IPSec configuration example with SCEP
Introduction
In computing, Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a secure network protocol suite of IPv4 that authenticates and encrypts the packets of data sent over an IPv4 network. IPsec includes protocols for establishing mutual authentication between agents at the beginning of the session and negotiation of cryptographic keys to use during the session. IPsec can protect data flows between a pair of hosts (host-to-host), between a pair of security gateways (network-to-network), or between a security gateway and a host (network-to-host). Internet Protocol security (IPsec) uses cryptographic security services to protect communications over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. IPsec supports network-level peer authentication, data origin authentication, data integrity, data confidentiality (encryption), and replay protection.
This article provides an extensive configuration example with details on how to create a tunnel connection authenticating with X.509 Certs with SCEP(Simple Certification Enrollment Protocol) between two IPsec instances, both of which are configured on RUTxxx routers.
Configuration overview and prerequisites
- Two RUTxxx routers of any type(After RUTX_R_00.07.10 FW)
- One RUTxxx router with public IP address;
- 1 SCEP Server Instance ( For this example Mikrotik Router is used)
- Both RUTxxx routers must be accessible from each other's WAN connections
- An end device (PC, Laptop) for configuration;
- (Optional) A second end device to test remote LAN access;
- Both devices needs to be in the same time zone
Router configuration
Choose SCEP(Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol) method for certificate enrollment from the System > Administration > Certificates section.
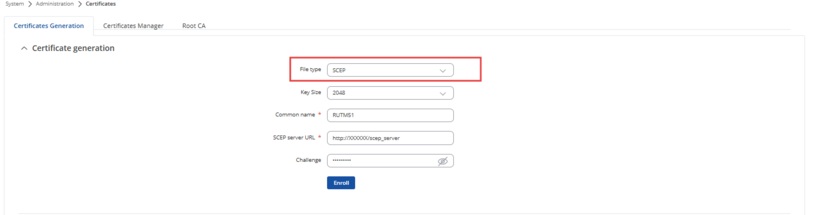
For this example Mikrotik Router is used as a SCEP server.
After the enrollment is triggered from the Teltonika Router the SCEP server also needs to grant an access.
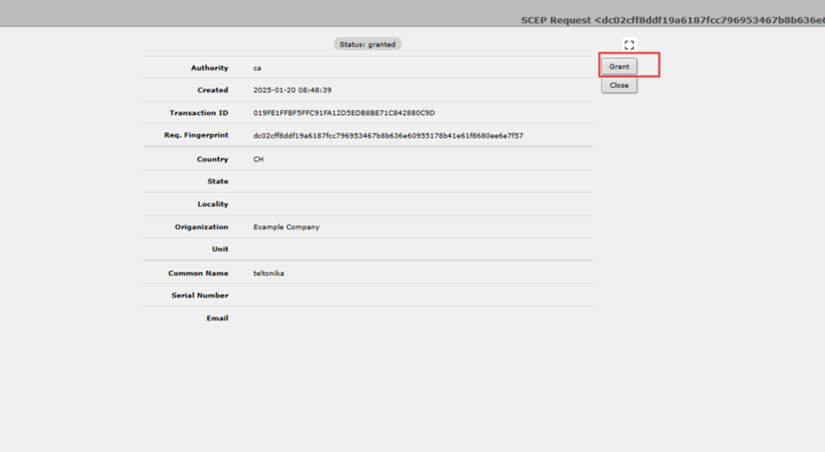
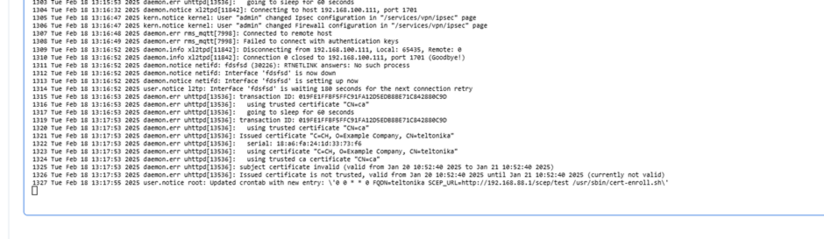
After the access is granted, certificate enrollment and connection establishment can be monitored in real time through the device’s CLI. Logs and status updates provide insights into each step, ensuring proper functionality and troubleshooting if needed.
After the certification enrollment process is finished, the certificates can be seen from the System > Administration > Certificates section.
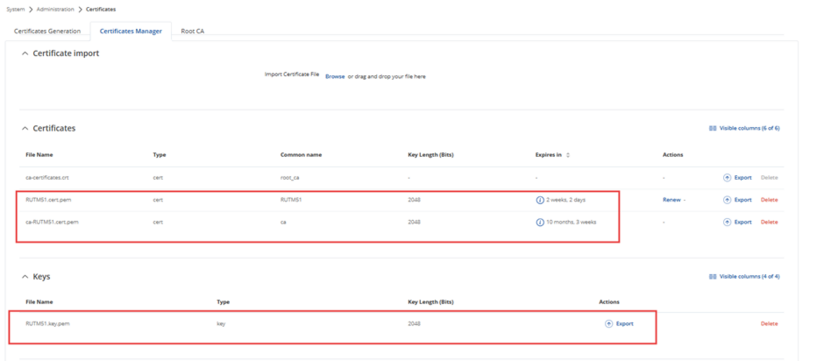
And then the certifications can be used to create the VPN. IPsec is used for this example.
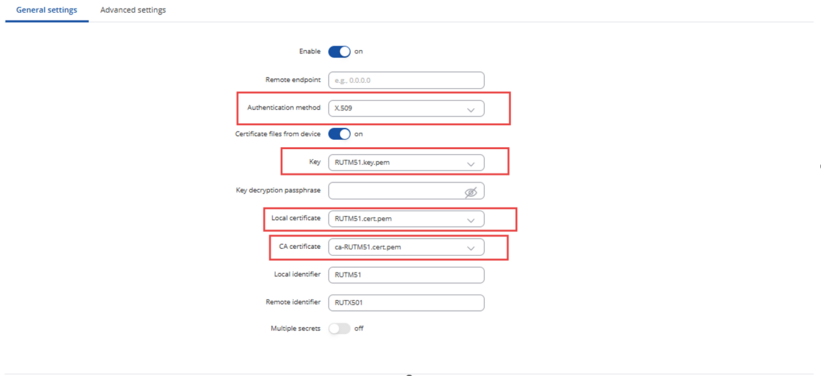
After completing the necessary configurations related to IPsec, you can test whether your tunnel is functioning successfully.
