SNMP configuration example
Summary
This chapter is a guide on configuring SNMP package to establish communication between devices.
SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) - is widely used in networking management for networking monitoring. SNMP uses MIB (Management Information Base) to organize management data in the form of variables, which describe the system configuration and status.
Trap
Traps are alert messages sent by SNMP agent to SNMP manager.
SNMP agent - Teltonika router. Device which sends Trap messages to the manager.
SNMP manager - device which listens for Trap messages from the agents.
Teltonika routers are able to send SNMP Trap messages to the manager on their own when they experience a problem or a situation described in the rules.
Preconditions
RUT9xx
To setup SNMP first make sure that SNMP package is installed, more information here RUT955 Packages and RUT950 Packages.
OID codes
OID code (Object identifier code) - is an address used to identify devices and their status.
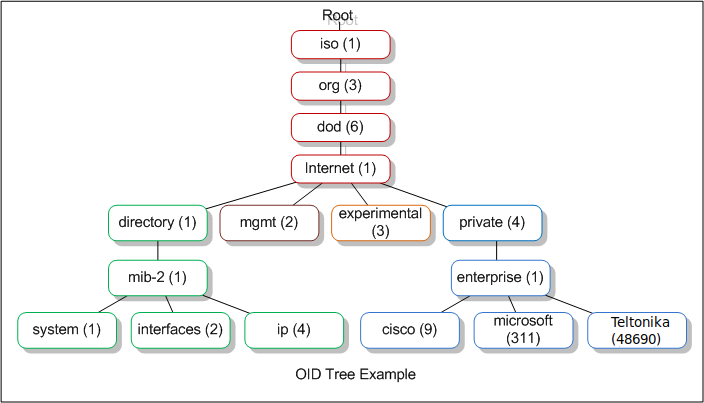
OID code is represented by the numbers in the boxes starting from "root".
| Number | Label | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | iso | ISO is the group that established the OID standard |
| 3 | org | An organization will be specified next |
| 6 | dod | The US Department of Defense (established the early internet) |
| 1 | internet | Communication will be via Internet/network |
| 4 | private | This is a device manufactured by a private entity |
| 1 | enterprise | The device manufacturer is classified as an enterprise |
| 48690 | Teltonika | Teltonika enterprise number |
| Field | Number | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| static | 1 | Static router information (Router name, Modem Imei, Modem Modle etc.) |
| gsm | 2 | Sim card information (Sim State, Operator, Mobile IP etc.) |
| hotspot | 3 | Hotspot information (Hotspot ip, users etc.) |
| Trap | 4 | Trap messages (Information sent through trap messages) |
| rut9x5 | 5 | Input/Output information |
| gps | 6 | GPS information (Latitude, accuracy etc.) |
| ethernet | 7 | Information about router ports |
MIB File
MIB File can be used with MIB browsers for easier access to router configuration and status information variables. Download the MIB file and upload/load it in MIB browser.
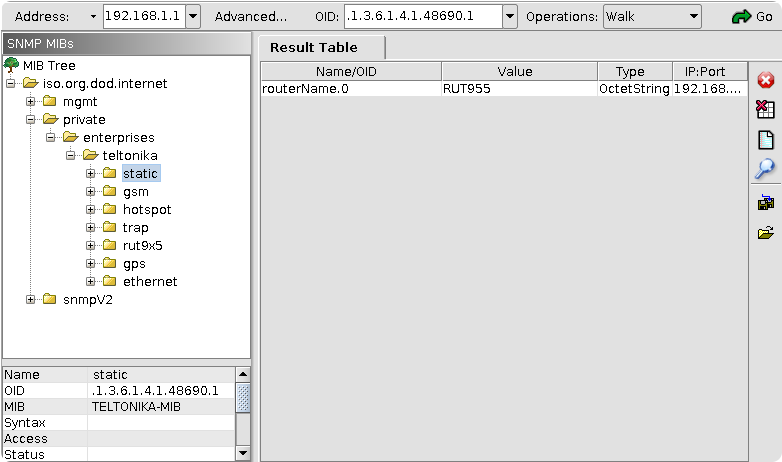
Generating OID code from MIB File
MIB File contains all OID codes.
Line containing numbers needed for OID code can be identified by this marking "::=".
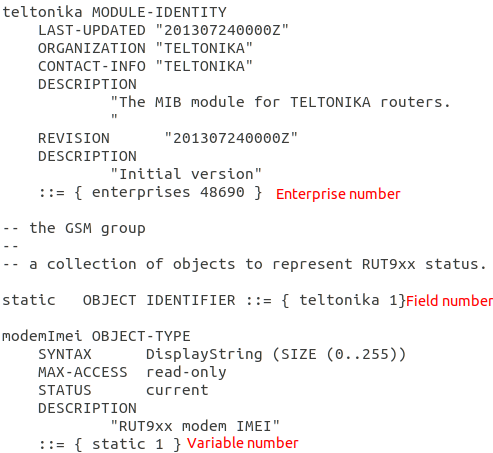
All that is left, is to add the numbers together. Example from given MIB File: 1.3.6.1.4.1.48690.1.1.0.
Important note: Do not forget to add .0 at the end of the generated OID code, except to Trap OID codes. Trap OID codes are only used by SNMP agent (router), using them in MIB browser or command line will not give any results.
SNMP Configuration
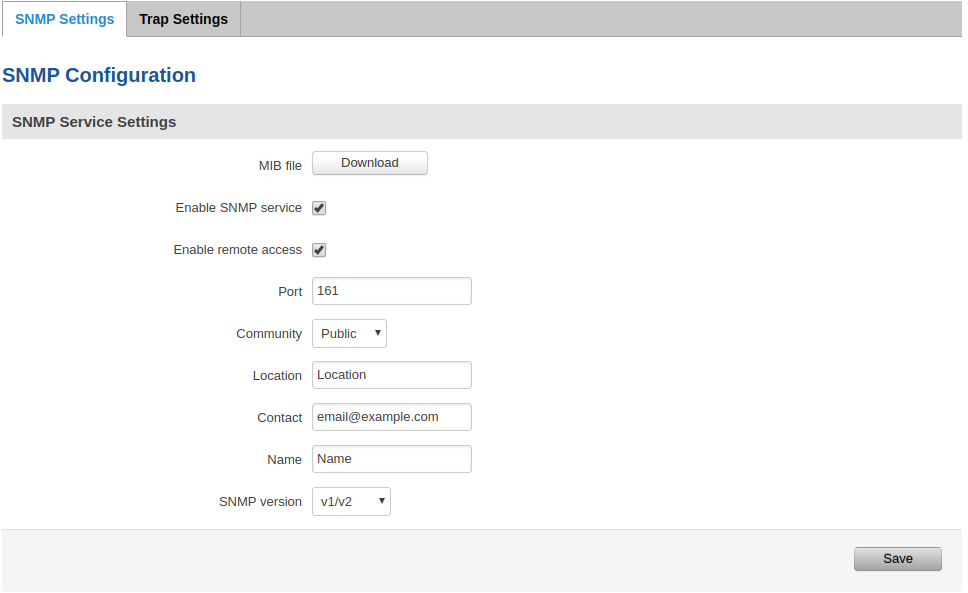
To configure SNMP, first enable SNMP service, leave or change the port, you can leave everything else as it is.
Testing SNMP with MIB browser
Use MIB browser to test if SNMP works. Make sure to use same port and IP address of the router in MIB browser, upload/load MIB file. MIB browser lets you walk through all OID codes, or return a distinct variable value.
Testing SNMP with console command
We can use snmpget command to get information from router:
$ snmpget -c public -v 2c IP_address:port OID_code
Example:
$ snmpget -c public -v 2c 192.168.1.1:161 1.3.6.1.4.1.48690.1.7.0
Trap Configuration
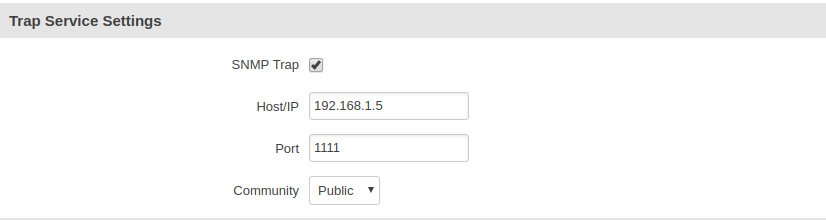
First enable SNMP Trap, then enter Host/IP, Hots/IP is the SNMP manager, computer to which SNMP agent will send Trap messages. If router is connected to PC via ethernet cable, enter the IP address of the interface the router is connected to. You can use ipconfig command on windows, ifconfig on linux to find IP address of the interface to which router is connected. Next choose port, preferably choose port number higher than 1024 so SNMP manager could establish connection without root/admin rights.
Trap rules
Trap rules describe on what event SNMP agent should send Trap messages.
