TRB140 Static Routes: Difference between revisions
(biski) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Summary == | ==Summary== | ||
'''Routing''' is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks. This chapter is an overview of the Routing section for TRB140 routers. | '''Routing''' is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks. This chapter is an overview of the Routing section for TRB140 routers. | ||
== Static IPV4 Routes == | ==Static IPV4 Routes== | ||
[[File:Networking rutx manual routing static routes v1.png | [[File:Networking rutx manual routing static routes v1.png|thumb|1154x1154px|alt=]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"><tr><th>field name</th><th>value</th><th>description</th></tr><tr><td>Interface</td><td>lan | mobile | eth0 </td><td>The zone where the target network resides</td></tr><tr><td>Tar'''get*'''</td><td>ip; Default: '''0.0.0.0'''</td><td>The address of the destination network</td></tr><tr><td>IPv4-Netmask'''*'''</td><td>ip; Default: '''0.0.0.0'''</td><td>A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies</td></tr><tr><td>IPv4-Gateway</td><td>ip; Default: " "</td><td>Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule</td></tr><tr><td>Metric</td><td>integer; Default: '''0'''</td><td>The '''Metric''' value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the higher metric is applied</td></tr><tr><td>MTU</td><td></td><td></td></tr><tr><td>Route Type</td><td></td><td></td></tr></table><br /> | <table class="nd-mantable"><tr><th>field name</th><th>value</th><th>description</th></tr><tr><td>Interface</td><td>lan | mobile | eth0 </td><td>The zone where the target network resides</td></tr><tr><td>Tar'''get*'''</td><td>ip; Default: '''0.0.0.0'''</td><td>The address of the destination network</td></tr><tr><td>IPv4-Netmask'''*'''</td><td>ip; Default: '''0.0.0.0'''</td><td>A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies</td></tr><tr><td>IPv4-Gateway</td><td>ip; Default: " "</td><td>Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule</td></tr><tr><td>Metric</td><td>integer; Default: '''0'''</td><td>The '''Metric''' value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the higher metric is applied</td></tr><tr><td>MTU</td><td></td><td></td></tr><tr><td>Route Type</td><td></td><td></td></tr></table><br /> | ||
Revision as of 17:26, 21 November 2019
Summary
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks. This chapter is an overview of the Routing section for TRB140 routers.
Static IPV4 Routes
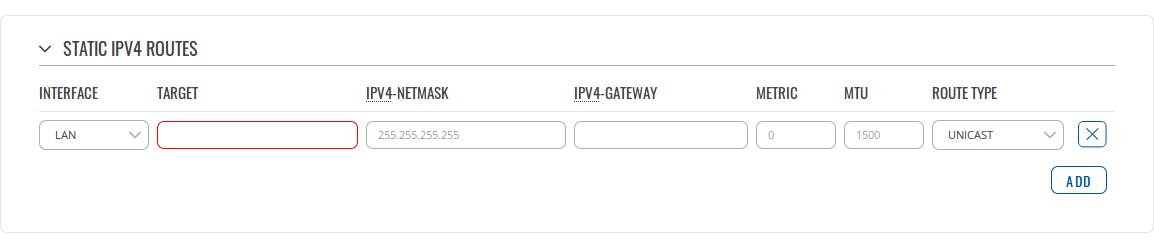
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | lan | mobile | eth0 | The zone where the target network resides |
| Target* | ip; Default: 0.0.0.0 | The address of the destination network |
| IPv4-Netmask* | ip; Default: 0.0.0.0 | A Mask that is applied to the Target to determine to what actual IP addresses the routing rule applies |
| IPv4-Gateway | ip; Default: " " | Defines where the router should send all the traffic that applies to the rule |
| Metric | integer; Default: 0 | The Metric value is used as a sorting measure. If a packet about to be routed fits two rules, the one with the higher metric is applied |
| MTU | ||
| Route Type |
