Template:Setting up mobile interface on rpi: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
[[File:Networking_trm240_example_rpi_get_interface_ip.png|border|class=tlt-border|650px|Image: 650 pixels]] | [[File:Networking_trm240_example_rpi_get_interface_ip.png|border|class=tlt-border|650px|Image: 650 pixels]] | ||
[[Category:TRM240]] | [[Category:TRM240]] | ||
Revision as of 08:54, 1 October 2020
Prerequisites
You will need:
- RPI3 B+ model
- Raspbian 10 operating system
- Internet connection
Step 1: preparing TRM240 for use
Before connecting the TRM240 to the RPI3, we need to prepare the device by inserting the SIM card in place. How to insert the SIM card you can find here. After inserting the card, don’t forget to mount the antenna for better GSM signal.
Step 2: connecting to RPI3
When the TRM240 device is ready, we need to connect it to one of the USB ports on the RPI3. After connecting it, wait about 15 seconds for device to boot up. After boot up you should see four new USB ports in the /dev directory. You can check them by executing this command in the terminal:
ls /dev/ttyUSB*
After executing the command yuo should see these devices:
We will be using ttyUSB3 port because this port is used for data flow.
Note: If you have connected more USB devices, the USB ports may differ.
Step 3: download necessary software
To start using the TRM240 device, first of all we need to install Debian’s Point-to-Point Protocol package. In the terminal execute these commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt install -y ppp
This package will be used to establish a dial-up connection which will give us a new network interface called ppp0.
Step 4: create necessary scripts
Now we need to create three scripts which will allow us to create the internet connection. In the command line first of all execute these commands:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/chatscripts sudo mkdir -p /etc/ppp/peers
When the necessary directories are created, inside the /etc/chatscripts directory create file by the name quectel-chat-connect and paste in these lines:
ABORT "BUSY" ABORT "NO CARRIER" ABORT "NO DIALTONE" ABORT "ERROR" ABORT "NO ANSWER" TIMEOUT 30 "" AT OK ATE0 OK ATI;+CSUB;+CSQ;+COPS?;+CGREG?;&D2 OK AT+CGDCONT=1,\"IP\",\"\\T\",,0,0 OK ATD*99# CONNECT
Lets create another script in the same directory by the name quectel-chat-disconnect and paste in these lines:
ABORT "ERROR" ABORT "NO DIALTONE" SAY "\nSending break to the modem\n" "" +++ "" +++ "" +++ SAY "\nGoodbay\n"
One more script is required inside directory /etc/ppp/peers. The script should be called gprs. Paste in these lines:
/dev/<usb_port> 115200 connect 'chat -s -v -f /etc/chatscripts/quectel-chat-connect -T <operator_apn>' disconnect 'chat -s -v -f /etc/chatscripts/quectel-chat-disconnect' hide-password noauth debug defaultroute noipdefault novj novjccomp noccp ipcp-accept-local ipcp-accept-remote local lock modem dump nodetach nocrtscts remotename 3gppp ipparam 3gppp ipcp-max-failure 30 usepeerdns
Before using this script, you need to change the lines <usb_port> and <operator_apn>. Usb port must be set to ttyUSB3 and apn to your operator’s provided apn.
Step 5: dial-up procedure
This is the last step. Now we need to dial-up the connection. In the terminal execute this command:
sudo pppd call gprs&
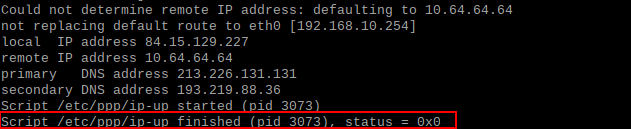
When you execute this command you will see a lot of debug output. Wait until you see the line “script /etc/ppp/ip-up finished”.
If you see this line you can check if the connection was created by executing this command in the terminal:
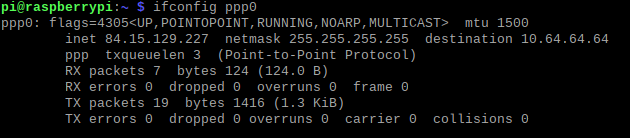
ifconfig ppp0
If you want to use the created connection as the default gateway, you need to add rule to the routing table. Execute this command in the terminal:
sudo route add default gw <your_ip_address> ppp0
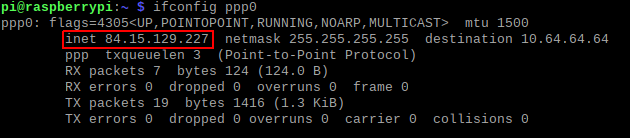
You can lookup your IP address by executing this command in the terminal:
ifconfig ppp0