Template:Networking rutos manual interfaces: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
The <b>static</b> protocol uses a predefined manual configuration instead of obtaining parameters automatically via a DHCP lease. | The <b>static</b> protocol uses a predefined manual configuration instead of obtaining parameters automatically via a DHCP lease. | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | | {{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | TRB1 | ||
| [[File:Networking_trb14x_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_general_setup_static_ip_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | | [[File:Networking_trb14x_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_general_setup_static_ip_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_general_setup_static_ip_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_general_setup_static_ip_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| Line 177: | Line 177: | ||
=====General Setup: PPPoE===== | =====General Setup: PPPoE===== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
The <b>PPPoE</b> protocol is used to set up a PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) connection over the Ethernet port{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}| | The <b>PPPoE</b> protocol is used to set up a PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) connection over the Ethernet port{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|TRB1| (in this case: an Ethernet connection simulated over the USB port)|}}. | ||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_general_setup_pppoe_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_general_setup_pppoe_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| Line 232: | Line 232: | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | | {{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | TRB1 | ||
| | | | ||
| <tr> | | <tr> | ||
| Line 625: | Line 625: | ||
The <b>Physical Settings</b> section is used to create associations with physical interfaces and bridge network interfaces. | The <b>Physical Settings</b> section is used to create associations with physical interfaces and bridge network interfaces. | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | | {{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | TRB1 | ||
| [[File:Networking_trb14x_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_physical_settings_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | | [[File:Networking_trb14x_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_physical_settings_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_physical_settings_wifi_{{{wifi}}}_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_physical_settings_wifi_{{{wifi}}}_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| Line 647: | Line 647: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Interface</td> | <td>Interface</td> | ||
<td>network interface(s); default: <b>{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}| | <td>network interface(s); default: <b>{{#ifeq:{{{series}}}|TRB1|rndis0|eth0}}{{#ifeq:{{{wifi}}}|1| wlan0 wlan1|}}</b></td> | ||
<td>Ties this network interface to physical device interfaces such as Ethernet {{#ifeq:{{{wifi}}}|1| or WiFi radios|}}.{{#ifeq:{{{name}}}|RUTXR1| If the <span style="color: red;">eth1</span> interface is selected, then port priority selection appears. </td> | <td>Ties this network interface to physical device interfaces such as Ethernet {{#ifeq:{{{wifi}}}|1| or WiFi radios|}}.{{#ifeq:{{{name}}}|RUTXR1| If the <span style="color: red;">eth1</span> interface is selected, then port priority selection appears. </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
Revision as of 08:00, 3 September 2020
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
The Interfaces page is used to to set up network interfaces.
This manual page provides an overview of the Interfaces page in {{{name}}} devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
Network Interfaces
The Network Interfaces section displays interfaces currently existing on this device.
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_{{{lan}}}_mobile_{{{mobile}}}_dualsim_{{{dualsim}}}_dualmodem_{{{dualmodem}}}_wired_{{{wired}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
Add Interface
The Add Interface section is used to create additional network interfaces. To create a new interface, simply enter a custom name for it and click the 'Add' button.
Interface configuration
This section provides information on network interface configuration. There are {{{no_of_if}}} main types of interfaces on the device:
- Ethernet LAN
Different types of interfaces can be configured under different protocols:
| Static | DHCP | DHCPv6 | PPPoE | Mobile | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethernet LAN |
To begin configuring an interface, click the 'Edit' button on the right side of the interface:
Interfaces: if_name
This section covers all parameters directly related to a network interface.
General Setup
The General Setup section is used to configure the protocol and all the different parameters that go along with each protocol. This section is different for each protocol.
General Setup: Static
The static protocol uses a predefined manual configuration instead of obtaining parameters automatically via a DHCP lease.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan general setup static ip v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IPv4 address | ip4; default[for LAN]: 192.168.1.1 | The IPv4 address interface of this interface. An IP address identifies a device on a network and allows it to communicate with other devices. |
| IPv4 netmask | netmask; default[for LAN]: 255.255.255.0 | The IPv4 netmask of this interface. A netmask is used to define how "large" a network is by specifying which part of the IP address denotes the network and which part denotes a device. |
| IPv4 gateway | ip4; default: none | The IPv4 gateway address used by this interface. An interface's default gateway is the default address through which all outgoing traffic is directed. |
| IPv4 broadcast | ip4; default: none | The IPv4 broadcast address used by this interface. IP broadcasts are used by BOOTP and DHCP clients to find and send requests to their respective servers. |
| DNS servers | ip4; default: none | DNS server addresses that this interface will use. If left empty, DNS servers are assigned automatically. To see what DNS servers are currently used, you can check the contents of the /tmp/resolv.conf.auto file. |
General Setup: DHCP
The DHCP protocol is used to set up an interface which obtains its configuration parameters automatically via a DHCP lease.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan general setup dhcp v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hostname to send when requesting DHCP | string; default: none | A hostname for this interface used to identify this machine on the DHCP server. |
General Setup: DHCPv6
The DHCPv6 protocol is used to set up an IPv6 interface which obtains its configuration parameters automatically via a DHCP lease.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan general setup dhcpv6 v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Request IPv6-address | try | force | disabled; default: try | Defines the behaviour for requesting an address. |
| Request IPv6-prefix of length | integer [0..64] | Automatic | disabled ; default: Automatic | Defines how this will request a IPv6 ULA-Prefix length. If set to 'disabled' the interface will obtain a single IPv6 address without a subnet for routing. |
General Setup: PPPoE
The PPPoE protocol is used to set up a PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) connection over the Ethernet port.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan general setup pppoe v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PAP/CHAP username | string; default: none | Username used in PAP/CHAP authentication. |
| PAP/CHAP password | string; default: none | Password used in PAP/CHAP authentication. |
| Access Concentrator | string; default: none | The Access Concentrator to connect to. ISPs used Access Concentrators to route their PPPoE connections. Usually, the settings are received automatically, however in some cases it is required to specify the name for an Access Concentrator. Leave empty to detect Access Concentrators automatically. |
| Service name | string; default: none | The Service Name to connect to. Leave empty to detect Service name automatically. |
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings section is used to set up some of the more specific and less frequently used interface parameters. This section is different for each protocol.
Advanced Settings: Static
Advanced Settings information for Static protocol is provided in the table below.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan advanced settings static v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether the interface should be launched during the boot process. If set to off, the interface would have to be brought up manually after each boot. |
| Use built in IPv6-management | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether to enable prefix delegation. |
| Force link | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether interface settings (IP, route, gateway) are assigned to the interface regardless of the link being active or only after the link has become active. |
| Override MAC address | mac; default: none | When set, uses a user-defined MAC address for the interface. |
| Override MTU | integer [1..9200]; default: none | Changes the interface's allowed maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
| Use gateway metric | integer; default: none | A metric specifies the priority of the gateway. The lower the metric, the higher the priority (0 for highest priority). |
| IPv6 assignment length | integer [0..64] | disabled; default: 60 | Delegates a prefix of given length to the interface. |
| IPv6 address | ip6; default: none | The interface's IPv6 address. An IP address identifies a device on a network and allows it to communicate with other devices. NOTE: this field only becomes visible when IPv6 assignment length is set to disabled. Note: this field only becomes visible when IPv6 assignment length is set to disabled |
| IPv6 gateway | ip6; default: none | IPv6 prefix routed here for use on other interfaces. Note: this field only becomes visible when IPv6 assignment length is set to disabled. |
| IPv6 routed prefix | ip6; default: none | IPv6 prefix routed here for use on other interfaces. Note: this field only becomes visible when IPv6 assignment length is set to disabled. |
| IPv6 assignment hint | string; default: none | The subprefix-ID that should be delegated as hexadecimal number. |
| IPv6 suffix | ip6 suffix; default: none | When an IPv6 prefix (like 'a:b:c:d::') is received from a delegating server, use a suffix (like '::1') to form an IPv6 address ('a:b:c:d::1') for the interface. Leave empty to generate a random suffix. |
Advanced Settings: DHCP
Advanced Settings information for DHCP protocol is provided in the table below.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan advanced settings dhcp v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether the interface should be launched during the boot process. If set to off, the interface would have to be brought up manually after each boot. |
| Use built-in IPv6 management | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether to enable prefix delegation. |
| Force link | off | on; default: off | Specifies whether interface settings (IP, route, gateway) are assigned to the interface regardless of the link being active or only after the link has become active. |
| Use broadcast flag | off | on; default: off | Required for certain ISPs. For example, Charter with DOCSIS 3. |
| Use default gateway | off | on; default: on | When checked, creates a default route for the interface. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether to use DNS servers obtained automatically or specified manually. |
| Use custom DNS servers | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether to use DNS servers obtained automatically or specified manually. Note: this field only becomes visible when Use DNS servers advertised by peer is set to off |
| Use gateway metric | integer; default: none | A metric specifies the priority of the gateway. The lower the metric, the higher the priority (0 for highest priority). |
| Client ID to send when requesting DHCP | string; default: none | Client ID which will be sent when requesting a DHCP lease. |
| Vendor Class to send when requesting DHCP | string; default: none | Vendor class which will be sent when requesting a DHCP lease. |
| Override MAC address | mac; default: none | Override MAC address of the WAN interface. For example, your ISP (Internet Service Provider) gives you a static IP address and it might also bind it to your computers MAC address (i.e., that IP will only work with your computer but not with your device). In this field you can enter your computer’s MAC address and fool the gateway in to thinking that it is communicating with your computer. |
| Override MTU | integer [1..9200]; default: none | Changes the interfaces allowed maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
Advanced Settings: DHCPv6
Advanced Settings information for DHCPv6 protocol is provided in the table below.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan advanced settings dhcpv6 v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether the interface should be launched during the boot process. If set to off, the interface would have to be brought up manually after each boot. |
| Use built in IPv6-management | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether to enable prefix delegation. |
| Force link | off | on; default: off | Specifies whether interface settings (IP, route, gateway) are assigned to the interface regardless of the link being active or only after the link has become active. |
| Use default gateway | off | on; default: on | When checked, creates a default route for the interface. |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether to use DNS servers obtained automatically or specified manually. |
| Use custom DNS servers | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether to use DNS servers obtained automatically or specified manually. Note: this field only becomes visible when Use DNS servers advertised by peer is set to off |
| Custom delegated IPv6-prefix | ip6 prefix; default: none | Uses an (additional) user-provided IPv6 prefix for distribution to clients. |
| Client ID to send when requesting DHCP | string; default: none | Client ID which will be sent when requesting a DHCP lease. |
| Override MAC address | mac; default: none | When set, uses a user-defined MAC address for the interface. |
| Override MTU | integer [1..9200]; default: none | Changes the interface's allowed maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
Advanced Settings: PPPoE
Advanced Settings information for PPPoE protocol is provided in the table below.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan advanced settings pppoe v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bring up on boot | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether the interface should be launched during the boot process. If set to off, the interface would have to be brought up manually after each boot. |
| Use built-in IPv6 management | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether to enable prefix delegation. |
| Force link | off | on; default: off | Specifies whether interface settings (IP, route, gateway) are assigned to the interface regardless of the link being active or only after the link has become active. |
| Obtain IPv6 address | Automatic | Disabled | Manual; default: Automatic | Defines behaviour for obtaining an IPv6 address. |
| Use default gateway | off | on; default: on | When checked, creates a default route for the interface. |
| Use gateway metric | integer; default: none | A metric specifies the priority of the gateway. The lower the metric, the higher the priority (0 for highest priority). |
| Use DNS servers advertised by peer | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether to use DNS servers obtained automatically or specified manually. |
| Use custom DNS servers | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether to use DNS servers obtained automatically or specified manually. Note: this field only becomes visible when Use DNS servers advertised by peer is set to off |
| LCP echo failure threshold | integer; default: none | Presumes peer to be dead after given amount of LCP echo failures. Leave it at 0 to ignore failures. |
| LCP echo interval | integer; default: none | Sends LCP echo requests at the given interval in seconds. This function is only effective in conjunction with failure threshold. |
| Host-Uniq tag content | raw hex-encoded bytes; default: none | Leave empty unless your ISP require this. |
| Inactivity timeout | mac; default: none | Close inactive connection after the given amount of seconds. Leave it at 0 to persist connection. |
| Override MTU | integer [1..1500]; default: none | Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) – specifies the largest possible size of a data packet. |
Physical Settings
The Physical Settings section is used to create associations with physical interfaces and bridge network interfaces.
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_interfaces_network_interfaces_lan_physical_settings_wifi_{{{wifi}}}_v1.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bridge interfaces | off | on; default: on | Bridges physical interfaces specified in this configuration. |
| Enable STP | off | on; default: off | Turns the use of Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) for this interface on or off. |
| Interface | network interface(s); default: eth0 | Ties this network interface to physical device interfaces such as Ethernet . |
Firewall Settings
The Firewall Settings section is used to specify to which firewall zone if any this interface belongs.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces firewall settings v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Create / Assign firewall-zone | firewall zone; default: none | Assigns this interface to the specified firewall zone. |
DHCP Server
A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server is a service that can automatically configure the TCP/IP settings of any device that requests such a service. If you connect a device that has been configured to obtain an IP address automatically, the DHCP server will lease out an IP address from the available IP pool and the device will be able to communicate within the private network.
In order to view the DHCP server configuration, the interface protocol must be set to Static.
DHCP Server: General Setup
The General Setup section is used to set up the main operating parameters of the DHCP server.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan dhcp server general setup v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
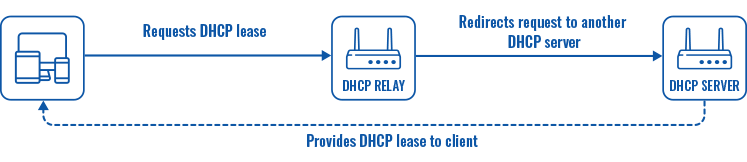
| Enable DHCP | Enable | Disable | DHCP Relay*; default: Enable | Turns the DHCP server on or off or enables DHCP relay*. If DHCP Relay* is selected, you will be prompted to enter an IP address of another DHCP server in your LAN. In this case, whenever a new machine connects to this device, it will redirect any DHCP requests to the specified DHCP Server. |
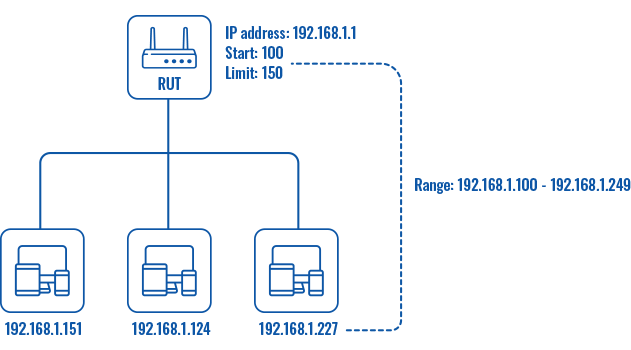
| Start | integer [1..255]; default: 100 | The starting IP address value. e.g., if your device’s LAN IP is 192.168.1.1 and your subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 that means that in your network a valid IP address has to be in the range of [192.168.1.0..192.168.1.254] (192.168.1.255 is a special unavailable address). If the Start value is set to 100 then the DHCP server will only lease out addresses starting from 192.168.1.100. |
| Limit | integer [1..255]; default: 150 | How many addresses the DHCP server can lease out. Continuing from the example above: if the start address is 192.168.1.100 and the server can lease out 150 addresses, available addresses will be from 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.249 (100 + 150 – 1 = 249; this is because the first address is inclusive). |
| Lease time | integer [2..999999]m/h; default: 12h | A DHCP lease will expire after the amount of time specified in this field and the device that was using the lease will have to request a new one. However, if the device stays connected, its lease will be renewed after half of the specified amount of time passes (e.g., if lease time is 12 hours, then every 6 hours the device will ask the DHCP server to renew its lease). The minimal amount of time that can be specified is 2 minutes. |
* When an interface is set to act as a DHCP Relay, it redirects all received DHCP request messages to another specified DHCP server:
DHCP Server: Advanced Settings
Refer to the table below for information on the Advanced Settings section.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan dhcp server advanced settings v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic DHCP | off | on; default: on | Enables dynamic allocation of client addresses. If this is disabled, only clients that have static IP leases will be served. |
| Force | off | on; default: off | The DHCP force function ensures that the device will always start it’s DHCP server, even if there is another DHCP server already running in the its network. By default the device’s DHCP server will not start when it is connected to a network segment that already has a working DHCP server. |
| IPv4 Netmask | netmask; default: none | Sends a different netmask than the LAN netmask to DHCP clients. |
| DHCP Options | dhcp options; default: none | Additional options to be added to the DHCP server. For example with '26,1470' or 'option:mtu, 1470' you can assign an MTU value per DHCP. You can find more information on DHCP Options here. |
DHCP Server: IPv6 Settings
Refer to the table below for information on the IPv6 Settings section.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan dhcp server ipv6 settings v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Router Advertisement Service | disabled | relay mode | server mode | hybrid mode; default: Disabled | Specifies whether router advertisements should be enabled (server mode), relayed or disabled. |
| DHCPv6 Service | disabled | relay mode | server mode | hybrid mode; default: Disabled | Specifies whether DHCPv6 server should be enabled (server), relayed (relay) or disabled (disabled). |
| NDP Proxy | disabled | relay mode | hybrid mode; default: Disabled | Specifies whether NDP should be relayed or disabled. |
| DHCPv6 Mode | stateless | stateful-only | stateless + stateful; default: stateless + stateful | Router announcement (RA) mode. |
| Always announce default router | off | on; default: off | Default router lifetime in the the router announcement (RA) message will be set if default route is present and a global IPv6 address or if default route is present but no global IPv6 address or neither of both conditions. |
| Announced DNS server | ip; default: none | Supplements DHCP-assigned DNS server entries with ones specified in this field. |
| Announced DNS domains | ip; default: none | DNS domain handed out to DHCP clients. |
Static Lease
Static IP leases are used to reserve specific IP addresses for specific devices by binding them to their MAC address. This is useful when you have a stationary device connected to your network that you need to reach frequently, e.g., printer, IP phone, etc.
This section displays static IP leases currently existing on this device.
In order to view the Static Lease section, the interface protocol must be set to Static.
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan static lease v1.png
Static Lease: Settings
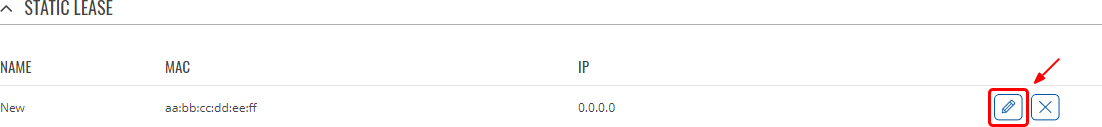
To access a lease's settings page, click the 'Edit' button located to the right of the lease:
You should be directed to a window that looks like this:
File:Networking rutos manual interfaces network interfaces lan static lease settings v1.png
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MAC address | mac; default: none | MAC address of a device that is on this interface's network. |
| IP address | ip; default: none | The IP address that will be reserved for the specified device. |
Static Lease: Add Lease
The Add Lease section is used to create new static leases. To create a new lease, simply enter a custom name for it and click the 'Add' button.
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]