Template:Networking rutos manual wireless: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
The <b>Global Settings</b> section is used for configuring WiFi hardware parameters. You can find this section by clicking the 'Edit' button next to a wireless device (<u>not an interface</u>) in the Network → Wireless page: | The <b>Global Settings</b> section is used for configuring WiFi hardware parameters. You can find this section by clicking the 'Edit' button next to a wireless device (<u>not an interface</u>) in the Network → Wireless page: | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | TCR1 | [[File:Networking_tcr_manual_wireless_global_settings_edit_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wireless_global_settings_edit_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wireless_global_settings_edit_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
}}} | |||
===General Setup=== | ===General Setup=== | ||
| Line 240: | Line 242: | ||
The <b>Interface Configuration</b> section is used to configure the parameters of Wireless Access Points or Clients. You can find this section by clicking the 'Edit' button next to a wireless device (<u>not an interface</u>) in the Network → Wireless page: | The <b>Interface Configuration</b> section is used to configure the parameters of Wireless Access Points or Clients. You can find this section by clicking the 'Edit' button next to a wireless device (<u>not an interface</u>) in the Network → Wireless page: | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | TCR1 | [[File:Networking_tcr_manual_wireless_interface_configuration_edit_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wireless_interface_configuration_edit_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wireless_interface_configuration_edit_button.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
}}} | |||
===General Setup=== | ===General Setup=== | ||
| Line 246: | Line 250: | ||
The <b>General Setup</b> tab contains basic options for ESSID and network interface. | The <b>General Setup</b> tab contains basic options for ESSID and network interface. | ||
{{#ifeq: {{{series}}} | TCR1 | [[File:Networking_tcr_manual_wireless_interface_configuration_general_setup.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | | |||
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wireless_interface_configuration_general_setup.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | [[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wireless_interface_configuration_general_setup.png|border|class=tlt-border]] | ||
}} | |||
<table class="nd-mantable"> | <table class="nd-mantable"> | ||
Revision as of 15:15, 4 August 2021
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
The Wireless section of the Network tab can be used to manage and configure WiFi Access Points and WiFi Stations (clients) . This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the Wireless section for {{{name}}} devices.
If you're having trouble finding this page or some of the parameters described here on your device's WebUI, you should turn on "Advanced WebUI" mode. You can do that by clicking the "Advanced" button, located at the top of the WebUI.
Wireless technology
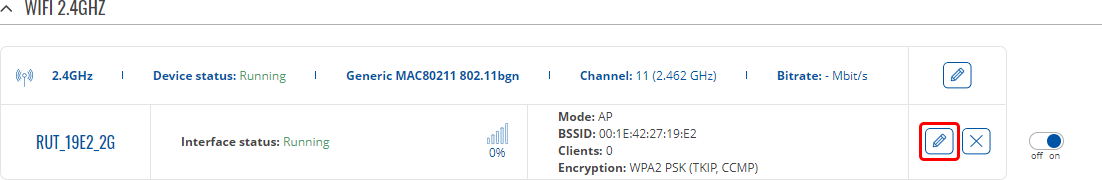
WiFi 2.4 GHz
The WiFi 2.4 GHz section is used to configure your wireless access points (AP) and wireless clients (STA).
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wireless_wifi_{{{wifi}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
Above is the overview of the Wireless Overview window. It displays active access points and stations.
Here you can turn on or off your WiFi interfaces, remove them or start configuring by clicking on
![]() Edit button on the right side of interface.
You can also configure your WiFi devices by clicking
Edit button on the right side of interface.
You can also configure your WiFi devices by clicking ![]() Edit button
in the right side of each table header.
To configure your Wireless device as Client press Scan button to scan the surrounding area and attempt to connect to a new wireless access point.
Edit button
in the right side of each table header.
To configure your Wireless device as Client press Scan button to scan the surrounding area and attempt to connect to a new wireless access point.
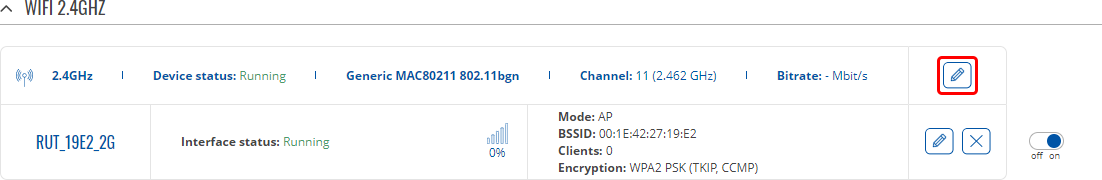
Global Settings
The Global Settings section is used for configuring WiFi hardware parameters. You can find this section by clicking the 'Edit' button next to a wireless device (not an interface) in the Network → Wireless page:
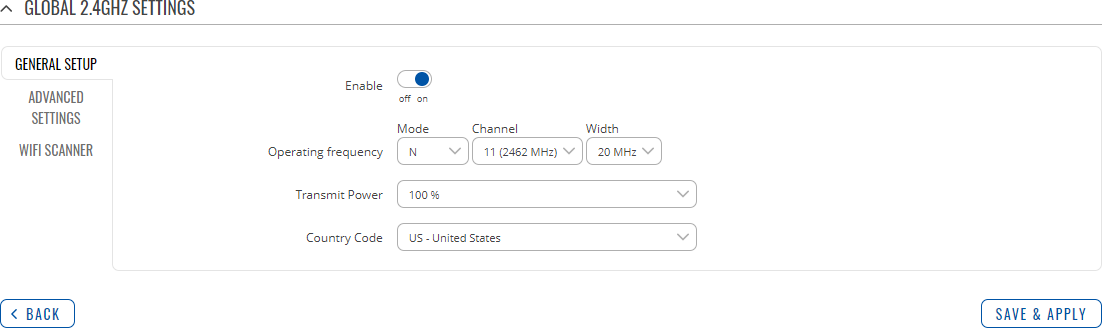
General Setup
The General Setup section is used to turn a wireless device on or off, select the operating frequency (WiFi mode and channel), transmit power and define a country code.
A wireless 2.4 GHz WiFi channel requires a signaling band roughly 22 MHz wide, radio frequencies of neighboring channels numbers significantly overlap each other. Choose a WiFi channel according to the busyness of other channels. You can download a free WiFi analyzer app on your phone, laptop or other WiFi device and check which channel is the least populated.
Many home networks utilize routers that by default run on channel 6 on the 2.4 GHz band. Neighboring WiFi home networks that run over the same channel generate radio interference that can cause significant network performance slowdowns for users. Reconfiguring a network to run on a different wireless channel helps minimize these slowdowns. Therefore, pick a channel with no other active Access Points and preferably one that has no active Access Point on two adjacent channels on each side as well. If you don't feel like doing this, set the 'Channel' field to Auto and the device will pick the least busy channel in your location automatically.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: on | Turns Wireless device on or off. |
| Operating Frequency (2.4 GHz) | ||
| Mode | N | Legacy; default: N | Wireless N (802.11n) supports a maximum theoretical transfer rate of 300mbps with 2 antennas. It can reach up to 450 Mbps with 3 antennas. Though typical speeds are more accurately around 130 Mbps. The legacy standards include 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g. |
| Channel | Auto | 1 (2412 MHz) | 2 (2417 MHz) | 3 (2422 MHz) | 4 (2427 MHz) | 5 (2432 MHz) | 6 (2437 MHz) | 7 (2442 MHz) | 8 (2447 MHz) | 9 (2452 MHz) | 10 (2457 MHz) | 11 (2462 MHz); default: 11 (2462 MHz) | A wireless 2.4 GHz WiFi channel requires a signaling band roughly 22 MHz wide, radio frequencies of neighboring channels numbers significantly overlap each other. Therefore, pick a channel with no other active Access Points and preferably one that has no active Access Point on two adjacent channels on each side as well. |
| Width | 20 MHz | 40 MHz; default: 20 MHz | A 40 MHz channel width bonds two 20 MHz channels together, forming a 40 MHz channel width; therefore, it allows for greater speed and faster transfer rates. But not if those channels are crowded with noise and interference. In crowded areas with a lot of frequency noise and interference, a single 20MHz channel will be more stable. 40MHz channel width allows for greater speed and faster transfer rates but it doesn’t perform as well in crowded areas. |
| Transmit Power | [5%...100%]; default: 100 % | The transmit power of an access point radio is proportional to its effective range – the higher the transmit power, the more distance that a signal can travel, and/or the more physical materials that it can effectively penetrate and still have data successfully resolved at the receiver. |
| Country code | country code; default: US - United States | SO/IEC 3166 alpha2 country codes as defined in ISO 3166-1 standard. |
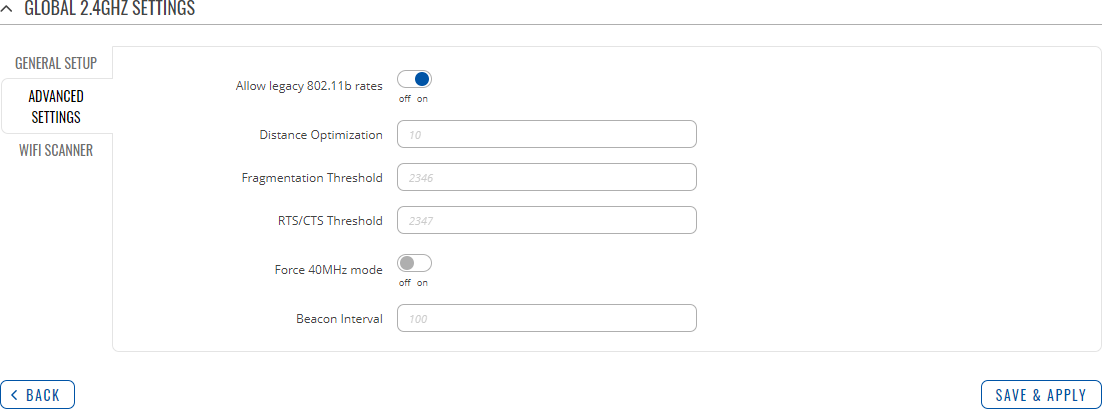
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings section is used to configure how the wireless Access Point will work from a hardware perspective.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Frequency (2.4 GHz) | ||
| Allow legacy 802.11b rates | off | on; default: on | Turn on to enable connections that uses legacy 802.11b standard. |
| Distance Optimization | integer [0..65535]; default: none | HT Distance to farthest network member in meters. |
| Fragmentation threshold | integer [256..2346]; default: none | The smallest packet size that can be fragmented and transmitted by multiple frames. In areas were interference is a problem, setting a lower fragment threshold might help reduce the probability of unsuccessful packet transfers, thus increasing speed |
| RTS/CTS threshold | integer [0..2347]; default: none | RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to Send) are mechanisms, used to reduce frame collisions introduced by the hidden node problem. It can help resolve problems arising when several access points are in the same area, contending |
| Force 40MHz mode | off | on; default: off | Always use 40MHz channels even if the secondary channel overlaps. Using this option does not comply with IEEE 802.11n-2009! |
| Beacon interval | integer [15..65535]; default: none | Beacon signal interval in seconds. |
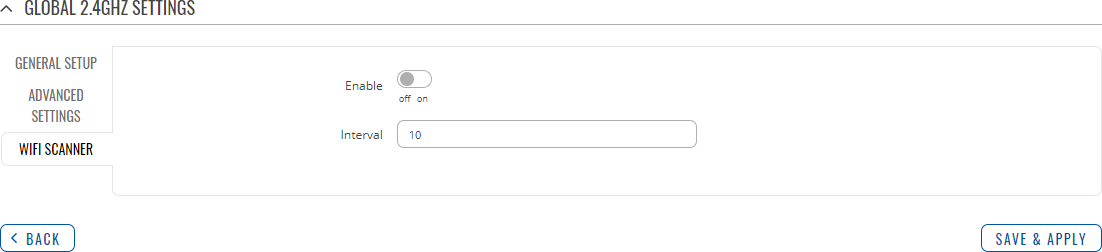
WiFi Scanner
The WiFi Scanner provides you with the possibility to scan and collect information about connected devices and surrounding access points. The collected data is sent using the [[{{{name}}} Data to Server|Data to Server]] functionality with Kinesis argument.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | off | on; default: off | Enables or disables WiFi scanner. |
| Interval | integer; default: 10 | Interval between scans in seconds. |
Interface Configuration
The Interface Configuration section is used to configure the parameters of Wireless Access Points or Clients. You can find this section by clicking the 'Edit' button next to a wireless device (not an interface) in the Network → Wireless page:
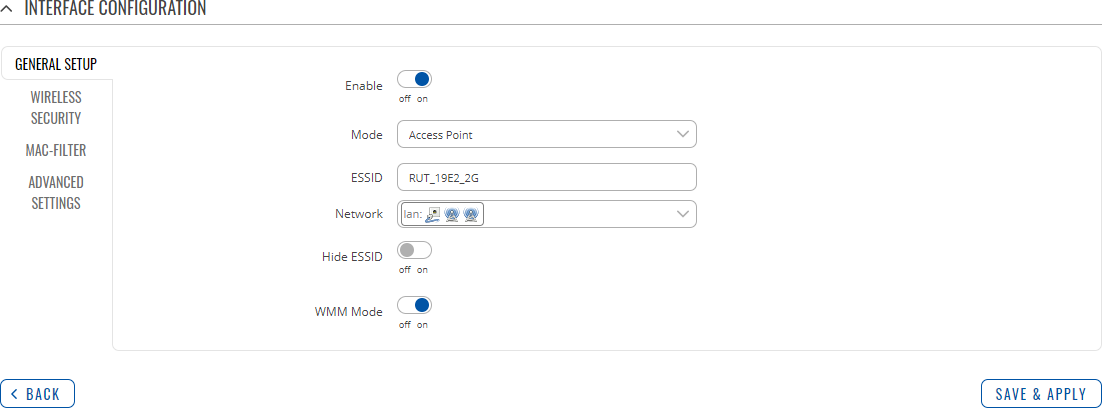
General Setup
The General Setup tab contains basic options for ESSID and network interface.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mode | Access Point | Client; default: Access Point | Defines what role this interface will do, Access point to supply WiFi for other devices, or as Client to use other devices WiFi for WWAN. |
| ESSID | Factory ESSID is different for every device; default: none | Extended Service Set Identifier. |
| Network | network interfaces; default: lan | Choose the network(s) you want to attach to this wireless interface or fill out the create field to define a new network. |
| Access Point mode | ||
| ESSID | off | on; default: off | Hide extended Service Set Identifier. |
| WMM Mode | off | on; default: on | Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM), previously known as Wireless Multimedia Extensions (WME), is a subset of the 802.11e wireless LAN (WLAN) specification that enhances quality of service (QoS) on a network by prioritizing data packets according to four categories. |
| Client mode | ||
| BSSID | off | on; default: off | Basic service set identifier. |
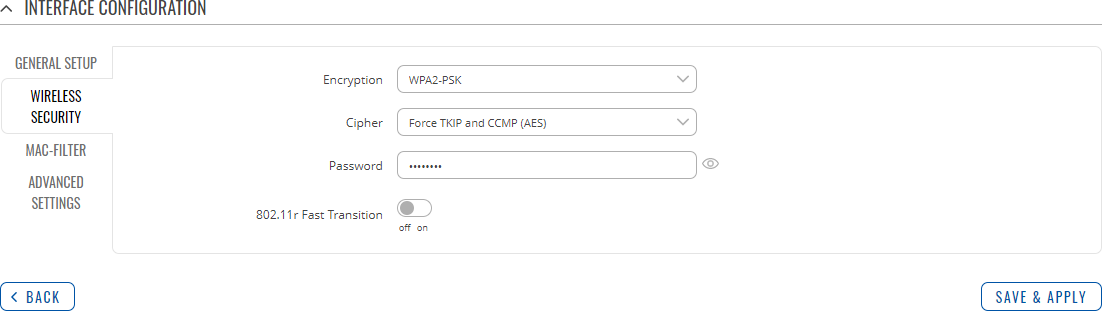
Wireless Security
The Wireless Security tab is used to determine what kind of encryption your WLAN will use.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | No encryption | WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Mixed Mode | WPA2-PSK | WPA2-EAP |
WPA2-EAP/WPA3-EAP Mixed Mode | WPA3-EAP | WPA2-PSK/WPA3-SAE Mixed Mode | WPA3-SAE | OWE; default: WPA2-PSK |
The type of encryption used on this Wireless Interface.
Opportunistic Wireless Encryption (OWE) - no password is required and all wireless traffic is encrypted (safer than No Encryption). |
| With all encryptions | ||
| Cipher | Auto | Force CCMP (AES) | Force TKIP | Force TKIP and CCMP (AES); default: Force TKIP and CCMP (AES) | An algorithm for performing encryption or decryption. |
| WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK Mixed Mode, WPA2-PSK, WPA2-PSK/WPA3-SAE Mixed Mode, WPA3-SAE | ||
| Password | string; default: random | A custom passphrase used for authentication (at least 8 characters long). |
| WPA2-EAP, WPA2-EAP/WPA3-EAP Mixed Mode, WPA3-EAP | ||
| Radius-Authentication-Server | string; default: none | Ip address of the authentification server. |
| Radius-Authentication-Port | string; default: none | Default port for the server is 1812. |
| Radius-Authentication-Secret | string; default: none | Server's shared secret. |
| Radius-Accounting-Server | string; default: none | Ip address of the accounting server. |
| Radius-Accounting-Port | string; default: none | Default port for the server is 1813. |
| Radius-Accounting-Secret | string; default: none | Server's shared secret. |
| NAS id | string; default: none | Network access server identifier. |
| 802.11r Fast Transition | off | on; default: off | Enables or disables 802.11r Fast Transition functionality |
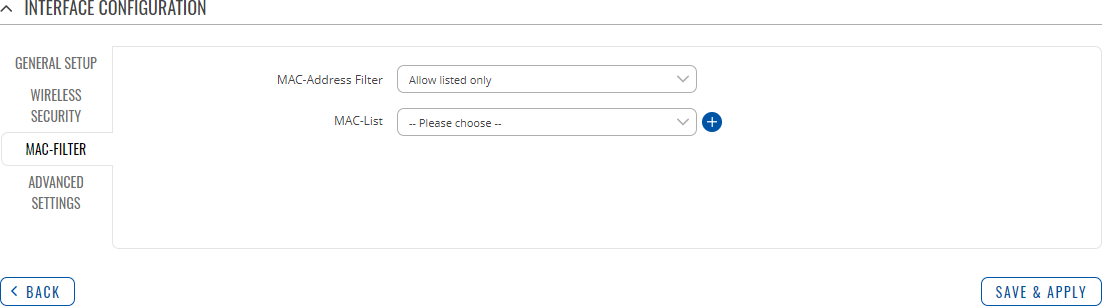
MAC Filter
The MAC Filter tab is used for setting up rules that allow or exclude devices with specified MAC addresses from connecting to your WiFi network. This tab is only visible when Wireless interface Mode is set to Access Point.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MAC-address filter | Disable | Allow listed only | Allow all except listed; default: Disable | Defines how the MAC Filter should function.
|
| MAC-List | MAC; default: none | List of MAC addresses to be included or excluded from connecting to your Wireless Access Point. |
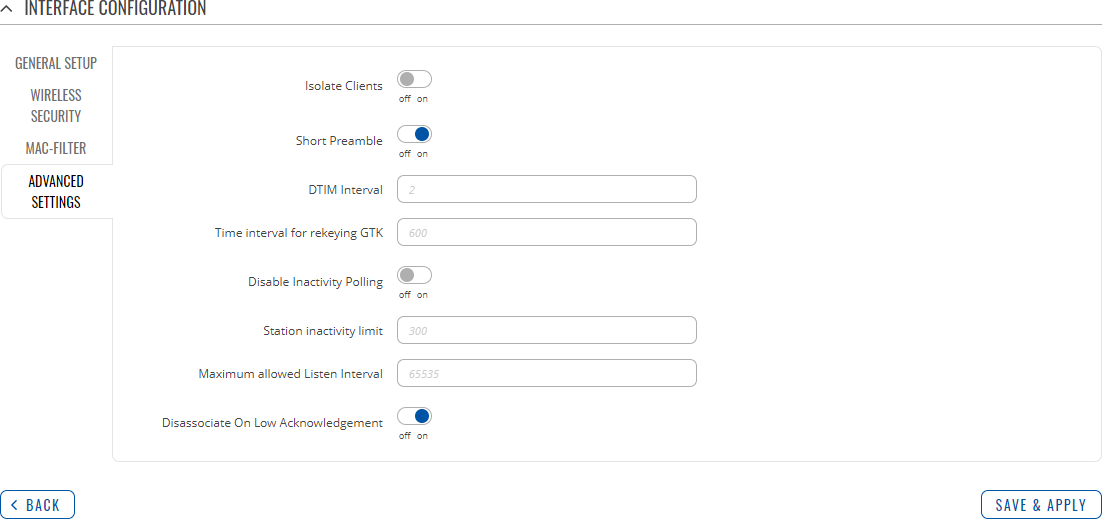
Advanced Settings
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Isolate Clients | off | on; default: off | Prevents client to client communication on the same subnet. |
| Short Preamble | off | on; default: on | Uses Short Preamble, it uses shorter data strings that adds less data to transmit the error redundancy check which means that it is much faster. |
| DTIM interval | seconds; default: none | Delivery Traffic Indication Message Interval. |
| Time interval for rekeying GTK | seconds; default: none | Period of time in between automatic changes of the group key, which all devices on the network share. |
| Disable Inactivity Polling | off | on; default: off | Inactivity polling can be disabled to disconnect stations based on inactivity timeout so that idle stations are more likely to be disconnected even if they are still in range of the AP. |
| Station inactivity limit | seconds; default: none | Station inactivity limit in seconds. If a station/client does not send anything in st time frame, an empty data frame is sent to it in order to verify whether it is still in range. If this frame is not acknowledged, the station will be disassociated and then deauthenticated. |
| Maximum allowed Listen Interval | positive integer; default: none | Association will be refused if a client/station attempts to associate with a listen interval greater than this value. |
| Disassociate On Low Acknowledgement | off | on; default: on | Allow AP mode to disconnect stations/clients based on low Acknowledgement condition. |
Client Mode
{{{name}}} can also work as a WiFi client. Configuring client mode is nearly identical to Access Point, except for the fact that most of the options are dictated by the WiFi Access Point that the router is connecting to. Changing them can result in an interrupted connection to that router.
To begin configuring WiFi Client first click the 'Scan' button to scan the surrounding area and attempt to connect to a new wireless access point.
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wireless_scan_button_wifi_{{{wifi}}}.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
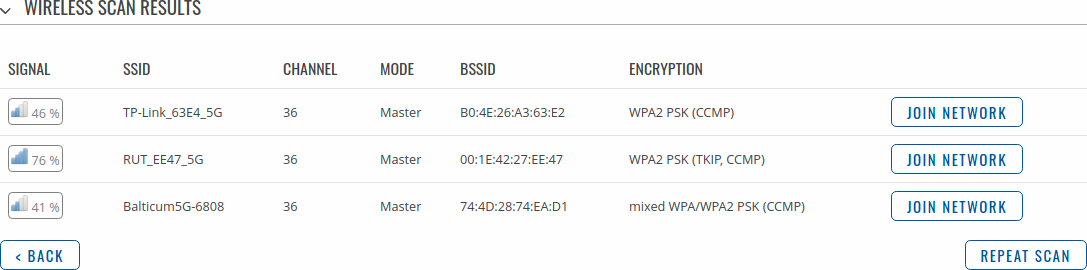
After which you will be redirected to the window shown below, where you will see list of available WiFi Access Points in the area. Choose one according to your liking and press the Join Network button next to it.
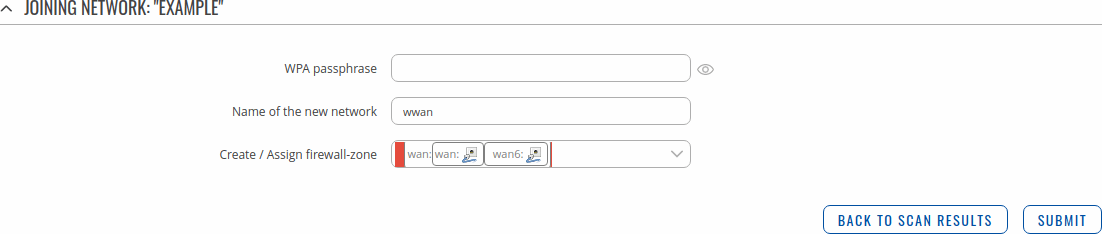
You again will be redirected to following window, where you will need to enter WPA passphrase or other security password depending on AP that you are connecting to, name yours network (it will be name of your wireless WAN interface) and assign firewall rule.
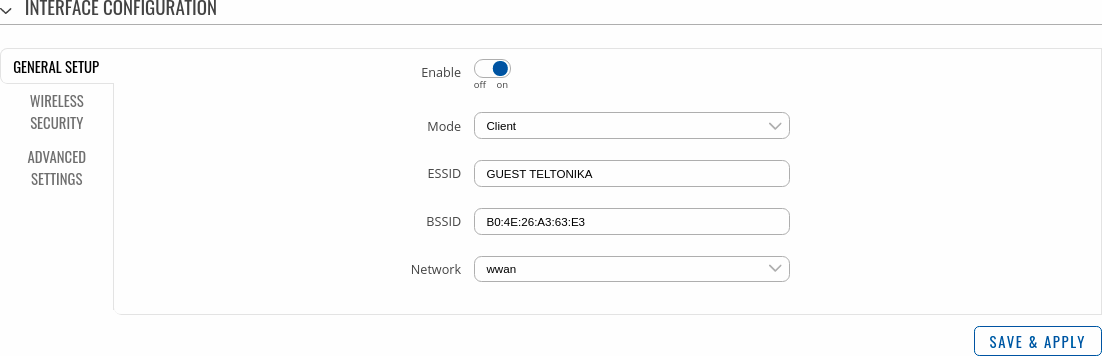
Next window that opens will be Device Configuration. Values there, mostly, should be left unchanged to avoid connection problems, because they are dictated by Access Point. Other than that, only difference from Access Point settings are in Interface Configuration → General Setup section, where Mode is set to Client, and Network attached to this wireless interface is WAN instead of LAN
Click Save & Apply and if you configured correctly, you will have Wireless Client working.
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]