Template:Networking rutos manual firewall: Difference between revisions
| Line 342: | Line 342: | ||
You will be redirected to that rule's configuration page: | You will be redirected to that rule's configuration page: | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_firewall_traffic_rules_configuration_mobile_{{{mobile}}}_dualsim_{{{dualsim}}_wired_{{{wired}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_firewall_traffic_rules_configuration_mobile_{{{mobile}}}_dualsim_{{{dualsim}}}_wired_{{{wired}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
Revision as of 11:54, 18 August 2020
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
{{{name}}} devices use a standard Linux iptables package as its firewall, which uses routing chains and policies to facilitate control over inbound and outbound traffic. This chapter is an overview of the Firewall section for {{{name}}} devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
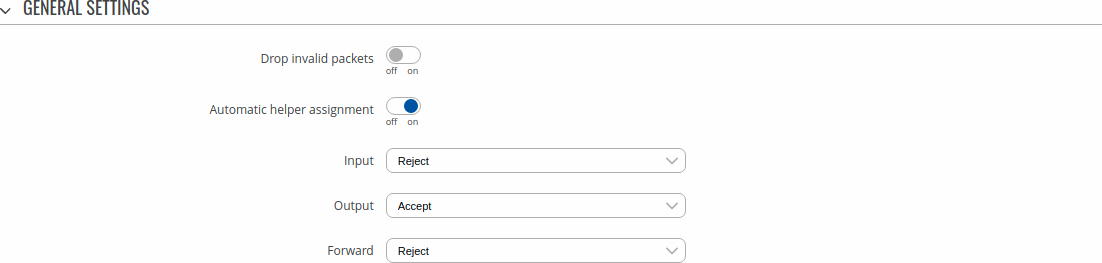
General settings
The General Settings section is used to configure the main policies of the device's firewall. The figure below is an example of the General Settings section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable SYN flood protection | off | on; Default: on | Enables protection from SYN flood type attacks. A SYN flood is a type of denial-of-service (DOS) attack where an attacker sends bursts of SYN requests in an attempt to make the target host machine consume enough resources and become unresponsive. |
| Drop invalid packets | off | on; Default: off | If enabled, a "Drop" action will be performed on packets that are determined to be invalid. |
| Input | Reject | Drop | Accept; Default: Accept | Default action* of the INPUT chain if a packet does not match any existing rule on that chain. |
| Output | Reject | Drop | Accept; Default: Accept | Default action* of the OUTPUT chain if a packet does not match any existing rule on that chain. |
| Forward | Reject | Drop | Accept; Default: Reject | Default action* of the FORWARD chain if a packet does not match any existing rule on that chain. |
* When a packet goes through a firewall chain it is matched against all the rules of that specific chain. If no rule matches said packet, an according Action (Drop, Reject or Accept) is performed:
- Accept – packet gets to continue to the next chain.
- Drop – packet is stopped and deleted.
- Reject – packet is stopped, deleted and, differently from Drop, a message of rejection is sent to the source from which the packet came.
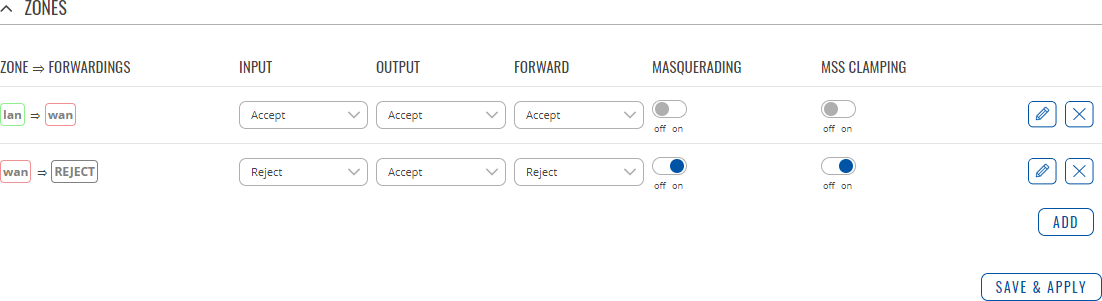
Zones
The Zones section is used to manage default traffic forwarding policies between different device zones. The figure below is an example of the Zones section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
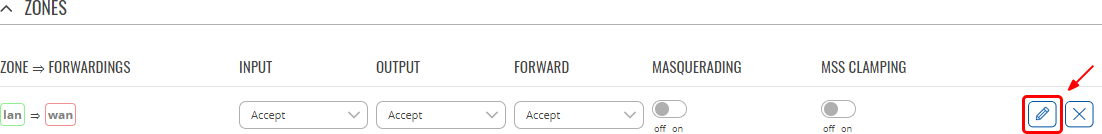
You can change a zone's settings from this page by interacting with entries in the zones table. For a more in-depth configuration click the button that looks like a pencil ![]() next to a zone:
next to a zone:
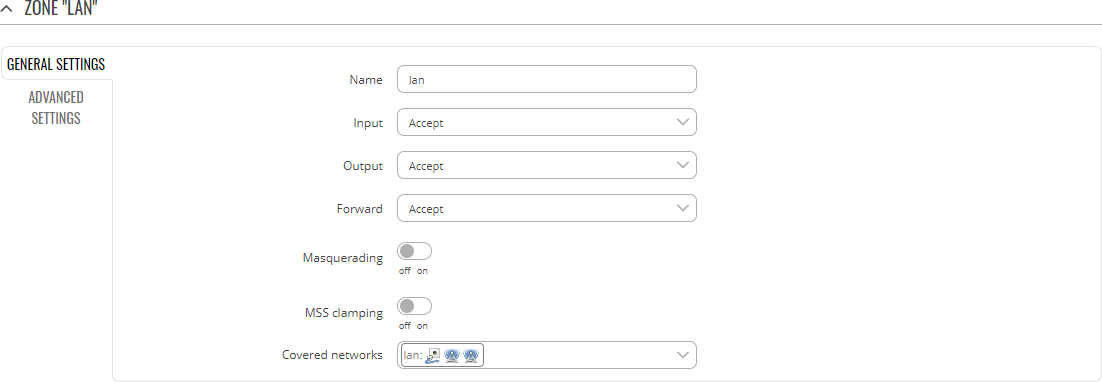
Zones: general settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: newzone | A custom name for the zone. Used for easier management purposes. |
| Input | Reject | Drop | Accept; Default: Accept | Default policy for traffic entering the zone. |
| Output | Reject | Drop | Accept; Default: Accept | Default policy for traffic originating from and leaving the zone. |
| Forward | Reject | Drop | Accept; Default: Reject | Default policy for traffic forwarded between the networks belonging to the zone. |
| Masquerading | off | on; default: off | Turns Masquerading off or on. MASQUERADE is an iptables target that can be used instead of the SNAT (source NAT) target when the external IP of the network interface is not known at the moment of writing the rule (when the interface gets the external IP dynamically). |
| MSS clamping | off | on; default: off | Turns MSS clamping off or on. MSS clamping is a workaround used to change the maximum segment size (MSS) of all TCP connections passing through links with an MTU lower than the Ethernet default of 1500. |
| Covered networks | network interface(s); default: none | Network or networks that belong to the zone. |
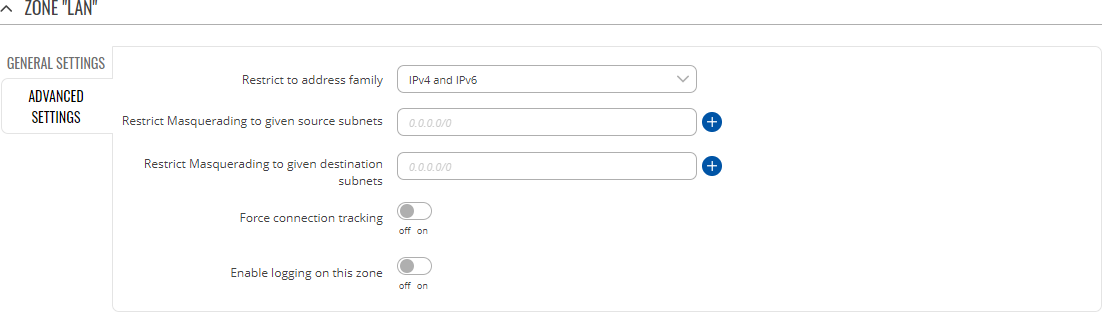
Zones: advanced settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Restrict to address family | IPv4 and IPv6 | IPv4 only | IPv6 only; default: IPv4 and IPv6 | IP address family to which to rule will apply. |
| Restrict Masquerading to given source subnets | network/subnet; default: none | Applies Masquerading only to the specified source network/subnet. |
| Restrict Masquerading to given destinations subnets | network/subnet; default: none | Applies Masquerading only to the specified destination network/subnet. |
| Force connection tracking | off | on; default: off | Always maintains connection state (NEW, ESTABLISHED, RELATED) information. |
| Enable logging on this zone | off | on; default: off | Logs packets that hit this rule. |
| Limit log messages | integer/minute; default: none | Limit how many messages can be logged in the span of 1 minute. For example, to log 50 packets per minute use: 50/minute. |
Zones: inter-zone forwarding
The Inter-zone forwarding options control the forwarding policies between the currently edited zone and other zones.
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_firewall_general_settings_zones_inter-zone_forwarding_mobile_{{{mobile}}}_dualsim_{{{dualsim}}}_wired_{{{wired}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Allow forward to destination zones | zone(s); default: none | Allows forward traffic to specified destination zones. Destination zones cover forwarded traffic originating from this source zone. |
| Allow forward from source zones | zone(s); default: none | Allows forward traffic to specified source zones. Source zones match forwarded traffic originating from other zones that is targeted at this zone. |
Port forwards
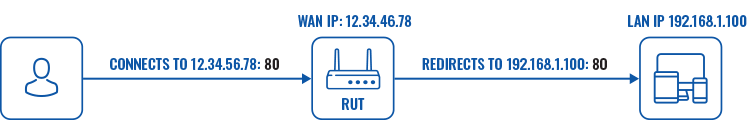
Port forwarding is a way of redirecting an incoming connection to another IP address, port or the combination of both:
The Port forwards table displays configured port forwarding rules currently configured on the device.
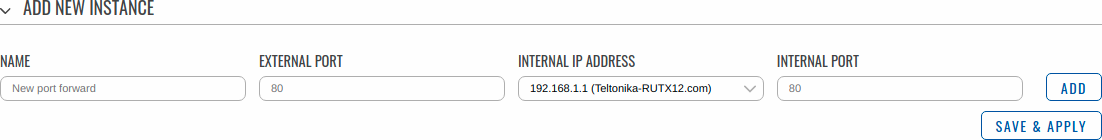
New port forward
The New port forward section is used to quickly add additional port forwarding rules. The figure below is an example of the New port forward section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: none | Name of the rule. This is used for easier management purposes. | |
| Protocol | TCP+UDP | TCP | UDP | Other; default: TCP+UDP | Specifies to which protocols the rule should apply. | |
| External zone | firewall zone name; default: wan | The zone to which hosts will be connecting. | |
| External port | integer [0..65535] | range of integers [0..65534] - [1..65535]; default: none | The port number to which hosts will be connecting. | |
| Internal zone | firewall zone name; default: lan | The zone to which the incoming connection will be redirected. | |
| Internal IP address | ip; default: none | The IP address to which the incoming connection will be redirected. | |
| Internal port | integer [0..65535] | range of integers [0..65534] - [1..65535]; default: none | The port number to which the incoming connection will be redirected. |
Port forwards configuration
While the New port forward section provides the possibility to add port forwarding rules fast, it does not contain all possible configuration options to customize a rule. In order to create a more complicated rule, add one using the New port forward section and click the button that looks like a pencil ![]() next to it:
next to it:
You will be redirected to that rule's configuration page:
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_firewall_port_forwards_configuration_mobile_{{{mobile}}}_dualsim_{{{dualsim}}}_wired_{{{wired}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on ; default: on | Turns the rule on or off | |
| Name | string; default: none | Name of the rule. This is used for easier management purposes. | |
| Protocol | TCP+UDP | TCP | UDP | Other; default: TCP+UDP | Specifies to which protocols the rule should apply. | |
| Source zone | firewall zone name; default: wan | The zone to which the third party will be connecting. (Same thing as "External zone" in the New port forward section.) | |
| Source MAC address | mac; default: none | MAC address(es) of connecting hosts. The rule will apply only to hosts that match MAC addresses specified in this field. Leave empty to make the rule skip MAC address matching. |
|
| Source IP address | ip | ip/netmask; default: any | IP address or network segment used by connecting hosts. The rule will apply only to hosts that connect from IP addresses specified in this field. To specify a network segment instead of one IP address, add a forward slash followed by the netmask length after the network indication (for example, 10.0.0.0/8). |
|
| Source port | integer [0..65535] | range of integers [0..65534] - [1..65535]; default: none | Port number(s) used by the connecting host. The rule will match the source port used by the connecting host with the port number(s) specified in this field. Leave empty to make the rule skip source port matching. | |
| External IP address | ip | ip/netmask; default: any | IP address or network segment to which hosts will be connecting. The rule will apply only to hosts that connect to IP addresses specified in this field. To specify a subnet instead of one IP, add a forward slash followed by the netmask length after the network indication (for example, 10.0.0.0/8). |
|
| External port | integer [0..65535] | range of integers [0..65534] - [1..65535]; default: none | Port number(s) to which hosts will be connecting. The rule will apply only to hosts that connect to the port number(s) specified in this field. Leave empty to make the rule skip external port matching. | |
| Internal zone | firewall zone name; default: lan | The zone to which the incoming connection will be redirected. | |
| Internal IP address | ip; default: none | The IP address to which the incoming connection will be redirected. | |
| Internal port | integer [0..65535] | range of integers [0..65534] - [1..65535]; default: none | The port number to which the incoming connection will be redirected. | |
| Enable NAT loopback | off | on ; default: on | NAT loopback a.k.a. NAT reflection a.k.a. NAT hairpinning is a method of accessing an internal server using a public IP. NAT loopback enables your local network (i.e., behind your NAT device) to connect to a forward-facing IP address of a machine that it also on your local network. | |
| Extra arguments | string; default: none | Adds extra iptables options to the rule. |
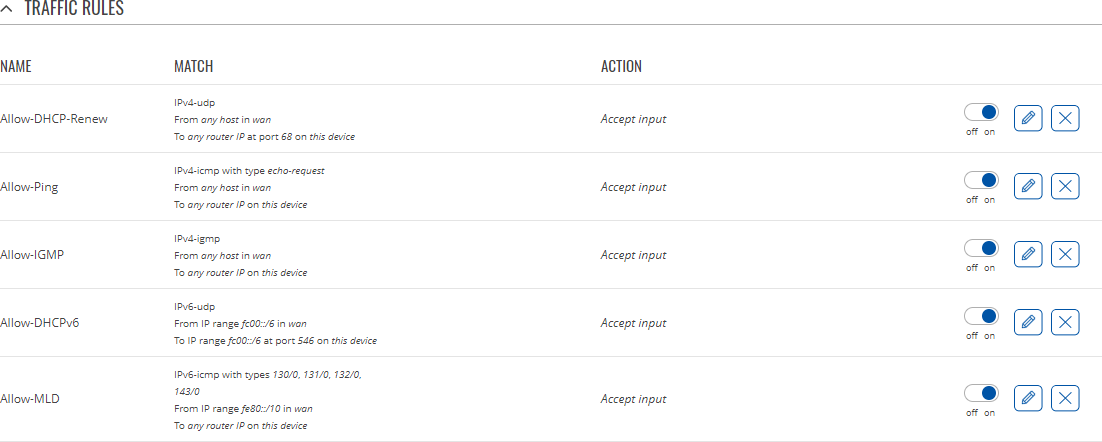
Traffic rules
The Traffic rules tab is used to set firewall rules that filter traffic moving through the device. The figure below is an example of the Traffic rules table:
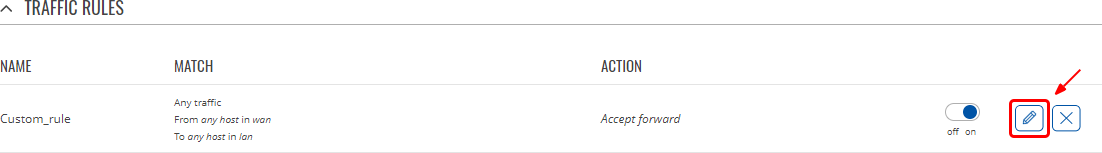
Traffic rules configuration
In order to begin editing a traffic rule, click the button that looks like a pencil ![]() next to it:
next to it:
You will be redirected to that rule's configuration page:
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_firewall_traffic_rules_configuration_mobile_{{{mobile}}}_dualsim_{{{dualsim}}}_wired_{{{wired}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default on | Turns the rule on or off. | |
| Name | string; default none | Name of the rule. This is used for easier management purposes. | |
| Restrict to address family | IPv4 and IPv6 | IPv4 only | IPv6 only; default: IPv4 and IPv6 | IP address family to which the rule will apply to. | |
| Protocol | TCP+UDP | TCP | UDP | ICMP | -- custom --; default: TCP+UDP | Specifies to which protocols the rule should apply. | |
| Source zone | firewall zone name; default: wan | The zone to which the third party will be connecting. | |
| Source MAC address | mac; default: none | MAC address(es) of connecting hosts. The rule will apply only to hosts that match MAC addresses specified in this field. Leave empty to make the rule skip MAC address matching. |
|
| Source address | ip | ip/netmask; default: any | IP address or network segment used by connecting hosts. The rule will apply only to hosts that connect from IP addresses specified in this field. To specify a network segment instead of one IP address, add a forward slash followed by the netmask length after the network indication (for example, 10.0.0.0/8). |
|
| Source port | integer [0..65535] | range of integers [0..65534] - [1..65535]; default: none | Port number(s) used by the connecting host. The rule will match the source port used by the connecting host with the port number(s) specified in this field. Leave empty to make the rule skip source port matching. | |
| Destination zone | firewall zone; default: Device (input) | Target zone of the incoming connection. | |
| Destination address | ip | ip/netmask; default: any | Tagert IP address or network segment of the incoming connection. | |
| Destination port | integer [0..65535] | range of integers [0..65534] - [1..65535]; default: none | Tagert port or range of ports of the incoming connection. | |
| Action | DROP | ACCEPT | REJECT; default: ACCEPT | Action that is to be taken when a packet meets the MATCH conditions.
|
|
| Extra arguments | string; default: none | Adds extra .iptables options to the rule. | |
| Week days | days of the week [Sunday..Saturday]; default: none | Specifies on which days of the week the rule is valid. | |
| Month days | days of the month [1..31]; default: none | Specifies on which days of the month the rule is valid. | |
| Start Time (hh:mm:ss) | time [0..23:0..59:0..59]; default: none | Indicates the beginning of the time period during which the rule is valid. | |
| Stop Time (hh:mm:ss) | time [0..23:0..59:0..59]; default: none | Indicates the end of the time period during which the rule is valid. | |
| Start Date (yyyy-mm-dd) | date [0000..9999:1..12:1..31]; default: none | Indicates the first day of the date of the period during which the rule is valid. | |
| Stop Date (yyyy-mm-dd) | date [0000..9999:1..12:1..31]; default: none | Indicates the last day of the date of the period during which the rule is valid. | |
| Time in UTC | yes | no; default: no | Specifies whether the device should use UTC time. If this is disabled, the time zone specified in the [[{{{name}}} NTP|NTP]] section will be used. |
Open Ports on Router
The Open Ports on Router section provides a quick way to set simple rules that allow traffic on specified ports of the device. The figure below is an example of the Open ports on device section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: none | The name of the rule. This is used for easier management purposes. The name field is filled automatically when port numbers are specified, unless the name was specified beforehand by the user. |
| Protocol | TCP+UDP | TCP | UDP | Other; default: TCP+UDP | Specifies to which protocols the rule should apply. |
| External port | integer [0..65535] | range of integers [0..65534] - [1..65535]; default: none | Specifies which port(s) should be opened. |
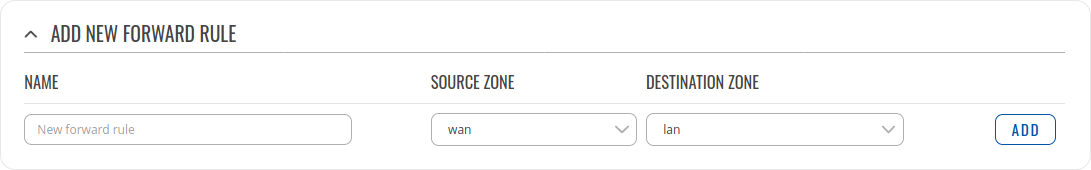
New forward rule
The New forward rule section is used to create firewall rules that control traffic on the FORWARD chain. The figure below is an example of the New forward rule section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: none | The name of the rule. This is used for easier management purposes. |
| Source zone | firewall zone; default: wan | The zone from which traffic has originated. |
| Destination zone | firewall zone; default: lan | The zone to which traffic will be forwarded to. |
| Add | - (interactive button) | Creates the rule and redirects you to the rule's configuration page |
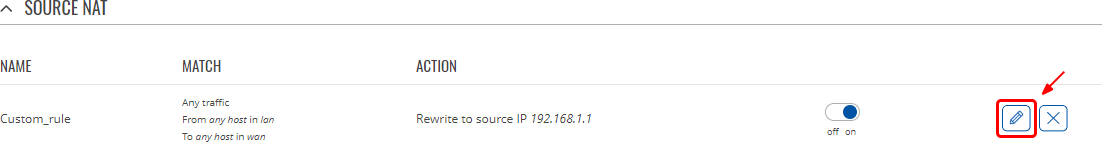
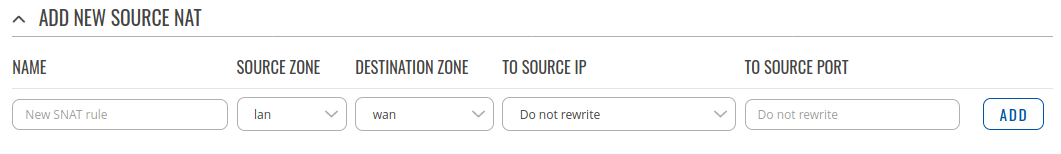
Source NAT
Source NAT is a specific form of masquerading which allows fine grained control over the source IP used for outgoing traffic. For example, to map multiple WAN addresses to internal subnets.
New source NAT
The New Source NAT section is used to add custom source NAT rules. The figure below is an example of the New source NAT section and the table below provides information on the fields contained in that section:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | string; default: none | The name of the rule. This is used for easier management purposes. |
| Source zone | firewall zone; default: LAN | The zone from which traffic has originated. |
| Destination zone | firewall zone; default: WAN | The zone to which traffic will be forwarded to. |
| To source IP | ip | do not rewrite; default: Do not rewrite | Changes the source IP in the packet header to the value specified in this field. |
| To source port | integer [0..65335] | do not rewrite; default: Do not rewrite | Changes the source port in the packet header to the value specified in this field. |
| Add | - (interactive button) | Creates the rule and redirects you to the rule's configuration page. |
Custom rules
The Custom rules tab provides you with the possibility to execute iptables commands which are not otherwise covered by the device's firewall framework. The commands are executed after each firewall restart, right after the default rule set has been loaded.
The figure below is an example of the Custom rules tab:
File:Networking rutx manual firewall custom rules v1.png
The rules added here are saved in the /etc/firewall.user file. Feel free to edit that file instead for the same effect in case you don't have access to the device's WebUI.
The Save button restarts the firewall service. Thus, adding the custom rules specified in this section to the device's list of firewall rules.
The Reset button resets the custom rules field to its default state.
Attack Prevention
SYN Flood Protection
SYN Flood Protection allows you to protect yourself from attacks that exploit part of the normal TCP three-way handshake to consume resources on the targeted server and render it unresponsive. Essentially, with SYN flood DDOS, the offender sends TCP connection requests faster than the targeted machine can process them, causing network over-saturation.
File:Networking rutos manual firewall attack prevention syn.PNG
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable SYN flood protection | yes | no; Default: yes | Toggles the rule ON or OFF |
| SYN flood rate | integer; Default: 5 | Set rate limit (packets per second) for SYN packets above which the traffic is considered flooded |
| SYN flood burst | integer; Default: 10 | Set burst limit for SYN packets above which the traffic is considered flooded if it exceeds the allowed rate |
| TCP SYN cookies | yes | no; Default: no | Enable the use of SYN cookies (particular choices of initial TCP sequence numbers by TCP servers) |
Remote ICMP Requests
Some attackers use ICMP echo request packets directed to IP broadcast addresses from remote locations to generate denial-of-service attacks. You can set up some custom restrictions to help protect your router from ICMP bursts.
File:Networking rutos manual firewall attack prevention icmp.PNG
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable ICMP requests | yes | no; Default: yes | Toggles the rule ON or OFF |
| Enable ICMP limit | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles ICMP echo-request limit in selected period ON or OFF |
| Limit period | Second | Minute | Hour | Day; Default: Second | Select ICMP echo-request period limit |
| Limit | integer; Default: 5 | Maximum ICMP echo-request number during the period |
| Limit burst | integer; Default: 10 | Indicate the maximum burst before the above limit kicks in |
SSH Attack Prevention
Prevent SSH (allows a user to run commands on a machine's command prompt without them being physically present near the machine) attacks by limiting connections in a defined period.
File:Networking rutos manual firewall attack prevention ssh.PNG
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable SSH limit | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles the rule ON or OFF |
| Limit period | Second | Minute | Hour | Day; Default: Second | The period in which SSH connections are to be limited |
| Limit | integer; Default: 5 | Maximum SSH connections during the set period |
| Limit burst | integer; Default: 10 | Indicate the maximum burst before the above limit kicks in |
HTTP Attack Prevention
An HTTP attack sends a complete, legitimate HTTP header, which includes a 'Content-Length' field to specify the size of the message body to follow. However, the attacker then proceeds to send the actual message body at an extremely slow rate (e.g. 1 byte/100 seconds.) Due to the entire message being correct and complete, the target server will attempt to obey the 'Content-Length' field in the header, and wait for the entire body of the message to be transmitted, hence slowing it down.
File:Networking rutos manual firewall attack prevention http.PNG
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable HTTP limit | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles the rule ON or OFF |
| Limit period | Second | Minute | Hour | Day; Default: Second | The period in which HTTP connections are to be limited |
| Limit | integer; Default: 5 | Maximum HTTP connections during the set period |
| Limit burst | integer; Default: 10 | Indicate the maximum burst before the above limit kicks in |
HTTPS Attack Prevention
This section allows you to enable protection against HTTPS attacks, also known as man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM).
In cryptography and computer security, a man-in-the-middle attack (MITM) is an attack where the perpetrator secretly relays and possibly alters the communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other. One example of man-in-the-middle attacks is active eavesdropping, in which the attacker makes independent connections with the victims and relays messages between them to make them believe they are talking directly to each other over a private connection, when in fact the entire conversation is controlled by the attacker.
File:Networking rutos manual firewall attack prevention hhtps.PNG
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable HTTPS limit | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles the rule ON or OFF |
| Limit period | Second | Minute | Hour | Day; Default: Second | The period in which HTTPS connections are to be limited |
| Limit | integer; Default: 5 | Maximum HTTPS connections during the set period |
| Limit burst | integer; Default: 10 | Indicate the maximum burst before the above limit kicks in |
Port Scan Prevention
Port scan attacks scan which of the targeted host's ports are open. Network ports are the entry points to a machine that is connected to the Internet. A service that listens on a port is able to receive data from a client application, process it and send a response back. Malicious clients can sometimes exploit vulnerabilities in the server code so they gain access to sensitive data or execute malicious code on the machine remotely. Port scanning is usually done in the initial phase of a penetration test in order to discover all network entry points into the target system. The Port Scan section provides you with the possibility to enable protection against port scanning software. The Defending Type section provides the possibility for the user to enable protections from certain types of online attacks. These include SYN-FIN, SYN-RST, X-Mas, FIN scan and NULLflags attacks.
File:Networking rutos manual firewall attack prevention port scan def.PNG
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles the function ON or OFF |
| Scan count | integer [5..65534]; Default: 5 | How many port scans before blocked |
| Interval | integer [10..60]; Default: 10 | Time interval in seconds in which port scans are counted |
| SYN-FIN attack | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles protection from SYN-FIN attacks ON or OFF |
| SYN-RST attack | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles protection from SYN-RST attacks ON or OFF |
| X-Mas attack | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles protection from X-Mas attacks ON or OFF |
| FIN scan | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles protection from FIN scan attacks ON or OFF |
| NULLflags attack | yes | no; Default: no | Toggles protection from NULLflags attacks ON or OFF |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]