TCR100 WAN: Difference between revisions
Created page with "{{Template: Networking_rutos_manual_wan <!------------------------DEVICE-----------------------> | name = TCR100 | series = TCR1 <!----------------------SEPARATORS----..." |
Gytispieze (talk | contribs) m Gytispieze moved page Draft:TCR100 WAN to TCR100 WAN |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 14:44, 18 November 2021
Main Page > TCR Routers > TCR100 > TCR100 Manual > TCR100 WebUI > TCR100 Network section > TCR100 WANThe information in this page is updated in accordance with firmware version TCR1_R_00.07.14.4.
Summary
The WAN page is used to to set up WAN network interfaces, which are used to connect device with external networks.
This manual page provides an overview of the WAN windows in TCR100 devices.
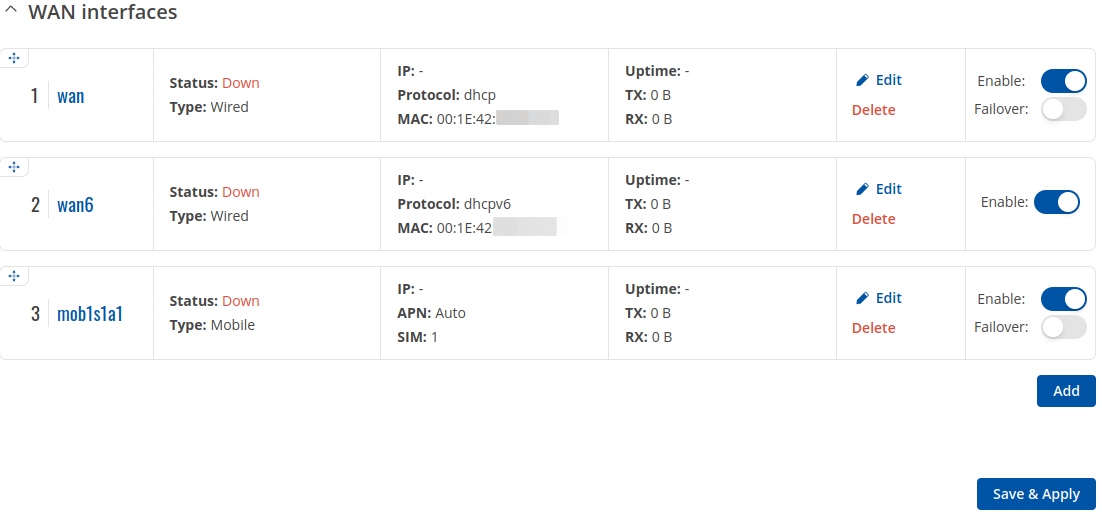
WAN
The WAN section displays WAN network interfaces currently existing on this device.
From here you can turn the interfaces, enable/disable interface's failover, create interfaces, change their priority* or enter an interface's configuration page.
* You can change the priority by dragging and dropping an interface to another position. Moving an interface changes its metric value in the configuration file. Interfaces that are higher on the list have greater priority.
If you hover mouse over the information mark ![]() global IPv6 addresses and IPv6 prefix delegation will be displayed.
global IPv6 addresses and IPv6 prefix delegation will be displayed.
Interface configuration
This section provides information on network interface configuration. There are {{{no_of_if}}} main types of interfaces on the device:
- Ethernet WAN
- Mobile WAN
Different types of interfaces can be configured under different protocols:
| Static | DHCP | DHCPv6 | PPPoE | Mobile | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethernet WAN | |||||
| Mobile WAN |
To begin configuring an interface, click the 'Edit' button on the right side of the interface:
General Setup
The General Setup section is used to configure the protocol of an interface and all the different parameters that go along with each protocol. If None protocol is chosen, all other interface settings will be ignored. The following sections are different for each protocol.
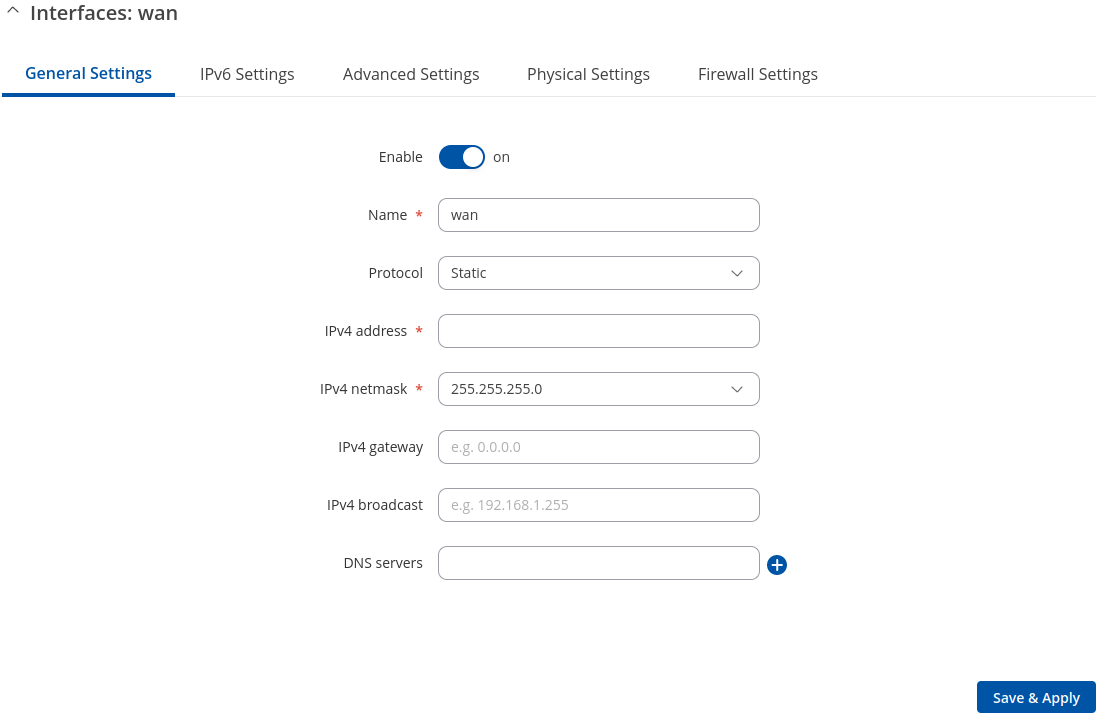
General Settings: Static
The static protocol uses a predefined manual configuration instead of obtaining parameters automatically via a DHCP lease.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | on | off; default: on | Enable interface. |
| IPv4 address | ip4; default: none | The IPv4 address interface of this interface. An IP address identifies a device on a network and allows it to communicate with other devices. |
| IPv4 netmask | netmask; default: 255.255.255.0 | The IPv4 netmask of this interface. A netmask is used to define how "large" a network is by specifying which part of the IP address denotes the network and which part denotes a device. |
| IPv4 gateway | ip4; default: none | The IPv4 gateway address used by this interface. An interface's default gateway is the default address through which all outgoing traffic is directed. |
| IPv4 broadcast | ip4; default: none | The IPv4 broadcast address used by this interface. IP broadcasts are used by BOOTP and DHCP clients to find and send requests to their respective servers. |
| DNS servers | ip4; default: none | DNS server addresses that this interface will use. If left empty, DNS servers are assigned automatically. To see what DNS servers are currently used, you can check the contents of the /tmp/resolv.conf.auto file. |
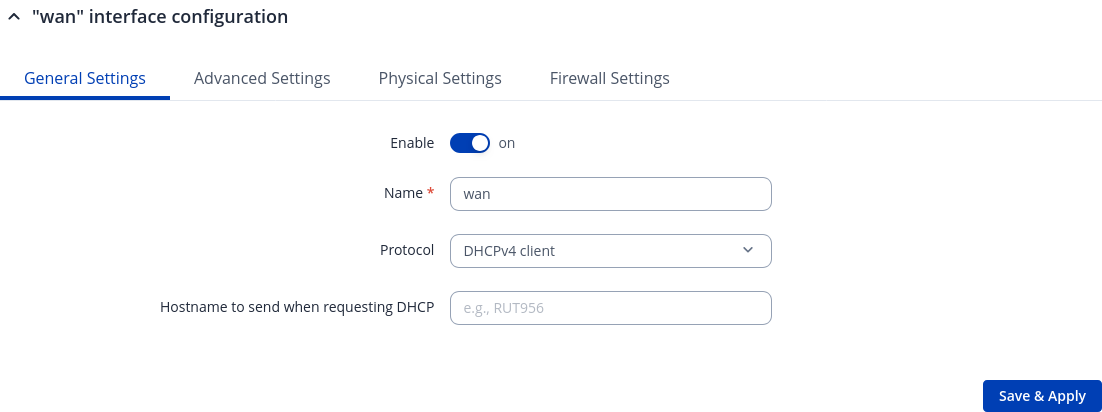
General Settings: DHCPv4
The DHCPv4 protocol is used to set up an interface which obtains its configuration parameters automatically via a DHCP lease.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | on | off; default: on | Enable interface. |
| Hostname to send when requesting DHCP | string; default: none | A hostname for this interface used to identify this machine on the DHCP server. |
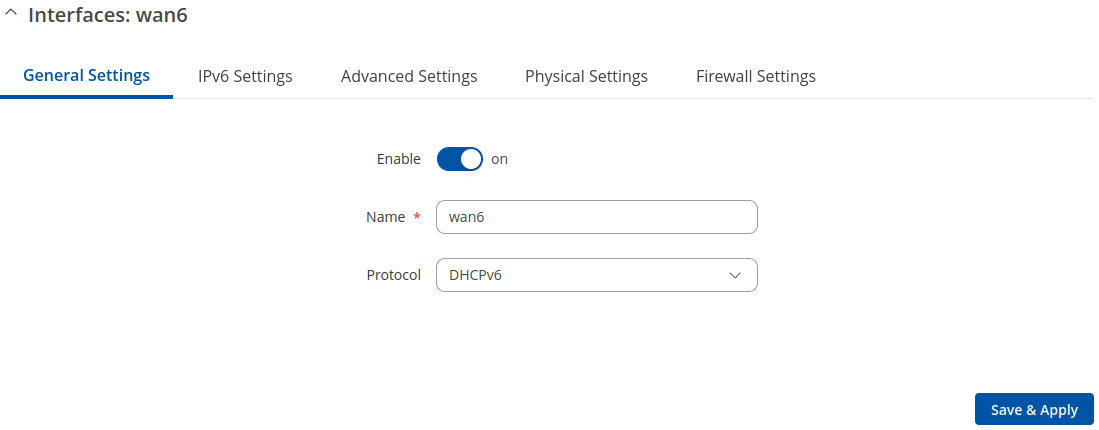
General Settings: DHCPv6
The DHCPv6 protocol is used to set up an IPv6 interface which obtains its configuration parameters automatically via a DHCP lease.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | on | off; default: on | Enable interface. |
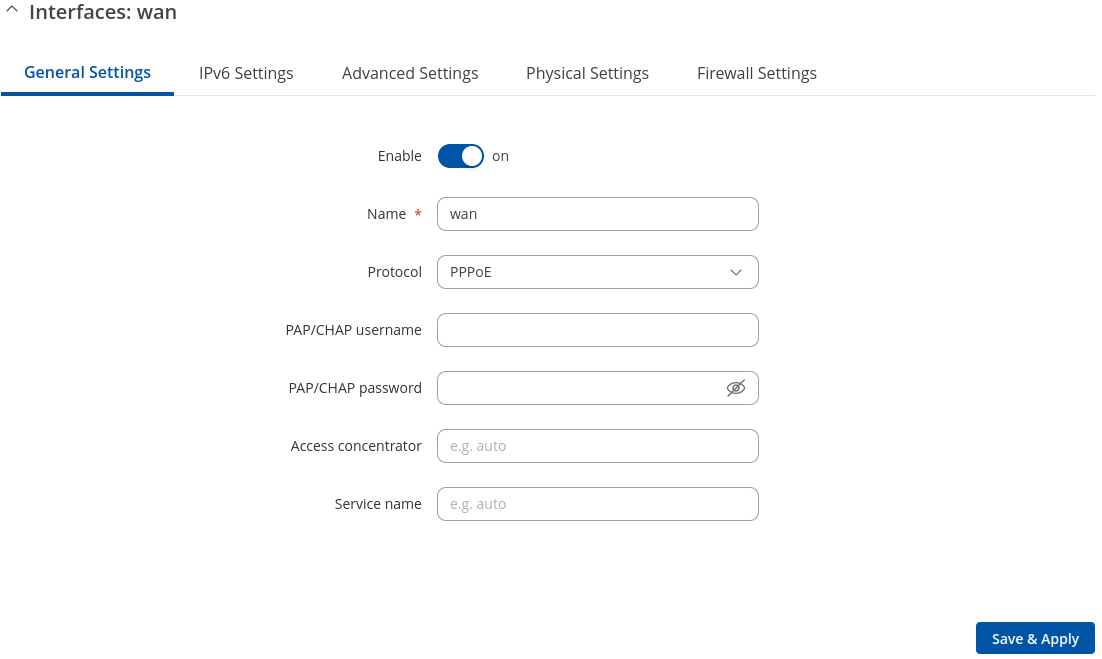
General Settings: PPPoE
The PPPoE protocol is used to set up a PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) connection over the Ethernet port.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable | on | off; default: on | Enable interface. |
| PAP/CHAP username | string; default: none | The username that you use to connect to your carrier’s network. |
| PAP/CHAP password | string; default: none | The password that you use to connect to your carrier’s network. |
| Access Concentrator | string; default: none | The Access Concentrator to connect to. ISPs used Access Concentrators to route their PPPoE connections. Usually, the settings are received automatically, however in some cases it is required to specify the name for an Access Concentrator. Leave empty to detect Access Concentrators automatically. |
| Service name | string; default: none | The Service Name to connect to. Leave empty to detect Service name automatically. |
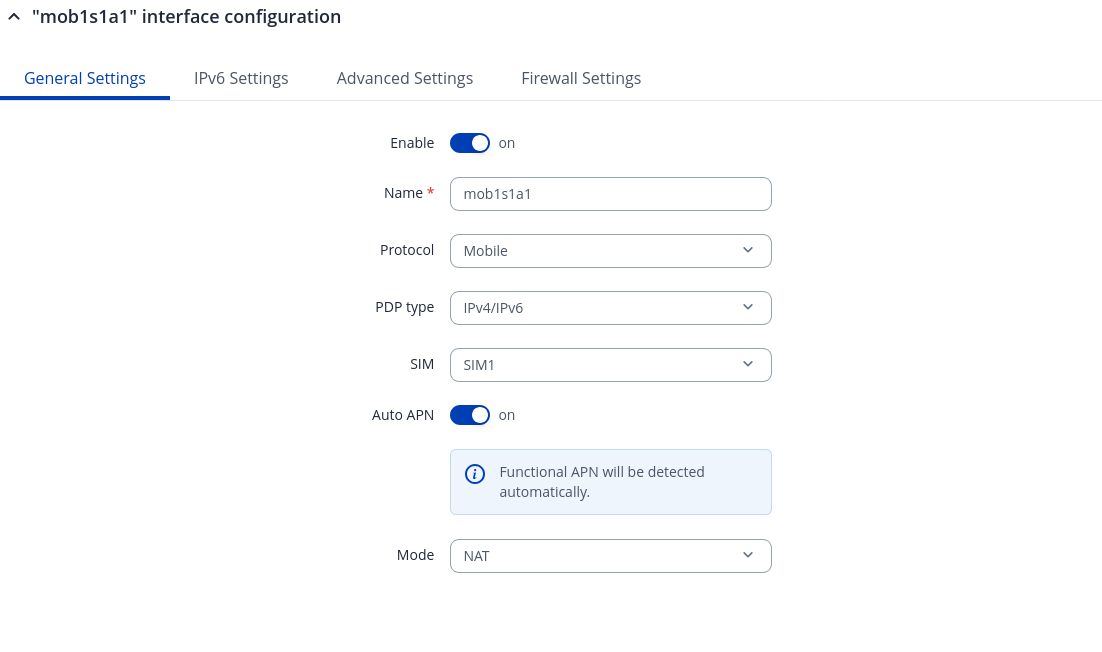
General Settings: Mobile
The Mobile protocol is used to set up an interface which can establish a mobile WAN connection.
Mode: NAT
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PDP Type | IPv4 | IPv6 | IPv4/IPv6; default: IPv4/IPv6 | Specifies what of address will be requested from the operator. |
| Auto APN | off | on; default: on | The Auto APN feature scans an internal Android APN database and selects an APN based on the SIM card's operator and country. If the first automatically selected APN doesn't work, it attempts to use the next existing APN from the database. |
| APN / Custom APN | string; default: none | An Access Point Name (APN) is a gateway between a GSM, GPRS, 3G or 4G mobile network and another computer network. Depending on the contract, some operators may require you to use an APN just to complete the registration on a network. In other cases, APN is used to get special parameters from the operator (e.g., a public IP address) depending on the contract. An APN Network Identifier cannot start with any of the following strings:
|
| Authentication Type | NONE | PAP | CHAP; default: NONE | Authentication method that your GSM carrier uses to authenticate new connections on its network. If you select PAP or CHAP, you will also be required to enter a username and password. |
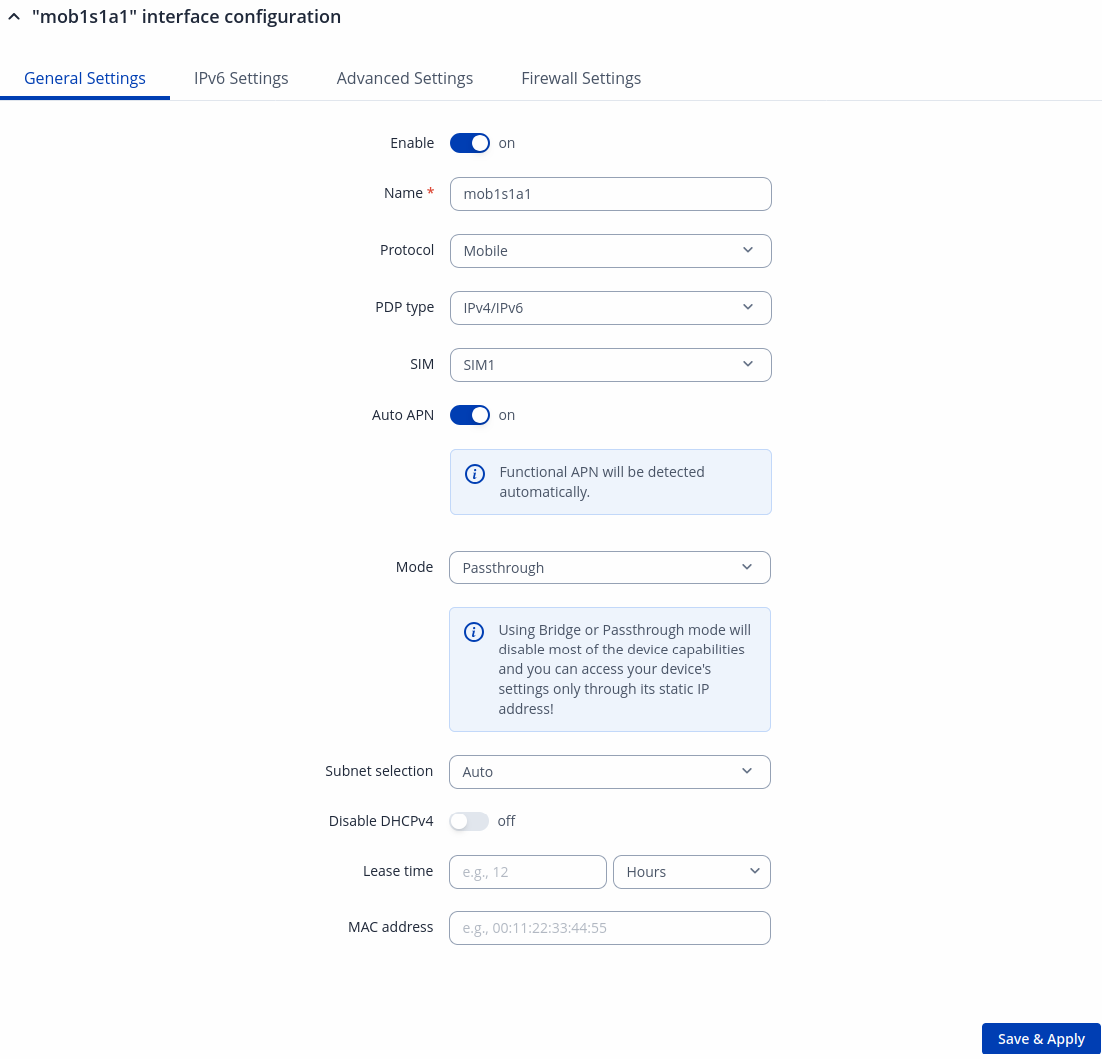
| Mode | NAT | Bridge | Passthrough; default: NAT | Mobile connection operating mode.
|
Mode: Passthrough
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PDP Type | IPv4 | IPv6 | IPv4/IPv6; default: IPv4 | Specifies what of address will be requested from the operator. |
| Auto APN | off | on; default: on | The Auto APN feature scans an internal Android APN database and selects an APN based on the SIM card's operator and country. If the first automatically selected APN doesn't work, it attempts to use the next existing APN from the database. |
| APN / Custom APN | string; default: none | An Access Point Name (APN) is a gateway between a GSM, GPRS, 3G or 4G mobile network and another computer network. Depending on the contract, some operators may require you to use an APN just to complete the registration on a network. In other cases, APN is used to get special parameters from the operator (e.g., a public IP address) depending on the contract. An APN Network Identifier cannot start with any of the following strings:
|
| Authentication Type | NONE | PAP | CHAP; default: NONE | Authentication method that your GSM carrier uses to authenticate new connections on its network. If you select PAP or CHAP, you will also be required to enter a username and password. |
| Mode | NAT | Bridge | Passthrough; default: Passthrough | Mobile connection operating mode.
|
| Subnet selection | Auto | P2P; default: Auto | Subnet selection method. |
| Disable DHCPv4 | on | off; default: off | When disabled, only a single IPv4 address from the mobile provider will be leased. Otherwise, multiple IPv4 addresses will be leased and routed via NAT. |
| Lease Time | integer; default: 1 | Expiry time of leased address. The minimum value for hours is 1, the minimum value for minutes is 2 and the minimum value for seconds is 120 |
| Units | Hours | Minutes | Second; default: Hours | Specifies the time measurement unit |
| MAC Address | mac; default: none | Specifies the MAC address of the device that will receive the mobile interface's IP address in Bridge or Passthrough mode. Note: this field only becomes visible when using Bridge or Passthrough mode. |
Mode: Bridge
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PDP Type | IPv4 | IPv6 | IPv4/IPv6; default: IPv4 | Specifies what of address will be requested from the operator. |
| Auto APN | off | on; default: on | The Auto APN feature scans an internal Android APN database and selects an APN based on the SIM card's operator and country. If the first automatically selected APN doesn't work, it attempts to use the next existing APN from the database. |
| APN / Custom APN | string; default: none | An Access Point Name (APN) is a gateway between a GSM, GPRS, 3G or 4G mobile network and another computer network. Depending on the contract, some operators may require you to use an APN just to complete the registration on a network. In other cases, APN is used to get special parameters from the operator (e.g., a public IP address) depending on the contract. An APN Network Identifier cannot start with any of the following strings:
|
| Authentication Type | NONE | PAP | CHAP; default: NONE | Authentication method that your GSM carrier uses to authenticate new connections on its network. If you select PAP or CHAP, you will also be required to enter a username and password. |
| Mode | NAT | Bridge | Passthrough; default: Bridge | Mobile connection operating mode.
|
| Subnet selection | Auto | P2P; default: Auto | Subnet selection method. |
| MAC Address | mac; default: none | Specifies the MAC address of the device that will receive the mobile interface's IP address in Bridge or Passthrough mode. Note: this field only becomes visible when using Bridge or Passthrough mode. |
| Local DHCPv4 leases | off | on; default: on | Provides local DHCPv4 leases until a mobile connection is established or a mobile IP address is leased. |
Multi-APN
TCR100 supports Multiple PDN feature in order to establish connections to multiple mobile networks using a single SIM card. You can find a configuration example here.
IPv6 Settings
The IPv6 Settings section is used to set up some of the more specific and less frequently used interface parameters. This section is different for each protocol.
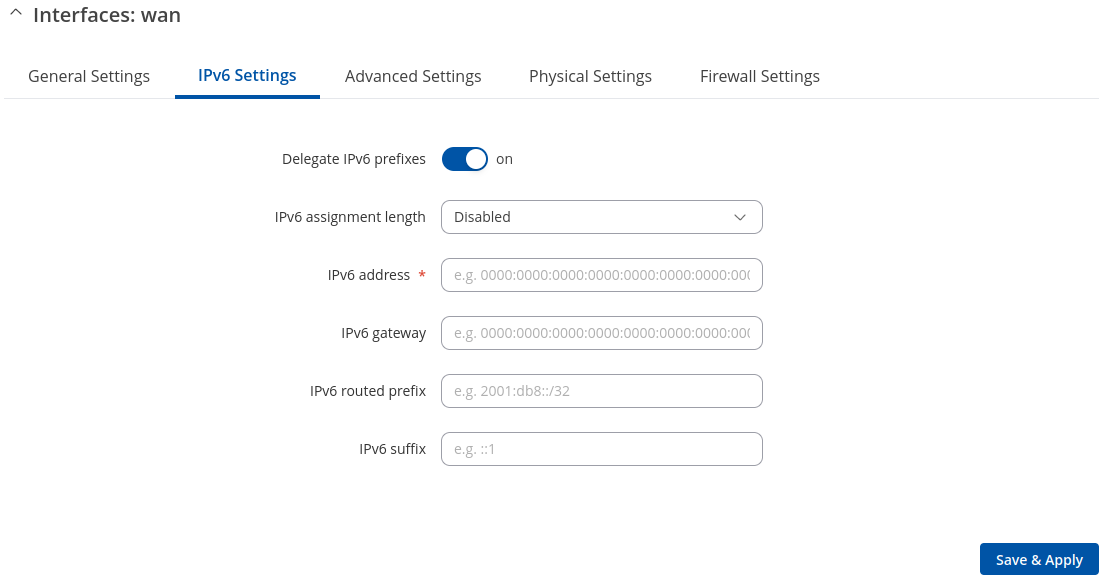
IPv6 Settings: Static
Advanced Settings information for Static protocol is provided in the table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Delegate IPv6 prefixes | off | on; default: on | Enable downstream delegation of IPv6 prefixes available on this interface. |
| IPv6 assignment length | Disabled | 64 | Custom; default: Disabled | A metric specifies the priority of the gateway. The lower the metric, the higher the priority (0 for highest priority). |
| IPv6 address | IPv6 addresses with or without mask prefix are accepted; default: none | Assigns an IPv6 address for this interface. CIDR notation: address/prefix. |
| IPv6 gateway | IPv6 addresses are accepted. E.g. ::0000:8a2e:0370:7334; default: none | IPv6 default gateway. |
| IPv6 routed prefix | IPv6 addresses with mask prefix are accepted E.g ::1/128; default: none | Public prefix routed to this device for distribution to clients. |
| IPv6 suffix | Allowed values: "eui64", "random", fixed value like "::1" or "::1:2"; default: none | Optional. Allowed values: 'eui64', 'random', fixed value like '::1' or '::1:2'. When IPv6 prefix (like 'a:b:c:d::') is received from a delegating server, use the suffix (like '::1') to form the IPv6 address ('a:b:c:d::1') for the interface. |
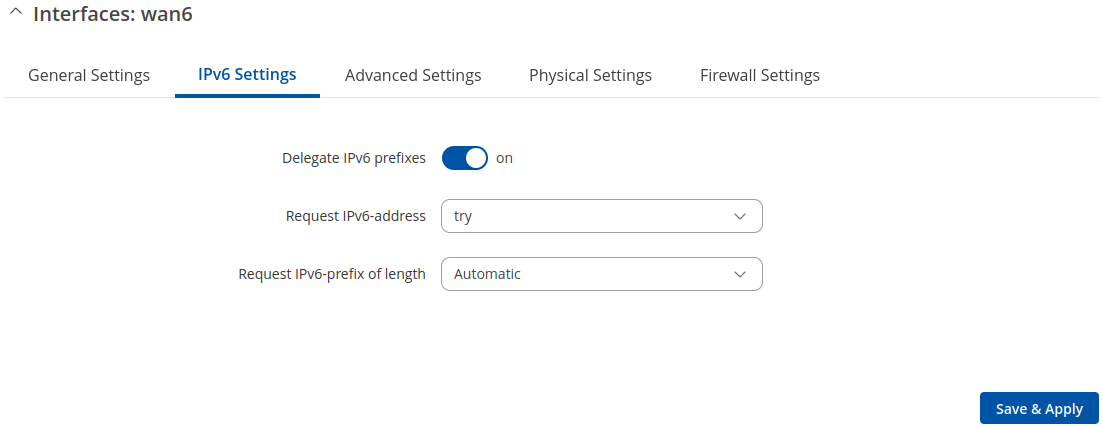
IPv6 Settings: DHCPv6
Advanced Settings information for DHCPv6 protocol is provided in the table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Delegate IPv6 prefixes | off | on; default: on | Enable downstream delegation of IPv6 prefixes available on this interface. |
| Request IPv6-address | try | force | disabled; default: try | Defines the behaviour for requesting an address. |
| Request IPv6-prefix of length | integer [0..64] | Automatic | disabled ; default: Automatic | Defines how this will request a IPv6 ULA-Prefix length. If set to 'disabled' the interface will obtain a single IPv6 address without a subnet for routing. |
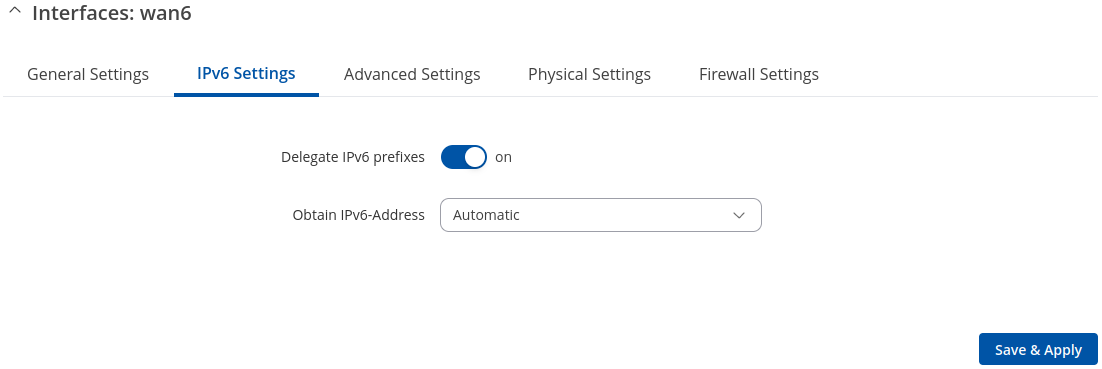
IPv6 Settings: PPPoE
Advanced Settings information for PPPoE protocol is provided in the table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Delegate IPv6 prefixes | off | on; default: on | Enable downstream delegation of IPv6 prefixes available on this interface. |
| Obtain IPv6 address | Automatic | Disabled | Manual; default: Automatic | Defines behaviour for obtaining an IPv6 address. |
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings section is used to set up some of the more specific and less frequently used interface parameters. This section is different for each protocol.
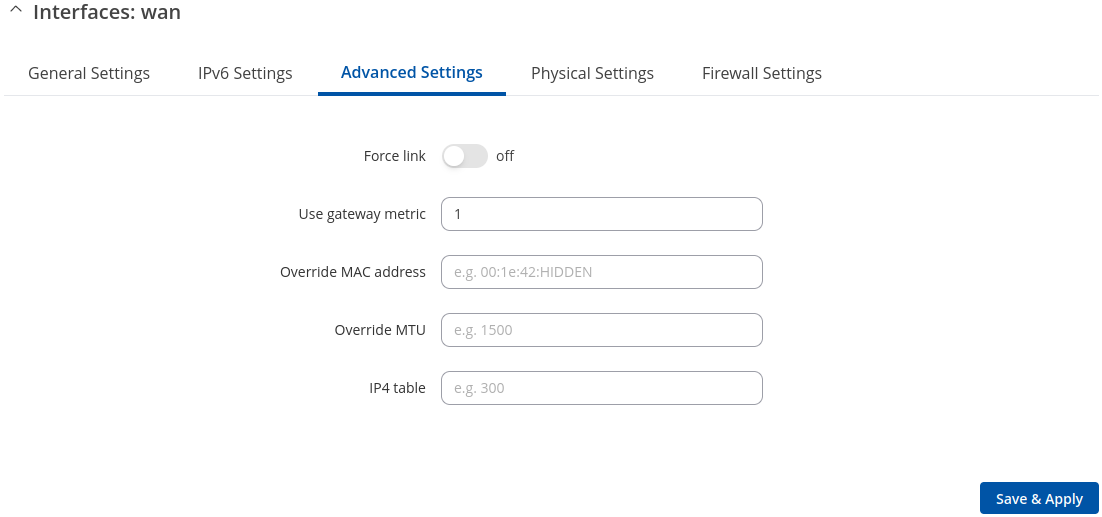
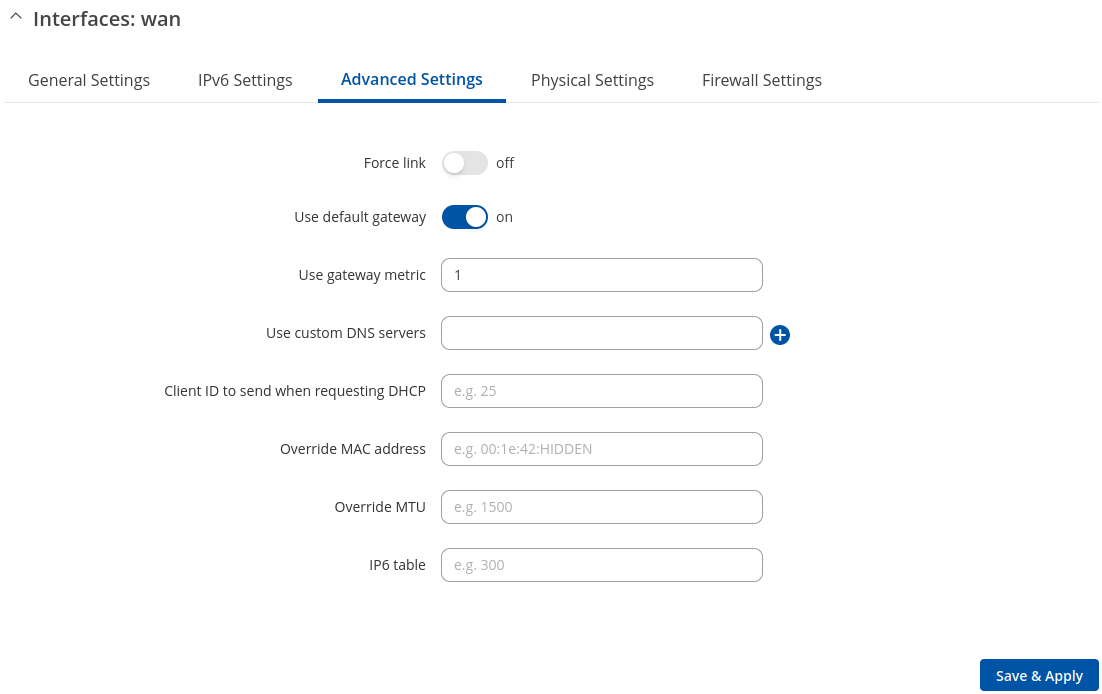
Advanced Settings: Static
Advanced Settings information for Static protocol is provided in the table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Force link | off | on; default: on | Specifies whether interface settings (IP, route, gateway) are assigned to the interface regardless of the link being active or only after the link has become active. |
| Use gateway metric | integer [0..4294967295]; default: 3 | A metric specifies the priority of the gateway. The lower the metric, the higher the priority (0 for highest priority). |
| Override MAC address | mac; default: none | When set, uses a user-defined MAC address for the interface instead of the default one. |
| Override MTU | integer [1..9200]; default: none | Changes the interface's allowed maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction.
|
| IP4 table | integer [0..99999999]; default: none | ID of the routing table in Routing tables page. |
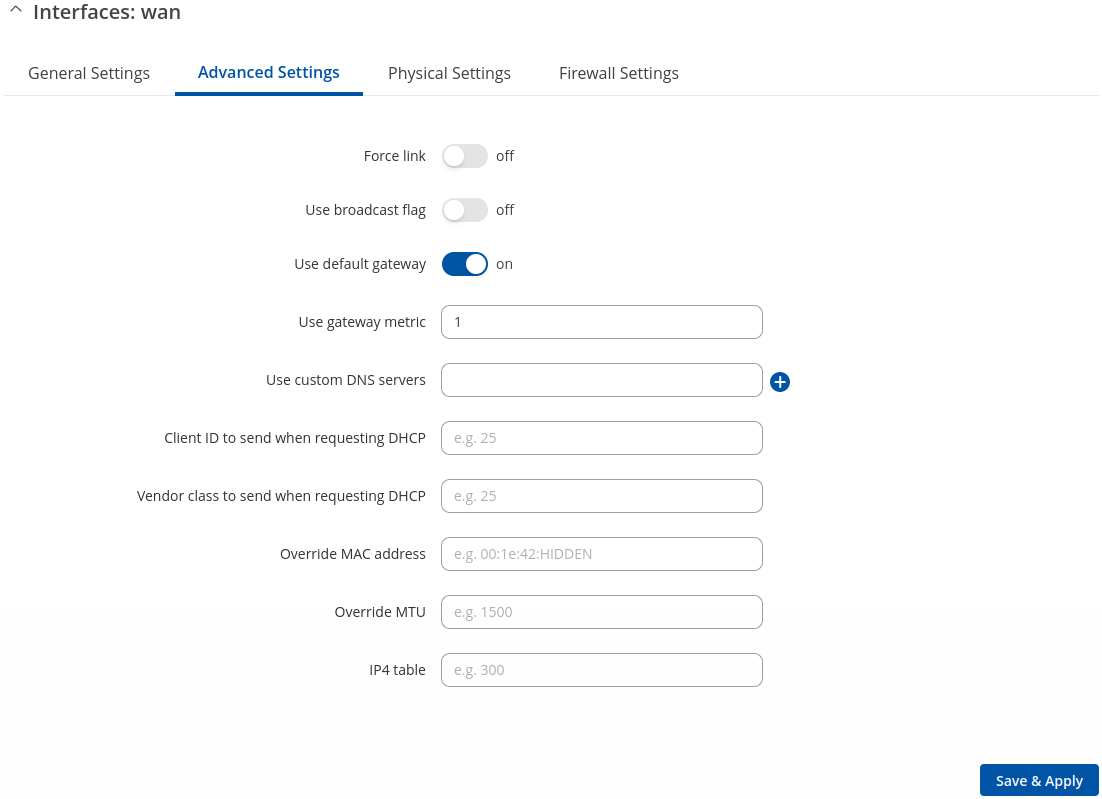
Advanced Settings: DHCP
Advanced Settings information for DHCP protocol is provided in the table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Force link | off | on; default: off | Specifies whether interface settings (IP, route, gateway) are assigned to the interface regardless of the link being active or only after the link has become active. |
| Use broadcast flag | off | on; default: off | Required for certain ISPs. For example, Charter with DOCSIS 3. |
| Use default gateway | off | on; default: on | When checked, creates a default route for the interface. |
| Use gateway metric | integer[0..4294967295]; default: none | A metric specifies the priority of the gateway. The lower the metric, the higher the priority (0 for highest priority). |
| Use custom DNS servers | ip4; default: none | Specifies custom DNS servers. If left empty, DNS servers advertised by peer are used. |
| Client ID to send when requesting DHCP | string; default: none | Client ID which will be sent when requesting a DHCP lease. |
| Vendor Class to send when requesting DHCP | string; default: none | Vendor class which will be sent when requesting a DHCP lease. |
| Override MAC address | mac; default: none | When set, uses a user-defined MAC address for the interface instead of the default one. |
| Override MTU | integer [1..9200]; default: none | Changes the interfaces allowed maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction.
|
| IP4 table | integer [0..99999999]; default: none | ID of the routing table in Routing tables page. |
Advanced Settings: DHCPv6
Advanced Settings information for DHCPv6 protocol is provided in the table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Force link | off | on; default: off | Specifies whether interface settings (IP, route, gateway) are assigned to the interface regardless of the link being active or only after the link has become active. |
| Use default gateway | off | on; default: on | When checked, creates a default route for the interface. |
| Use gateway metric | integer[0..4294967295]; default: 2 | The configuration by default generates a routing table entry. In this field you can alter the metric of that entry. Lower metric means higher priority. |
| Use custom DNS servers | ip4; default: none | Specifies custom DNS servers. If left empty, DNS servers advertised by peer are used. |
| Client ID to send when requesting DHCP | string; default: none | Client ID which will be sent when requesting a DHCP lease. |
| Override MAC address | mac; default: none | When set, uses a user-defined MAC address for the interface instead of the default one. |
| Override MTU | integer [1..9200]; default: none | Changes the interface's allowed maximum transmission unit (MTU) size. It is the largest size of a protocol data unit (PDU) that can be transmitted in a single network layer transaction.
|
| IP6 table | integer [0..2^46]; default: none | ID of the routing table in Routing tables page. |
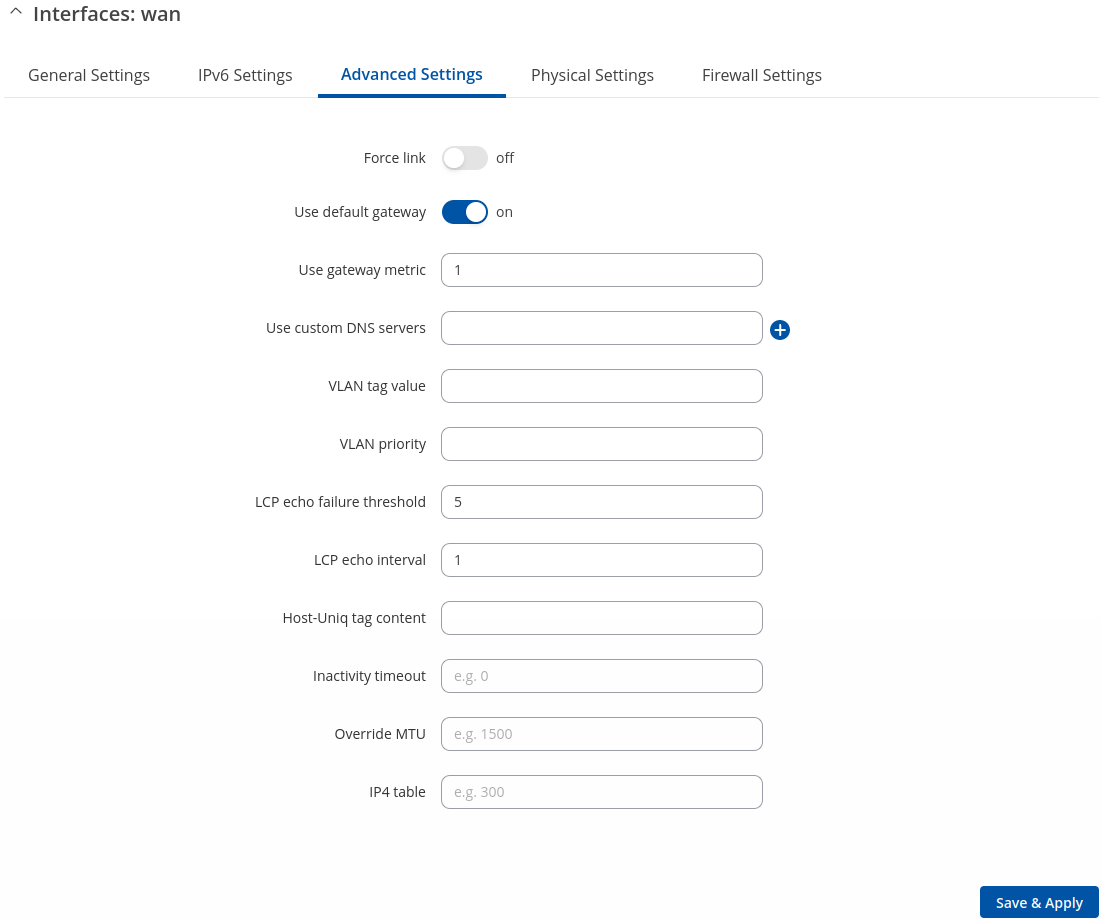
Advanced Settings: PPPoE
Advanced Settings information for PPPoE protocol is provided in the table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Force link | off | on; default: off | Specifies whether interface settings (IP, route, gateway) are assigned to the interface regardless of the link being active or only after the link has become active. |
| Use default gateway | off | on; default: on | When checked, creates a default route for the interface. |
| Use gateway metric | integer[0..4294967295]; default: none | A metric specifies the priority of the gateway. The lower the metric, the higher the priority (0 for highest priority). |
| Use custom DNS servers | ip4; default: none | Specifies custom DNS servers. If left empty, DNS servers advertised by peer are used. |
| VLAN tag value | integer [0..7]; default: none | VLAN tag value. |
| VLAN priority | integer [0..4095]; default: none | VLAN priority. |
| LCP echo failure threshold | integer; default: none | Presumes peer to be dead after given amount of LCP echo failures. Leave it at 0 to ignore failures. |
| LCP echo interval | integer; default: none | Sends LCP echo requests at the given interval in seconds. This function is only effective in conjunction with failure threshold. |
| Host-Uniq tag content | raw hex-encoded bytes; default: none | Leave empty unless your ISP require this. |
| Inactivity timeout | mac; default: none | Close inactive connection after the given amount of seconds. Leave it at 0 to persist connection. |
| Override MTU | integer [1..1500]; default: none | Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) – specifies the largest possible size of a data packet. |
| IP4 table | integer [0..99999999]; default: none | ID of the routing table in Routing tables page. |
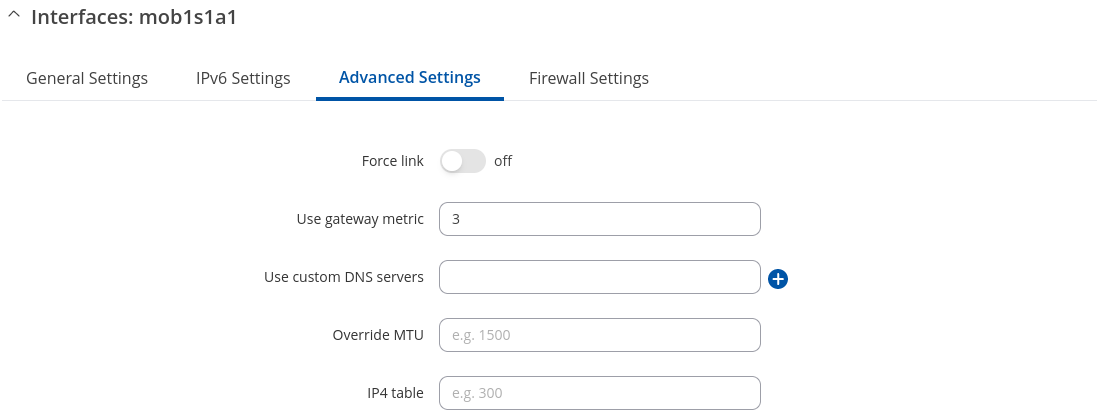
Advanced Settings: Mobile
Advanced Settings information for Mobile protocol is provided in the table below.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Force link | off | on; default: off | Specifies whether interface settings (IP, route, gateway) are assigned to the interface regardless of the link being active or only after the link has become active. |
| Use gateway metric | integer[0..4294967295]; default: none | A metric specifies the priority of the gateway. The lower the metric, the higher the priority (0 for highest priority). |
| Use custom DNS servers | ip4; default: none | Specifies custom DNS servers. If left empty, DNS servers advertised by peer are used. |
| Override MTU | integer [98..65535]; default: none | Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) – specifies the largest possible size of a data packet. If Override MTU field will be left – empty dynamic MTU will be used. |
| IP4 table | integer [0..99999999]; default: none | ID of the routing table in Routing tables page. |
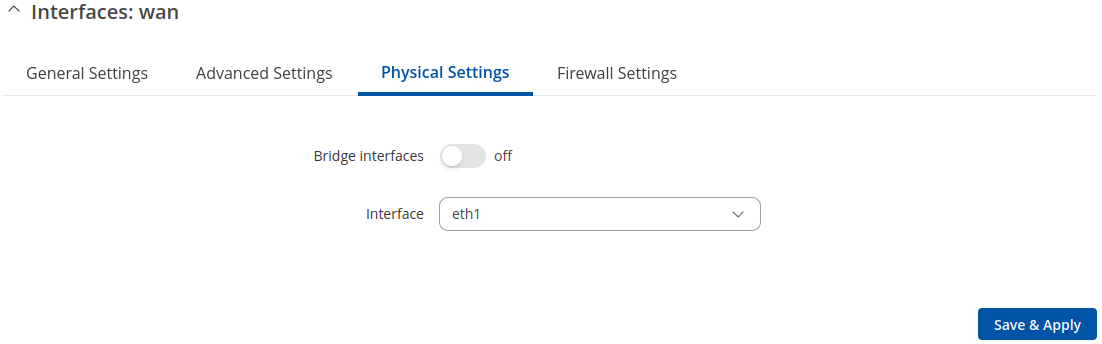
Physical Settings
The Physical Settings section is used to create associations with physical interfaces and bridge network interfaces.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Bridge interfaces | off | on; default: off | Bridges physical interfaces specified in this configuration. |
| Interface | network interface(s); default: wan physical interface | Ties this network interface to physical device interfaces such as Ethernet. |
Firewall Settings
The Firewall Settings section is used to specify to which firewall zone if any this interface belongs. Assigning an interface to a zone may provide easier configuration of firewall rules. For example, instead of configuring separate rules for each WAN interface, you can add all WAN interfaces into a single firewall zone and make the rule apply to that zone instead.
More firewall zone settings can be configured from the Network → Firewall → General Settings → Zones section.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Create / Assign firewall-zone | firewall zone; default: none | Assigns this interface to the specified firewall zone. |