Template:Networking rutos manual wan: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td>Hostname to send when requesting DHCP</td> | ||
<td> | <td>string; default: <b>none</b></td> | ||
<td> | <td>A hostname for this interface used to identify this machine on the DHCP server.</td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table>|}} | |||
====Static: DHCP Server==== | ====Static: DHCP Server==== | ||
Revision as of 10:45, 24 November 2022
Template:Networking rutos manual fw disclosure
Summary
The WAN page is used to to set up WAN network interfaces, which are used to connect device with external networks.
This manual page provides an overview of the WAN windows in {{{name}}} devices.
WAN
The WAN section displays WAN network interfaces currently existing on this device.
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wan_mobile_{{{mobile}}}_dualsim_{{{dualsim}}}_dualmodem_{{{dualmodem}}}_wired_{{{wired}}}_v2.png|border|class=tlt-border]]
From here you can turn the interfaces on or off, change their priority* or enter an interface's configuration page.
* You can change the priority by dragging and dropping an interface to another position. Moving an interface changes its metric value in the configuration file. Interfaces that are higher on the list have greater priority.
Interface configuration
This section provides information on WAN interface configuration. There is one type of WAN interface on the device:
To begin configuring an interface, click the 'Edit' button on the right side of the interface:
[[File:Networking_rutos_manual_wan_begin_to_edit_eth_{{{wired}}}_v2.png]]
Static: DHCP Server
A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server is a service that can automatically configure the TCP/IP settings of any device that requests such a service. If you connect a device that has been configured to obtain an IP address automatically, the DHCP server will lease out an IP address from the available IP pool and the device will be able to communicate within the private network.
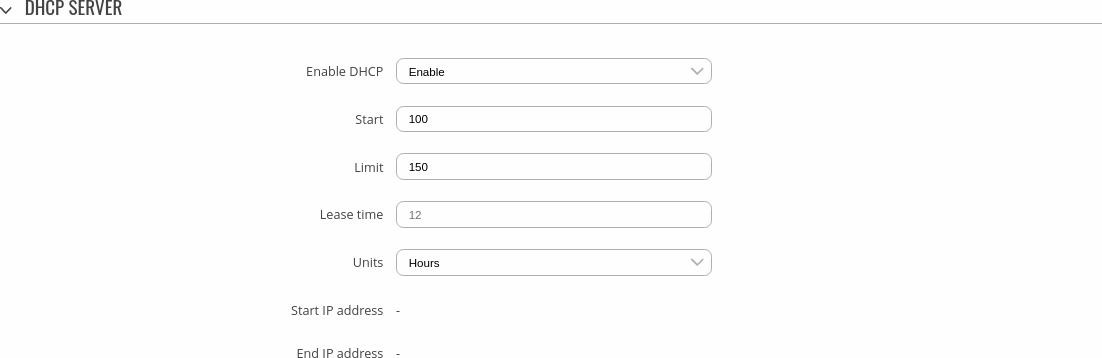
This section is used to set up the main operating parameters of the DHCP server.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Enable DHCP | Enable | Disable | DHCP Relay*; default: Enable | Turns the DHCP server on or off or enables DHCP relay*. If DHCP Relay* is selected, you will be prompted to enter an IP address of another DHCP server in your LAN. In this case, whenever a new machine connects to this device, it will redirect any DHCP requests to the specified DHCP Server. |
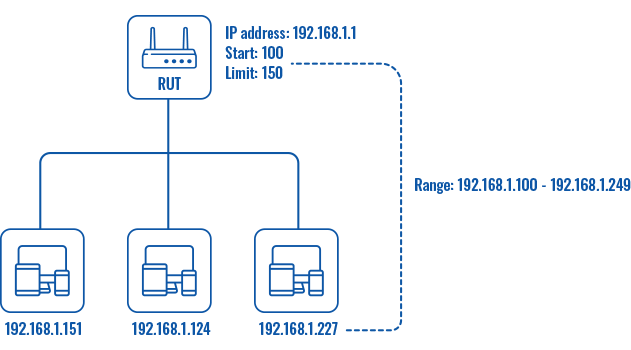
| Start | integer [1..255]; default: 100 | The starting IP address value. e.g., if your device’s LAN IP is 192.168.1.1 and your subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 that means that in your network a valid IP address has to be in the range of [192.168.1.0..192.168.1.254] (192.168.1.255 is a special unavailable address). If the Start value is set to 100 then the DHCP server will only lease out addresses starting from 192.168.1.100. |
| Limit | integer [1..255]; default: 150 | How many addresses the DHCP server can lease out. Continuing from the example above: if the start address is 192.168.1.100 and the server can lease out 150 addresses, available addresses will be from 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.249 (100 + 150 – 1 = 249; this is because the first address is inclusive). |
| Lease time | integer [1..999999]; default: none integer [2..999999]* integer [120..999999]** |
A DHCP lease will expire after the amount of time specified in this field and the device that was using the lease will have to request a new one. However, if the device stays connected, its lease will be renewed after half of the specified amount of time passes (e.g., if lease time is 12 hours, then every 6 hours the device will ask the DHCP server to renew its lease). The minimal amount of time that can be specified is 2 minutes. *If selected Units is Minutes. **If selected Units is seconds. |
| Units | Hours | Minutes | Seconds; default: Hours | Lease time units. |
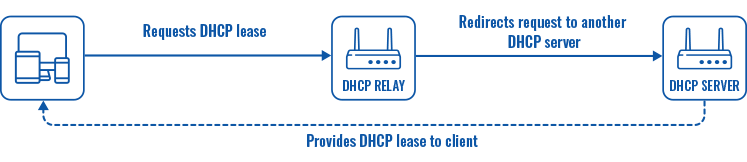
* When an interface is set to act as a DHCP Relay, it redirects all received DHCP request messages to another specified DHCP server:
DHCP
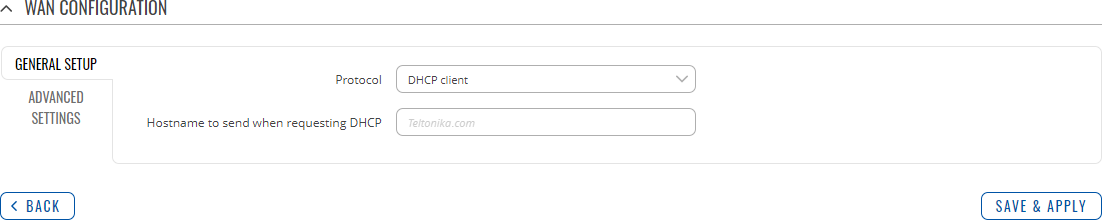
The DHCP client protocol is used to set up an interface which obtains its configuration parameters automatically via a DHCP lease.
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hostname to send when requesting DHCP | string; default: none | A hostname for this interface used to identify this machine on the DHCP server. |
|}}
[[Category:{{{name}}} Network section]]