Azure IoT Hub Cloud Connection
Azure IoT Hub is an open and flexible cloud platform that supports open-source SDKs and multiple protocols.
Introduction
This article contains instructions on how to configure a RUT router in order to connect to the Azure IoT Hub.
The information in this page is updated in accordance with the RUTX_R_00.02.01.1 firmware version.
Prerequisites
You will need:
- A router from the RUTX09 or RUTX11
- An Azure IoT Hub account
Azure account creation
Visit https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/ and create an account that will suit your needs, for testing purposes we will be using free Azure account.
Managing Azure services
- First you will want to create a Resource group for easier management of resources that you will add later. In Microsoft Azure home page.
- In new window, select Add
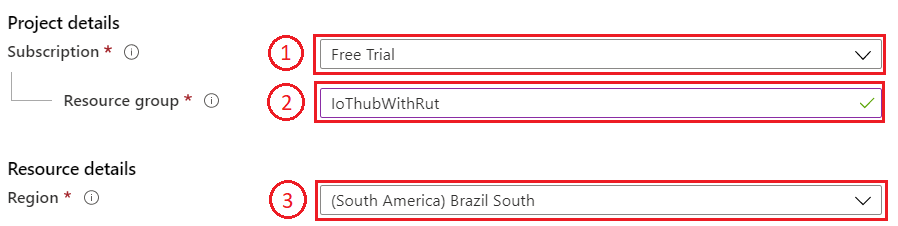
- And then finish creating yours Resource group Select your subscription, we are using Free Trial for this test.
- Name your group
- Finally, choose server location for meta data. We will choose (South America) Brazil South and will use it during test where available.
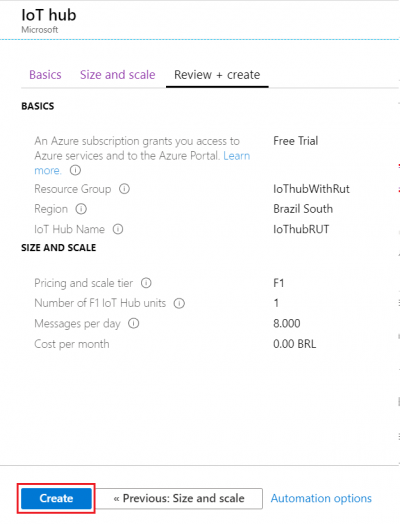
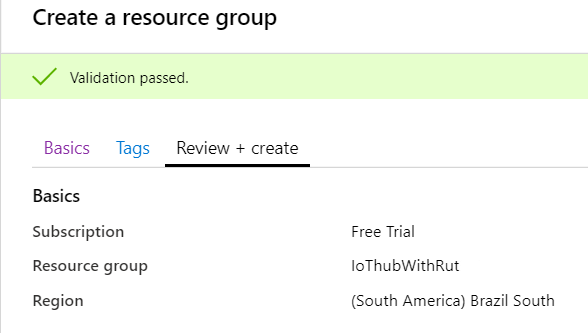
- At this moment we will skip adding Tags since we will be able to do that later if needed, so simply press Review + create at the bottom of screen and then click Create to finish setup.
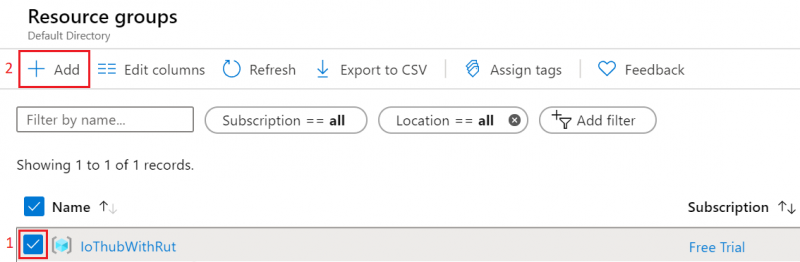
- You will be redirected to Homepage, then click on Resource groups. You should see yours newly created group, select it, and press Add.
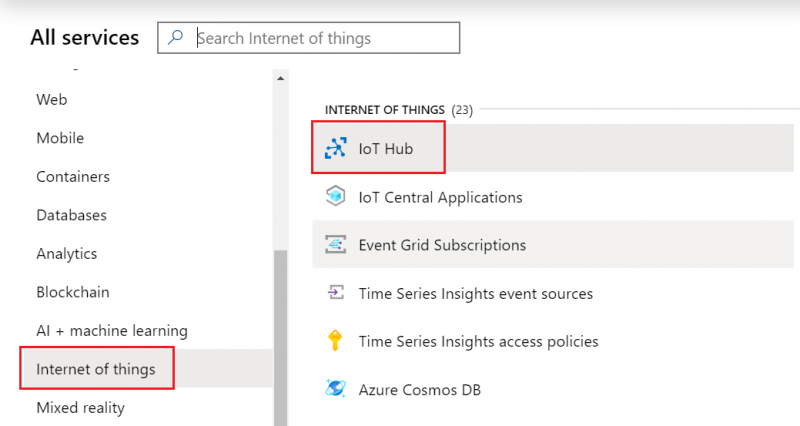
- Select Internet of Things or simply search IoT Hub and press Create.
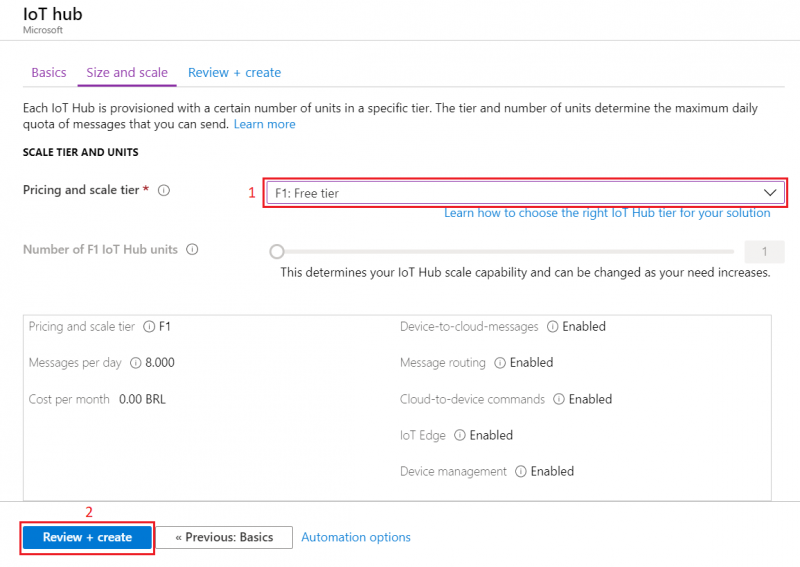
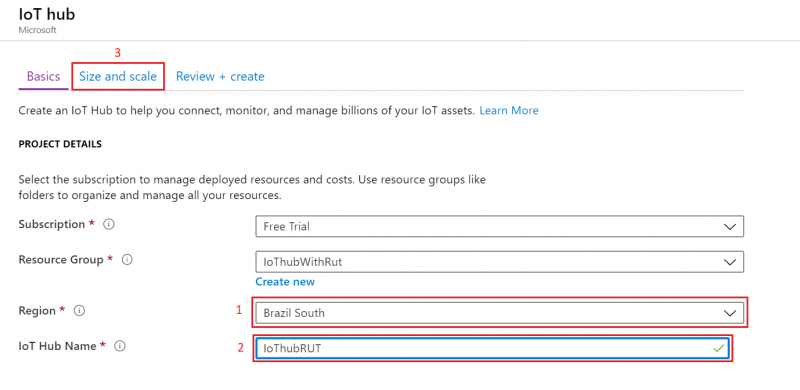
- We leave default subscription and resource group and choose:
1. Region – (South America) Brazil South as before2. Create a name for IoT Hub3. Then go to Size and scale tab
- For testing purposes, we are using F1: Free tier
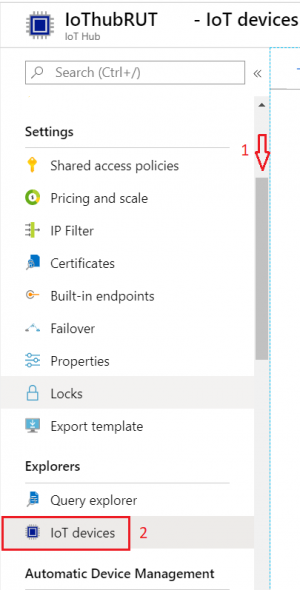
- Inside IoT Hub list:
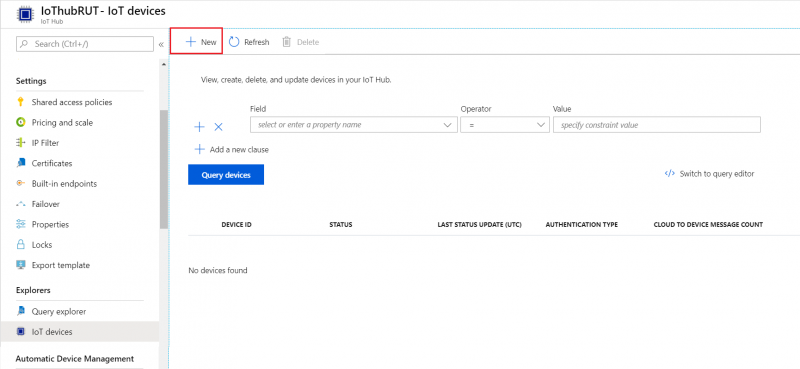
Scroll down to Explorers and select IoT devices
- Press New
-
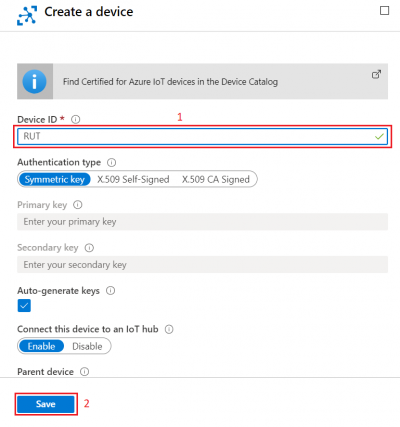
In new device creation1. Enter Device ID2. Leave everything else on default and press Save
- After you finish creation, you will be redirected back to IoT devices select yours newly created Device ID
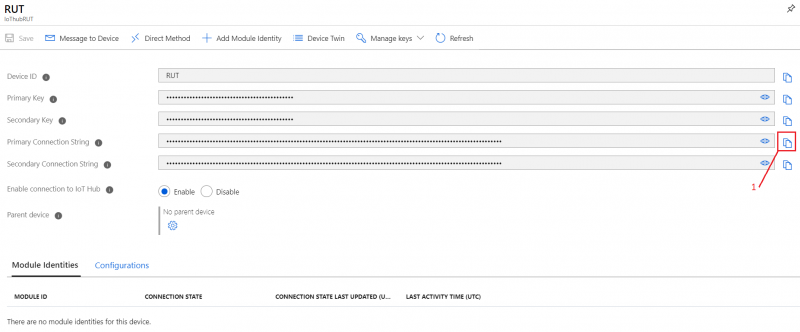
- In your device window you will find information needed to connect RUT devices to Azure IoT Hub.
- Select Resource groups
If it is not in very first page, click More services and locate it there.

Configuring Azure IoT Hub on RutOS
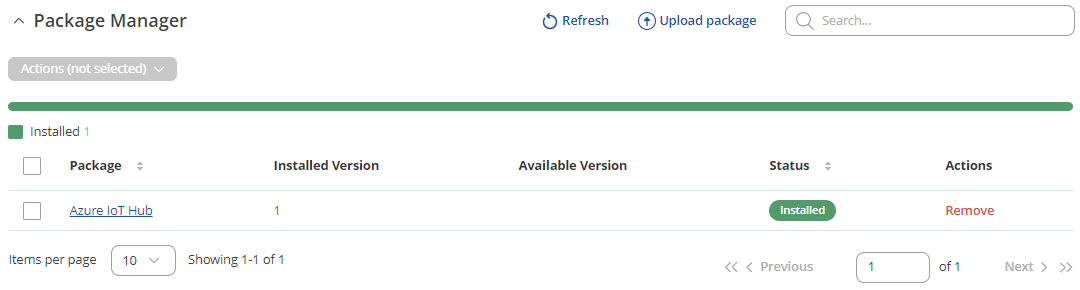
To configure an Azure IoT Hub instance on a RUT device, it is essential to first install the Azure IoT Hub package via the package manager.
- To install required package, please on the router WebUI, navigate System > Package Manager and install Azure IoT Hub package
Now navigate to Services > Cloud solutions > Azure IoT Hub and add a new instance. In the pop-up window, you will notice two different connection types available:
- Shared Access signature (SAS) key
- Device Provisioning Service (DPS)
In this article, we will demonstrate the configuration steps for both connection types.
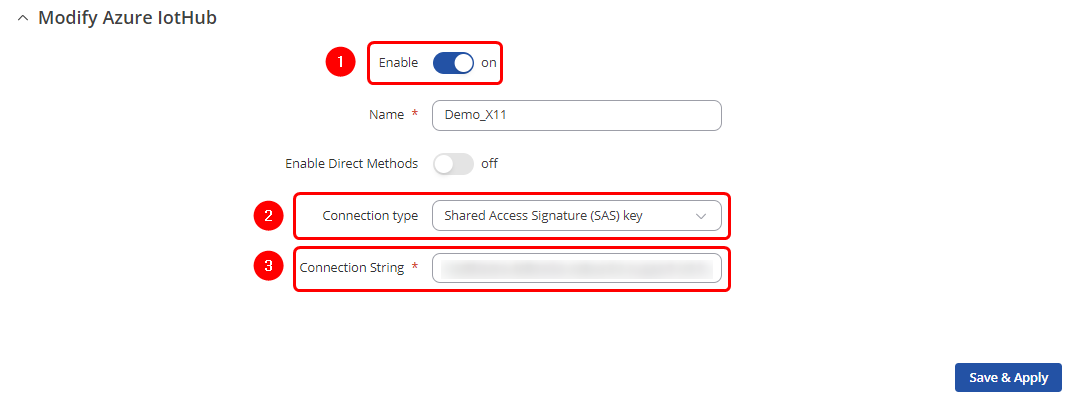
SAS key connection type configuration
Configuring Azure IoT Hub using the SAS key connection type is quite simple and straightforward. Please follow these three steps:
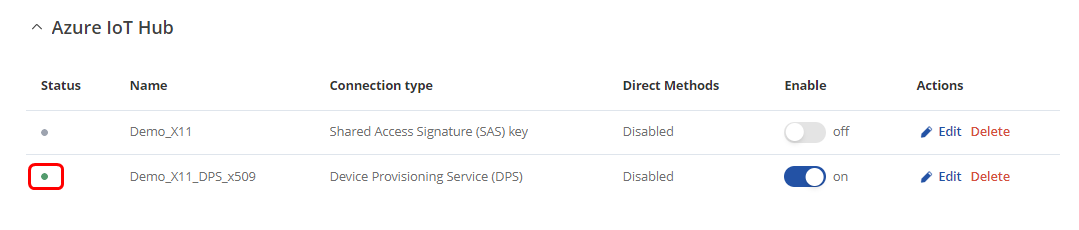
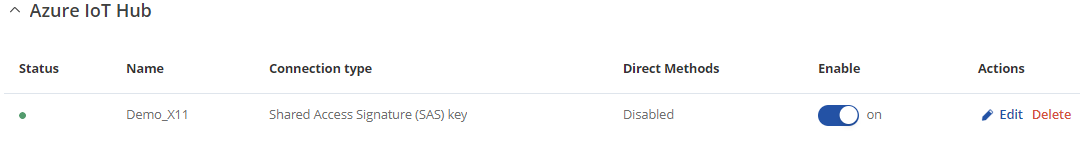
After the instance is correctly configured, you will be able to see the connection status on the Azure IoT Hub page of the WebUI. A green dot indicates that the connection is successful.
 Additionally, you can check the connection status through the router command line by executing the following command:
Additionally, you can check the connection status through the router command line by executing the following command:
ubus call azure.1 get_connection_status
Upon executing this command, you will see its output. If the connection is successful, you will see the following output:

If you are able to see that the connection status is succesfully and authorized it means that connection is established using SAS key connection type. Now, lets move foward with configuration of Device Provisioning Service (DPS) connection type.
Device Provisioning Service (DPS) configuration
One of the primary features of DPS is its capability to dynamically manage multiple device identities. This service manages the device identity creation process using mechanisms called attestations. There are two such mechanisms:
- 1. X.509
- 2. Symmetric keys
DPS X.509 mechanism
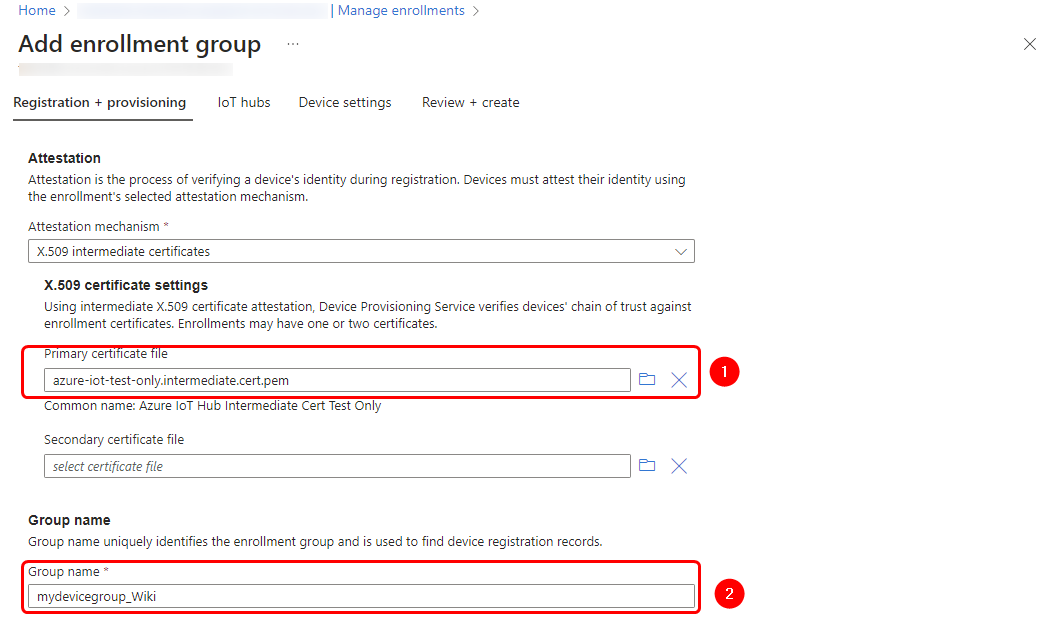
The first mechanism utilizes X.509 certificates. Each DPS service includes one or more services known as enrollment groups, which handle this task. Each enrollment group is configured to function with a specific IoT Hub, considering there may be multiple IoT Hubs. At the DPS, the root CA certificate needs to be registered. Additionally, each enrollment group should have one or more intermediate CAs that are signed by the root CA. Each RUT device must have a unique certificate signed by an intermediate CA. This certificate contains additional information, such as the subject ID field, which will serve as the device identity name on the IoT Hub. Now, let's delve into an actual example of configuring such a service.
- Root CA certificate
- Intermediate CA certificate
- Devices certificates Please ensure to carefully follow the Microsoft guide to create certificates, making sure not to miss any steps as they are all crucial. Following the Microsoft guide, after creating the Root CA certificate, you will notice that it is named "Azure IoT Hub CA Cert Test Only".
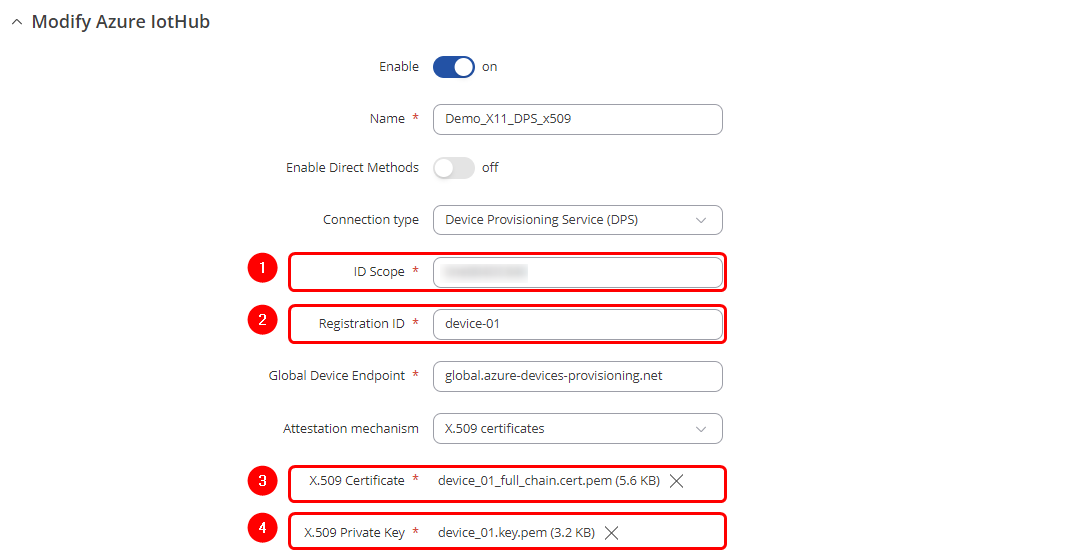
- In the "ID scope" field, specify your Azure DPS service ID.
- In the "Registration ID" field, enter the "REG_ID" value you specified in the script. For example, "wiki-newly-generated-device".
- In the "Symmetric key" field, enter the "SharedAccessKey" obtained from the script execution.
The required certificates and keys:
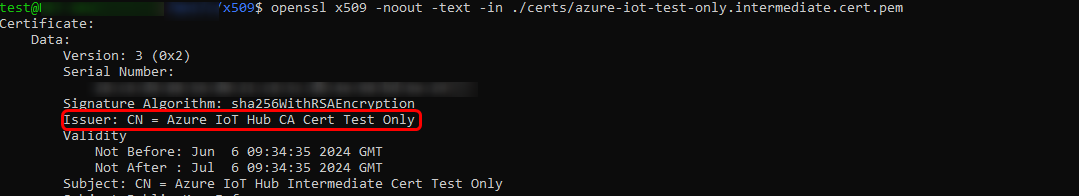
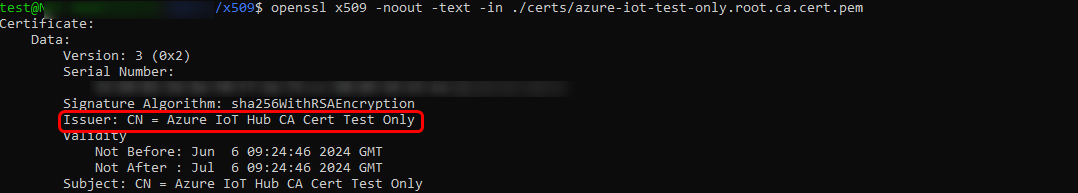 After creating the root CA certificate, an intermediate CA certificate must be generated. Upon inspecting this certificate, you should notice that it is issued by the "Azure IoT Hub CA Cert Test Only", as seen previously.
After creating the root CA certificate, an intermediate CA certificate must be generated. Upon inspecting this certificate, you should notice that it is issued by the "Azure IoT Hub CA Cert Test Only", as seen previously.
 After successfully creating the intermediate CA certificate, proceed with creating the device certificate and signing it using the intermediate authority. It's crucial to note that the subject field will be the name of the newly registered identity on the IoT Hub page. If you are following the provided Microsoft guide, you can observe "device-01" name, remember it as it will be used in later configurations steps.
After successfully creating the intermediate CA certificate, proceed with creating the device certificate and signing it using the intermediate authority. It's crucial to note that the subject field will be the name of the newly registered identity on the IoT Hub page. If you are following the provided Microsoft guide, you can observe "device-01" name, remember it as it will be used in later configurations steps.
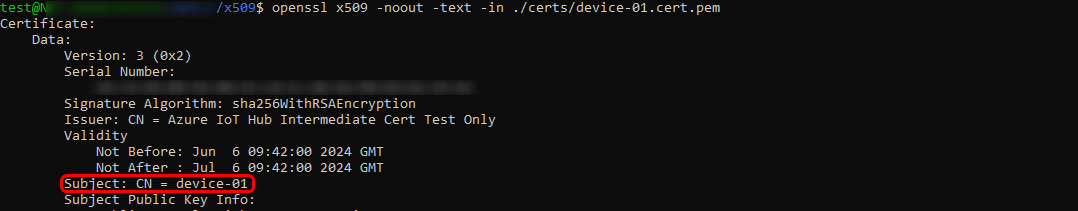 Finally, we append the root CA, intermediate CA, and device certificates into one certificate chain. If you are following the guide, the "device-01-full-chain.cert.pem" file will be created. Later, we will upload this file to the RUT device WebUI page.
Finally, we append the root CA, intermediate CA, and device certificates into one certificate chain. If you are following the guide, the "device-01-full-chain.cert.pem" file will be created. Later, we will upload this file to the RUT device WebUI page.
2. After successfully generating the certificates, return to the Azure portal page and navigate to your Azure IoT Hub Device Provisioning Service (DPS) page. From there, proceed to the certificate page and upload the root CA file.
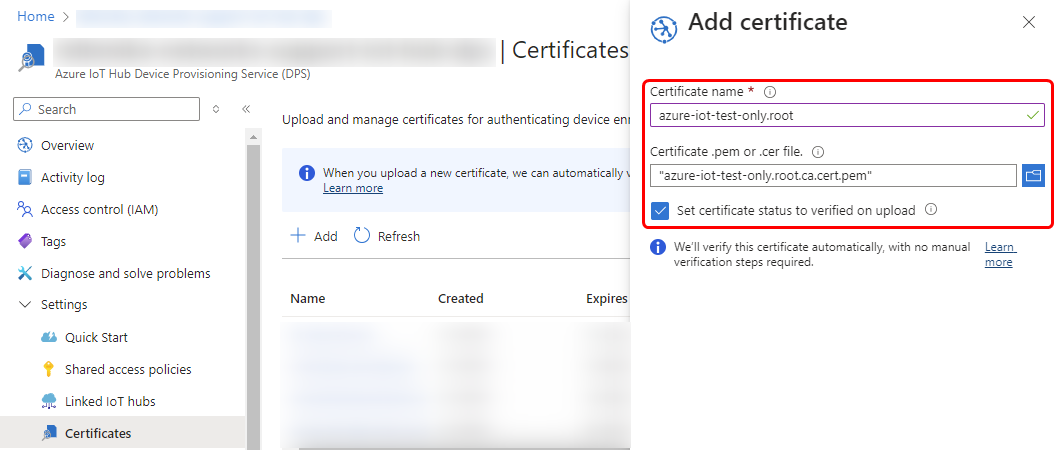
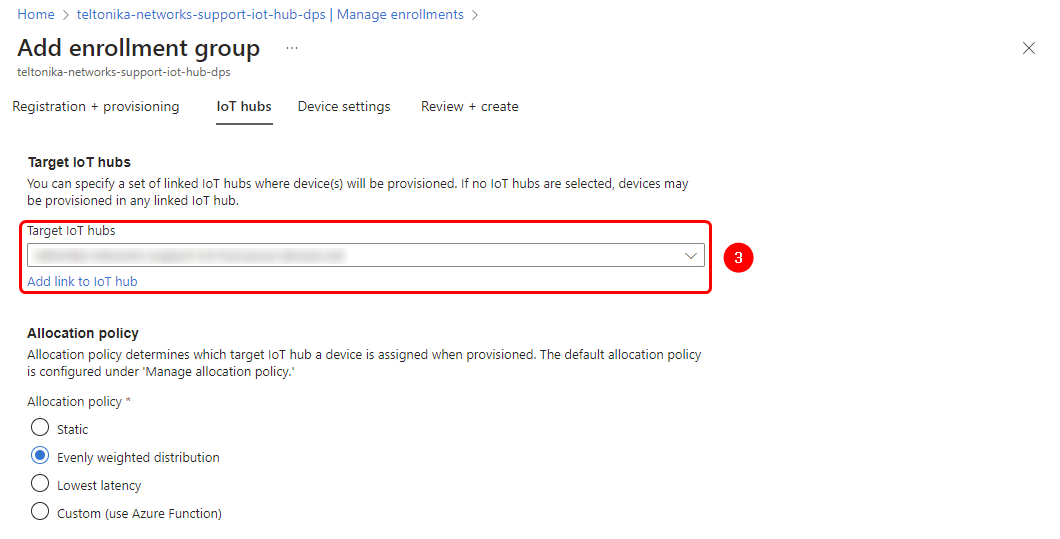
3. Next, navigate to the "Manage Enrollments" page to register the intermediate CA and target our IoT Hub service instance.
4. The final step is to return to the RUT device WebUI and navigate to Services -> Cloud Solutions -> Azure IoT Hub page to create a new configuration instance. In the configuration pop-up window, please follow these steps: 4.1 Set connection type as a Device Provisioning Service (DPS); 4.2 Enter ID Scope of your DPS service page on Azure; 4.3 Specify the Registration ID. Remember the "device-01" one? If you followed the Microsoft guide step by step, you need to enter "device-01" in the "Registration ID" field. 4.4 Lastly, upload the certificate chain file and the private key file.
With all the required values in place, the configuration pop-up window should resemble the screenshot below:
After a couple of seconds, you will be able to observe the status of your configured instance in the Azure IoT Hub page on the router WebUI.
The device successfully connects to the Azure IoT Hub.
DPS Symmetric key mechanism
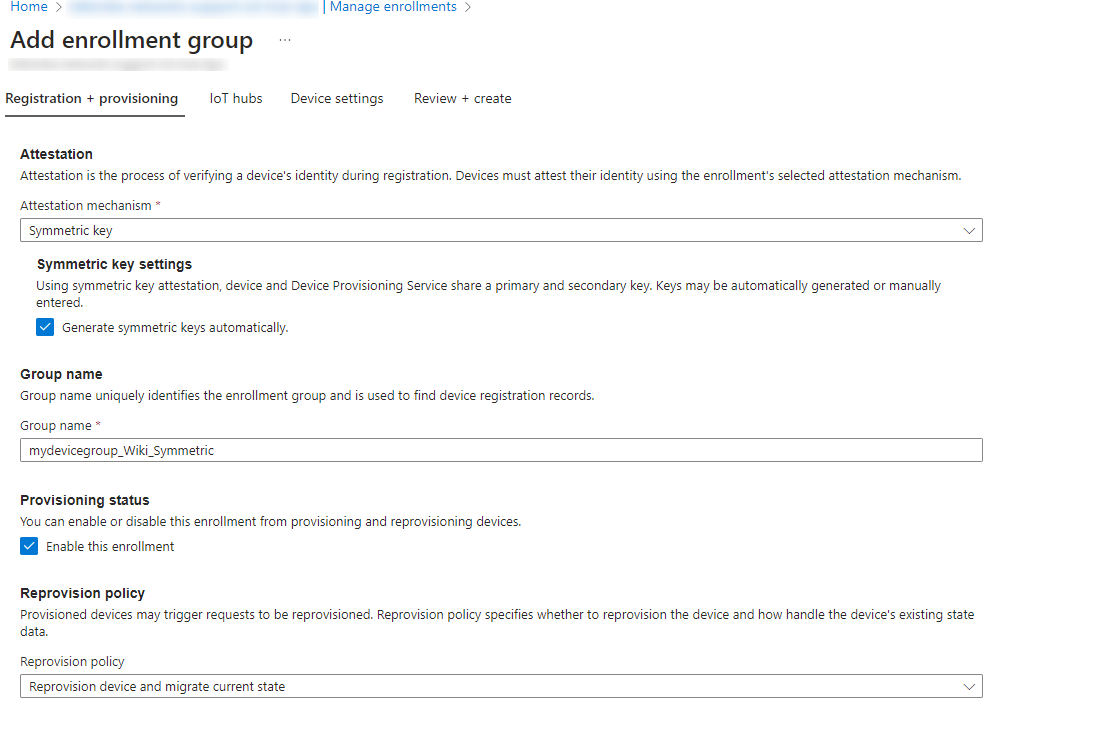
The Symmetric key mechanism configuration is more straightforward. To configure it, first, go back to the Azure portal, navigate to your DPS service page, and create a new enrollment group with the Symmetric key attestation mechanism.
Inspecting the newly created enrollment group will reveal some keys. The primary key will be used to derive each individual device identity. This can be done using a simple script, which is available in the following Microsoft guide.: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-dps/how-to-legacy-device-symm-key?tabs=linux&%3Bpivots=programming-language-ansi-c&pivots=programming-language-ansi-c#derive-a-device-key
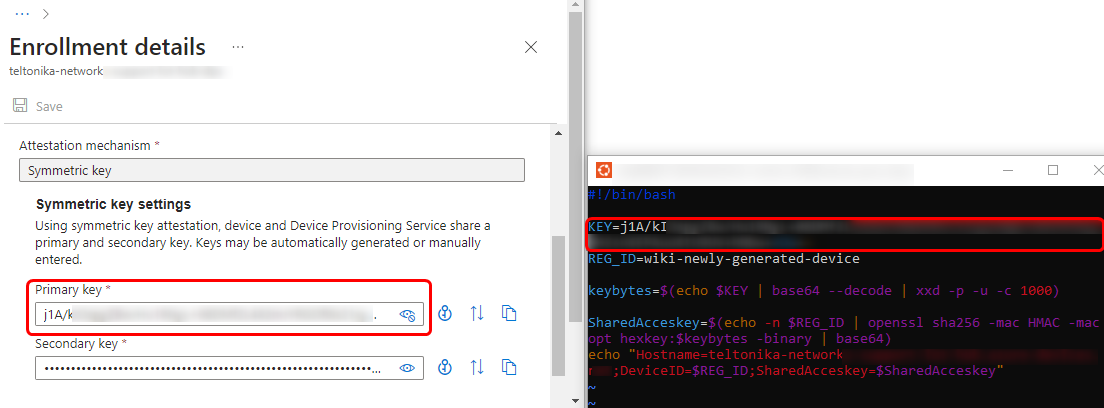
In the script, you will notice a couple of important variables: KEY and REG_ID. In the KEY field, you must specify the primary key, which can be obtained from the newly created enrollment group.
In the REG_ID field, you can specify any name you want. Upon executing the script, a shared access key will be created. Please copy this key, as we will need it in the following steps.
After executing the script, go back to the RUT device Services -> Cloud Solutions -> Azure IoT Hub configurations page and add a new instance. In the configuration window, select DPS connection type and Symmetric Key connection type.
If you are following this guide, your configuration window should look similar to the screenshot below.
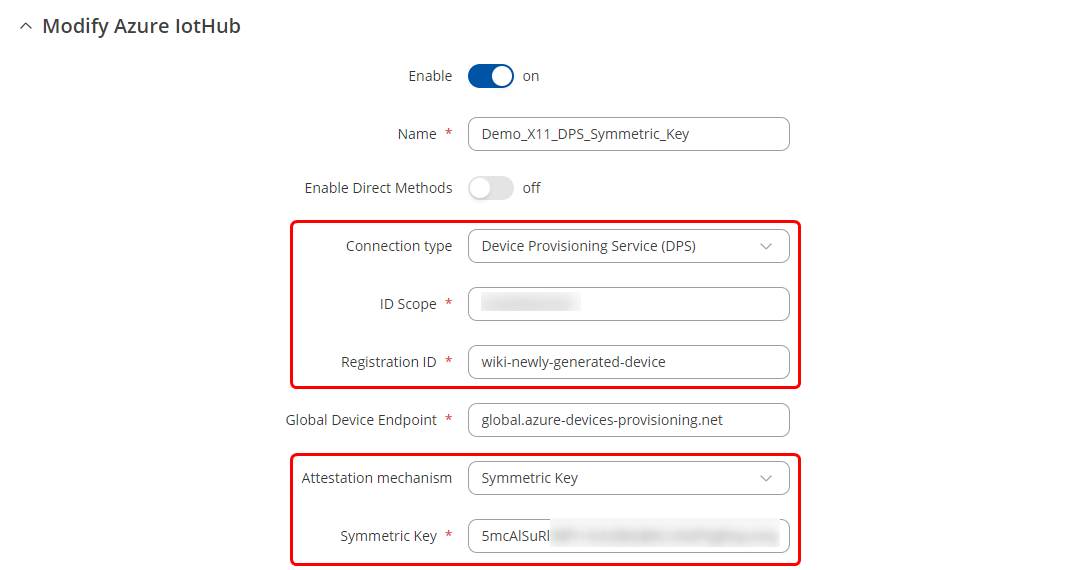 Don't forget to press the Save & Apply button! A few seconds after saving the configuration, you should be able to observe that the device successfully connects to Azure.
Don't forget to press the Save & Apply button! A few seconds after saving the configuration, you should be able to observe that the device successfully connects to Azure.
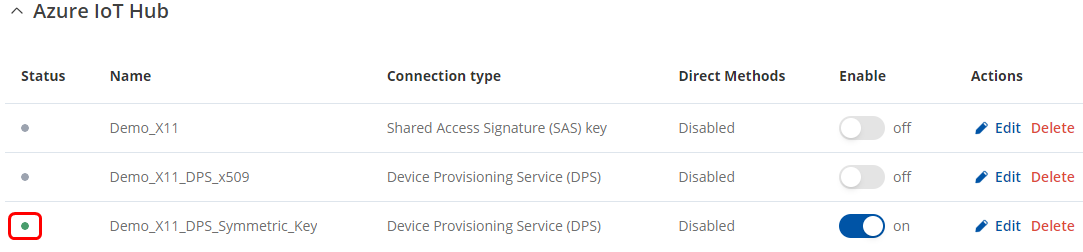 Moreover, we can return to the IoT Hub services in the Azure portal and check the device list. There, we will see that the DPS service has created a new device identity, named the same as what we specified in the "REG_ID" field in the script earlier.
Moreover, we can return to the IoT Hub services in the Azure portal and check the device list. There, we will see that the DPS service has created a new device identity, named the same as what we specified in the "REG_ID" field in the script earlier.
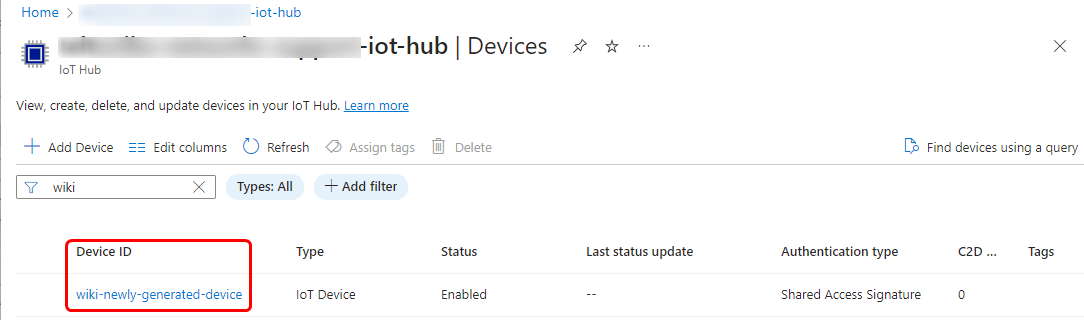 If you see that the connection is successful on the router WebUI page and the newly created device appears in the Azure IoT Hub device list, it means that you have configured everything correctly.
If you see that the connection is successful on the router WebUI page and the newly created device appears in the Azure IoT Hub device list, it means that you have configured everything correctly.
Direct methods configuration
Direct method is a term that describes process where some action is called from the Azure IoT Hub to a specific device identity. The receiving device executes certain actions and returns an answer back to the Azure portal. Let's see how it works on our devices.
By default, all configurations instances will have this option disabled. To enabled it, you should navigate on router WebUI to Services -> Cloud Solutions -> Azure IoT Hub and press edit button on specific instance. There, you will be able to see "Enable Direct Methods" button, which you need to press.
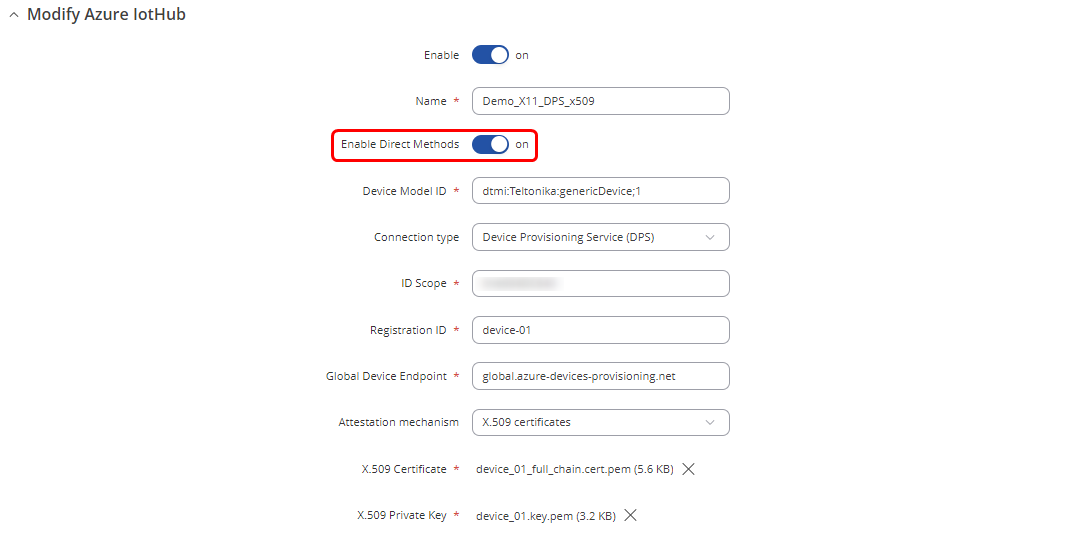
For testing and demonstration purposes we will use Azure IoT explorer application. The Azure IoT explorer is a graphical tool for interacting with devices connected to your IoT hub. If you are not familiar with it, you can follow this Microsoft installation and usage guide https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot/howto-use-iot-explorer
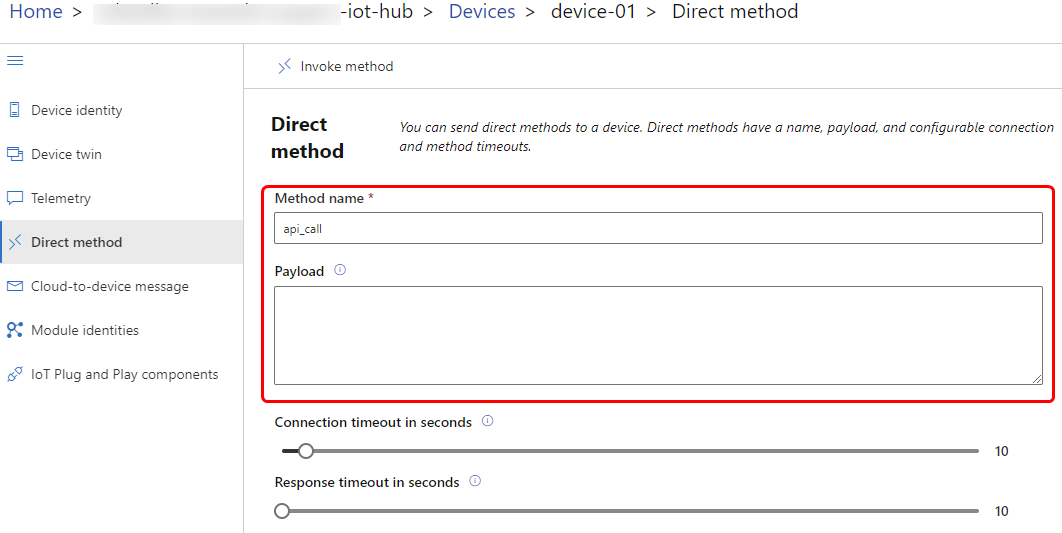
After enabling the Direct Method feature manually, go to Azure IoT Explorer, select proper device indentity and head to direct methods tab. All our RUT devices supports api_call direct method, which exposes the API interface to be used from the Azure side. In this example, we will call simple get request to retrieve I/O status of the device. Full documentation of Teltonika devices API can be found here https://developers.teltonika-networks.com/
In the Azure IoT explorer direct method tab you can see Payload field. It expects to have JSON formatted information.
 API call expects at least two parameters. The first one is called "method". This needs to have an integer value between zero and three, which corresponds to API method type - either "get", "out", "post", "delete". The second one is endpoint which expects a string value of the API endpoint. In this case we will call the /io/status endpoint.
API call expects at least two parameters. The first one is called "method". This needs to have an integer value between zero and three, which corresponds to API method type - either "get", "out", "post", "delete". The second one is endpoint which expects a string value of the API endpoint. In this case we will call the /io/status endpoint.
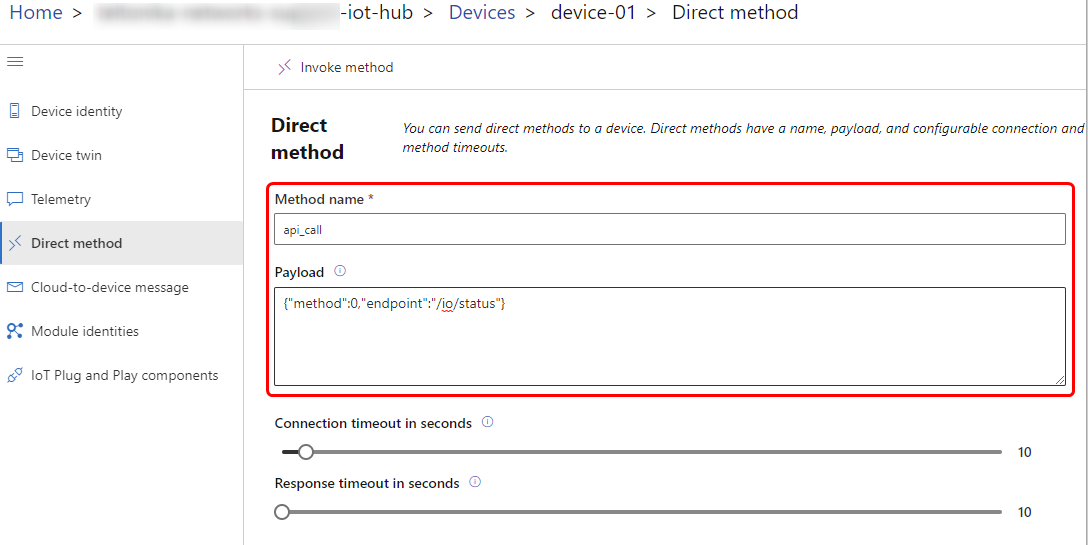
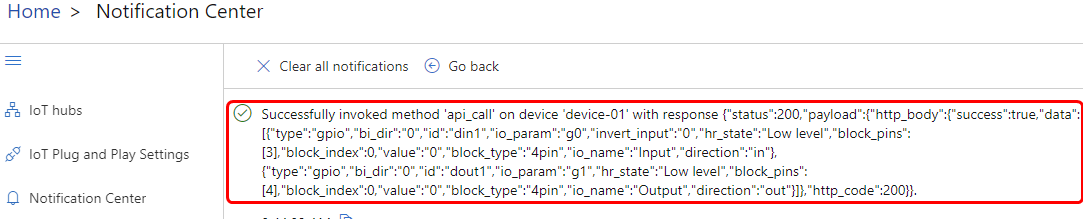
After pressing "Invoke Method" button, we can a response from the device.
Checking if Data reaches Azure IoT Hub
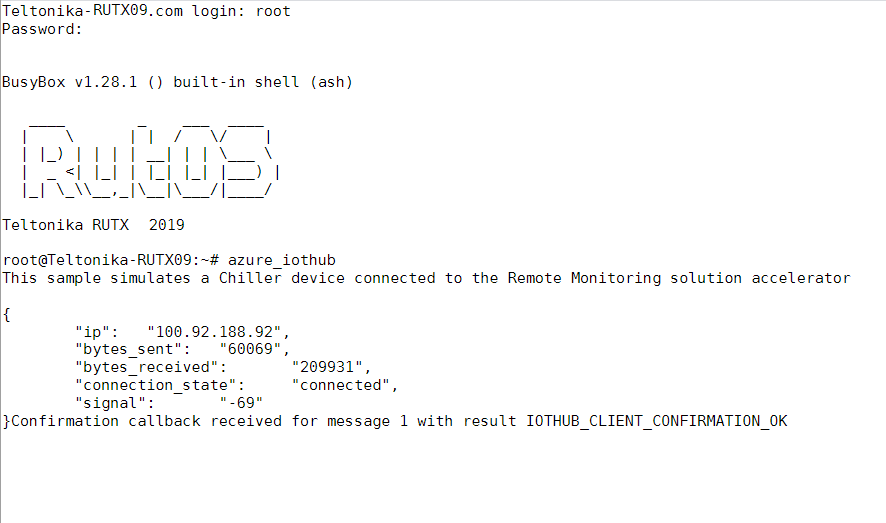
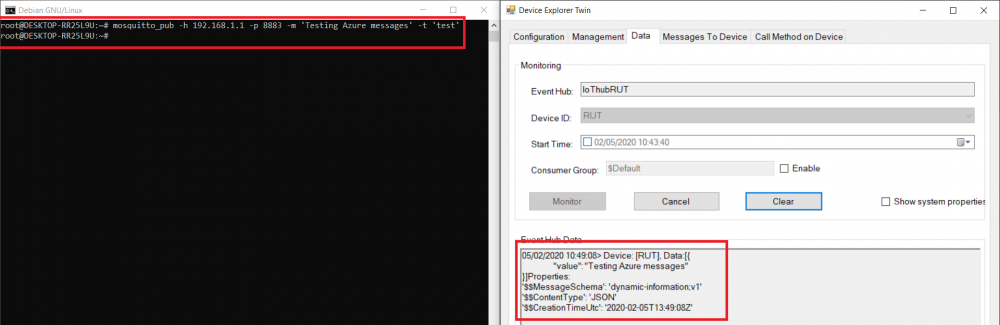
- From router side, connect to it with CLI or SSH client and write in command azure_iothub and press Enter
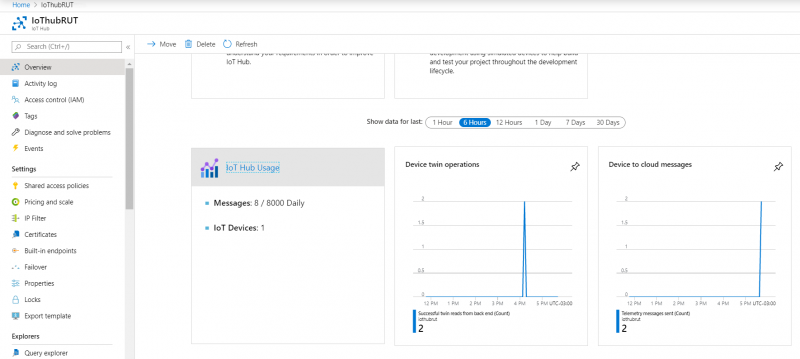
- From Azure IoT Hub side you can check if it receives data. Go to IoT Hub that you created previously. Select Overview, there you can see:
- To capture logs you will need Device Explorer for IoT Hub Devices.
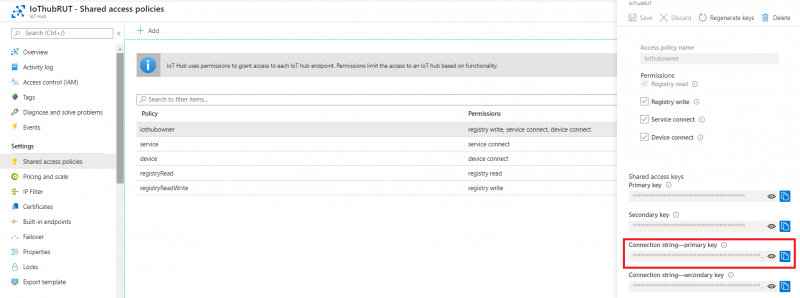
- Now you will need connection string of yours Azure IoT Hub, Not device. Navigate to IoT hub in your browser, then:
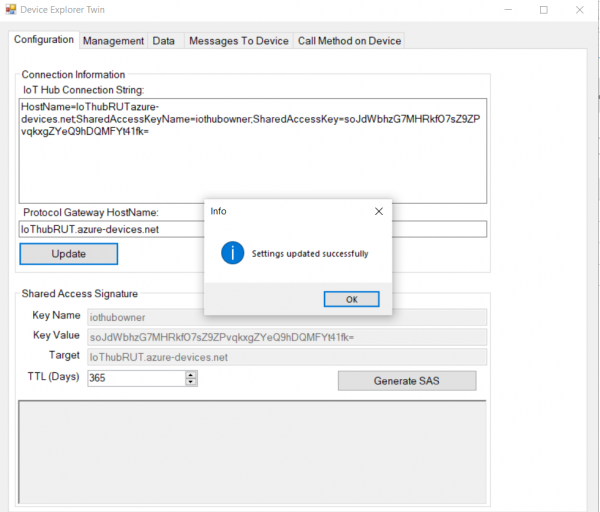
- After that go back to Device Explorer:
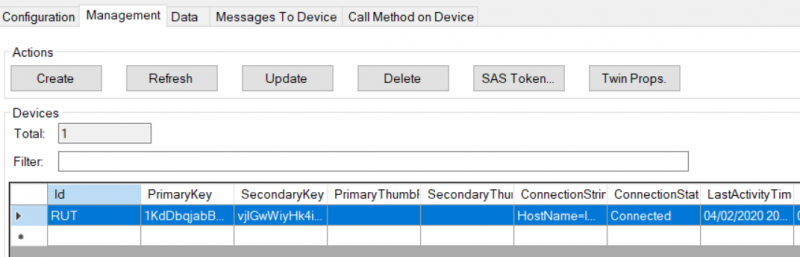
- Open Management tab
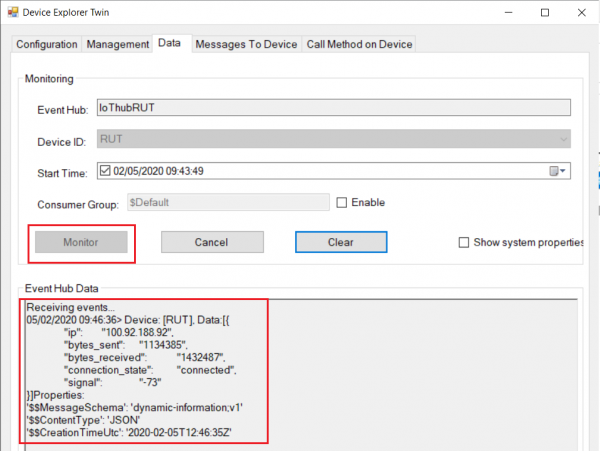
- Go to Data tab
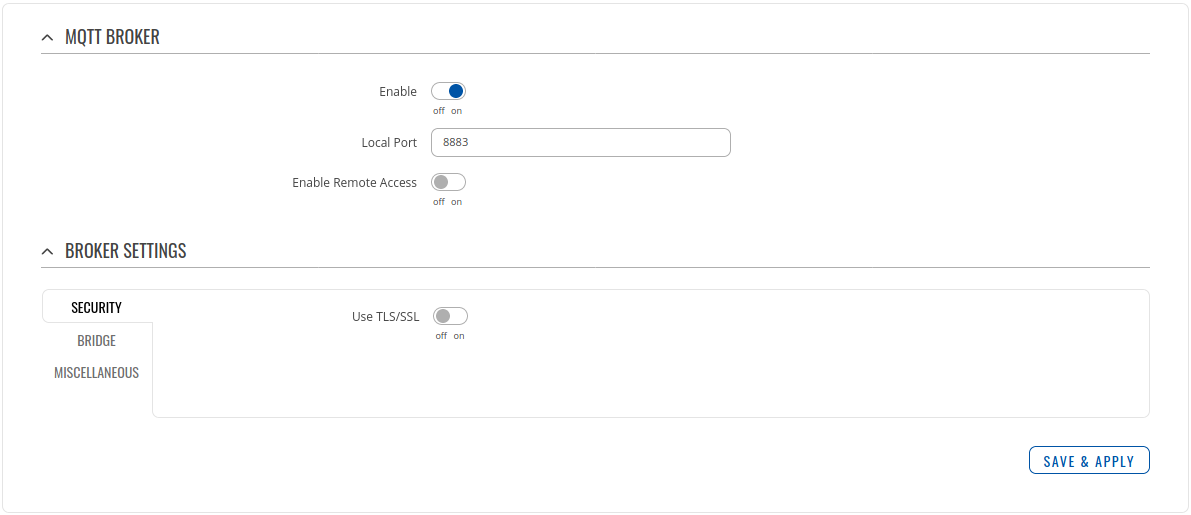
- Go to Services > MQTT > Broker
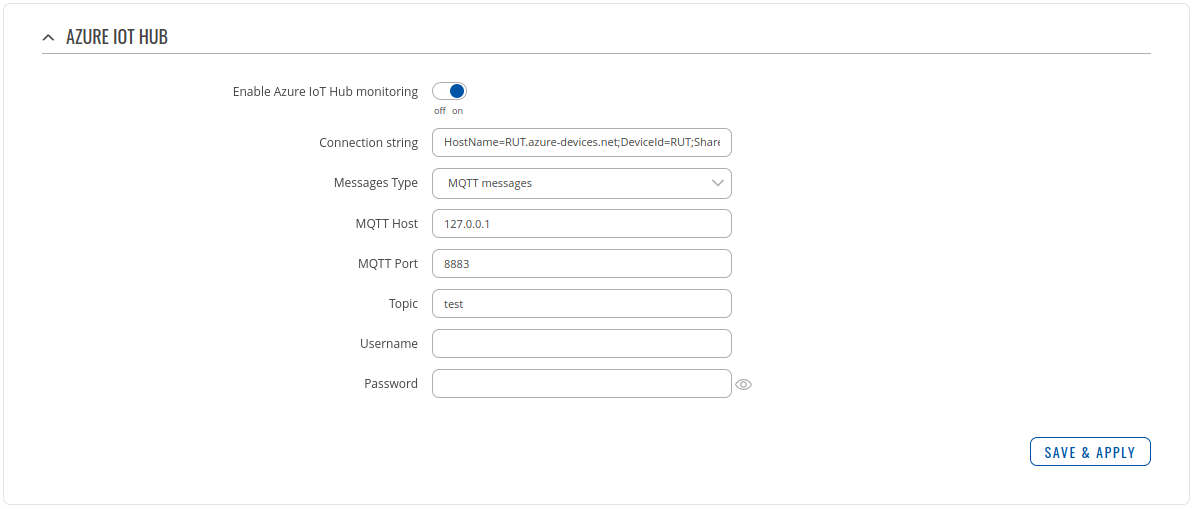
- Go to Services > Cloud solutions > Azure IoT Hub
Setting router to Forward MQTT messages/commands to Azure IoT Hub
Checking if MQTT messages are being forwarded to Azure IoT Hub
Linux
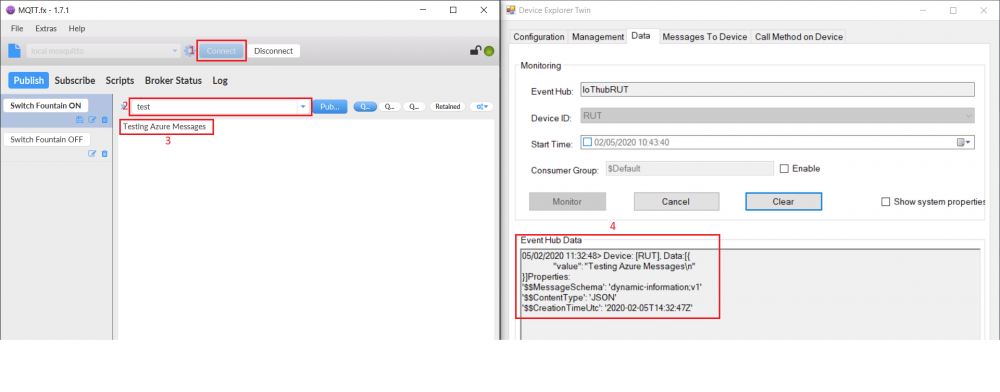
- Open terminal and publish to MQTT Broker message with previously chosen topic.
For our example we are using example: mosquito_pub -h 192.168.1.1 -p 8883 -m ‘testing Azure MQTT messages’ -t test
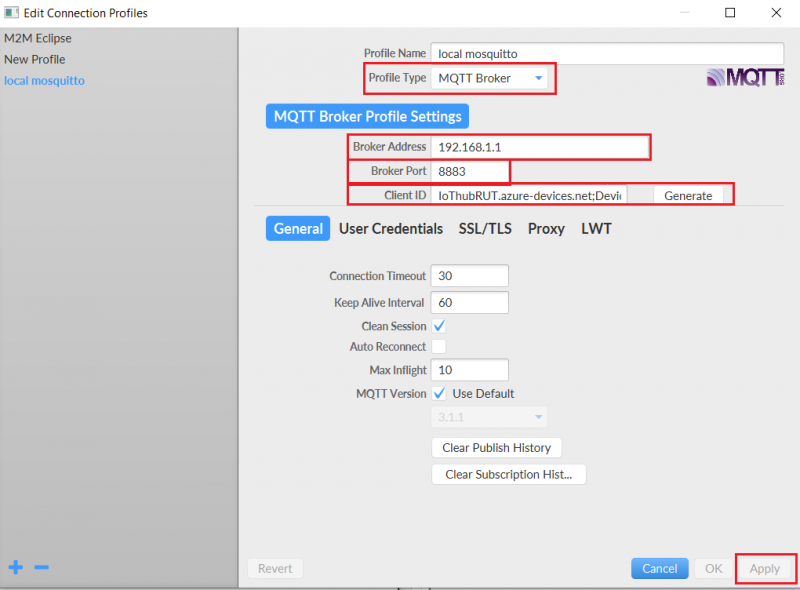
Windows
- Install a MQTT client software to do the test, for this example we used MQTT.fx
- If you did everything right this message will be shown in the device explorer