Template:Networking rutos manual serial utilities: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Renewed |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | RUT9 |<i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} RS232/RS485 (legacy WebUI)#RS232|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT9XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i>|}} | {{#ifeq: {{{series}}}| RUT9 |<i><b>Note</b>: <b>[[{{{name}}} RS232/RS485 (legacy WebUI)#RS232|click here]]</b> for the old style WebUI (FW version {{Template: Networking_device_manual_latest_fw | series = RUT9XX}} and earlier) user manual page.</i>|}} | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| Line 351: | Line 351: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Device</td> | <td>Device</td> | ||
<td>{{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_serial_ports | rs232={{{rs232}}} | rs485={{{rs485}}} | usb={{{usb}}} }}; default: <b>{{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_default_serial_port | rs232={{{rs232}}} | rs485={{{rs485}}} | usb={{{usb}}} }}</b></td> | <td>{{#ifeq:{{{default}}}|mbus|MBUS| {{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_serial_ports | rs232={{{rs232}}} | rs485={{{rs485}}} | usb={{{usb}}} }}}}; default: <b>{{#ifeq:{{{default}}}|mbus|MBUS| {{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_default_serial_port | rs232={{{rs232}}} | rs485={{{rs485}}} | usb={{{usb}}} }}}}</b></td> | ||
<td>Specifies which serial port will be used for serial communication.</td> | <td>Specifies which serial port will be used for serial communication.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 440: | Line 440: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Stop bits</td> | <td>Stop bits</td> | ||
<td>1 {{!}} 2; default: <b>1</b></td> | <td>{{#switch: {{{name}}} | TRB143 = 1; default: <b>1</b> | #default = 1 {{!}} 2; default: <b>1</b> }}</td> | ||
<td>Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used.</td> | <td>Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Parity</td> | <td>Parity</td> | ||
<td>None {{!}} Odd {{!}} Even {{!}} Mark {{!}} Space; default: <b>None</b></td> | <td>{{#switch: {{{name}}} | TRB143 = Even {{!}} default: Even | #default = None {{!}} Odd {{!}} Even {{!}} Mark {{!}} Space; default: <b>None</b> }}</td> | ||
<td>In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check. | <td>In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check. | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| Line 480: | Line 480: | ||
You can configure network related parameters of the serial connection in the <b>Over IP Configuration</b> secion. | You can configure network related parameters of the serial connection in the <b>Over IP Configuration</b> secion. | ||
[[File:Networking rutos manual serial utilities over ip mbus configuration | [[File:Networking rutos manual serial utilities over ip mbus configuration general_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
Revision as of 14:32, 6 May 2024
The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version .
Summary
The Serial Utilities page is used to make serial communication configurations of different types. This manual page provides an overview of the Serial Utilities page in {{{name}}} devices.
Console
Console mode requires no further configuration than the settings above and is used as a direct-access method to the device's shell interface. For this purpose you may want use such applications as PuTTY on Windows and microcom, minicom, picocom or similar applications on Linux.
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_serial_utilities_console_default_{{{default}}}_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns the instance on or off. |
| Name | string; default: none | Instance name, generated by the user when first creating the configuration. |
| Device | ; default: | Specifies which serial port will be used for serial communication. |
| Baud rate | integer [300..3000000]; default: 9600 | Data rate for serial data transmission (in bits per second (bps)). |
| Data bits | 8; default: 8 | Number of data bits for each character. |
| Stop bits | 1 | 2; default: 1 | Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronize with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used. |
| Parity | None | Odd | Even | Mark | Space; default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check.
|
| Flow control | None; default: None | In many circumstances a transmitter might be able to send data faster than the receiver is able to process it. To cope with this, serial lines often incorporate a "handshaking" method, usually distinguished between hardware and software handshaking. |
Over IP
The Over IP serial type is used to manage serial connections over a TCP/IP network.
Serial Device Configuration
Configure serial port communication parameters in the Serial Device Configuration section.
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_serial_utilities_over_ip_serial_default_{{{default}}}_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns the instance on or off. |
| Name | string; default: none | Instance name, generated by the user when first creating the configuration. |
| Device | ; default: | Specifies which serial port will be used for serial communication. |
| Baud rate | integer [300..3000000]; default: 9600 | Data rate for serial data transmission (in bits per second (bps)). |
| Data bits | 8; default: 8 | Number of data bits for each character. |
| Stop bits | 1 | 2; default: 1 | Stop bits sent at the end of every character allow the receiving signal hardware to detect the end of a character and to resynchronise with the character stream. Electronic devices usually use one stop bit. Two stop bits are required if slow electromechanical devices are used. |
| Parity | None | Odd | Even | Mark | Space; default: None | In serial transmission, parity is a method of detecting errors. An extra data bit is sent with each data character, arranged so that the number of 1 bits in each character, including the parity bit, is always odd or always even. If a byte is received with the wrong number of 1s, then it must have been corrupted. However, an even number of errors can pass the parity check.
|
| Flow control | None; default: None | In many circumstances a transmitter might be able to send data faster than the receiver is able to process it. To cope with this, serial lines often incorporate a "handshaking" method, usually distinguished between hardware and software handshaking. |
Over IP Configuration Settings
You can configure network related parameters of the serial connection in the Over IP Configuration secion.
File:Networking rutos manual serial utilities over ip mbus configuration general v2.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mode | Server | Client | Client + server | Bidirect; default: Server | This device's role in the connection:
|
| Protocol | TCP | UDP; default: TCP | Protocol used in the communication process. |
| Client: Destination address | IP | Port; default: empty | Specify server address and port for client to connect to. E.g first field for address second for port. 16 destination addresses are allowed. |
| Server: UDP: Predefined addresses | IP | Port; default: empty | Set predefined IP and port for UDP connection. E.g first field for address second for port. |
| Listening port | [1..65535]; default: empty | When enabled, all data will be transmitted transparently. |
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
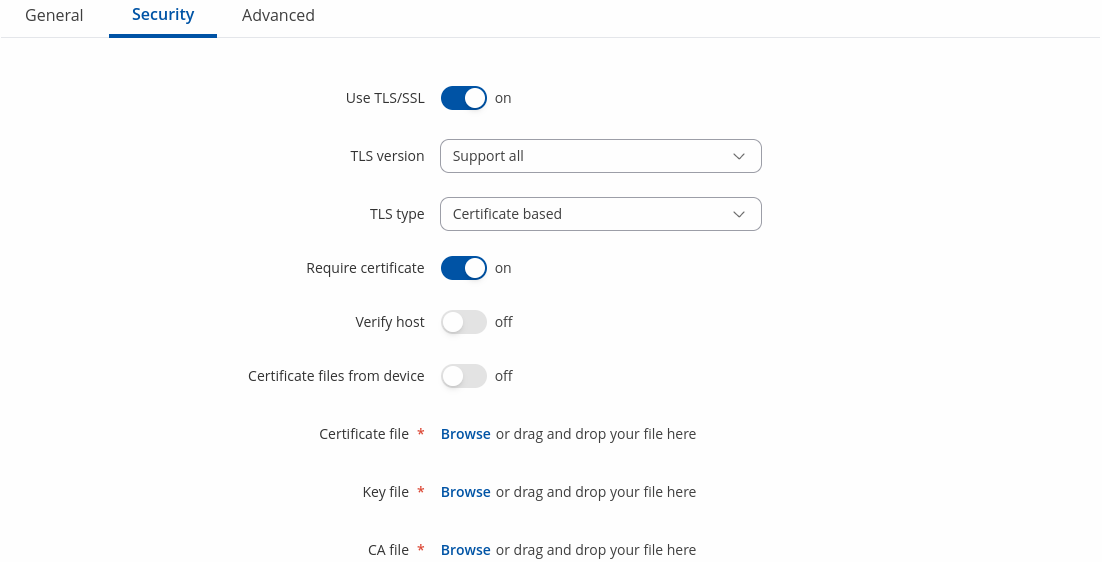
| Use TLS/SSL | off | on; default: off | Mark to use TLS/SSL for connection. |
| TLS version | Support all | tlsv1.0 | tlsv1.1 | tlsv1.2 | tlsv1.3; default: Support all | Minimum TLS version allowed to be used. |
| TLS type | Certificate based | Pre-Shared-Key based; default: Certificate based | Select the type of TLS encryption. |
| Require certificate | off | on; default: on | Demand certificate and key from peer and verify them against certificate authority. |
| Verify host | off | on; default: off | Check if the server certificates Common Name (CN) matches hostname to which client is connecting. |
| Certificate files from device | off | on; default: off | Choose this option if you want to select certificate files from device. Certificate files can be generated <a class=link href="/system/admin/certificates/generation">here</a>. |
| Certificate file | .crt file; default: none | Upload certificate file. |
| Key file | .key file; default: none | Upload key file. |
| CA file | .ca file; default: none | Upload CA file. |
| Pre-Shared-Key | string; default: none | The pre-shared-key in hex format with no leading “0x”. |
| Identify | string; default: none | Specify the identity. |
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
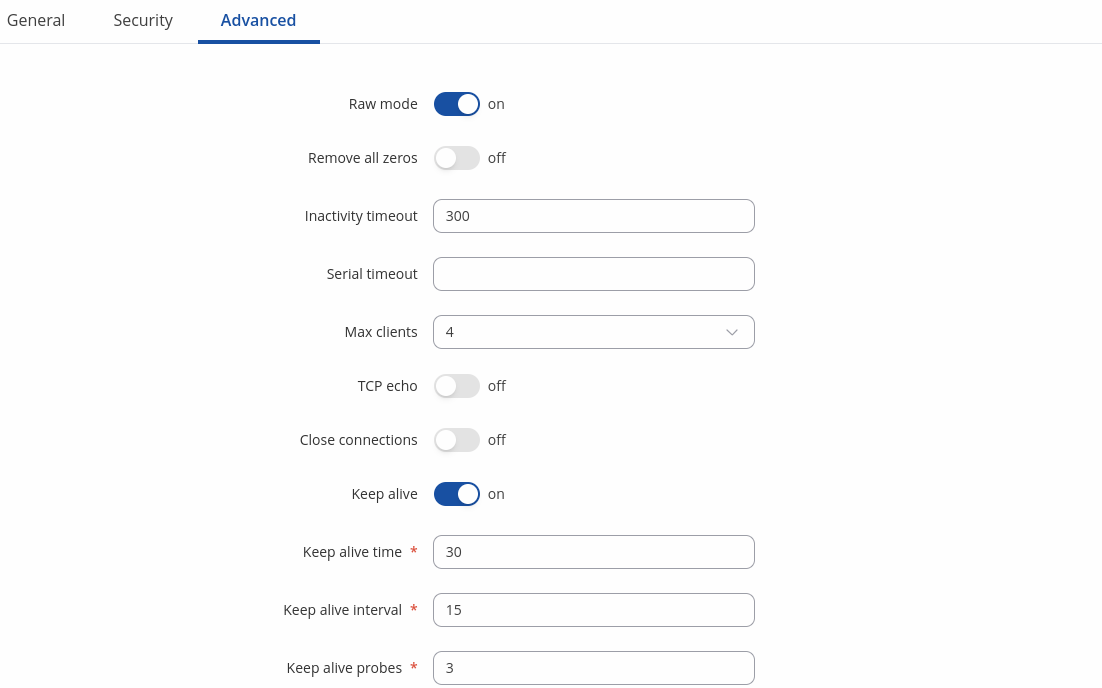
| Raw mode | off | on; default: on | When enabled, all data will be transmitted transparently. |
| Remove all zeros | off | on; default: off | When checked, indicates that the first hex zeros should be skipped. |
| Inactivity timeout | integer [0..36000]; default: 300 | Specifies period of time in seconds, where server connection must be inactive, to disconnect client. To disable timeout input 0. |
| Serial timeout | integer [0..1000]; default: none | Specifies the maximum milliseconds to wait for serial data. |
| Max clients | integer [1..32]; default: 4 | Specify how many clients are allowed to connect simultaneously. |
| TCP echo | on | off; default: off | Enable software TCP echo. |
| Close connections | on | off; default: off | Close TCP connections everytime data is sent or received (might result in serial data loss). |
| Keep alive | on | off; default: off | Enable keep alive. |
| Keep alive time | integer [0..32000]; default: 0 | Close TCP connections everytime data is sent or received (might result in serial data loss). |
| Keep alive interval | integer [0..32000]; default: 0 | The interval between subsequential keepalive probes. |
| Keep alive probes | integer [0..32000]; default: 0 | The number of unacknowledged probes. |
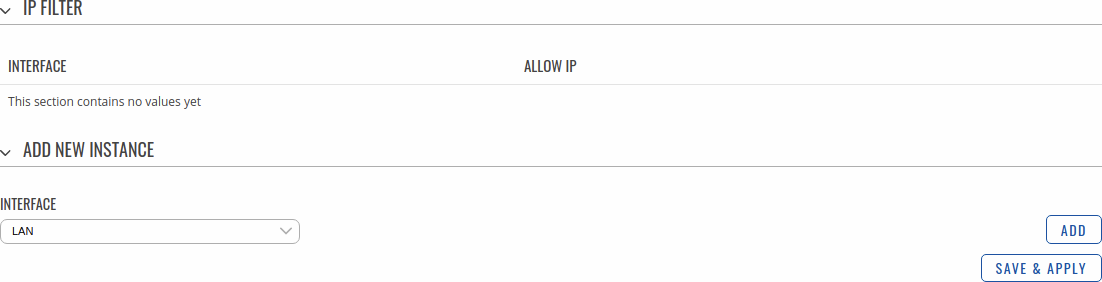
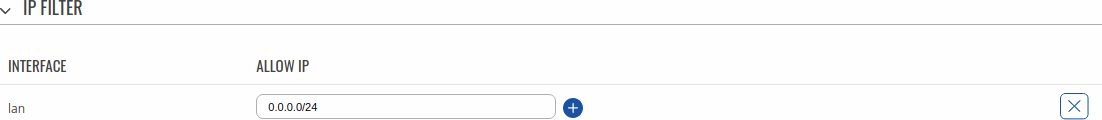
IP Filter
The IP Filter section is used for configuring which network is allowed to communicate with the device. You may add a new instance by selecting the Interface and pressing Add.
Then enter the IP address and save.
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]]