Template:Networking rutos configuration example l2tp over ipsec android: Difference between revisions
| Line 220: | Line 220: | ||
'''Disclaimer:''' | '''Disclaimer:''' | ||
This configuration example was created by using Android version 10. The IPsec '''Phase 1''' and '''Phase 2''' settings, which were used in this configuration example, might not work with other Android versions. | This configuration example was created by using Android version 10. The IPsec '''Phase 1''' and '''Phase 2''' settings, which were used in this configuration example, might not work with other Android versions and might require adjustment. | ||
Revision as of 14:58, 25 May 2020
 |
|
|---|---|
|
|
Configuration overview and prerequisites
Prerequisites:
- One RUTX router of any type
- A Public Static or Public Dynamic IP address
- At least one Android device
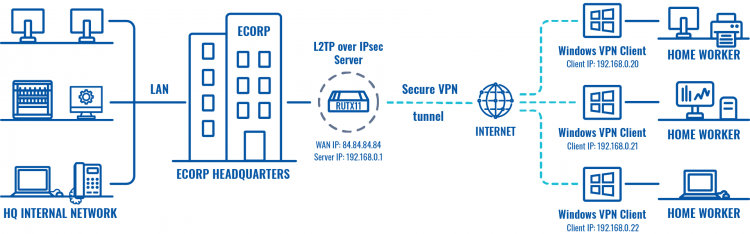
The topology above depicts the L2TP/IPsec scheme. - The router with the Public IP address (RUTX11) acts as the L2TP/IPsec server and the Android device acts as client. L2TP connects the networks of RUTX11 and Android client, IPsec provides the encryption for the L2TP tunnel. Created VPN tunnel will allow Android device to reach home network behind the RUTX11 router, but the rest of Android device network traffic will not be redirected through VPN. This way the VPN tunnel will not be under a huge load and will provide greater speeds.
When the scheme is realized, you will be able to reach your home internal network with all internal systems, cameras, or other IOT devices globally.
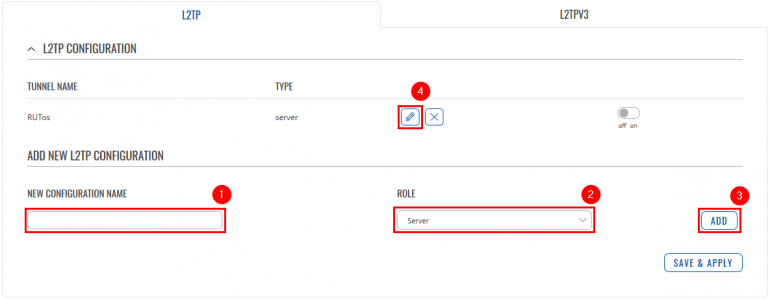
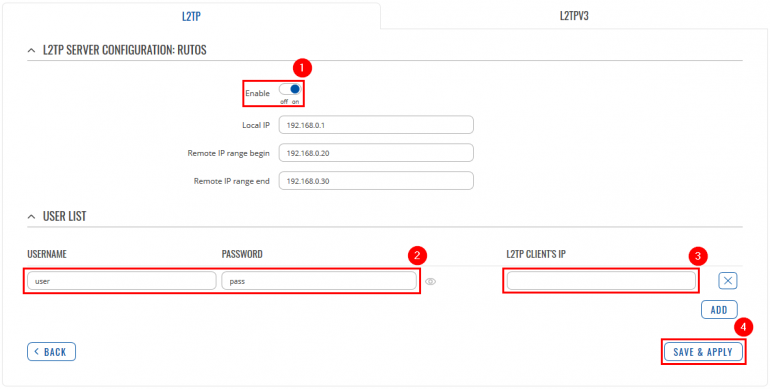
Configuring home router (RUTX)
L2TP
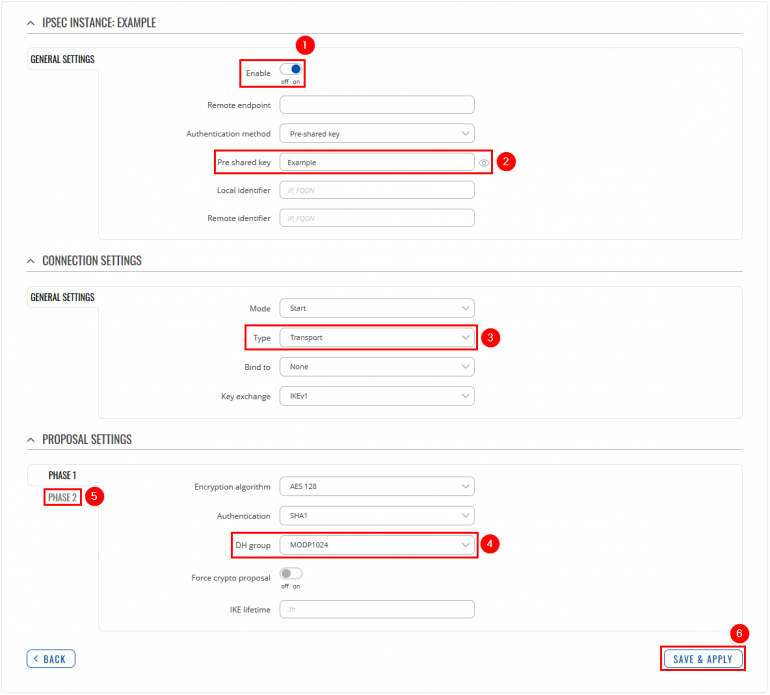
IPsec
 |
|
|---|---|
|
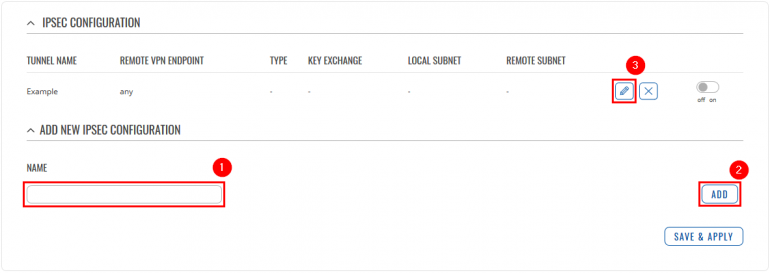
Go to the Services → VPN → IPsec page and do the following:
|
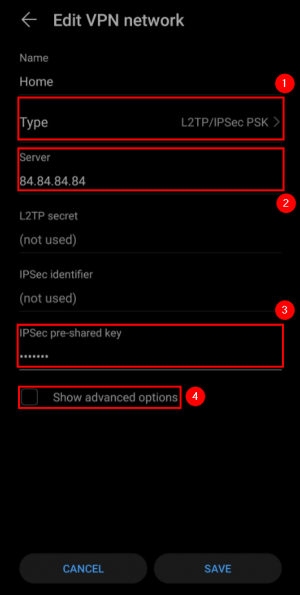
Android phone
 |
|
|---|---|
|
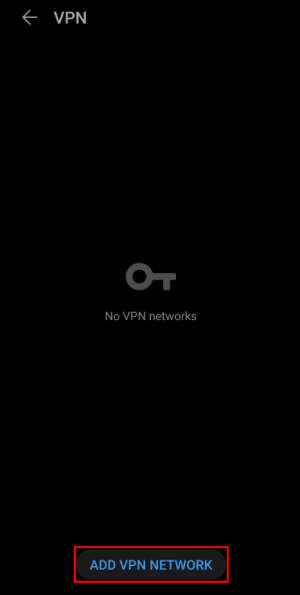
Go to your Android device VPN settings and create a new VPN network: |
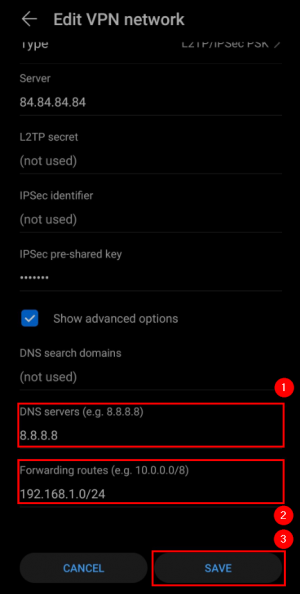 |
|
|---|---|
|
 |
|
|---|---|
|
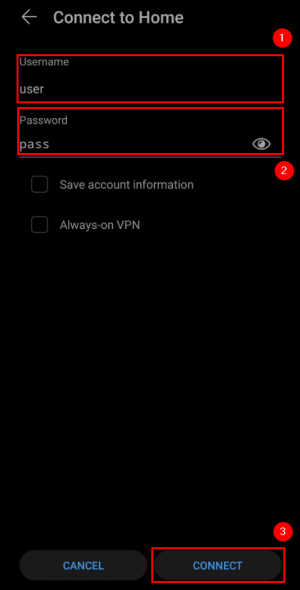
Now open your newly created VPN instance and connect to it:
|
 |
|
|---|---|
|
If you applied the configuration correctly, after a moment it should indicate Connected: |
Results
Disclaimer:
This configuration example was created by using Android version 10. The IPsec Phase 1 and Phase 2 settings, which were used in this configuration example, might not work with other Android versions and might require adjustment.