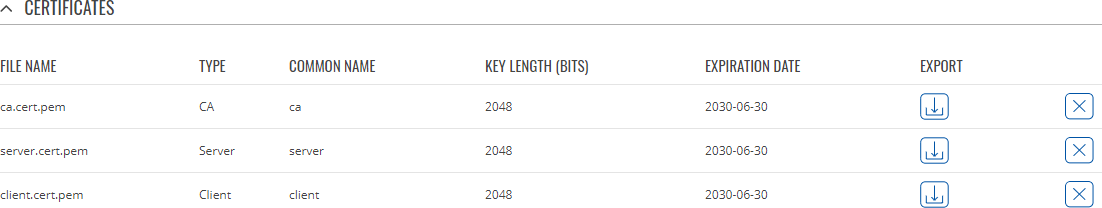
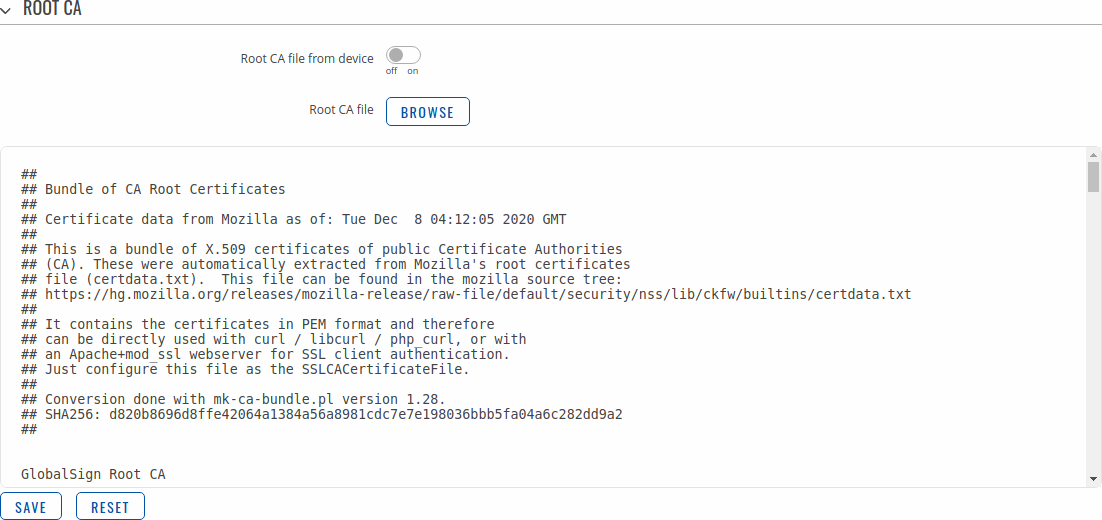
Certificate ManagerThe Certificate Manager page displays information on all certificate and key files stored on the device and provides the possibility export these files for use on another machine or import files generated elsewhere. Certificate ImportThe Certificate Import section provides the possibility to import certificates and files generated on another machine. To upload such a file simply click 'Browse' and locate the file on your computer, it should then start uploading automatically. Certificates, Keys & RequestsThe Certificates, Keys and Requests section display files generated on or imported to the device along with the most important information related to them. By default, the lists are empty. A set certificates generated using 'Simple' file type would look something like this: The 'Export' buttons are used to download the files from the device onto your local machine. The 'X' buttons located to the right of each entry are used to delete related files. Root CAThe Root CA section is used to add a root CA certificate file to the device. There is a default file already preloaded on the device which will be overwritten by any uploaded file. The certificates must be in .pem format, maximum file size is 300 KB. These certificates are only needed if you want to use HTTPS for your services and the default file should be sufficient in most cases.
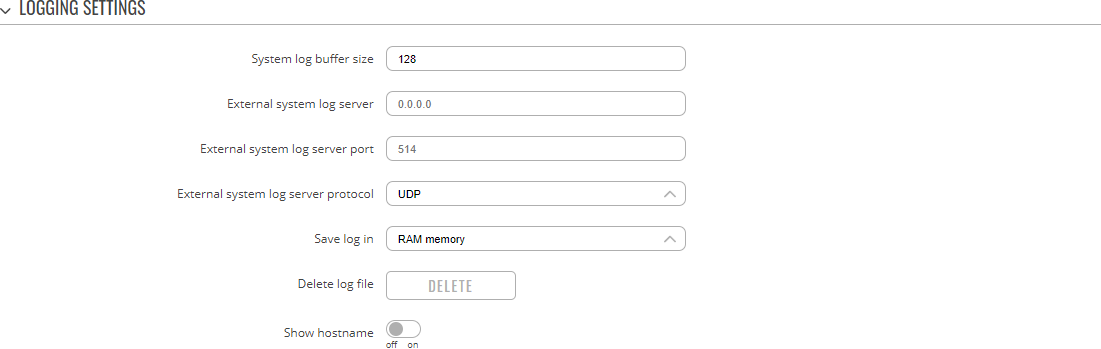
TroubleshootLogging SettingsThe Logging Settings section is used to configure how and where the device stores system log data. The system log is a file that contains information on various system related events and is useful to engineers for troubleshooting the device.
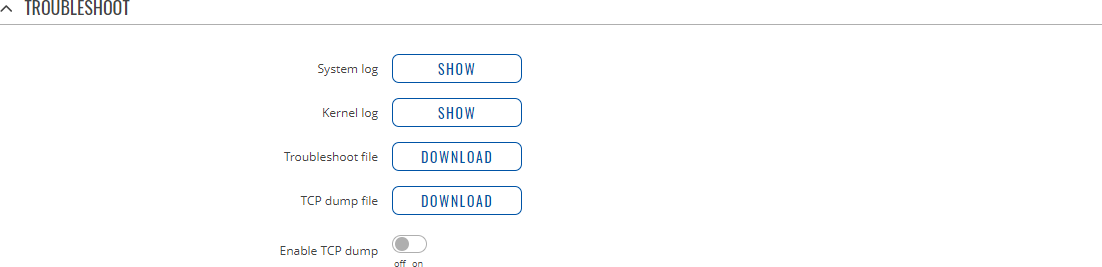
TroubleshootThe Troubleshoot section is used to download various files that contain information used for troubleshooting the device. Refer to the figure and table below for information on the Troubleshoot page.
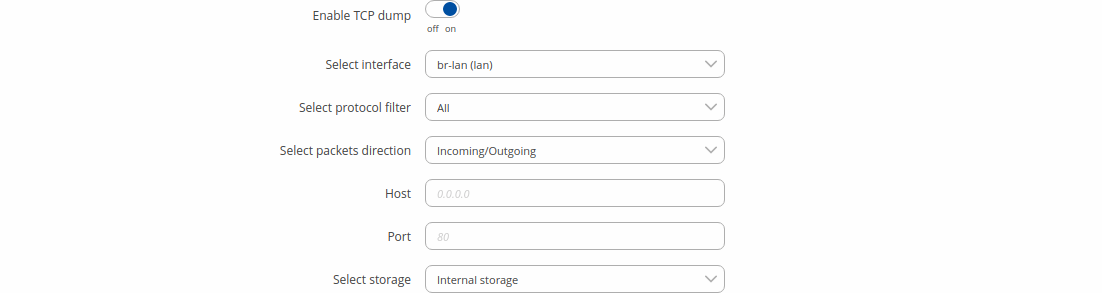
* As of {{{series}}}_R_00.07.00, TCPdump is not part of core functionality anymore. To see these options, the TCPdump package must be downloaded from [[{{{name}}}_Package_Manager|Package Manager]]. TCP dumpTCP dump is an optional downloadable functionality* used to capture packets moving through network interfaces. By default, the device does not store TCP dump information. You must enable TCP dump and save the changes before you can download the file. If you enable TCP dump, you will notice additional configuration fields appear. Refer to the figure and table below for realted information. * You can download the TCPdump package from [[{{{name}}}_Package_Manager|Package Manager]].
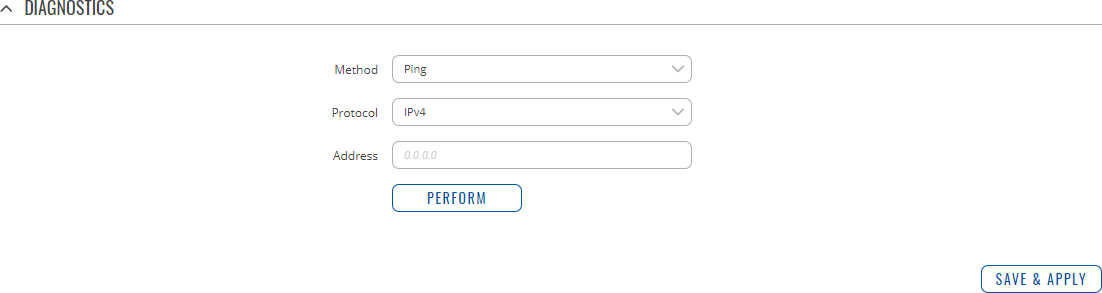
DiagnosticsThe Diagnostics section is used to execute simple network diagnostic tests, including ping, traceroute and nslookup.
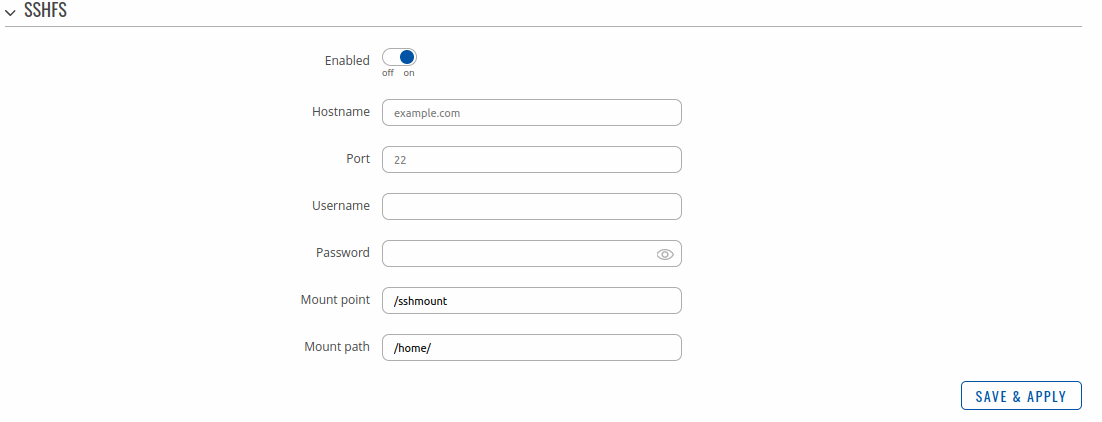
Storage Memory ExpansionSSHFSSSHFS is a tool, which allows you to mount a remote filesystem (in remote SSH server) to your {{{name}}} device using SSH. This service is safe to use as it authenticates connections and encrypts them. SSHFS configuration consists of setting up authentication, port and mount information parameters. Below is an example oh the SSHFS configuration page.
[[Category:{{{name}}} System section]] |