Template:Networking rutos manual mqtt: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:Networking_rutos_manual_fw_disclosure | {{Template:Networking_rutos_manual_fw_disclosure | ||
| fw_version = {{{series}}}_R_00.02. | | fw_version = {{{series}}}_R_00.02.05 | ||
| series = {{{series}}} | | series = {{{series}}} | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
<b>MQTT (MQ Telemetry Transport or Message Queue Telemetry Transport)</b> is an ISO standard (ISO/IEC PRF 20922) publish-subscribe-based "lightweight" messaging protocol for use on top of the TCP/IP protocol. It is designed to send short messages from one client (<i>publisher</i>) to another (<i>subscriber</i>) through <i>brokers</i>, which are responsible for message delivery to the end point. | |||
{{{name}}} devices support this functionality via an open source Mosquitto broker. The messages are sent this way: a client (subscriber) subscribes to a topic(s); a publisher posts a message to that specific topic(s). The broker then checks who is subscribed to that particular topic(s) and transmits data from the publisher to the subscriber. | |||
This chapter is an overview of the MQTT page for {{{name}}} devices. | |||
==MQTT Broker== | ==MQTT Broker== | ||
The | The <b>MQTT Broker</b> is an entity that listens for connections on the specified port and relays received messages to MQTT client. To begin using this devices as an MQTT Broker, enable it in this page. In order to make the device accept MQTT connections from WAN (remote networks), you also need to turn the 'Enable Remote Access' slider on. | ||
[[ | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_mqtt_broker.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>Toggles MQTT Broker between on and off.</td> | <td>Toggles MQTT Broker between on and off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 32: | ||
<td>Local Port</td> | <td>Local Port</td> | ||
<td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b>1883</b></td> | <td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b>1883</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>The TCP port on which the MQTT broker will listen for connections.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable Remote Access</td> | <td>Enable Remote Access</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns remote access to this MQTT broker on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
==Broker Settings== | |||
===Security=== | ===Security=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
The | The <b>Security</b> section is used to configure TLS/SSL . | ||
[[ | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_mqtt_broker_settings_security.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 51: | Line 57: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Use TLS/SSL</td> | <td>Use TLS/SSL</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns the use of TLS/SSL for this MQTT connection on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Certificate files from device</td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>When turned on, provides the possibility to use certificate files generated on this device instead of uploading certificate files. You can generate TLS certificates on your device in the System → Administration → [[{{{name}}} Administration#Certificates|Certificates]] page.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>CA File</td> | <td>CA File</td> | ||
<td>.ca file; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>.ca file; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Uploads a Certificate Authority (CA) file. A Certificate Authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>CERT File</td> | <td>CERT File</td> | ||
<td>.crt file; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>.crt file; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Uploads a server (broker) certificate file. A certificate file is a type of digital certificate that is used by client systems to make authenticated requests to a remote server.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Key File</td> | <td>Key File</td> | ||
<td>.key file; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>.key file; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Uploads a server (broker) key file.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>TLS version</td> | <td>TLS version</td> | ||
<td>tlsv1 | tlsv1.1 | tlsv1.2 | Support all; default: | <td>tlsv1 | tlsv1.1 | tlsv1.2 | Support all; default: <b>Support all</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Specifies which TLS version(s) is will be supported by this broker.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 89: | ||
===Bridge=== | ===Bridge=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
An <b>MQTT Bridge</b> is used for the communication between MQTT brokers. The window of Bridge parameters is presented below. | |||
<b>Note</b>: this table has a coloring scheme to indicate which fields can be seen with different configuration. | |||
[[ | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_mqtt_broker_settings_bridge.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns MQTT Bridge on and off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Connection Name</td> | <td>Connection Name</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Name of the Bridge connection. | <td>Name of the Bridge connection. This is used for easier management purposes.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 112: | Line 125: | ||
<td>off | <span style="color:blue"><b>on</b></span>; default: '''off'''</td> | <td>off | <span style="color:blue"><b>on</b></span>; default: '''off'''</td> | ||
<td>Enables the use of TSL/SSL certificates of the remote broker. If this is checked, you will be prompted to upload TLS/SSL certificates. More information can be found in the [[#Security|Security]] section of this chapter.</td> | <td>Enables the use of TSL/SSL certificates of the remote broker. If this is checked, you will be prompted to upload TLS/SSL certificates. More information can be found in the [[#Security|Security]] section of this chapter.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Certificate files from device</td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>When turned on, provides the possibility to use certificate files generated on this device instead of uploading certificate files. You can generate TLS certificates on your device in the System → Administration → [[{{{name}}} Administration#Certificates|Certificates]] page.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Bridge CA File</td> | <td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Bridge CA File</td> | ||
<td>.ca file; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>.ca file; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Uploads a Certificate Authority (CA) file. A Certificate Authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Bridge CERT File</td> | <td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Bridge CERT File</td> | ||
<td>.crt file; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>.crt file; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Uploads a server (broker) certificate file. A certificate file is a type of digital certificate that is used by client systems to make authenticated requests to a remote server.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Bridge Key File</td> | <td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Bridge Key File</td> | ||
<td>.key file; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>.key file; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Uploads a server (broker) key file.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Bridge TLS version</td> | <td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Bridge TLS version</td> | ||
<td>tlsv1 | tlsv1.1 | tlsv1.2; default: | <td>tlsv1 | tlsv1.1 | tlsv1.2; default: <b>tlsv1</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>TLS version used by the other broker.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Use Remote Bridge Login</td> | <td>Use Remote Bridge Login</td> | ||
<td>off | <span style="color:red"><b>on</b></span>; default: | <td>off | <span style="color:red"><b>on</b></span>; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Indicates whether the remote side of the connection requires login information. If this is turned on, you will be required to enter a remote client ID, username and password.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:red">On:</span> Remote ID</td> | <td><span style="color:red">On:</span> Remote ID</td> | ||
<td>string; default: | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Identifier | <td>Identifier of the remote broker</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:red">On:</span> Remote Username</td> | <td><span style="color:red">On:</span> Remote Username</td> | ||
<td>string; default: | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Username | <td>Username for authentication to the remote broker.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:red">On:</span> Remote Password</td> | <td><span style="color:red">On:</span> Remote Password</td> | ||
<td>string; default: | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Password | <td>Password for authentication to the remote broker.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Try Private</td> | <td>Try Private</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>Check if the remote Broker is another instance of a daemon.</td> | <td>Check if the remote Broker is another instance of a daemon.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Clean Session</td> | <td>Clean Session</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>When turned on, discards session state after connecting or disconnecting.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
---- | |||
You can also create and manage MQTT topics in the <b>Topics</b> list below the Bridge section. To add a new topic, click the 'Add' button. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_mqtt_broker_settings_bridge_topics_add_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
You can then configure the newly added topic from the same page. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_mqtt_broker_settings_bridge_topics.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th>value</th> | <th>value</th> | ||
<th>description</th> | <th>description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Topic</td> | <td>Topic Name</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>The name of the topics that the broker will subscribe to.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Direction</td> | <td>Direction</td> | ||
<td>OUT | IN | BOTH; default: | <td>OUT | IN | BOTH; default: <b>OUT</b></td> | ||
<td>The direction that the messages will be shared | <td>The direction that the messages will be shared.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>QoS Level</td> | <td>QoS Level</td> | ||
<td>At most once (0) | At least once (1) | Exactly once (2); default: | <td>At most once (0) | At least once (1) | Exactly once (2); default: <b>At most once (0)</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Sets the publish/subscribe QoS level used for this topic.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 194: | Line 216: | ||
===Miscellaneous=== | ===Miscellaneous=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
The | The <b>Miscellaneous</b> section is used to configure MQTT broker parameters that are related to neither Security nor Bridge. | ||
[[ | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_mqtt_broker_settings_miscellaneous.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 207: | Line 229: | ||
<td>ACL File</td> | <td>ACL File</td> | ||
<td>ACL file; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>ACL file; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>The contents of this file are used to control client access to topics of the broker.</td> | <td>Uploads an ACL file. The contents of this file are used to control client access to topics of the broker.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Password File</td> | <td>Password File</td> | ||
<td>password file; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>password file; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Uploads a password. A password file stores usernames and corresponding passwords, used for authentication.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Persistence</td> | <td>Persistence</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>When turned on, connection, subscription and message data will be written to the disk. Otherwise, the data is stored in the device memory only.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Allow Anonymous</td> | <td>Allow Anonymous</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: | <td>off | on; default: <b>on</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns anonymous access to this broker on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 228: | Line 250: | ||
==MQTT Publisher== | ==MQTT Publisher== | ||
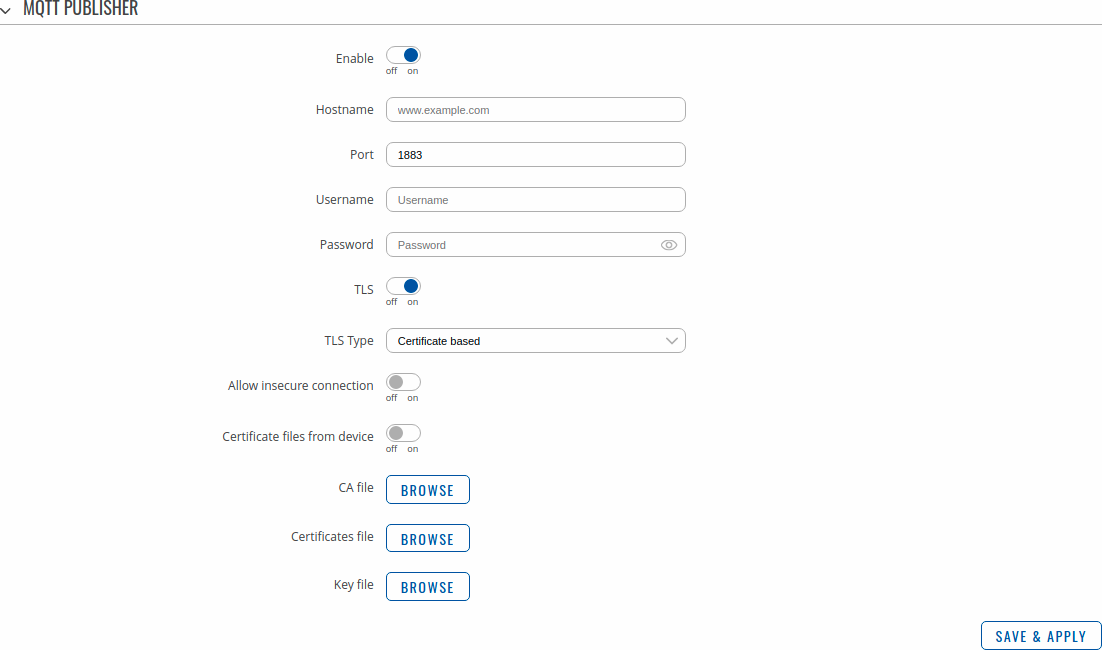
An | An <b>MQTT Publisher</b> is a client instance that can send messages to the Broker, who can forward these messages to other clients (subscribers). | ||
<b>Note</b>: this table has coloring scheme to indicate which fields can be seen with different configuration. | |||
[[ | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_mqtt_publisher.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<th> | <th>Field</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td>Toggles the MQTT Publisher ON or OFF.</td> | <td>Toggles the MQTT Publisher ON or OFF.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 250: | Line 274: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Port</td> | <td>Port</td> | ||
<td>integer [0..65535]; default: | <td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b>1883</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Broker's port number.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Username</td> | <td>Username</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Username used for authentication | <td>Username used for authentication to the Broker.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Password</td> | <td>Password</td> | ||
<td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Password used for authentication | <td>Password used for authentication to the Broker.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>TLS</td> | <td>TLS</td> | ||
<td>off | <span style="color:blue"><b>on</b></span>; default: | <td>off | <span style="color:blue"><b>on</b></span>; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns the use of Transport Layer Security (TLS) on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Allow insecure connection</td> | <td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Allow insecure connection</td> | ||
<td>off | on; default: | <td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Allows connections without verifying server authenticity.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td><span style="color:blue">On:</span> Certificate files from device</td> | |||
<td>off | on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>When turned on, provides the possibility to use certificate files generated on this device instead of uploading certificate files. You can generate TLS certificates on your device in the System → Administration → [[{{{name}}} Administration#Certificates|Certificates]] page.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 289: | Line 318: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]] | [[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]] | ||
Revision as of 10:00, 24 August 2020
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
MQTT (MQ Telemetry Transport or Message Queue Telemetry Transport) is an ISO standard (ISO/IEC PRF 20922) publish-subscribe-based "lightweight" messaging protocol for use on top of the TCP/IP protocol. It is designed to send short messages from one client (publisher) to another (subscriber) through brokers, which are responsible for message delivery to the end point.
{{{name}}} devices support this functionality via an open source Mosquitto broker. The messages are sent this way: a client (subscriber) subscribes to a topic(s); a publisher posts a message to that specific topic(s). The broker then checks who is subscribed to that particular topic(s) and transmits data from the publisher to the subscriber.
This chapter is an overview of the MQTT page for {{{name}}} devices.
MQTT Broker
The MQTT Broker is an entity that listens for connections on the specified port and relays received messages to MQTT client. To begin using this devices as an MQTT Broker, enable it in this page. In order to make the device accept MQTT connections from WAN (remote networks), you also need to turn the 'Enable Remote Access' slider on.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Toggles MQTT Broker between on and off. |
| Local Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 1883 | The TCP port on which the MQTT broker will listen for connections. |
| Enable Remote Access | off | on; default: off | Turns remote access to this MQTT broker on or off. |
Broker Settings
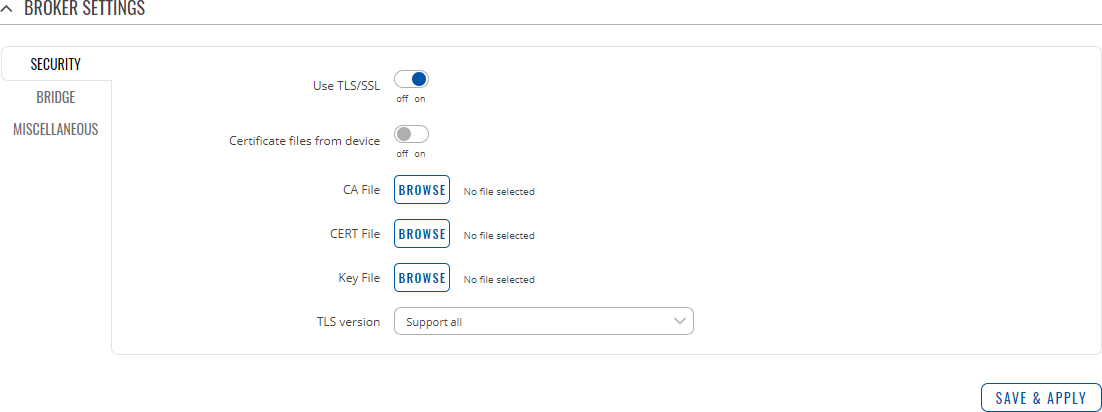
Security
The Security section is used to configure TLS/SSL .
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Use TLS/SSL | off | on; default: off | Turns the use of TLS/SSL for this MQTT connection on or off. |
| Certificate files from device | off | on; default: off | When turned on, provides the possibility to use certificate files generated on this device instead of uploading certificate files. You can generate TLS certificates on your device in the System → Administration → [[{{{name}}} Administration#Certificates|Certificates]] page. |
| CA File | .ca file; default: none | Uploads a Certificate Authority (CA) file. A Certificate Authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. |
| CERT File | .crt file; default: none | Uploads a server (broker) certificate file. A certificate file is a type of digital certificate that is used by client systems to make authenticated requests to a remote server. |
| Key File | .key file; default: none | Uploads a server (broker) key file. |
| TLS version | tlsv1 | tlsv1.1 | tlsv1.2 | Support all; default: Support all | Specifies which TLS version(s) is will be supported by this broker. |
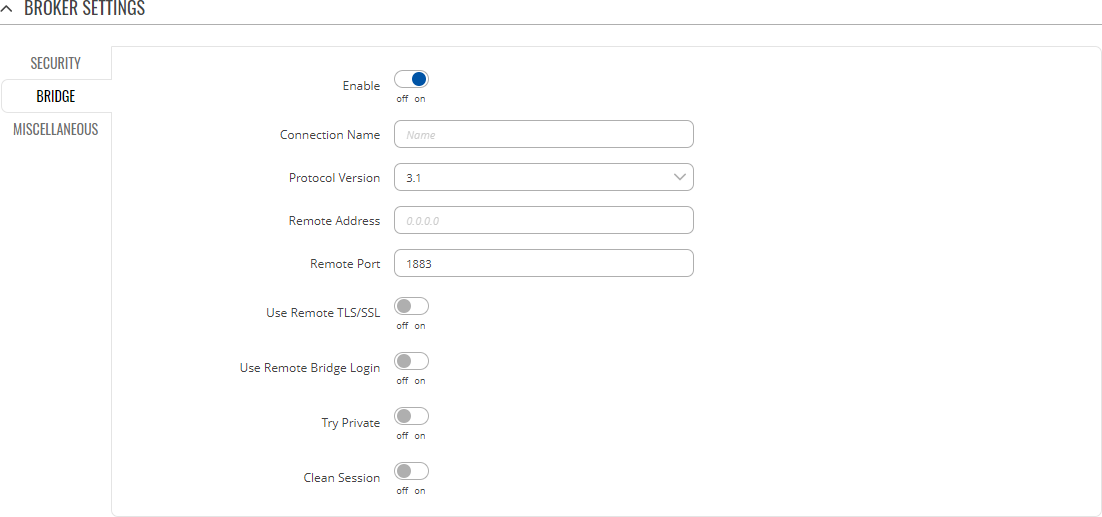
Bridge
An MQTT Bridge is used for the communication between MQTT brokers. The window of Bridge parameters is presented below.
Note: this table has a coloring scheme to indicate which fields can be seen with different configuration.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Turns MQTT Bridge on and off. |
| Connection Name | string; default: none | Name of the Bridge connection. This is used for easier management purposes. |
| Remote Address | ip; default: none | Remote Broker’s address. |
| Remote Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 1883 | Specifies which port the remote broker uses to listen for connections. |
| Use Remote TLS/SSL | off | on; default: off | Enables the use of TSL/SSL certificates of the remote broker. If this is checked, you will be prompted to upload TLS/SSL certificates. More information can be found in the Security section of this chapter. |
| On: Certificate files from device | off | on; default: off | When turned on, provides the possibility to use certificate files generated on this device instead of uploading certificate files. You can generate TLS certificates on your device in the System → Administration → [[{{{name}}} Administration#Certificates|Certificates]] page. |
| On: Bridge CA File | .ca file; default: none | Uploads a Certificate Authority (CA) file. A Certificate Authority (CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. |
| On: Bridge CERT File | .crt file; default: none | Uploads a server (broker) certificate file. A certificate file is a type of digital certificate that is used by client systems to make authenticated requests to a remote server. |
| On: Bridge Key File | .key file; default: none | Uploads a server (broker) key file. |
| On: Bridge TLS version | tlsv1 | tlsv1.1 | tlsv1.2; default: tlsv1 | TLS version used by the other broker. |
| Use Remote Bridge Login | off | on; default: off | Indicates whether the remote side of the connection requires login information. If this is turned on, you will be required to enter a remote client ID, username and password. |
| On: Remote ID | string; default: none | Identifier of the remote broker |
| On: Remote Username | string; default: none | Username for authentication to the remote broker. |
| On: Remote Password | string; default: none | Password for authentication to the remote broker. |
| Try Private | off | on; default: off | Check if the remote Broker is another instance of a daemon. |
| Clean Session | off | on; default: off | When turned on, discards session state after connecting or disconnecting. |
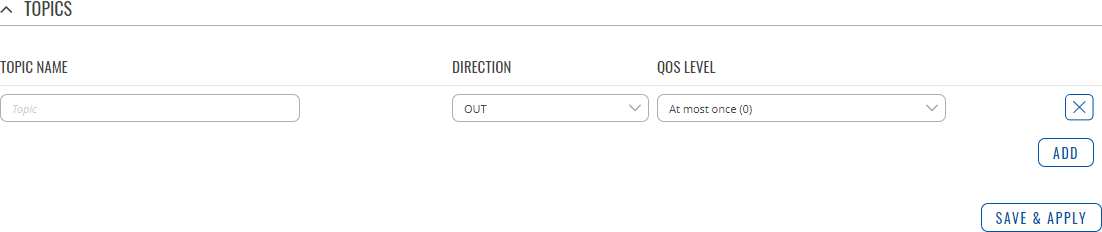
You can also create and manage MQTT topics in the Topics list below the Bridge section. To add a new topic, click the 'Add' button.
You can then configure the newly added topic from the same page.
| Field | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| Topic Name | string; default: none | The name of the topics that the broker will subscribe to. |
| Direction | OUT | IN | BOTH; default: OUT | The direction that the messages will be shared. |
| QoS Level | At most once (0) | At least once (1) | Exactly once (2); default: At most once (0) | Sets the publish/subscribe QoS level used for this topic. |
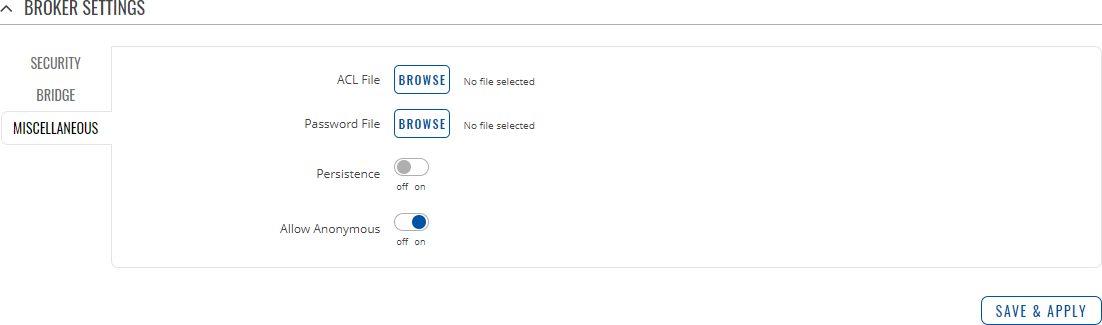
Miscellaneous
The Miscellaneous section is used to configure MQTT broker parameters that are related to neither Security nor Bridge.
| field name | value | description |
|---|---|---|
| ACL File | ACL file; default: none | Uploads an ACL file. The contents of this file are used to control client access to topics of the broker. |
| Password File | password file; default: none | Uploads a password. A password file stores usernames and corresponding passwords, used for authentication. |
| Persistence | off | on; default: off | When turned on, connection, subscription and message data will be written to the disk. Otherwise, the data is stored in the device memory only. |
| Allow Anonymous | off | on; default: on | Turns anonymous access to this broker on or off. |
MQTT Publisher
An MQTT Publisher is a client instance that can send messages to the Broker, who can forward these messages to other clients (subscribers).
Note: this table has coloring scheme to indicate which fields can be seen with different configuration.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Toggles the MQTT Publisher ON or OFF. |
| Hostname | host | ip; default: none | Broker’s IP address or hostname. |
| Port | integer [0..65535]; default: 1883 | Broker's port number. |
| Username | string; default: none | Username used for authentication to the Broker. |
| Password | string; default: none | Password used for authentication to the Broker. |
| TLS | off | on; default: off | Turns the use of Transport Layer Security (TLS) on or off. |
| On: Allow insecure connection | off | on; default: off | Allows connections without verifying server authenticity. |
| On: Certificate files from device | off | on; default: off | When turned on, provides the possibility to use certificate files generated on this device instead of uploading certificate files. You can generate TLS certificates on your device in the System → Administration → [[{{{name}}} Administration#Certificates|Certificates]] page. |
| On: CA file | .ca file; default: none | Certificate authority file used in Transport Layer Security. |
| On: Certificate file | .crt file; default: none | Certificate file used in Transport Layer Security. |
| On: Key file | .key file; default: none | Key file used in Transport Layer Security. |
[[Category:{{{name}}} Services section]]