Wireguard Peer To Peer Configuration example
Introduction
Introduction to a Peer-to-Peer WireGuard configuration example, this also covers LAN-TO-LAN connectivity aspect as well. WireGuard is simple, fast, lean, and modern VPN that utilizes secure and trusted cryptography.
This page will show you an example on how to configure a basic tunnel between WireGuard interface and its peers. Note: WireGuard is additional software that can be installed from the Services → Package Manager page (in RUT9/RUT2 this page is located in System → Package Manager).
Prerequisites
For this example you need:
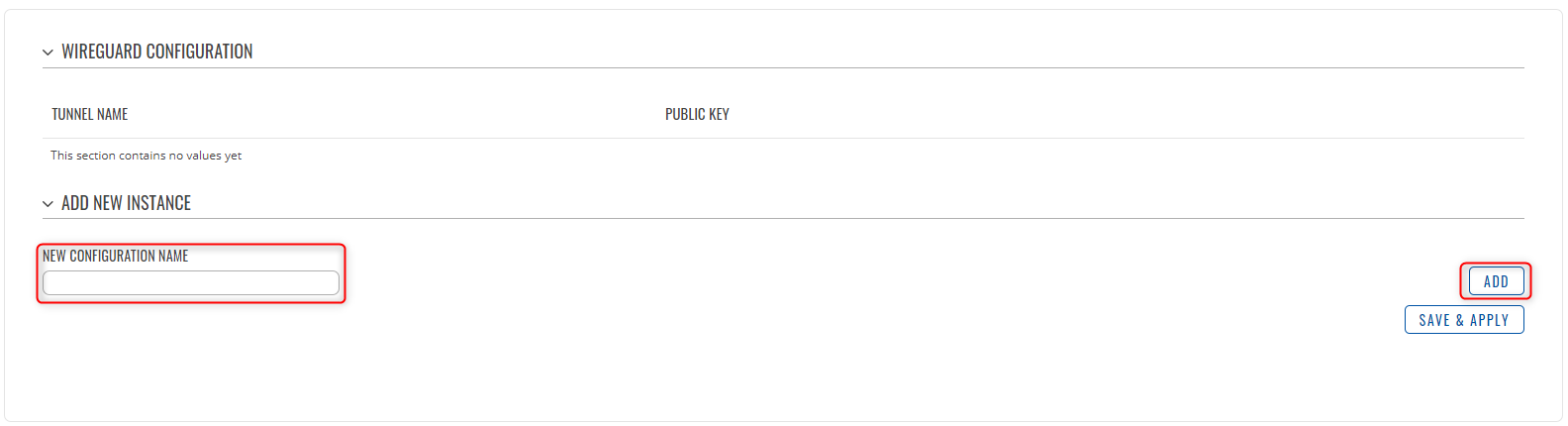
WireGuard Instances
To create Instance enter its name and click the Add button.
Then click the Edit![]() button to configure it.
button to configure it.
Server Configuration
Peer to Peer Setup
The following part of example applies to both devices.
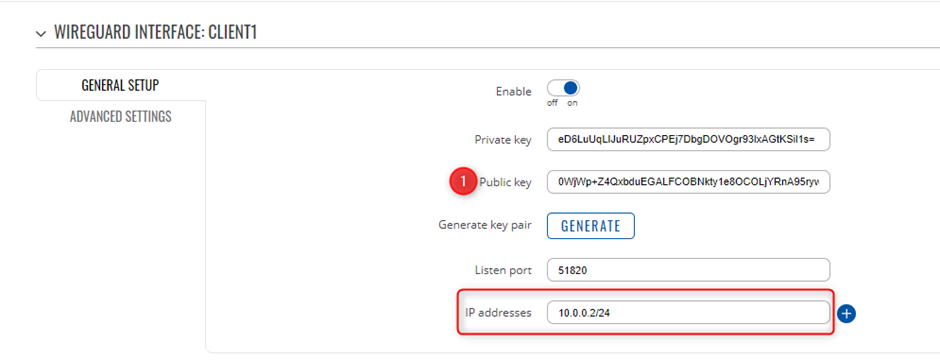
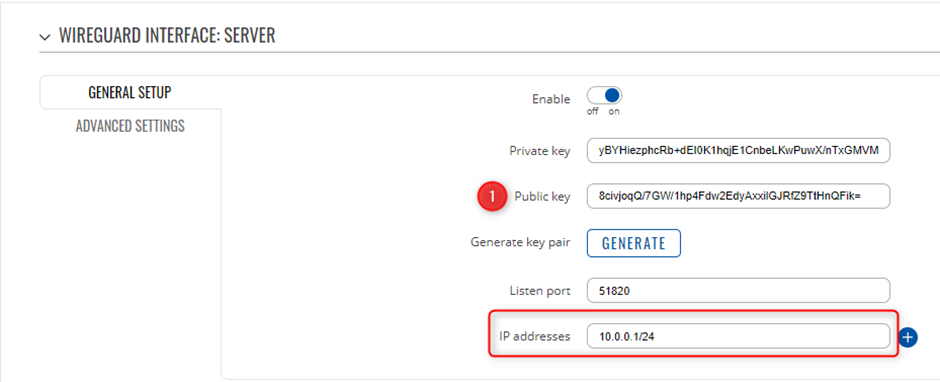
Before editing any fields click ![]() button to generate Public and Private keys.
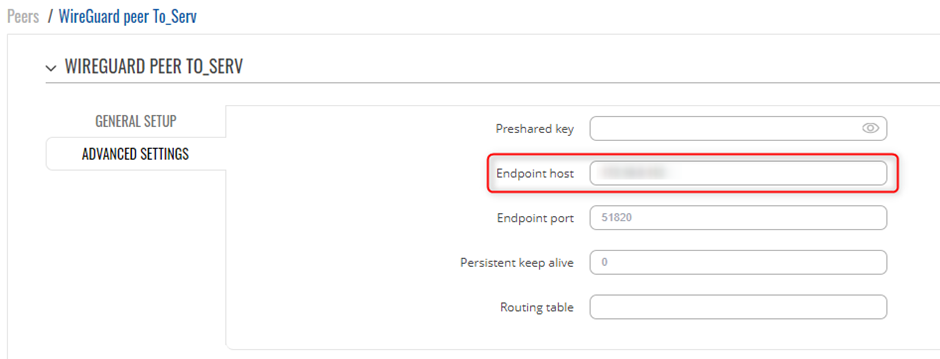
After that you need to Enable this instance and in the Listen Port field enter your desired port. WireGuard by default uses 51820 port which will be used in this example.
Lastly you need to enter IP Address for instance. We will set the SERVER will have 10.0.0.1 and Clients will have 10.0.0.2 IP addresses and increasing.
Note: enter IP address and its mask e.g. 10.0.0.1/24
Note: You will need to copy the Public and Private Keys for Peer instances between server and Clients
button to generate Public and Private keys.
After that you need to Enable this instance and in the Listen Port field enter your desired port. WireGuard by default uses 51820 port which will be used in this example.
Lastly you need to enter IP Address for instance. We will set the SERVER will have 10.0.0.1 and Clients will have 10.0.0.2 IP addresses and increasing.
Note: enter IP address and its mask e.g. 10.0.0.1/24
Note: You will need to copy the Public and Private Keys for Peer instances between server and Clients
 Please ensure that on the Server side, that you allow the Firewall to accept traffic going through the Server router for Peer-to-Peer traffic to flow
This can be located in Network -> Firewall -> General settings
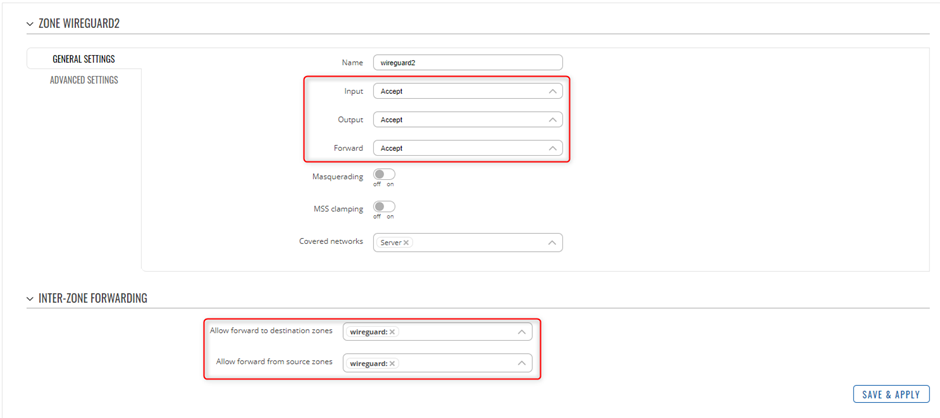
A zone for WireGuard to WireGuard can be created as below to ensure traffic is not restricted from the server
Please ensure that on the Server side, that you allow the Firewall to accept traffic going through the Server router for Peer-to-Peer traffic to flow
This can be located in Network -> Firewall -> General settings
A zone for WireGuard to WireGuard can be created as below to ensure traffic is not restricted from the server
Peers Configuration
Peer to Peer Setup
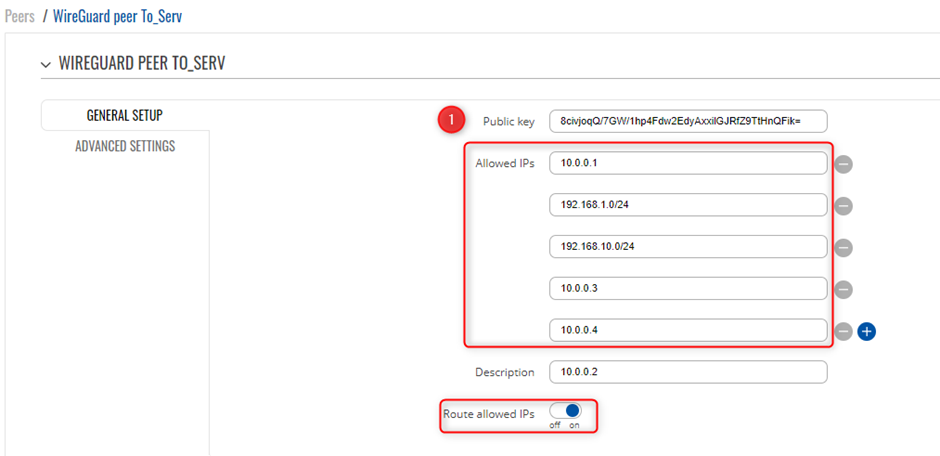
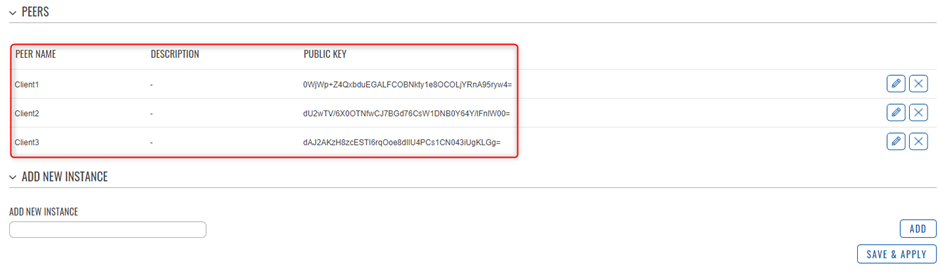
In the General Setup section you need to enter Public Key and Allowed IPs from the Remote instance you want to connect to. In this example a peer from Client1 needs to connect to RUTX11, which means SERVER will enter Public Key and Allowed IPs from Client1. You will need the Public Keys of the Client VPN users that you setup, so it is recommended to create the Instances to Generate the Keys for use of Peer instances
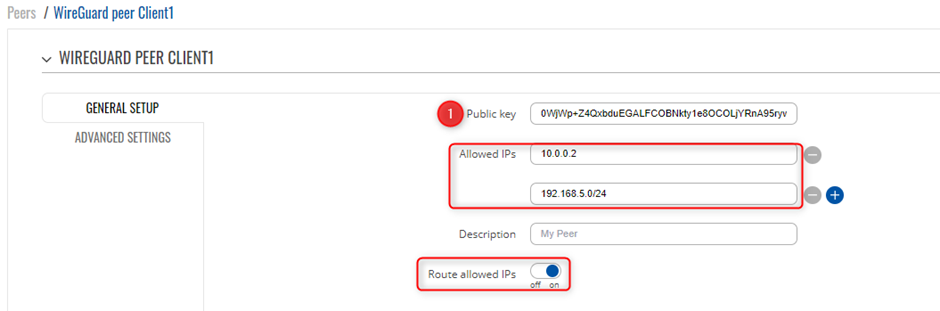
Peers Configuration Client 1
Client 1 is setup with the following details, WireGuard Interface IP is set as 10.0.0.2 with a LAN range of 192.168.5.0/24 You will need to create a new WireGuard instance and Peer connection, please ensure you copy the public Key that was generated via the creation of the instance, as this will be used on the Server side for the VPN.
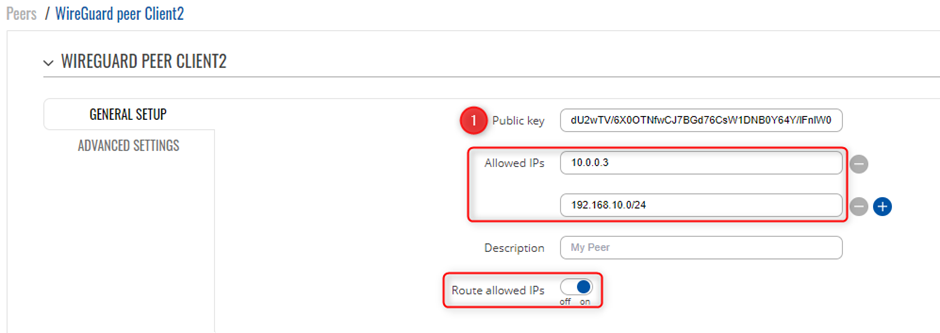
Peers Configuration Client 2
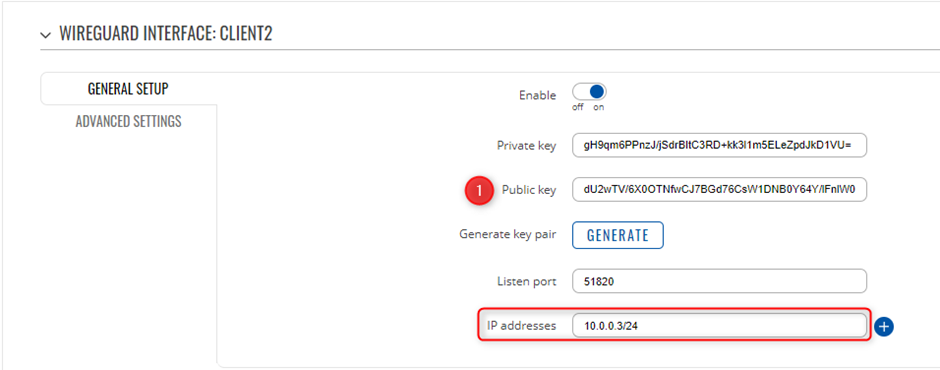
Client 2 is setup with the following details, WireGuard Interface IP is set as 10.0.0.3 with a LAN range of 192.168.10.0/24 You will need to create a new WireGuard instance and Peer connection, please ensure you copy the public Key that was generated via the creation of the instance, as this will be used on the Server side for the VPN.
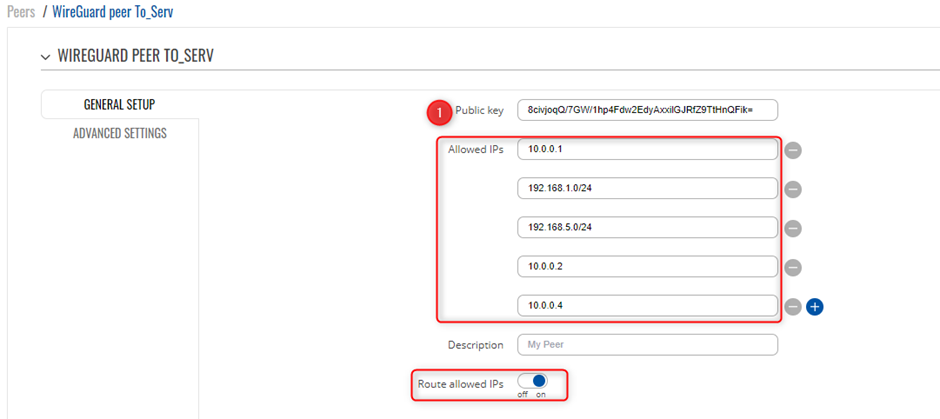
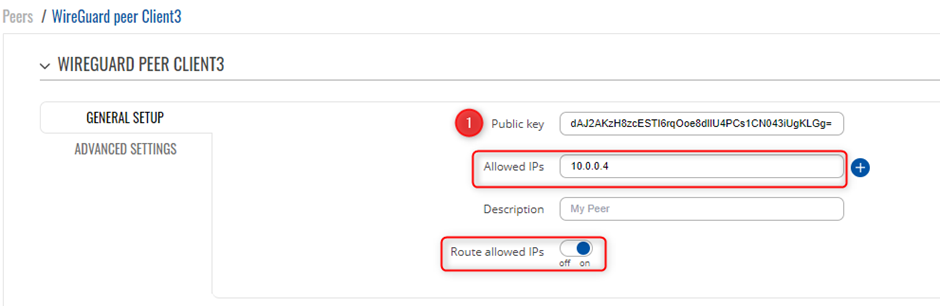
Peers Configuration Client 3
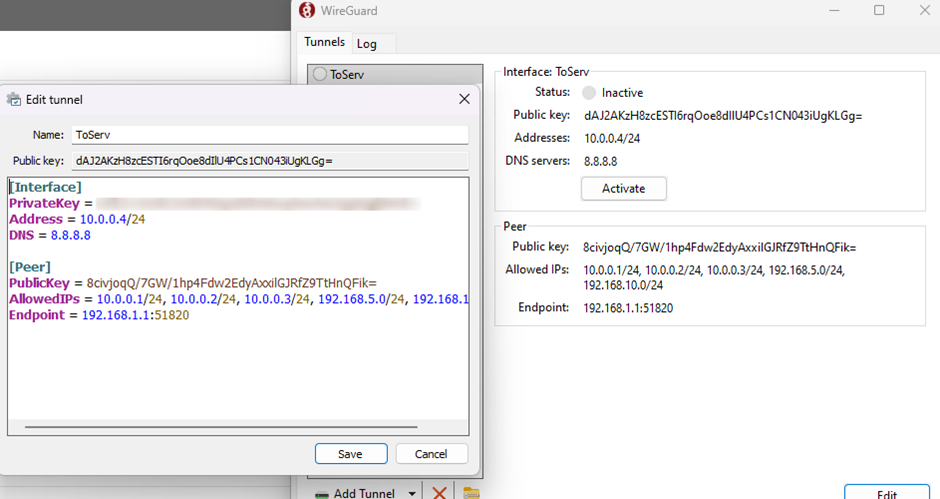
Please ensure you download WireGuard for your PC (Windows Client) Installation: https://www.wireguard.com/install/ Once you have created a new Tunnel, you will need to add the below lines of code to finish the VPN setup,
Peers Configuration Server
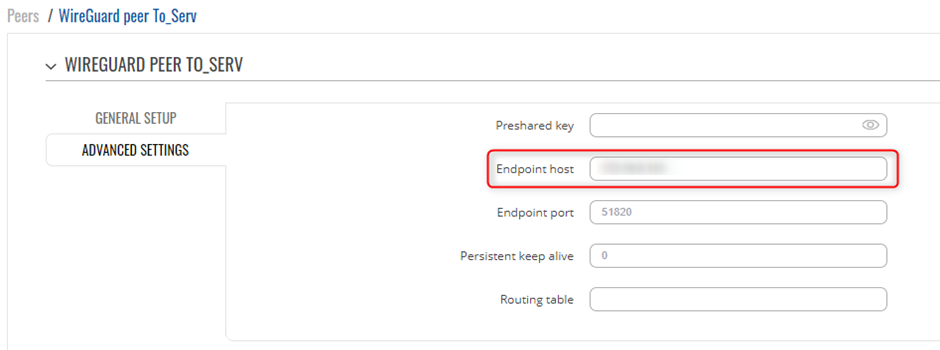
Server to Peer Setup
In the General Setup section you need to enter Public Key and Allowed IPs from the Remote instance you want to connect to. We will be creating 3 instances, these will be the remote Peers we created above and will make use of their Public Keys to create them, such as below
Server To Client 1
Create your 1st client peer under the server
Server To Client 2
Create your 2nd client peer under the server
Server To Client 3 (PC)
Create your 3rd client peer under the server
Testing the Setup
Testing
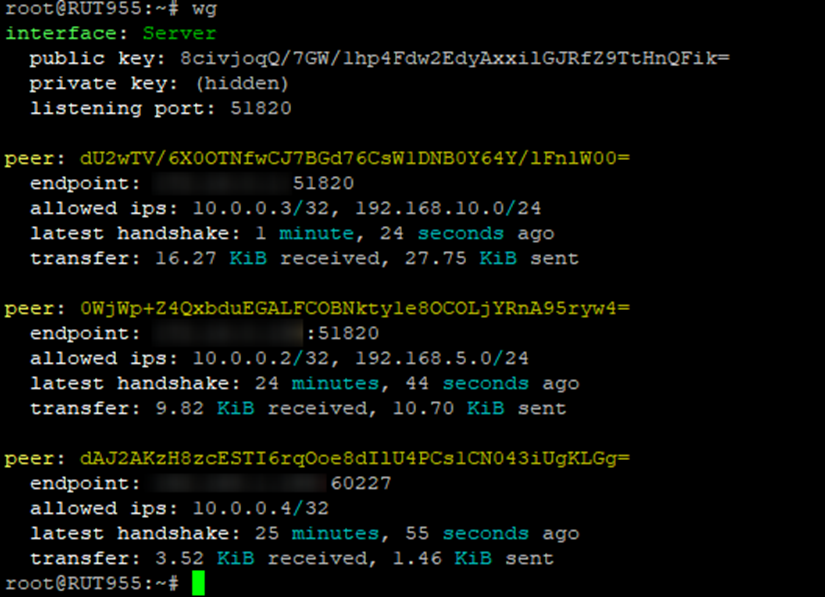
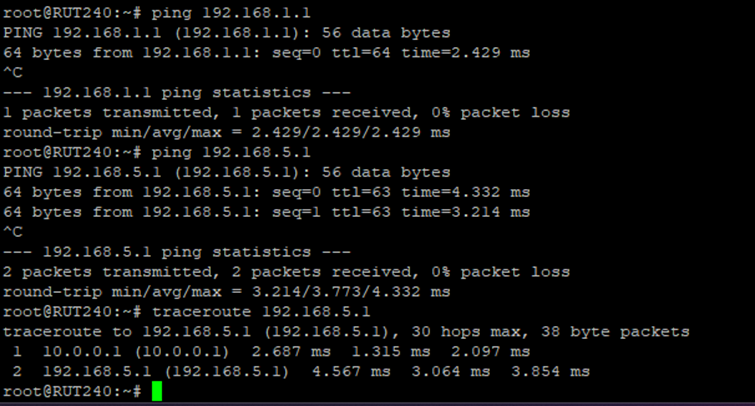
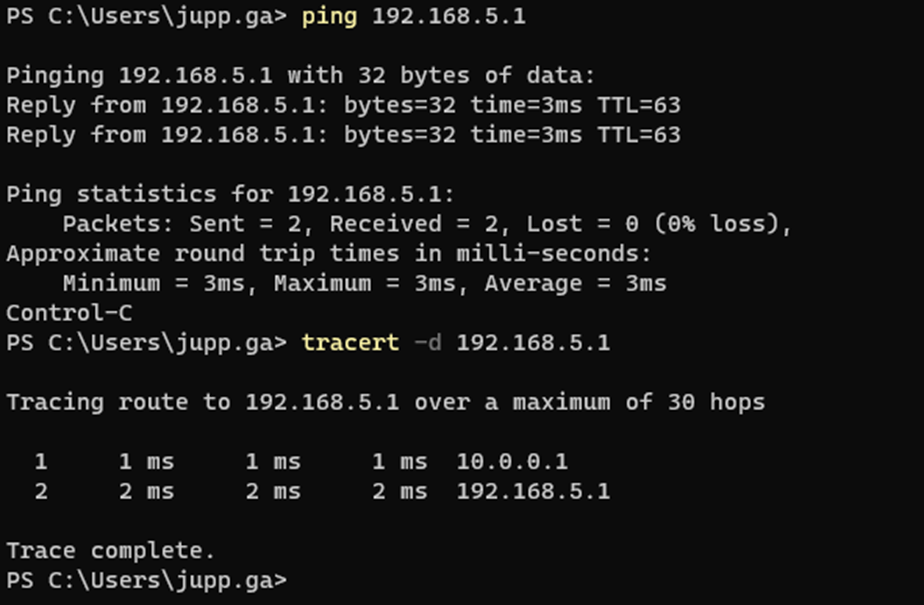
Once you have setup the WireGuard Server and Peer settings, you can test by making use of the below Once you have created your Peers and Host, via the CLI you will be able to see the new WireGuard interfaces and ping across the new VPN, below is an example Show peers and uptime of WireGuard instances with use of “wg” command in the CLI
Ping LAN to LAN
Ping PC Client to Client 1