RUT240 Routes (legacy WebUI): Difference between revisions
Gytispieze (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{Template: Networking_rut_manual_routes <!------------------------DEVICE-----------------------> | name = RUT240 | series = RUT2XX }}") |
Gytispieze (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template: | {{Template: Networking_rut_manual_routes_legacy | ||
<!------------------------DEVICE-----------------------> | <!------------------------DEVICE-----------------------> | ||
| name = RUT240 | | name = RUT240 | ||
| series = RUT2XX | | series = RUT2XX | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 07:51, 10 August 2021
Main Page > EOL Products > RUT240 > RUT240 Manual > RUT240 Legacy WebUI > RUT240 Status section (legacy) > RUT240 Routes (legacy WebUI)The information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version RUT2XX_R_00.01.14.7.
Note: this user manual page is for RUT240's old WebUI style available in earlier FW versions. Click here for information based on the latest FW version.
Summary
The Routes page displays the ARP table and active IPv4/IPv6 routes.
This chapter of the user manual provides an overview of the Routes page for RUT240 devices.
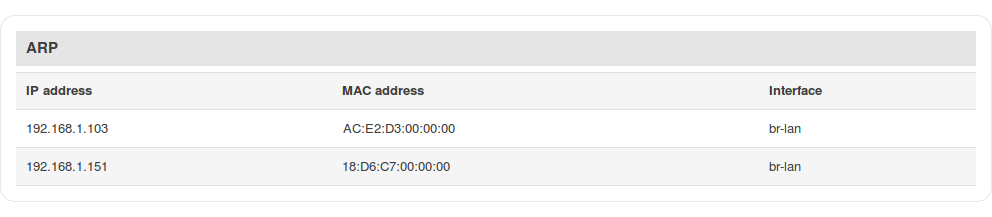
ARP
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a communication protocol used for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP address) to a physical machine's link layer address (MAC address) belonging to the local network.
The ARP section displays the router's ARP cache (also known as ARP table) data. The ARP cache contains information on each known MAC address and its corresponding IP address. When the router receives a packet destined for a local host, the ARP program attempts to find a physical host or MAC address in the ARP cache that matches the IP address. If the ARP cache doesn't contain the needed IP address, ARP broadcasts a request packet to all LAN machines in order to find the device with the IP address in question.
The figure below is an example of the ARP cache section:
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IP address | ip; default: none | IP address of a local host. |
| MAC address | mac; default: none | MAC address of a local host. |
| Interface | string; default: none | Interface through which the router is associated with the host. |
You can also view the ARP cache via shell using the arp or ip neigh commands, depending on which output your prefer:
root@Teltonika-RUT240:~# arp IP address HW type Flags HW address Mask Device 192.168.1.103 0x1 0x2 ac:e2:d3:00:00:00 * br-lan 192.168.1.151 0x1 0x2 18:d6:c7:00:00:00 * br-lan
root@Teltonika-RUT240:~# ip neigh 192.168.1.103 dev br-lan lladdr ac:e2:d3:00:00:00 REACHABLE 192.168.1.151 dev br-lan lladdr 18:d6:c7:00:00:00 REACHABLE
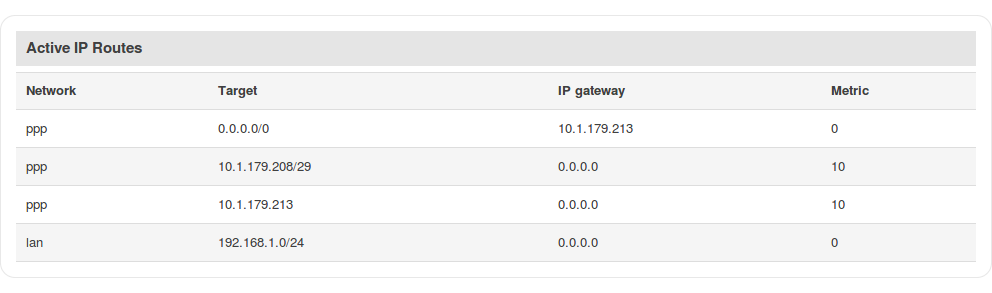
Active IP routes
The Active IP routes section displays the router's routing table. A routing table contains a list of routes to network destinations associated with and known by the router.
The figure below is an example of the Active IP routes section:
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Network | string; default: none | Associated network interface name. |
| Target | ip | ip/netmask; default: none | Destination network address. |
| IP gateway | ip; default: none | Indicates the IP address of the gateway through which the target network can be reached. |
| Metric | integer [0..4,294,967,295]; default: none | Metrics help the router choose the best route among multiple feasible routes to a destination. The route will go in the direction of the gateway with the lowest metric value. |
You can also view the routing table via shell using the route or ip route commands, depending on which output your prefer:
root@Teltonika-RUT240:~# route Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface default 10.1.179.213 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 wwan0 10.1.179.208 * 255.255.255.248 U 10 0 0 wwan0 10.1.179.213 * 255.255.255.255 UH 10 0 0 wwan0 192.168.1.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 br-lan
root@Teltonika-RUT240:~# ip route default via 10.1.179.213 dev wwan0 10.1.179.208/29 dev wwan0 proto static scope link metric 10 10.1.179.213 dev wwan0 proto static scope link src 10.1.179.212 metric 10 192.168.1.0/24 dev br-lan proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.1
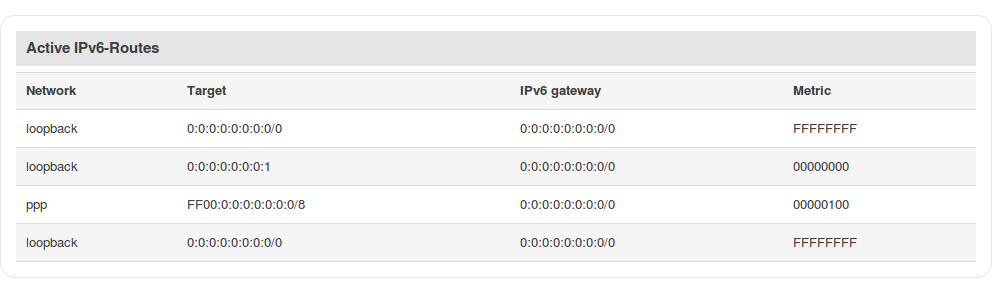
Active IPv6 routes
The Active IPv6 routes section displays the router's IPv6 routing table.
The figure below is an example of the Active IPv6 routes section:
| Field name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Network | string; default: none | Associated network interface name. |
| Target | ip6 | ip6/netmask; default: none | Destination network address. |
| IP gateway | ip6; default: none | Indicates the IPv6 address of the gateway through which the target network can be reached. |
| Metric | integer [0..4,294,967,295]; default: none | Metrics help the router choose the best route among multiple feasible routes to a destination. The route will go in the direction of the gateway with the lowest metric value. |
You can also view the routing table via shell using the route -A inet6 or ip -6 route show commands, depending on which output your prefer:
root@Teltonika-RUT240:~# ip -6 route fe80::/64 dev wwan0 proto kernel metric 256