Network Address Translation
Network Address Translation
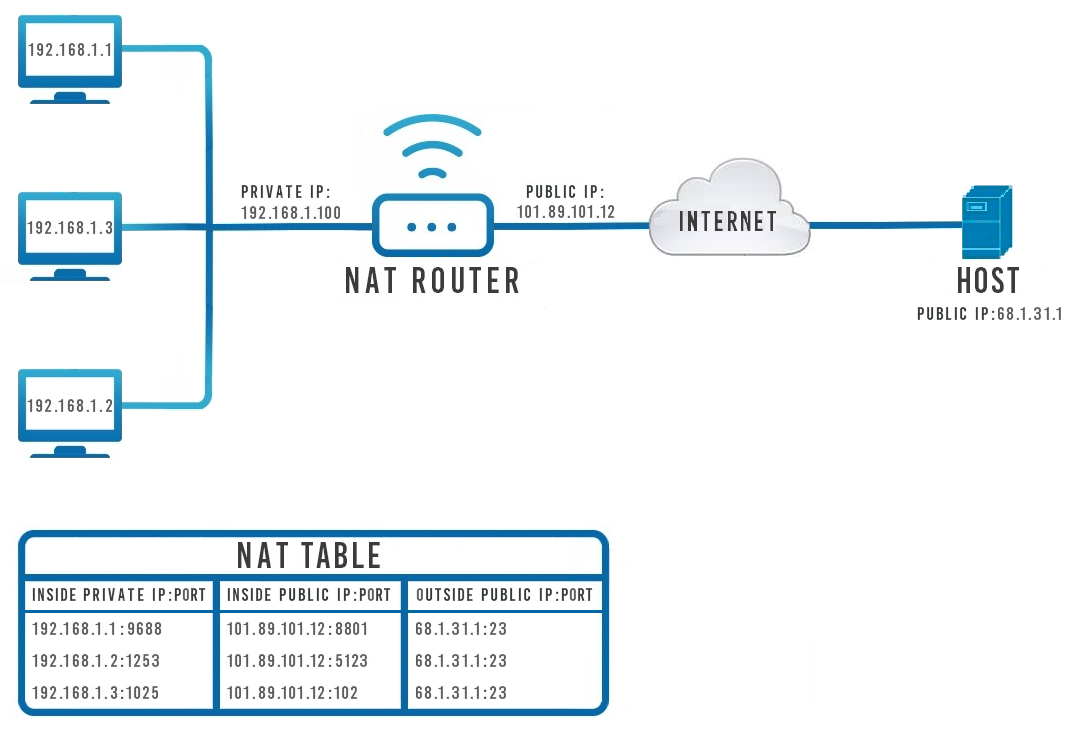
Network address translation (NAT) is a method of remapping one IP address space into another by modifying network address information in IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device. Or to put it in plain terms, NAT allows devices with private IP addresses to communicate with hosts via the internet using IP masquerading.
IP masquerading is a technique that hides an entire IP address space, usually consisting of private IP addresses, behind a single IP address in another, usually public address space. The address that has to be hidden is changed into a single (public) IP address as "new" source address of the outgoing IP packet so it appears as originating not from the hidden host but from the routing device itself:
The scheme above roughly describes how devices with private IP addresses communicate with a remote host on the Internet (and vice versa) with the help of NAT. Bellow the scheme is a depiction of a NAT mapping table. It illustrates how the router differentiates to which device in the local network to redirect incoming data packets.