Template:Networking rutos manual routing: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 344: | Line 344: | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns BGP protocol usage on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Enable vty</td> | <td>Enable vty</td> | ||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns vty access on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Import config</td> | <td>Import config</td> | ||
<td>-</td> | <td>-</td> | ||
<td>Uploads an external BGP configuration</td> | <td>Uploads an external BGP configuration.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 373: | Line 373: | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns the BGP instance on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>AS</td> | <td>AS</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>AS number is an identification of an autonomous system. BGP protocol uses the AS number for detecting whether the BGP connection is | <td>AS number is an identification of an autonomous system. The BGP protocol uses the AS number for detecting whether the BGP connection is internal or an external one.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>BGP router ID</td> | <td>BGP router ID</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>The router | <td>The router ID is used by BGP to identify the routing device from which a packet originated. Fefault router ID value is selected as the largest IP Address of the interface.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Network</td> | <td>Network</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Adds an announcement network(s).</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Redistribution options</td> | <td>Redistribution options</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Distributes selected routes. Route redistribution is a process that allows a network to use a routing protocol to dynamically route traffic based on information learned from a separate routing protocol.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Deterministic</td> | <td>Deterministic MED</td> | ||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Compares MEDs between same AS, while ignoring their age.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 404: | Line 404: | ||
====BGP Peers==== | ====BGP Peers==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
<b>BGP Peers</b> are routers in the same BGP Peer Group that can redistribute routes among other BGP Peers. Below is an example of the BGP Peers section, which is empty by default. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peers.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peers.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
To create a new Peer, look to the Add New Instance section under BGP Peer; type in a custom name for the BGP Peer and click the 'Add' button: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peers_add_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
The newly added BGP Peer configuration should look similar to this: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peers_added.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 413: | Line 421: | ||
<th>Value</th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th>Description</th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Remote AS</td> | <td>Remote AS</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Neighbour | <td>Remote autonomous system number of this remote BGP Neighbour.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Remote address</td> | <td>Remote address</td> | ||
<td> | <td>ip4; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>IPv4 address of this remote BGP Neighbour.</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable</td> | |||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns turns this BGP peer on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
To see more settings for a BGP Peer, click the 'Edit' button next to it: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peers_edit_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
The full BGP Peer configuration page should look similar to this: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peers_bgp_peer.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peers_bgp_peer.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| Line 444: | Line 456: | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns this BGP peer on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Remote AS</td> | <td>Remote AS</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Neighbour | <td>Remote autonomous system number of this remote BGP Neighbour.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Remote address</td> | <td>Remote address</td> | ||
<td> | <td>ip4; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>IPv4 address of this remote BGP Neighbour.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Remote port</td> | <td>Remote port</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>integer [0..65535]; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Neighbour | <td>Listening port number of the BGP Neighbour.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>EBGP Multihop</td> | <td>EBGP Multihop</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Time to Live value</td> | <td>Time to Live value for packets associated with this remote BGP Neighbour.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Default originate</td> | ||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Announces default routes to this peer.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Description</td> | <td>Description</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>A custom description for this BGP peer. Used for easier management purposes.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 480: | Line 492: | ||
====BGP Peer Groups==== | ====BGP Peer Groups==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
A <b>BGP Peer Group</b> is a collection of routers that use the BGP protocol to dynamically redistribute routes among peers (other routers). The figure below is an example of the BGP Peer Groups section, which is empty by default. | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peer_groups.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peer_groups.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
To create a new Peer Group, look to the Add New Instance section under BGP Peer Groups; type in a custom name for the BGP Peer Group and click the 'Add' button: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peers_add_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
The newly added BGP Peer Group configuration should look similar to this: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peer_groups_added.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
| Line 493: | Line 513: | ||
<td>Remote AS</td> | <td>Remote AS</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Remote autonomous system number.</td> | ||
</tr></table> | </tr> | ||
</table> | |||
To see more settings for a BGP Peer Group, click the 'Edit' button next to it: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peer_groups_edit_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | |||
The full BGP Peer Group configuration page should look similar to this: | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peer_groups_bgp_peer_group.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_bgp_peer_groups_bgp_peer_group.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
| Line 509: | Line 534: | ||
<td>Enable</td> | <td>Enable</td> | ||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns the BGP Peer Group configuration on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Remote AS</td> | <td>Remote AS</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Remote autonomous system number.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Neighbor address</td> | <td>Neighbor address</td> | ||
<td> | <td>ip4; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>IPv4 address(es) of a remote BGP Neighbour.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Advertisement interval</td> | <td>Advertisement interval</td> | ||
<td>default: <b>none</b></td> | <td>integer; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>BGP advertisement frequency (in seconds).</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Neighbor configuration</td> | <td>Neighbor configuration</td> | ||
<td>default: | <td>None | Route Reflector client | Route Server client; default: <b>None</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Defines the role of a BGP Neighbour. | ||
<ul> | |||
<li><b>Route Reflector client</b> - redistributes received routes.</li> | |||
<li><b>Route Server client</b> - distributes routes.</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Disable next hop calculation</td> | <td>Disable next hop calculation</td> | ||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns next hop calculation for this BGP Peer Group on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Inbound soft-reconfiguration</td> | <td>Inbound soft-reconfiguration</td> | ||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | <td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Turns inbound soft-reconfiguration for this neighbor on or off.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 550: | Line 580: | ||
====Access List Filters==== | ====Access List Filters==== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Below is an example of | The <b>Access List Filters</b> section is used to configure special filters that restrict or allow access to specified networks for BGP Peers. Below is an example of the Access List Filters section which is empty by default. You can add a new filter by clicking the 'Add' button | ||
[[File: | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_routing_dynamic_routes_bgp_access_list_filters_add_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
You can add a new list by simply pressing '''Add''' button. | You can add a new list by simply pressing '''Add''' button. | ||
| Line 563: | Line 593: | ||
<th>Value</th> | <th>Value</th> | ||
<th>Description</th> | <th>Description</th> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Peer</td> | <td>Peer</td> | ||
<td>bgp peer; default: | <td>bgp peer; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td>Applies the rule for the specified peer.</td> | <td>Applies the filter rule for the specified peer.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Action</td> | <td>Action</td> | ||
<td>default: | <td>Permit | Deny; default: <b>Permit</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>When BGP traffic matches this rule, the device will take the action specified in this field, which is to either allow or block traffic.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Network</td> | <td>Network</td> | ||
<td>default: | <td>ip/netmask | Any; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Matches traffic destined or originating from (depends on 'Direction' selection) to the network specified in this field.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>Direction</td> | <td>Direction</td> | ||
<td>default: | <td>Inbound | Outbound; default: <b>Inbound</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>Matches network traffic direction, which can either be traffic destined to this device (Inbound) or traffic originating from this device (Outbound).</td> | ||
</tr> | |||
<tr> | |||
<td>Enable</td> | |||
<td>off <nowiki>|</nowiki> on; default: <b>off</b></td> | |||
<td>Turns an Access filter on or off.</td> | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
Revision as of 09:18, 20 October 2020
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
The Routing page is used to set up static routes, routing tables and rules.
This manual page provides an overview of the Routing windows in {{{name}}} devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
Static Routes
Routes ensure that network traffic finds its path to a specified host or network, both in local and remote network scenarios. Static routes are simply fixed routing entries in the routing table(s).
This section provides the possibility to configure custom static routes.
Static IPv4 Routes
The Static IPv4 Routes section displays a list of user defined static IPv4 routes and provides the possibility to add and configure new ones. The list is empty by default.
To add a new route and begin editing, simply click the 'Add' button. Refer to the table below for information on static route configuration fields.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | network interface; default: lan | Network interface of the target network. |
| Target* | ip4; default: none | Destination network address. |
| IPv4-Netmask* | netmask; default: none | A netmask is used to divide an IP address into sub-networks (subnets). Combined together, the 'Netmask' and 'Target' values define the exact destination network or IP address to which this route applies. |
| IPv4-Gateway | ip4; default: none | A gateway can be any machine in a network that is capable of serving as an access point to another network. Traffic that matches this route will be directed over the IP address specified in this field. |
| Metric | integer [0..255]; default: none | The metric value acts as a measurement of priority. If a packet about to be routed matches two or more rules, the one with the lower metric is applied. |
| MTU | integer [64..9000]; default: 1500 | Sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
| Route Type | unicast | local | broadcast | multicast | unreachable | prohibit | backhole | anycast | -- custom -- ; default: unicast | Selects route type. Each type specifies a different behavior for the route:
|
*Additional notes on 'Target' & 'Netmask' fields:
You can define a rule that applies to a single IP like this:
- Target: some IP
- Netmask: 255.255.255.255
Furthermore, you can create target/netmask combinations that apply to a range of IPs. Refer to the table below for examples.
| Target | Netmask | Network range |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.2.0 | 255.255.255.240 | 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.2.15 |
| 192.168.2.240 | 255.255.255.240 | 192.168.2.240 - 192.168.2.255 |
| 192.168.2.161 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.55.255 |
| 192.168.0.0 | 255.255.0.0 | 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 |
| 192.168.2.161 | 255.255.255.255 | 192.168.2.161 |
Static IPv6 Routes
The Static IPv6 Routes section displays a list of user defined static IPv6 routes and provides the possibility to add and configure new ones. The list is empty by default.
To add a new route and begin editing, simply click the 'Add' button. Refer to the table below for information on static route configuration fields.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | network interface; default: lan | Network interface of the target network. |
| Target | ip6; default: none | Destination network address. |
| IPv6-Gateway | ip6; default: none | A gateway can be any machine in a network that is capable of serving as an access point to another network. Traffic that matches this route will be directed over the IP address specified in this field. |
| Metric | integer [0..255]; default: none | The metric value acts as a measurement of priority. If a packet about to be routed matches two or more rules, the one with the lower metric is applied. |
| MTU | integer [64..9000]; default: 1500 | Sets the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction. |
| Route Type | unicast | local | broadcast | multicast | unreachable | prohibit | backhole | anycast | -- custom -- ; default: unicast | Selects route type. Each type specifies a different behavior for the route:
|
Advanced Static Routes
The Advanced Static Routes section is used to configure policy-based routing infrastructures, which are usually used in more complex or specific networking scenarios.
Routing Tables
Routing Tables store network routes. Tables are checked before every routing decision until a matching route is found. Having multiple tables allows the user to set up a policy routing infrastructure. Policy-based routing is a technique where routing decisions are based on policies (rule) set by the user.
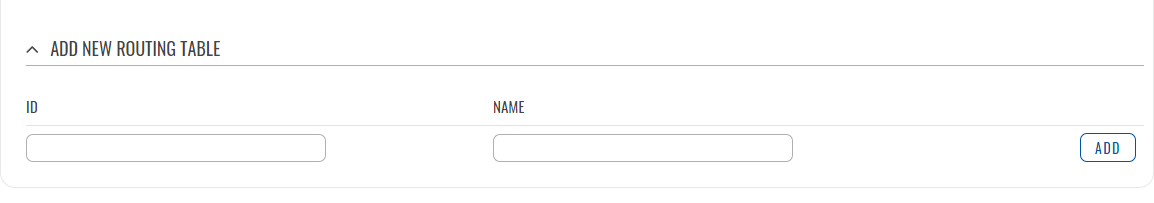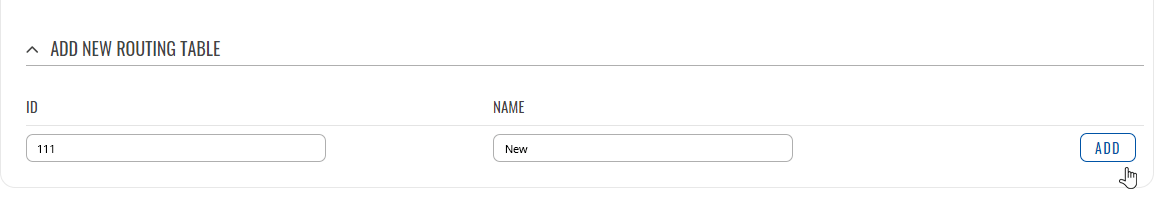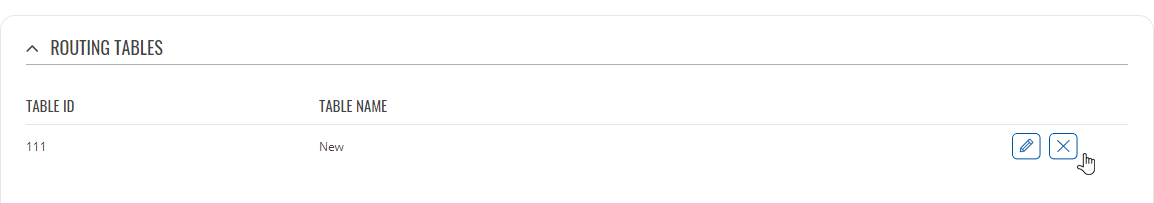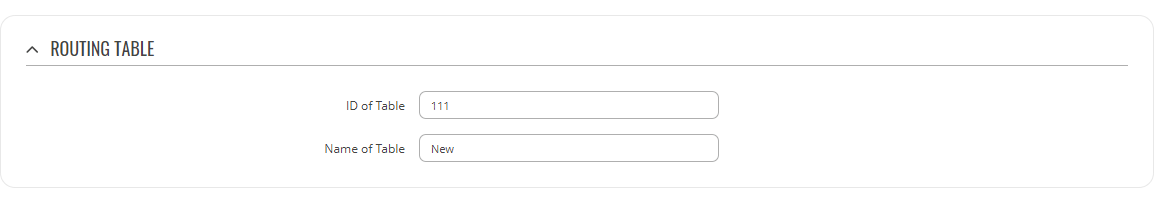
The 'Routing Tables' section displays user created routing tables. By default, the list is empty.
To create a new table, look to the 'Add New Routing Table' section below. Enter an ID for the new table in the range of [1..252], enter a custom name and click the 'Add' button. The new table should appear in the 'Routing Tables' list. Click the 'Edit' button next to it to begin editing.
Refer to the table below for information on configuration fields for routing tables.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ID of Table | integer [1..252]; default: none | Unique numerical identifier for the table. A table can be invoked by the both its ID or name. |
| Name of Table | string; default: none | A custom name for the table. A table can be invoked by the both its ID or name. |
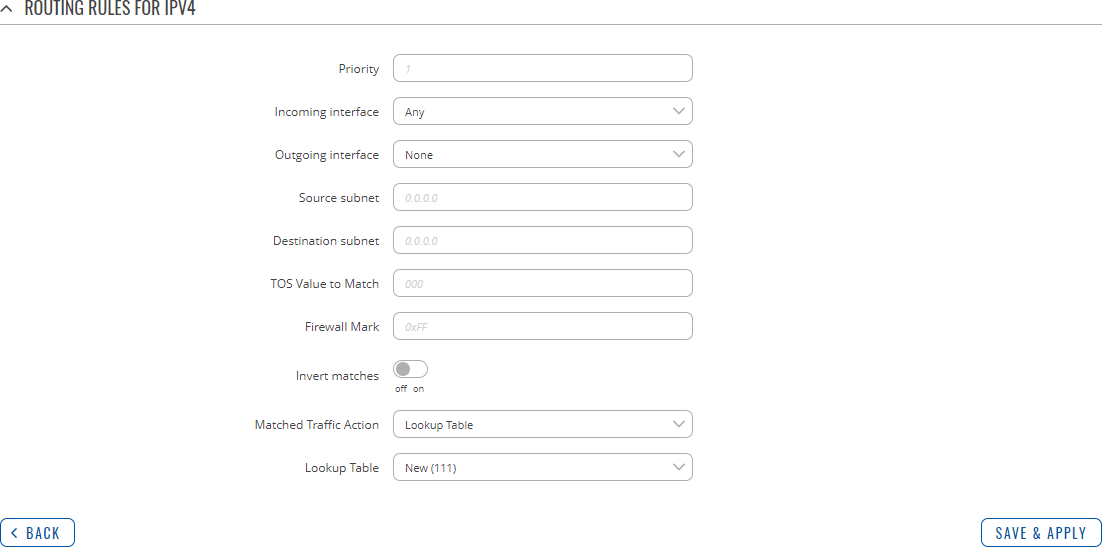
Routing Rules For IPv4
Routing Rules provide a way to route certain packets with exceptions, i.e., in accordance to a rule. 'Routing Rules For IPv4' displays user defined routing rules. It is empty by default. To create a new rule, click the 'Add' button and begin editing by clicking the 'Edit' button located to the right of the newly created rule.
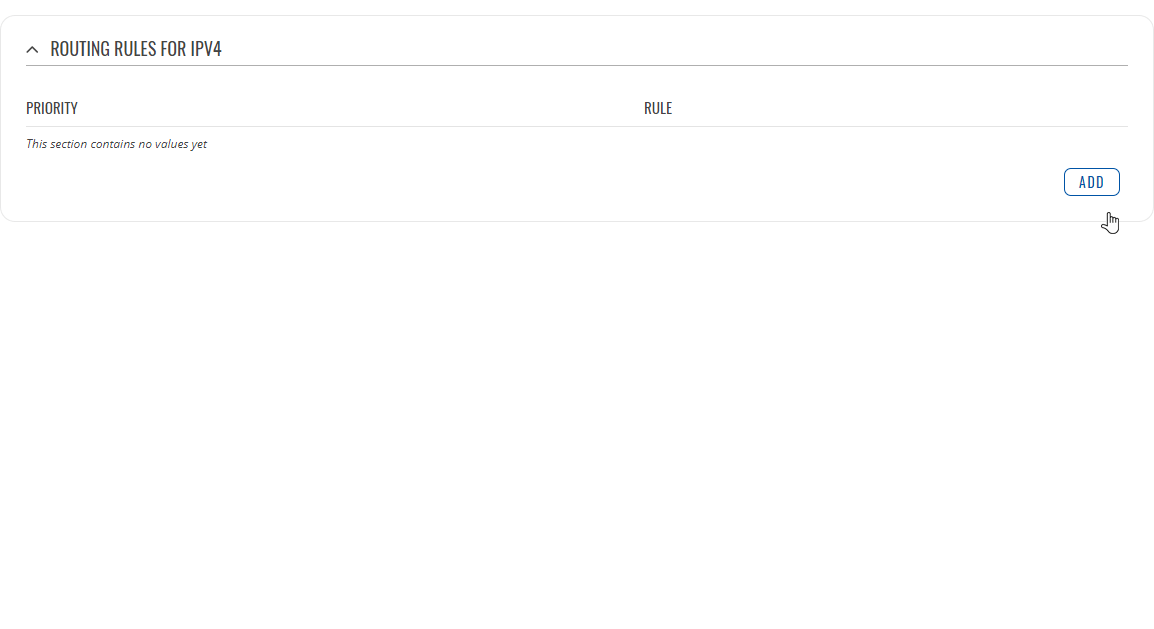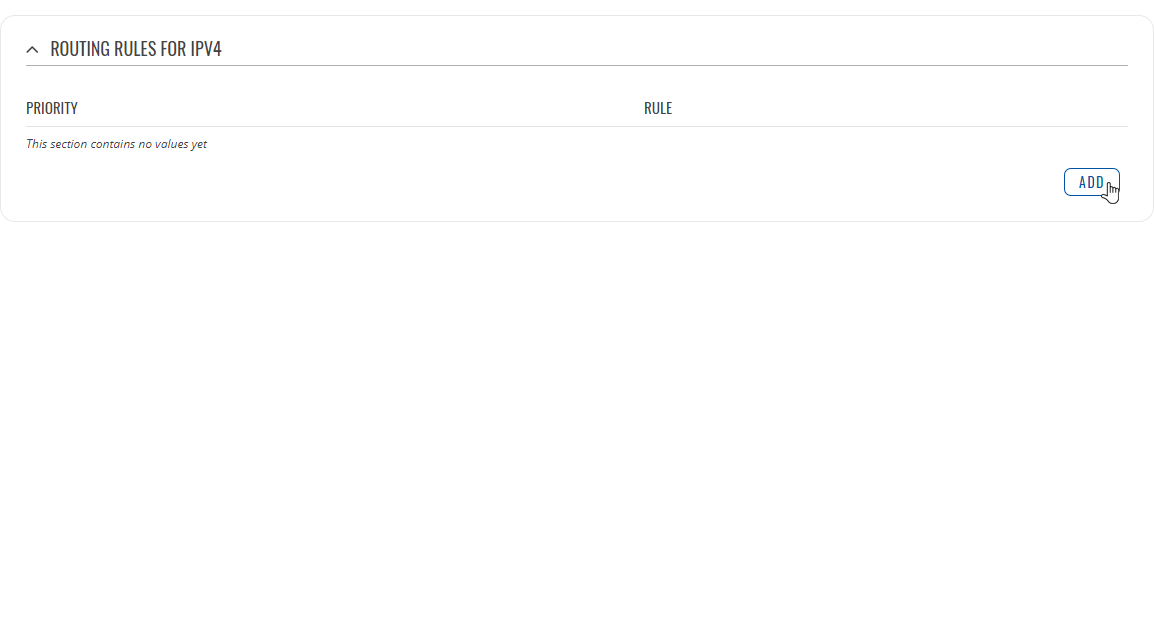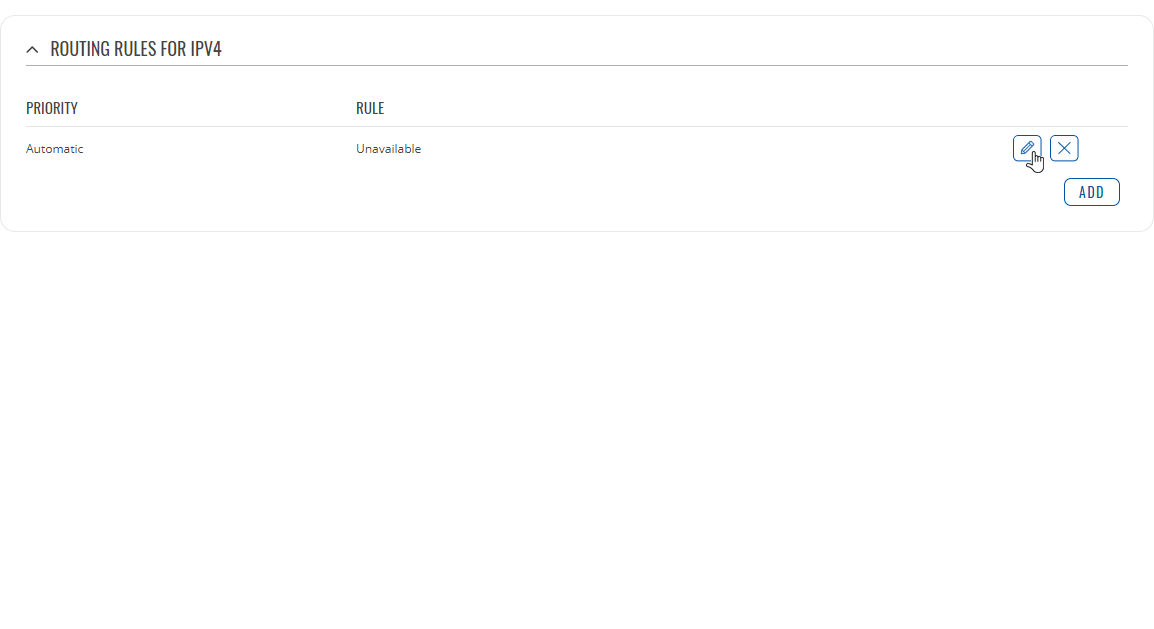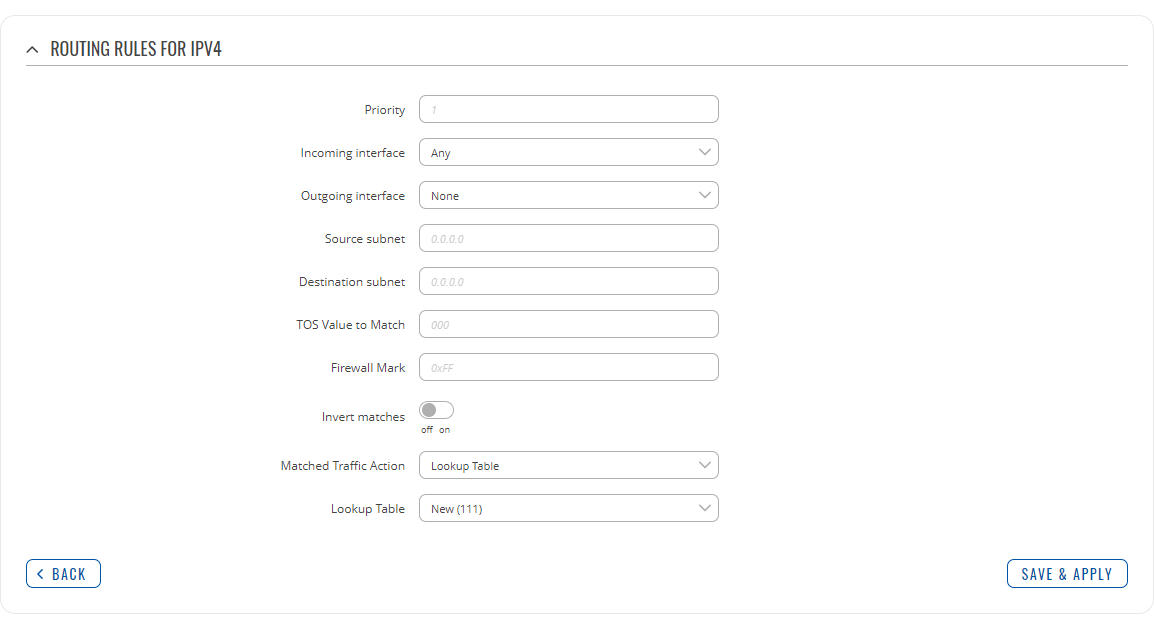
Refer to table below for information on each configuration field.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Priority | integer [0..65535]; default: none | Controls the order of IP rules. Rules with a lower priority value will be checked first. |
| Incoming interface | network interface | Any; default: Any | Logical interface name for incoming traffic. Select 'Any' to make the rule apply to all network interfaces. |
| Outgoing interface | network interface | None; default: None | Logical interface name for incoming traffic. Select 'None' to ignore outgoing interface. |
| Source subnet | netmask; default: none | Source subnet to match the rule. |
| Destination subnet | netmask; default: none | Destination subnet to match the rule. |
| TOS Value to Match | integer [0..255]; default: none | The type of service (ToS) value to match in IP headers. |
| Firewall Mark | integer [0..255] | hex [0x00..0xFF]; default: none | Specifies the fwmark and optionally its mask to match. For example, 0xFF to match mark 255 or 0x0/0x1 to match any even mark value. |
| Invert matches | off | on; default: off | If enabled, the meaning of the match options (Firewall Mark, TOS Value, Source and Destination subnets) is inverted. |
| Matched Traffic Action | Lookup Table | Jump to rule | Routing Action; default: Lookup Table | When network traffic matches this rule, the device will take an action specified in this field:
|
| Lookup Table | routing table; default: none | Specifies a table for routing traffic that matches this rule. This field is visible only when 'Matched Traffic Action' is set to Lookup Table. |
| Jump to rule | rule priority number; default: none | Specifies a another rule to follow for traffic that matches this rule. This field is visible only when 'Matched Traffic Action' is set to Jump to rule. |
| Routing Action | Prohibit | Unreachable | Blackhole | Throw; default: Prohibit | When traffic matches this rule, the action specified in this field will be executed. This field is visible only when 'Matched Traffic Action' is set to Routing Action. |
Route Reflector client [[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]